Influence of Manganese–Zinc Ferrite and Ageing on EMI Absorption Shielding Performance and Properties of Rubber Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Characterisation of the Filler
2.2.2. Fabrication and Curing of Composites
2.2.3. Cross-Link Density
2.2.4. Mechanical Properties
2.2.5. Absorption Shielding Characteristics
2.2.6. Electrical Conductivity
2.2.7. Thermal Conductivity
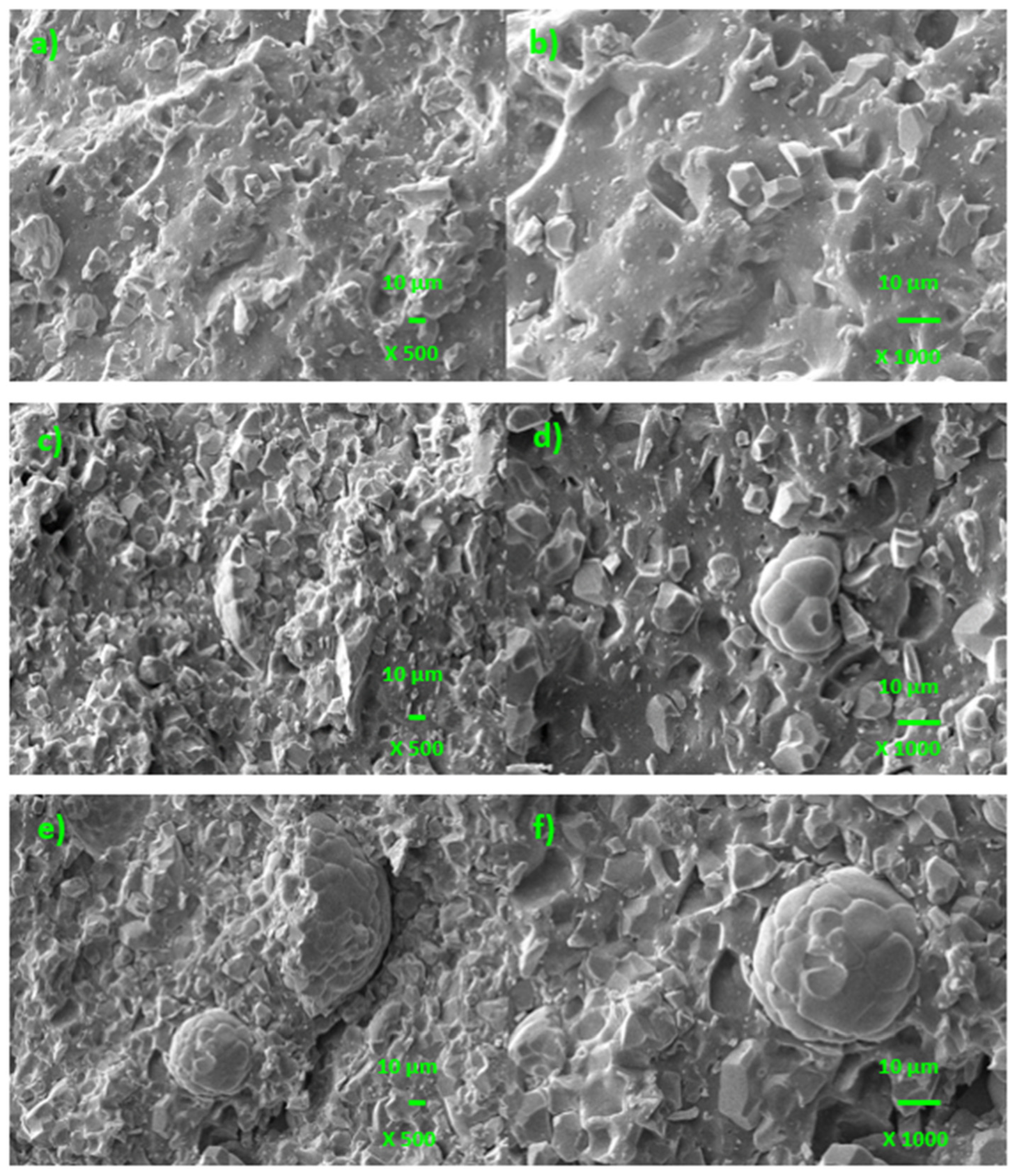
2.2.8. Microscopic Analysis
2.2.9. Thermo-Oxidative Ageing
2.2.10. Ozone Ageing
3. Results and Discussion
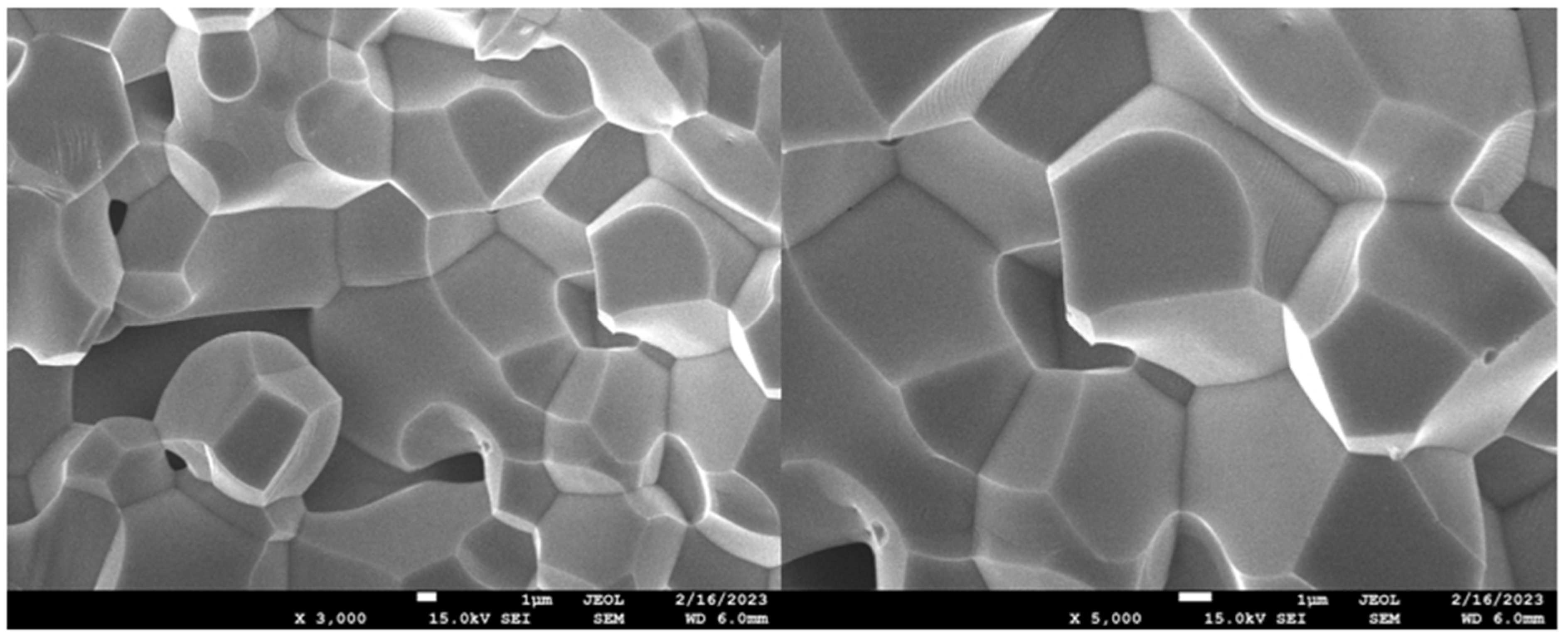
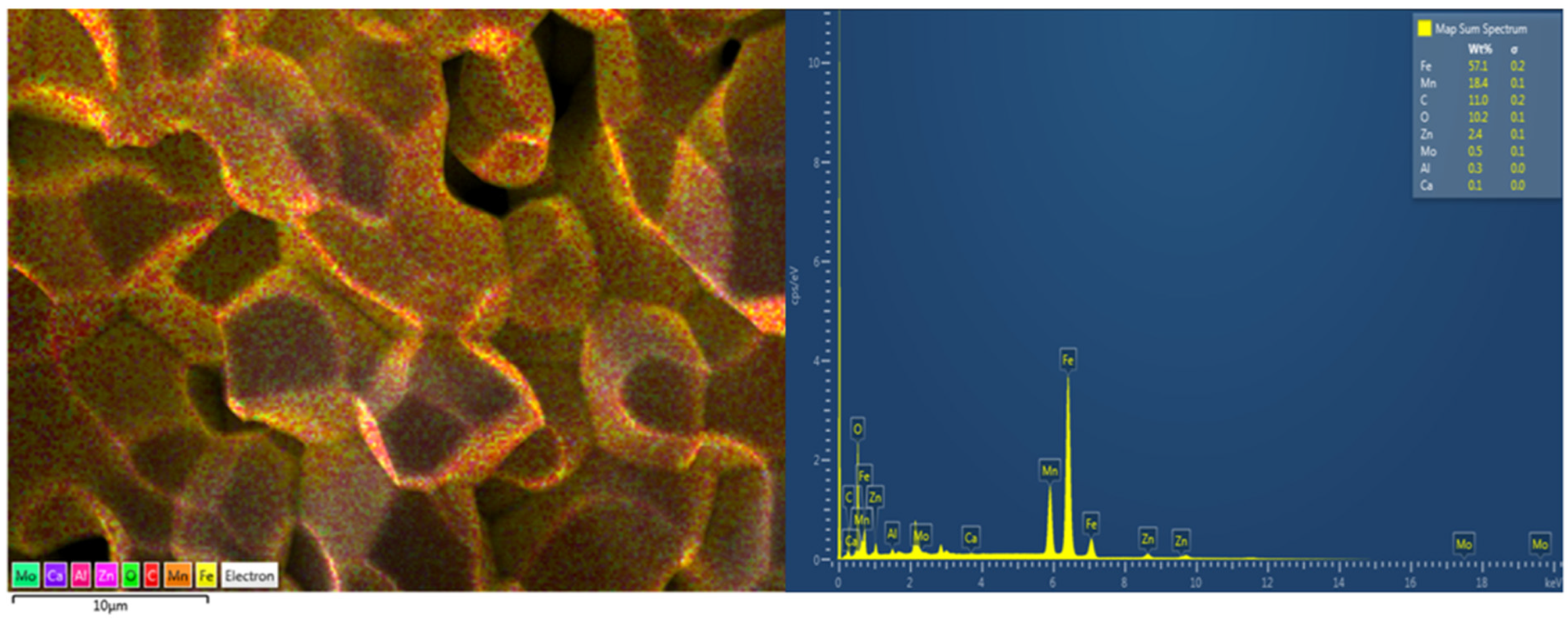
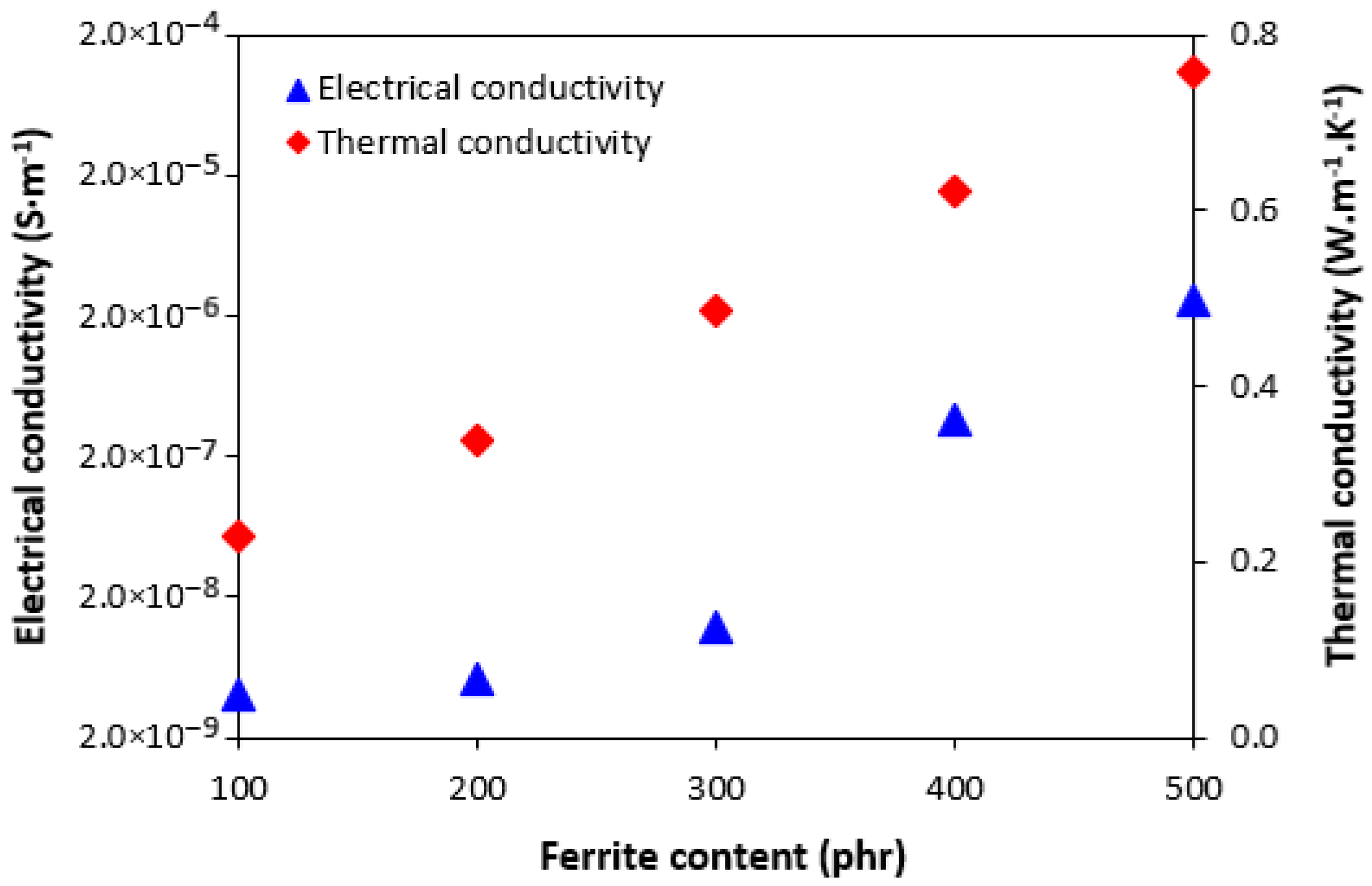
3.1. Characteristics of Ferrite
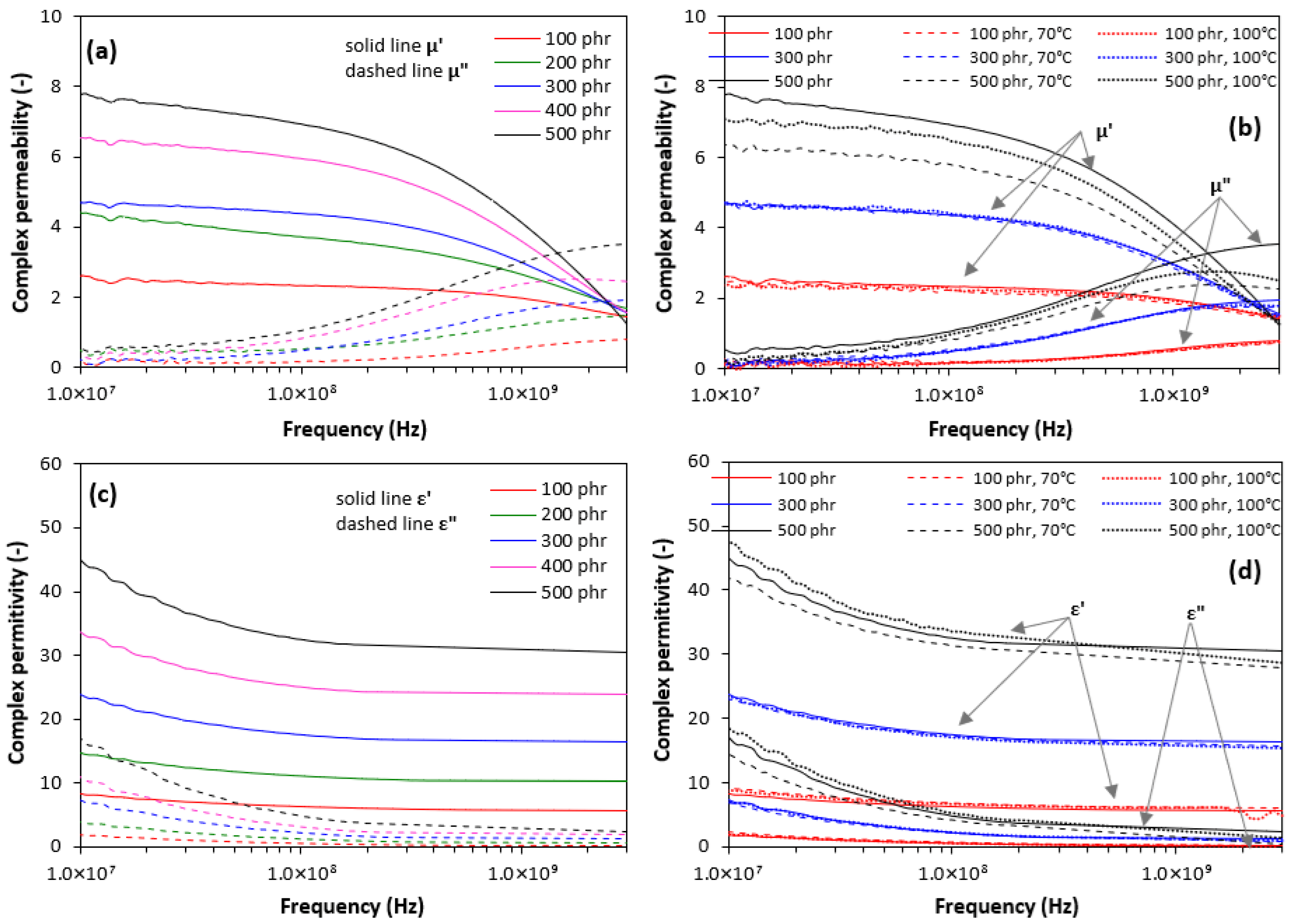
3.2. Influence of Ferrite and Ageing on Absorption Shielding Characteristics
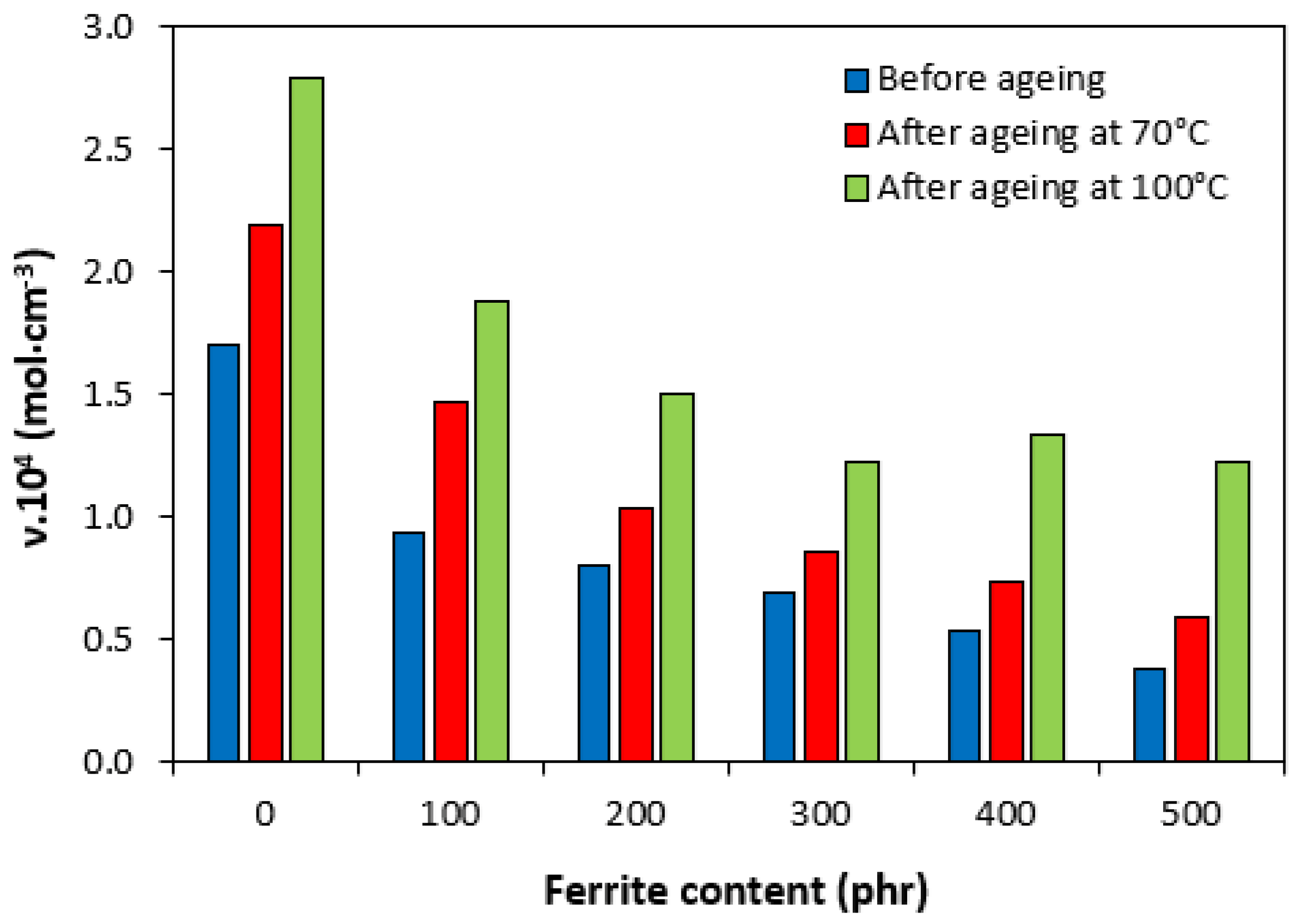
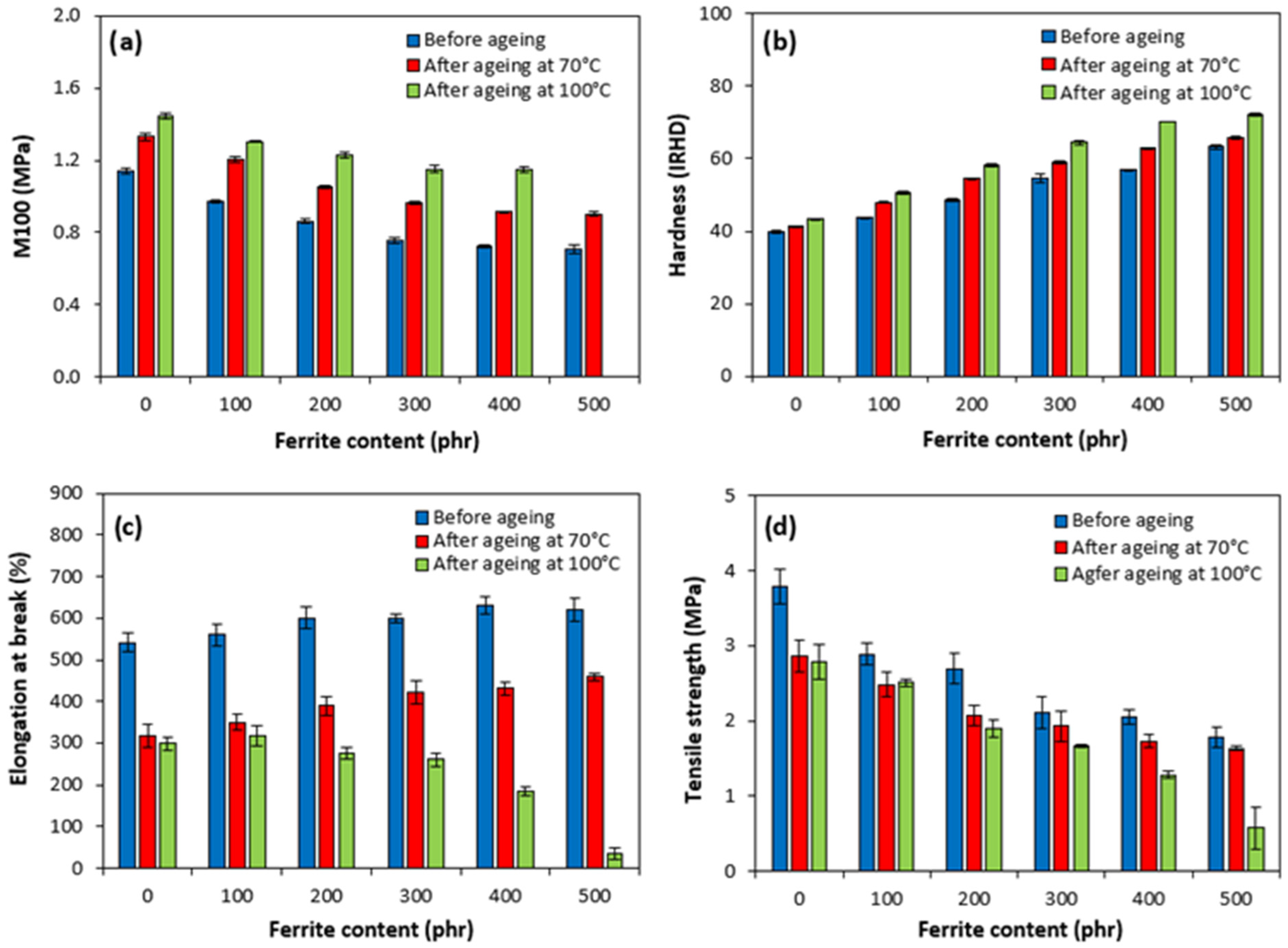
3.3. Influence of Ferrite and Thermo-Oxidative Ageing on Cross-Link Density and Mechanical Characteristics
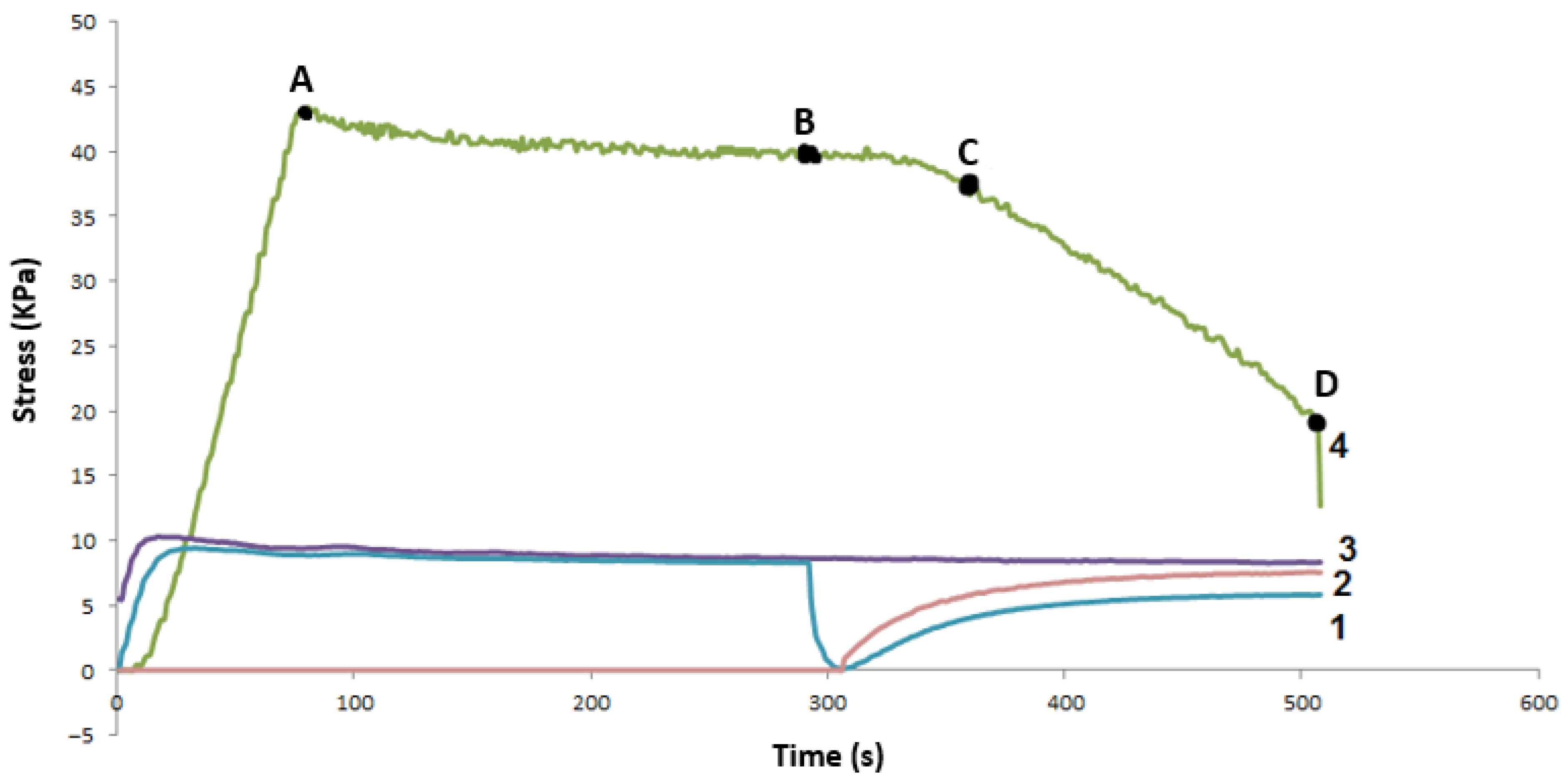
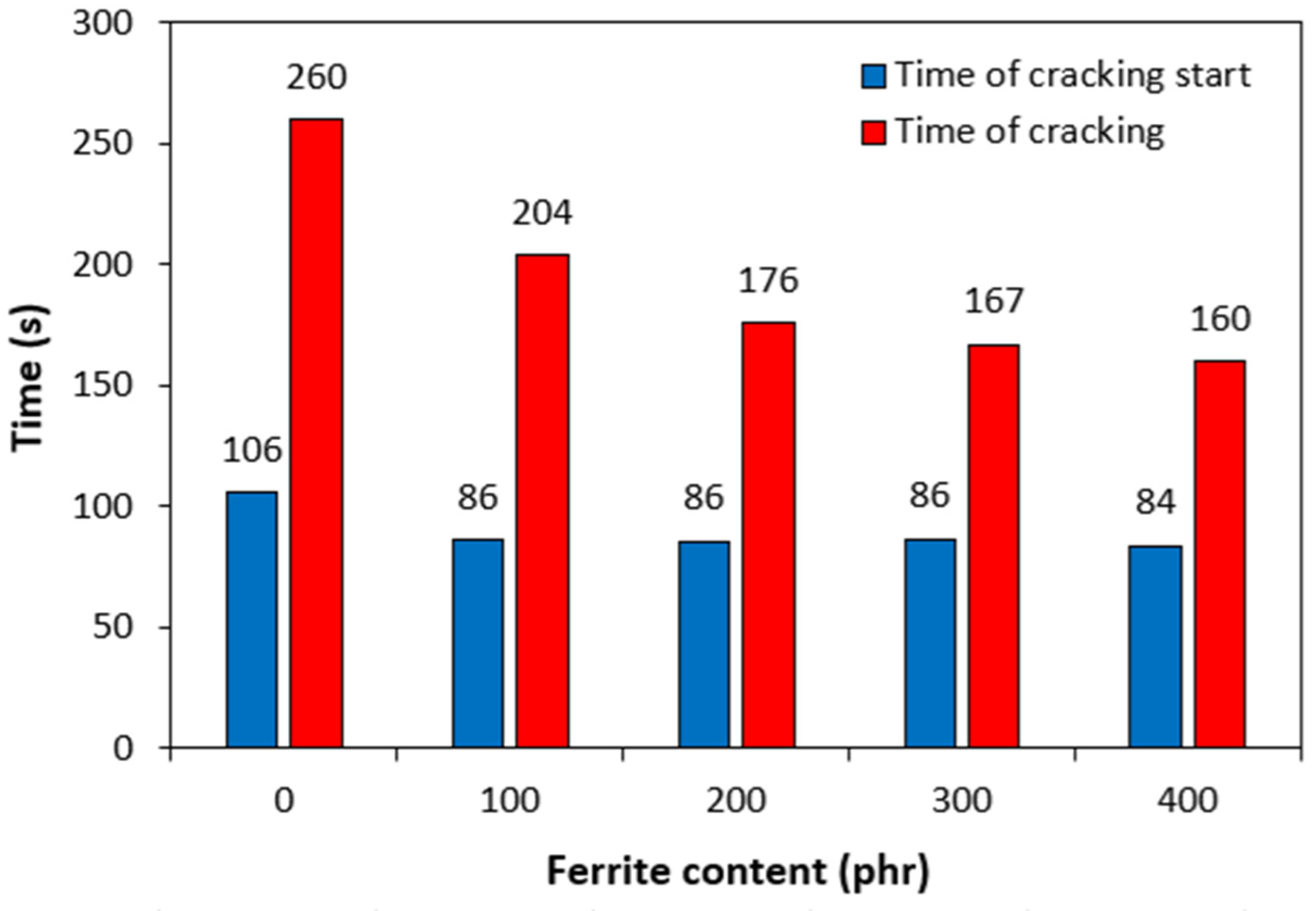
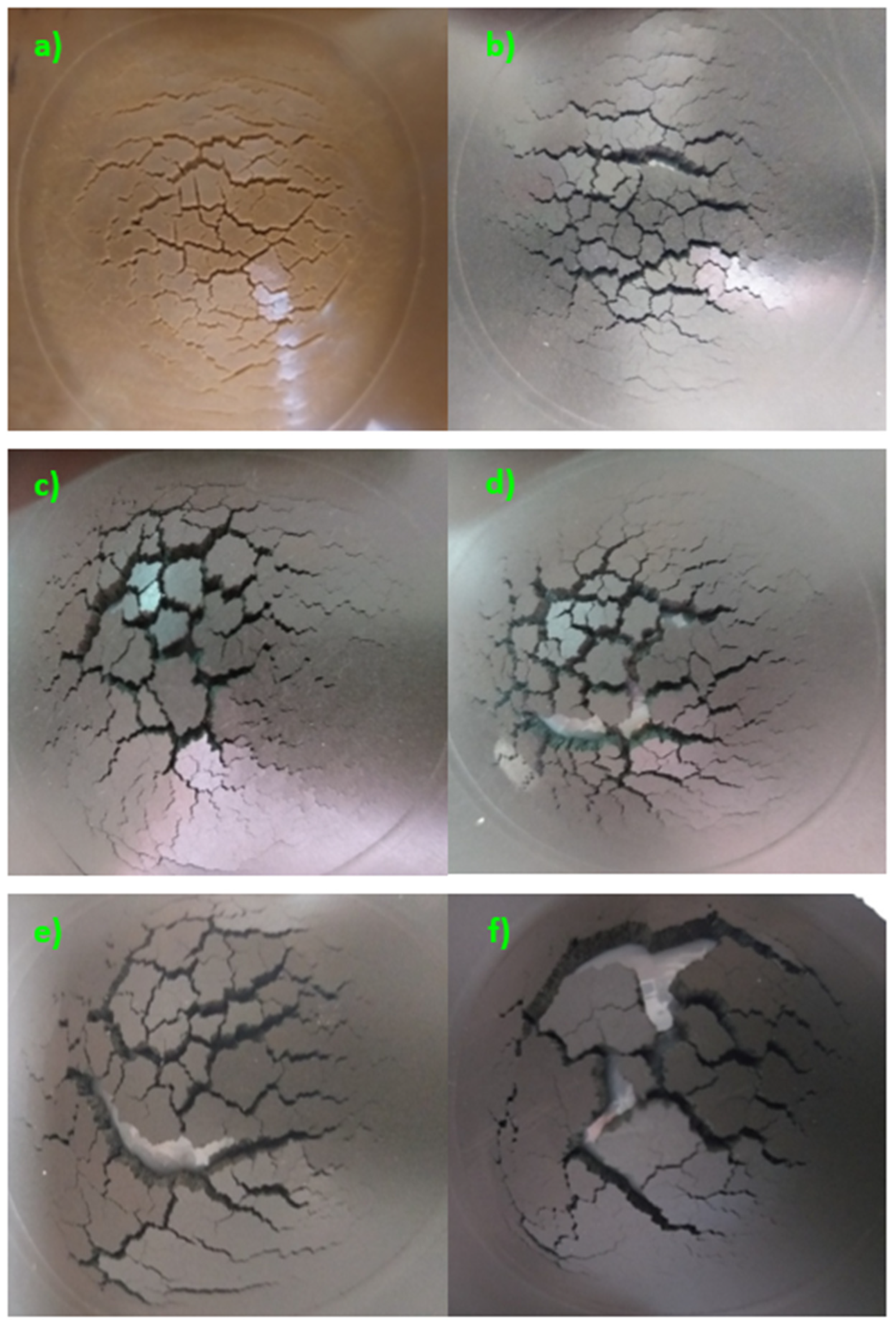
3.4. Influence of Ferrite on Ozone Ageing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, S.; Duan, Z.; Li, Y. Electromagnetic interference effect of portable electronic device with satellite communication to GPS antenna. Sensors 2025, 25, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, S.A.; Amneenah, N.S. Electromagnetic interference impacts on electronic systems and regulations. Int. J. Adv. Multidisc. Res. Stud. 2024, 4, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Deutschmann, B.; Winkler, O.V.E.G.; Kastner, P. Impact of electromagnetic interference on the functional safety of smart power devices for automotive applications. Elektrotechnik Informationstechnik 2018, 135, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.C.; Chiang, J.C.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Cheng, T.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Chuang, Y.T.; Hsu, T.; Guo, H.R. Physiological changes and symptoms associated with short-term exposure to electromagnetic fields: A randomized crossover provocation study. Environ. Health 2022, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousif, J.A.; Alsahlany, A.M. Review: Electromagnetic radiation effects on the human tissues. NeuroQuantology 2022, 20, 8130–8146. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.C. Health and safety practices and policies concerning human exposure to RF/microwave radiation. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1619781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokpinar, A.; Altuntaş, E.; Değermenci, M.; Yilmaz, H.; Baş, O. The Impact of electromagnetic fields on human health: A review. Middle Black Sea J. Health Sci. 2024, 10, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Xia, H. Constructing a segregated magnetic graphene network in rubber composites for integrating electromagnetic interference shielding stability and multi-sensing performance. Polymer 2021, 13, 3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; Ma, S.; Lin, G.; Zhang, X.; Huang, B.; Qian, Q.; Wu, C. Achieving acceptable electromagnetic interference shielding in UHMWPE/ground tire rubber composites by building a segregated network of hybrid conductive carbon black. Nanocomposites 2023, 9, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeddi, J.; Katbab, A.A.; Mehranvari, M. Investigation of microstructure, electrical behavior, and EMI shielding effectiveness of silicone rubber/carbon black/nanographite hybrid composites. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 4056–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.C.; Yan, D.X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Cui, C.H.; Bianco, E.; Lou, J.; Vajtai, R.; Li, B.; Ajayan, P.M.; et al. High Strain tolerant EMI shielding using carbon nanotube network stabilized rubber composite. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1700078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Fan, Y.; Shi, A. Bidirectionally oriented carbon fiber/silicone rubber composites with a high thermal conductivity and enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness. Materials 2023, 16, 6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muringayil Joseph, T.; Mariya, H.J.; Haponiuk, J.T.; Thomas, S.; Esmaeili, A.; Sajadi, S.M. Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of natural and chlorobutyl rubber blend nanocomposite. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansala, T.; Joshi, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Doong, R.; Chaudhary, M. Electrically conducting graphene-based polyurethane nanocomposites for microwave shielding applications in the Ku band. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 1546–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarian, A.; Naderi-Samani, H.; Razavi, R.S.; Jabbari, M.N.; Naderi-Samani, E.; Jahromi, M.G. Study of nickel-coated graphite/silicone rubber composites for the application of electromagnetic interference shielding gaskets. Next Mater. 2024, 2, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Gao, M.Y.; Miao, Y.; Wang, X.M. Recent progress in increasing the electromagnetic wave absorption of carbon-based materials. New Carbon Mater. 2023, 38, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, M.; Xie, A.; Xu, X. Recent advances in design and fabrication of nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave shielding and absorbing. Materials 2021, 14, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Z. Microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of Li-Zn ferrite-carbon nanotubes composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 528, 167808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yin, X.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Wei, H.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Constructing hollow graphene nano-spheres confined in porous amorphous carbon particles for achieving full X band microwave absorption. Carbon 2019, 142, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, J.; Lather, S.; Gupta, A.; Dahiya, S.; Maan, A.S.; Singh, K.; Dhawan, S.K.; Ohlan, A. EMI shielding properties of laminated graphene and PbTiO3 reinforced poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 165, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hema, S.N.; Jayakumar, O.D.; Sreedha, S. Advanced and sustainable EMI shielding composites: Natural rubber-nitrile rubber blends enhanced with hydrothermally synthesized polyaniline nanofibers and spinel strontium ferrites. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 54, 105211. [Google Scholar]
- Kruželák, J.; Kvasničáková, A.; Hložeková, K.; Hudec, I. Progress in polymers and polymer composites used as efficient materials for EMI shielding. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.N.; Wang, Y.; Yue, T.N.; Wang, M. Achieving absorption-type electromagnetic shielding performance in silver micro-tubes/barium ferrites/poly(lactic acid) composites via enhancing impedance matching and electric-magnetic synergism. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 249, 110402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, P.P.; Dobbidi, P. Development of spinel ferrite-based composites for efficient EMI shielding. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 301, 127581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Muniyappan, S.; Racik, K.M.; Manikandan, A.; Mani, D.; Nandhini, S.; Karuppasamy, P.; Pandian, M.S.; Ramasamy, P.; Chander, N.K. Fabrication of binary to quaternary PVDF based flexible composite films and ultrathin sandwich structured quaternary PVDF/CB/g-C3N4/BaFe11.5Al0.5O19 composite films for efficient EMI shielding performance. Synth. Met. 2022, 291, 117199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, N.; Shati, K.; Rehman, U.U.; Nedeen, M. Polyaniline-encapsulated carbon-coated nickel zinc ferrite: A hybrid composite for enhanced absorption-dominant EMI shielding. Synth. Met. 2025, 312, 117883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, L.G.; Petrescu, M.C.; Ionită, V.; Cazacu, E.; Constantinescu, C.D. Magnetic properties of manganese-zinc soft ferrite ceramic for high frequency applications. Materials 2019, 12, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Chahar, D.; Taneja, S.; Bhalla, N.; Thakur, A. A review on Mn-Zn ferrites: Synthesis, characterization and application. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 15740–15763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dippong, T.; Levei, E.A.; Cadar, O. Recent advances in synthesis and applications of MFe2O4 (M=Co, Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn) nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Aggarwal, N.; Kumar, N.; Sharma, A. A review paper: Synthesis techniques and advance application of Mn-Zn nano-ferrites. Mater. Today Proc. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkova, O.; Gagani, A.I.; Karl, C.W.; Rocha, L.B.C.M.; Burlakovs, J.; Krauklis, A.E. Modelling of environmental ageing of polymers and polymer composites—Durability prediction methods. Polymers 2022, 14, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y. Predictive modeling and degradation mechanisms of rubber sealing materials under stress-thermal oxidative aging for long-term sealing performance. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 23, e04949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čubrić, I.S.; Čubrić, G.; Križmančić, I.K.; Kovačević, M. Evaluation of changes in polymer material properties due to ageing in different environments. Polymers 2022, 14, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ke, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Study on the aging of three typical rubber materials under high- and low-temperature cyclic environment. e-Polymers 2023, 23, 20228089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Tri, P.; Triki, E.; Nguyen, T.A. Butyl rubber-based composite: Thermal degradation and prediction of service lifetime. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Y.; Dou, Z.F.; Li, H.S.; Li, N.; Liu, X.R.; Zhang, W.F. Degradation behavior and aging mechanisms of silicone rubber under ultraviolet–thermal–humidity coupling in simulated tropical marine atmospheric environment. Polymer 2025, 328, 128398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Tan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Tang, D.; Ma, B.; Tian, W.; et al. Aging behavior, mechanism and lifetime prediction of liquid crystal polymer films under thermal and oxidative conditions for 5G communication applications. Polymer 2025, 334, 128772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwase, Y.; Shindo, T.; Kondo, H.; Ohtake, Y.; Kawahara, S. Ozone degradation of vulcanized isoprene rubber as a function of humidity. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 142, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; Luo, J.; Yin, B. Effect of thermo-oxidative, ultraviolet and ozone aging on mechanical property degradation of carbon black-filled rubber materials. Buildings 2025, 15, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Zheng, X.; Zhan, S.; Zhou, J.; Liao, S. Study on the ozone aging mechanism of Natural Rubber. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 186, 109514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, F. Protection mechanism of rubbers from ozone attack. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Cho, Y. Estimation of synthetic rubber lifespan based on ozone accelerated aging tests. Polymers 2025, 17, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyselá, G.; Hudec, I.; Alexy, P. Manufacturing and Processing of Rubber, 1st ed.; Slovak University of Technology Press: Bratislava, Slovak, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, S.; Mandot, S.K.; Agrawal, S.L.; Ameta, R.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Das Gupta, S.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Deuri, A.S. Study of metal poisoning in natural rubber–based tire tread compound. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsman, P. Review on the thermo-oxidative degradation of polymers during processing and in service. e-Polymers 2008, 8, 727–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, G. Swelling of filler-reinforced vulcanizates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1963, 7, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Yang, Z.H. The studies of high-frequency magnetic properties and absorption characteristics for amorphous-filler composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 391, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegaonkar, A.P.; Baskey, H.B.; Alegaonkar, P.S. Microwave scattering parameters of ferro–nanocarbon composites for tracking range countermeasures. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hao, L.; Zhang, X.; Tan, S.; Li, H.; Zheng, J.; Ji, G. A novel strategy in electromagnetic wave absorbing and shielding materials design: Multi-responsive field effect. Small Sci. 2022, 2, 2100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.P.; Arjmand, M.; Pötschke, P.; Krause, B.; Fisher, D.; Bose, S.; Sundararaj, U. Tuneable dielectric properties derived from nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes in PVDF-based nanocomposites. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 9966–9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Fan, R. The simultaneously achieved high permittivity and low loss in tri-layer composites via introducing negative permittivity layer. Compos. Part A 2024, 177, 107921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Ke, X.; Zhong, L.; He, Y.; Ren, X. Enhancing dielectric permittivity for energy-storage devices through tricritical phenomenon. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Randall, C.A.; Manias, E. Polarization mechanism underlying strongly enhanced dielectric permittivity in polymer composites with conductive fillers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 7596–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Datar, S. Wideband (8–18 GHz) microwave absorption dominated electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding composite using copper aluminum ferrite and reduced graphene oxide in polymer matrix. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 104902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Kvasničáková, A.; Hložeková, K.; Džuganová, M.; Gregorová, J.; Vilčáková, J.; Gořalík, M.; Hronkovič, J.; Preťo, J.; Hudec, I. The study of electromagnetic absorption characteristics of manganese-zinc ferrite and MWCNT filled composites based on NBR. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2022, 95, 300–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.S.; Kuřitka, I.; Vilcakova, J.; Machovsky, M.; Skoda, D.; Urbánek, P.; Masař, M.; Jurča, M.; Urbánek, M.; Kalina, L.; et al. NiFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by dextrin from corn-mediated sol gel combustion method and its polypropylene nanocomposites engineered with reduced graphene oxide for the reduction of electromagnetic pollution. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 22069–22081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hareesh, M.S.; Joseph, P.; George, S. Electromagnetic interference shielding: A comprehensive review of materials, mechanisms, and applications. Nanoscale Adv. 2025, 7, 4510–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Herrera, C.A.; Gonzalez, H.; de la Torre, F.; Benitez, L.; Cabañas-Moreno, J.G.; Lozano, K. Electrical properties and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of interlayered systems composed by carbon nanotube filled carbon nanofiber mats and polymer composites. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaran, S.; Deshmukh, K.; Basheer Ahamed, M.; Khadheer Pasha, S.K. Recent advances in electromagnetic interference shielding properties of metal and carbon filler reinforced flexible polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A 2018, 114, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neruda, M.; Vojtech, L. Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of woven fabrics with high electrical conductivity: Complete derivation and verification of analytical model. Materials 2018, 11, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Kvasničáková, A.; Hložeková, K.; Plavec, R.; Dosoudil, R.; Gořalík, M.; Vilčáková, J.; Hudec, I. Mechanical, thermal, electrical characteristics and EMI absorption shielding effectiveness of rubber composites based on ferrite and carbon fillers. Polymers 2021, 13, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.Z.; Wang, H.R.; Guo, X.; Wei, Y.C.; Liao, S. Synergistic effect of thermal oxygen and UV aging on natural rubber. e-Polymers 2023, 23, 20230016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Huang, Y. Evolution of crosslinking structure in vulcanized natural rubber during thermal aging in the presence of a constant compressive stress. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 217, 110513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, R.; Lu, D. Investigation of polymer aging mechanisms using molecular simulations: A review. Polymers 2023, 15, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezig, N.; Bellahcene, T.; Aberkane, M.; Abdelaziz, M.N. Thermo-oxidative ageing of a SBR rubber: Effects on mechanical and chemical properties. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Huang, H.; Li, H.; Huang, G.; Lan, J.; Fu, J.; Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Ke, Z.; Guo, X.; et al. A study on the aging mechanism and anti-aging properties of nitrile butadiene rubber: Experimental characterization and molecular simulation. Polymers 2025, 17, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayefi, M.; Eesaee, M.; Hassanipour, M.; Elkoun, S.; David, E.; Nguyen-Tri, P. Thermal aging behavior and lifetime prediction of industrial elastomeric compounds based on styrene–butadiene rubber. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2025, 65, 3226–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, C.; He, A. Accelerated aging behavior and degradation mechanism of nitrile rubber in thermal air and hydraulic oil environments. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 2218–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, I.; Tayefi, M.; Eesaee, M.; Hassanipour, M.; Nguyen-Tri, P. Kinetic analysis of thermal degradation of styrene–butadiene rubber compounds under different aging conditions. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasland, F.; Chazeau, L.; Chenal, J.M.; Schach, R. About thermo-oxidative ageing at moderate temperature of conventionally vulcanized natural rubber. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 161, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Kvasničáková, A.; Dosoudil, R. Thermo-oxidative stability of rubber magnetic composites cured with sulfur, peroxide and mixed curing systems. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2018, 47, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghdoudi, M.; Kömmling, A.; Jaunich, M.; Wolff, D. Scission, cross-linking, and physical relaxation during thermal degradation of elastomers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Prabhahar, M.; Julyes Jaisingh, S.; Arun Prakash, V.R. Role of Magnetite (Fe3O4)-Titania (TiO2) hybrid particle on mechanical, thermal and microwave attenuation behaviour of flexible natural rubber composite in X and Ku band frequencies. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 016106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakošová, A.; Bakošová, D.; Dubcová, P.; Klimek, L.; Dedinský, M.; Lokšíková, S. Effect of thermal aging on the mechanical properties of rubber composites reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Polymers 2025, 17, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karekar, A.; Oßwald, K.; Reincke, K.; Langer, B.; Saalwächter, K. NMR Studies on the phase-resolved evolution of cross-link densities in thermo-oxidatively aged elastomer blends. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 11166–11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Kong, Y.R.; Chen, X.F.; Huang, Y.J.; Lv, Y.D.; Li, G.X. High-temperature thermo-oxidative aging of vulcanized natural rubber nanocomposites: Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 41, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospíšil, J.; Horák, J.; Pilař, J.; Billingham, N.C.; Zweifel, H.; Nešpůrek, S. Influence of testing conditions on the performance and durability of polymer stabilisers in thermal oxidation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 82, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Wang, X.; Huang, G.; Zheng, J.; Huang, J.; Li, G. Thermal ageing behavior of styrene-butadiene random copolymer: A study on the ageing mechanism and relaxation properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1704−1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Wan, C.; Song, P.; Xinyan, Y.; Wang, S. Efficient degradation of vulcanized natural rubber into liquid rubber by catalytic oxidation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 225, 110822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Guan, J.; Bai, W.; Gu, T.; Liu, H.; Liao, S. Role of divalent metal ions on the basic properties and molecular chains of natural rubber. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 452, 022057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Lu, M.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. The effect of different forms of iron substances on the aging properties of carbon-black filled natural rubber. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 4214–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
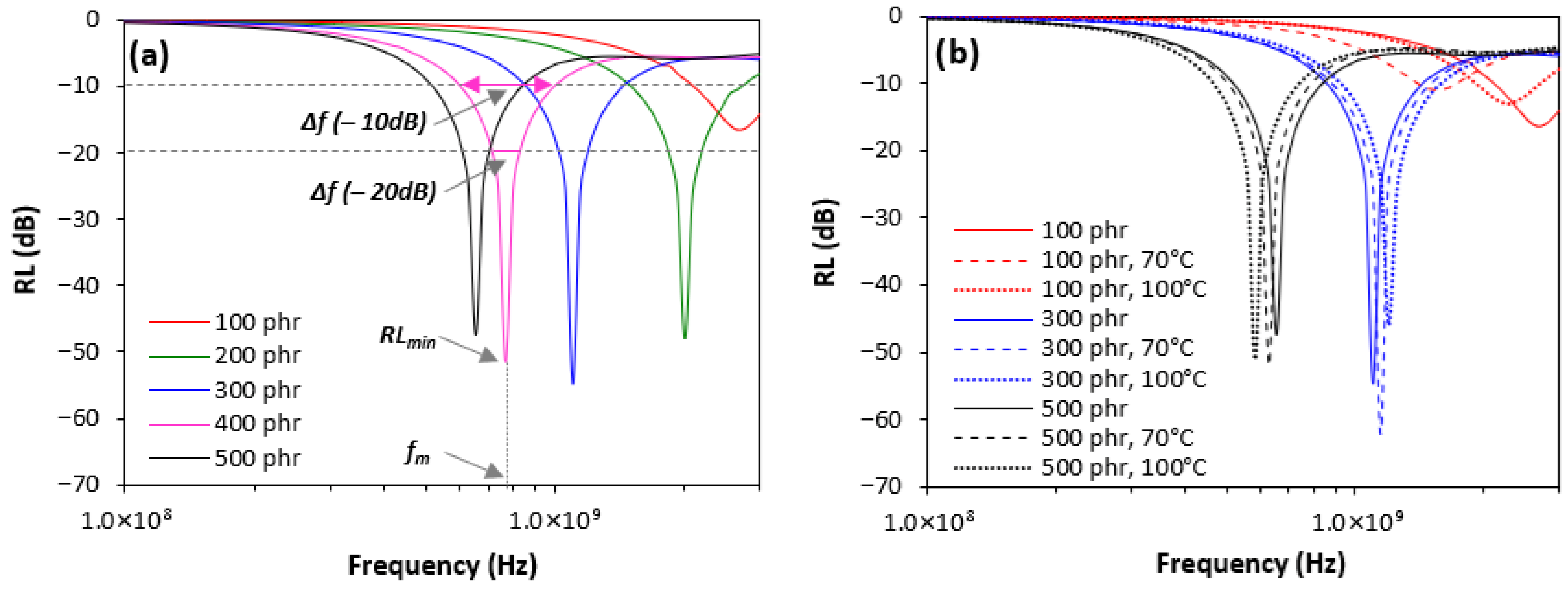
| phr | RLmin (dB) | fm (MHz) | Δf (MHz) −10 dB | Δf (MHz) −20 dB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | −16.5 | 2661 | 900 | − |
| 200 | −48.2 | 2010 | 1210 | 340 |
| 300 | −54.7 | 1103 | 580 | 160 |
| 400 | −51.5 | 769 | 400 | 110 |
| 500 | −47.3 | 655 | 320 | 80 |
| phr | RLmin (dB) | fm (MHz) | Δf (MHz) −10 dB | Δf (MHz) −20 dB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | −10.9 | 1581 | 320 | − |
| 200 | −62.1 | 1148 | 610 | 180 |
| 300 | −52 | 630 | 290 | 80 |
| phr | RLmin (dB) | fm (MHz) | Δf (MHz) −10 dB | Δf (MHz) −20 dB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | −13.1 | 2267 | 800 | − |
| 200 | −46 | 1195 | 650 | 190 |
| 300 | −51.2 | 581 | 280 | 80 |
| Cross-Link Density | M100 | Hardness | Tensile Strength | Elongation at Break | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 °C | 100 °C | 70 °C | 100 °C | 70 °C | 100 °C | 70 °C | 100 °C | 70 °C | 100 °C |
| 28.5 | 64.0 | 16.9 | 26.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | −24.6 | −26.7 | −41.3 | −44.9 |
| 57.2 | 101.1 | 24.3 | 34.3 | 3.1 | - | −14.1 | −13.2 | −37.5 | −43.4 |
| 28.4 | 86.7 | 21.8 | 42.4 | −1.4 | 2.8 | −23.3 | −29.7 | −35.3 | −54.0 |
| 24.0 | 77.5 | 27.3 | 52.5 | 0.3 | 5.9 | −8.7 | −21.4 | −29.6 | −56.6 |
| 36.3 | 146.8 | 26.7 | 59 | 0.9 | 8.0 | −15.9 | −37.5 | −31.7 | −70.7 |
| 56.1 | 223.6 | 27.8 | - | −2.0 | 8.1 | −8.6 | −67.5 | −26.0 | −94.4 |
| Ferrite (phr) | 0 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E100 (MPa) | 0.33 | 0.48 | 0.54 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.78 |
| Stress in the sample (MPa) | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.28 |
| Relaxation time (s) | 29.0 | 29.0 | 29.3 | 29.5 | 32.3 | 32.8 |
| Time of cracking start (s) | 106 | 86 | 86 | 86 | 84 | 83 |
| Time of cracking (s) | 260 | 204 | 176 | 167 | 160 | 139 |
| Rupture time (s) | 354 | 285 | 260 | 253 | 246 | 222 |
| Elongation (%) | 19.3 | 14.6 | 13.5 | 11.8 | 11.6 | 10.8 |
| Amount of ozone reacted during test duration (mg) | 2.0 | 1.5 | 1.17 | 1.15 | 1.03 | 0.88 |
| Amount of ozone reacted to “Time of cracking start” (mg) | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.18 |
| Amount of ozone reacted to “Time of cracking” (mg) | 1.77 | 1.32 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kruželák, J.; Džuganová, M.; Balcerčíková, L.; Dosoudil, R. Influence of Manganese–Zinc Ferrite and Ageing on EMI Absorption Shielding Performance and Properties of Rubber Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9120700
Kruželák J, Džuganová M, Balcerčíková L, Dosoudil R. Influence of Manganese–Zinc Ferrite and Ageing on EMI Absorption Shielding Performance and Properties of Rubber Composites. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(12):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9120700
Chicago/Turabian StyleKruželák, Ján, Michaela Džuganová, Lucia Balcerčíková, and Rastislav Dosoudil. 2025. "Influence of Manganese–Zinc Ferrite and Ageing on EMI Absorption Shielding Performance and Properties of Rubber Composites" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 12: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9120700
APA StyleKruželák, J., Džuganová, M., Balcerčíková, L., & Dosoudil, R. (2025). Influence of Manganese–Zinc Ferrite and Ageing on EMI Absorption Shielding Performance and Properties of Rubber Composites. Journal of Composites Science, 9(12), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9120700







