Understanding and Estimating the Electrical Resistance Between Surface Electrodes on a UD Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Composite Layer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analytical Proposed Method to Predict Surface Resistance in a UD CFRP Laminate
2.2. Testing Configuration
2.3. Experimentation
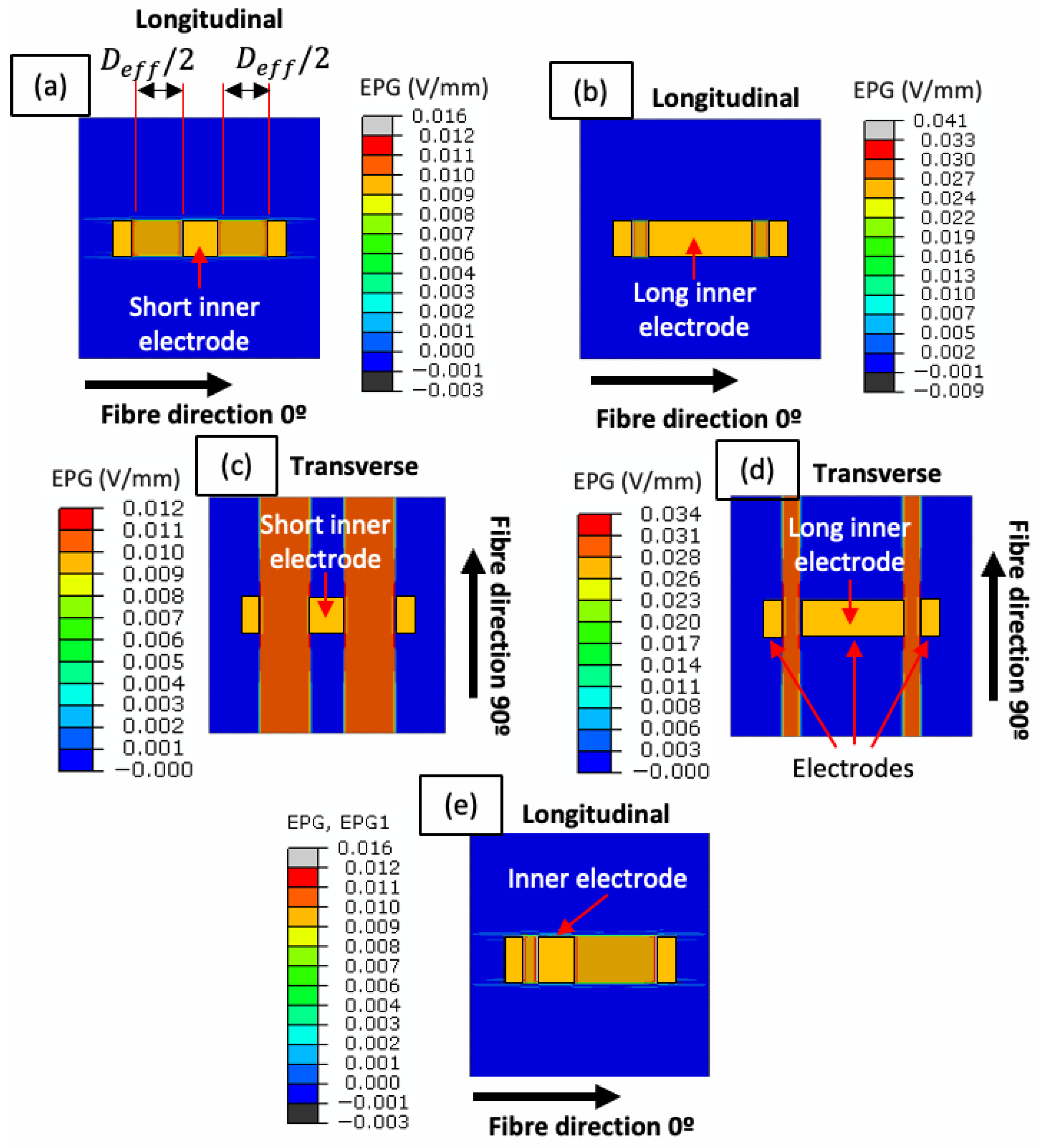
2.4. Finite Element Analysis
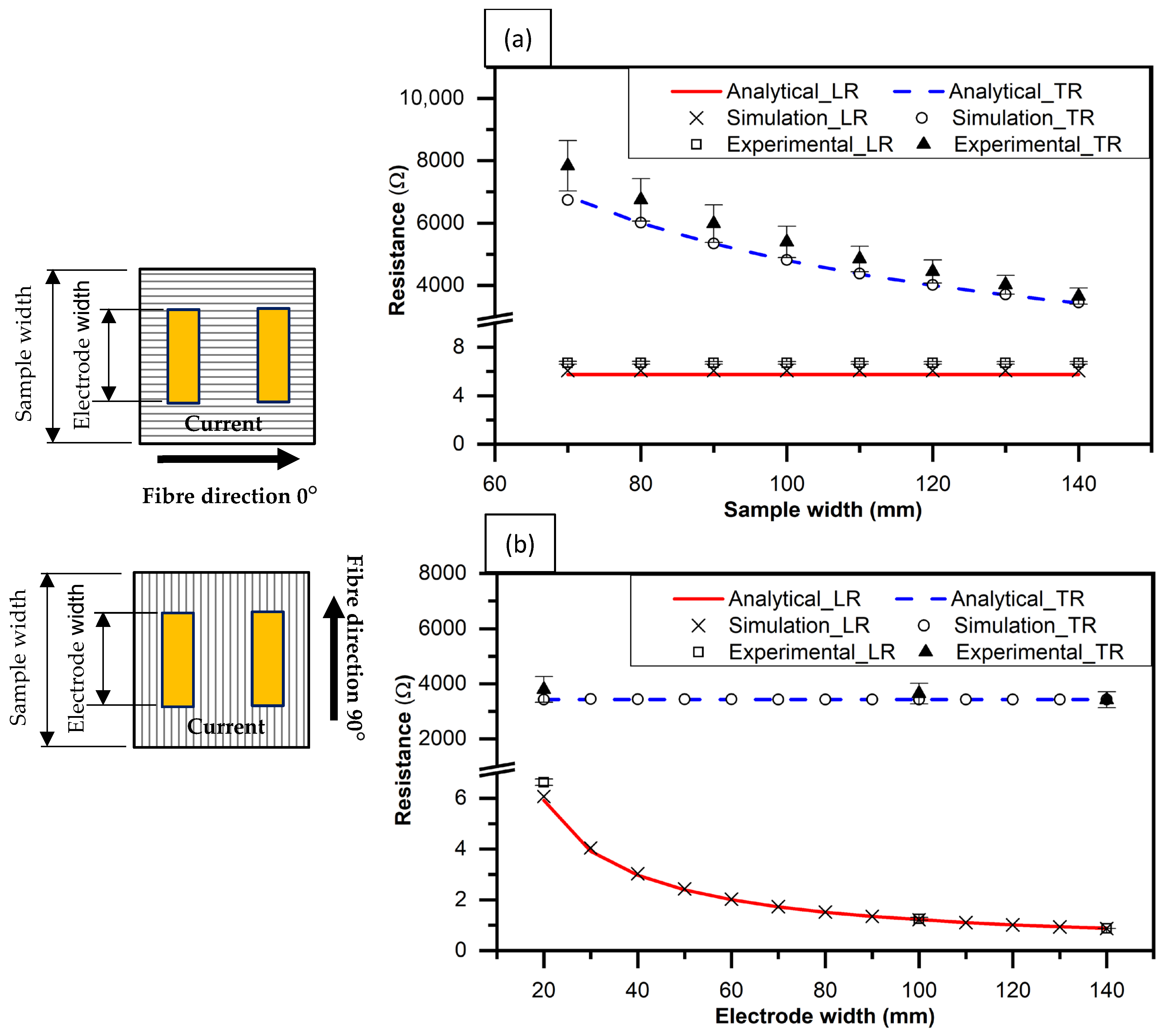
3. Results
Effect of Effective Width
4. Discussion
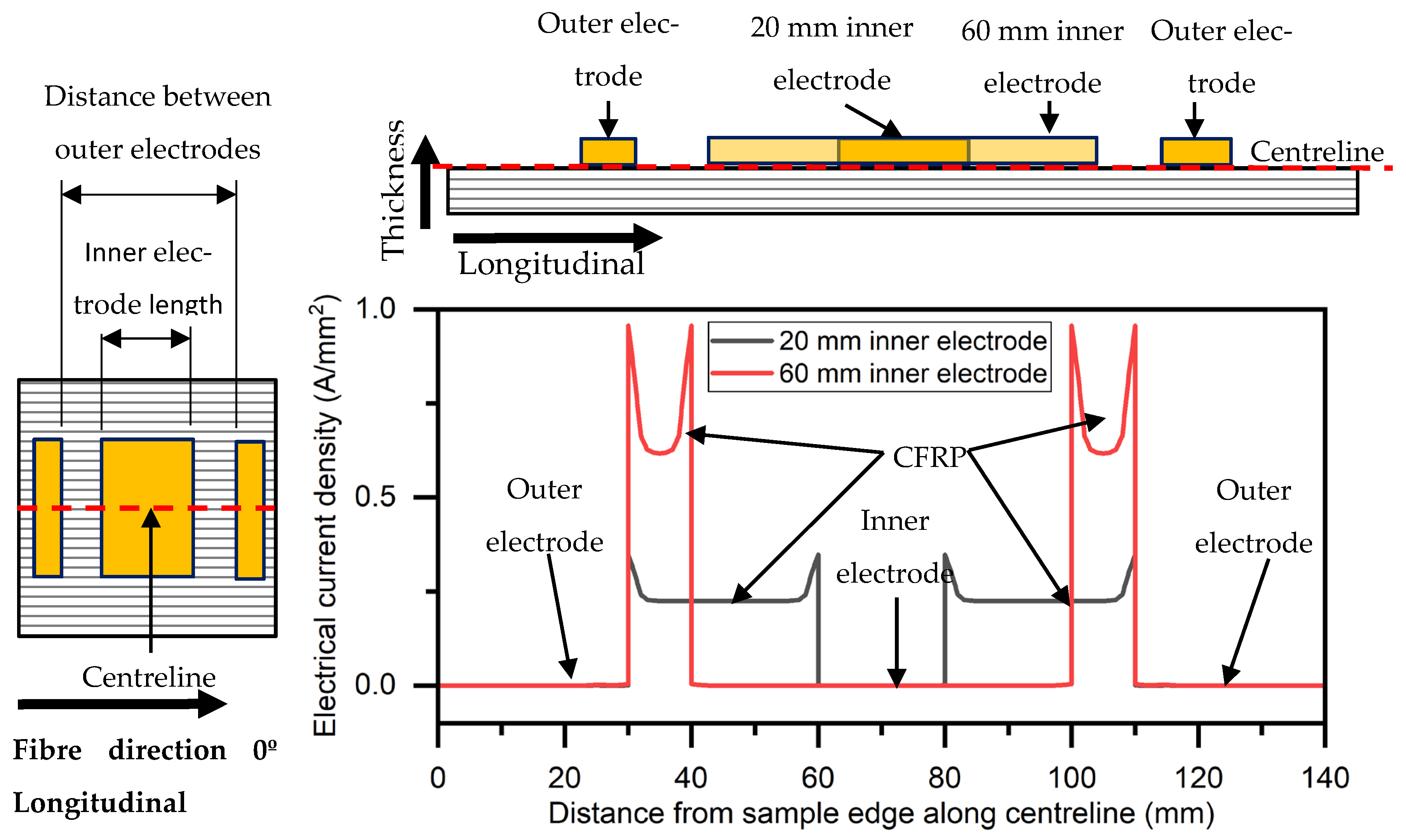
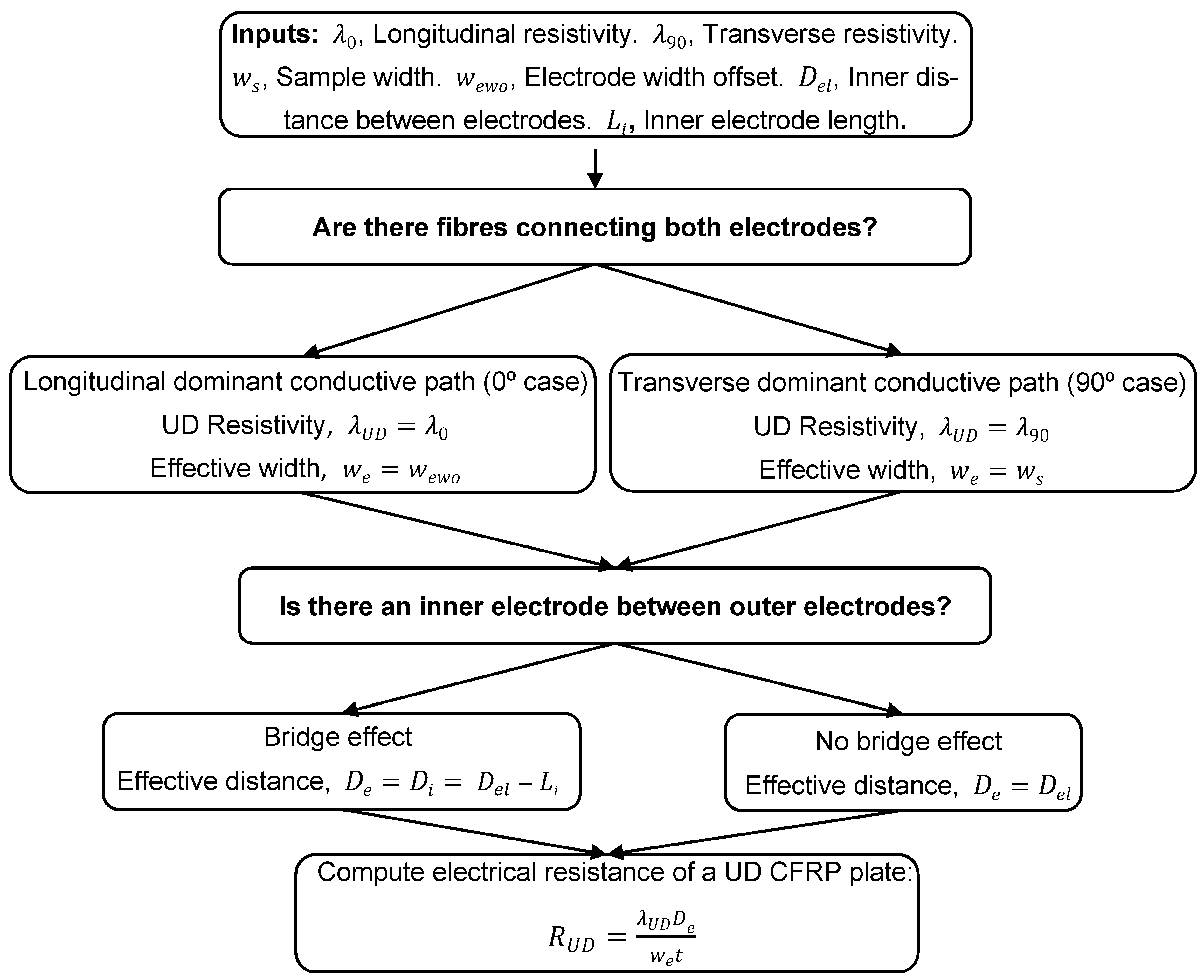
- Longitudinal conductive path: equals the electrode width overlap (), as only fibres bridging both electrodes contribute significantly to conduction.
- Transverse conductive path: equals the full specimen width (), since current spreads through inter-fibre contacts across the entire laminate.
- Without inner electrode: remains constant for all configurations without additional electrodes as , the inner distance between electrodes.
- With an inner electrode: is reduced by the length of the bridging electrode (). Therefore, the effective distance with an inner electrode () is defined as .
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostachowicz, W.; Güemes, A. New Trends in Structural Health Monitoring; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 542. [Google Scholar]
- Dafydd, I.; Khodaei, Z.S. Analysis of barely visible impact damage severity with ultrasonic guided Lamb waves. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 19, 1104–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinet, D.; Mégret, P.; Goossen, K.W.; Qiu, L.; Heider, D.; Caucheteur, C. Fiber Bragg grating sensors toward structural health monitoring in composite materials: Challenges and solutions. Sensors 2014, 14, 7394–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, A.; Regita, J.J.; Rane, B.; Lau, H.H. Structural health monitoring using wireless smart sensor network—An overview. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 163, 108113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagavathiappan, S.; Lahiri, B.B.; Saravanan, T.; Philip, J.; Jayakumar, T. Infrared thermography for condition monitoring—A review. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2013, 60, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addepalli, S.; Zhao, Y.; Roy, R.; Galhenege, W.; Colle, M.; Yu, J.; Ucur, A. Non-destructive evaluation of localised heat damage occurring in carbon composites using thermography and thermal diffusivity measurement. Measurement 2019, 131, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoroki, A.; Tanaka, M.; Shimamura, Y. High performance estimations of delamination of graphite/epoxy laminates with electric resistance change method. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1911–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Chung, D.D.L. Sensing damage in carbon fiber and its polymer-matrix and carbon-matrix composites by electrical resistance measurement. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 2703–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliotti, M.; Lafarie-Frenot, M.C.; Lin, Y.; Pugliese, A. Electro-mechanical fatigue of CFRP laminates for aircraft applications. Compos. Struct. 2015, 127, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Xia, Z.; Choy, F. Damage detection of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites via electrical resistance measurement. Compos. B Eng. 2011, 42, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoroki, A. New analytical method for electric current and multiple delamination cracks for thin CFRP cross-ply laminates using equivalent electric conductance. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2016, 25, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoroki, A.; Tanaka, M.; Shimamura, Y. Measurement of orthotropic electric conductance of CFRP laminates and analysis of the effect on delamination monitoring with an electric resistance change method. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abry, J.C.; Bochard, S.; Chateauminois, A.; Salvia, M.; Giraud, G. In situ detection of damage in CFRP laminates by electrical resistance measurements. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1999, 59, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Heider, D.; Advani, S. A 3D microstructure based resistor network model for the electrical resistivity of unidirectional carbon composites. Compos. Struct. 2015, 134, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadomski, J.; Pyrzanowski, P. Experimental investigation of fatigue destruction of CFRP using the electrical resistance change method. Measurement 2016, 87, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.D.; Oh, S.Y.; Park, Y.B. Self-sensing impact damage in and non-destructive evaluation of carbon fiber-reinforced polymers using electrical resistance and the corresponding electrical route models. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 332, 112762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Chung, D.D.L.; Chung, J.H. Sensitivity of the two-dimensional electric potential/resistance method for damage monitoring in carbon fiber polymer-matrix composite. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 4839–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.H.; Curtin, W.A. Modeling of mechanical damage detection in CFRPs via electrical resistance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1518–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.A.; Jalalvand, M.; Wadge, M.D.; Acosta, J.D.; Felfel, R.M. Robust Electrical Contact with Low Interface Resistance Using Embedded Co-cured Electrodes in Carbon Fibre Composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2025, 32, 2625–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoroki, A.; Suzuki, K.; Mizutani, Y.; Matsuzaki, R. Durability Estimates of Copper Plated Electrodes for Self-sensing CFRP Composites. J. Solid Mech. Mater. Eng. 2010, 4, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chung, D.D.L.; Chung, J.H. Self-sensing of damage in carbon fiber polymer-matrix composite by measurement of the electrical resistance or potential away from the damaged region. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 6463–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagáň, J.; Pelant, J.; Kyncl, M.; Kadlec, M.; Michalcová, L. Damage detection in carbon fiber–reinforced polymer composite via electrical resistance tomography with Gaussian anisotropic regularization. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 18, 1698–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingson, S.W.; Walz, A.; Browder, R. Electromagnetics; Volume, No. v. 1. in Open Textbook Library. Virginia Tech University Libraries, 2018. Available online: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=S3iwtAEACAAJ (accessed on 5 August 2025).

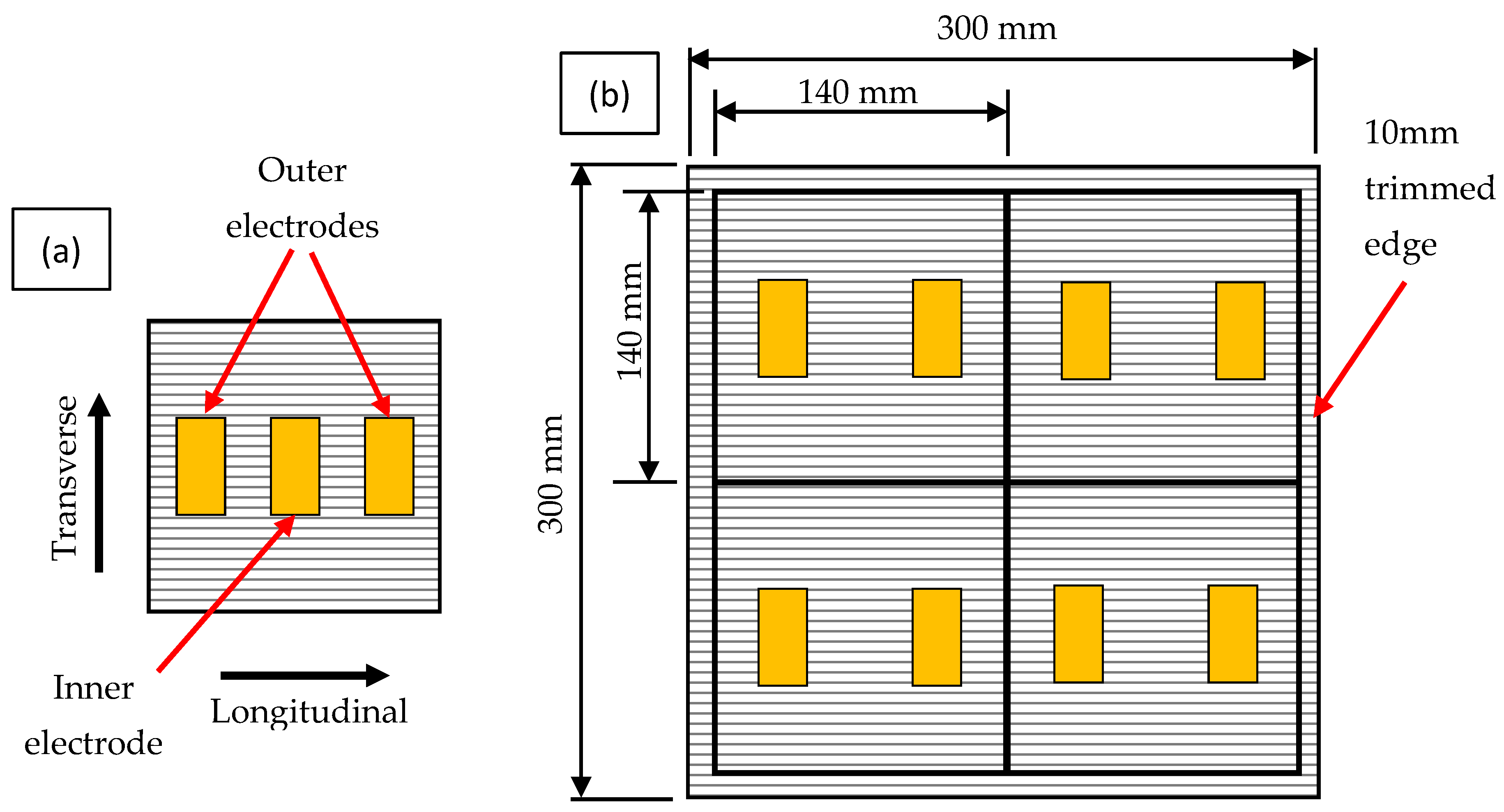



| Type of Sample | CFRP/Electrode Configuration | CFRP Length (mm) | CFRP Width (mm) | Electrode Width (mm) | Electrode Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Varying the electrode and sample width in the longitudinal and transverse directions | Wide sample, wide electrodes | 140 | 120 | 140 | 10 |
| Wide sample, narrow electrodes | 140 | 120 | 20 | 10 | |
| Narrow sample, narrow electrodes | 140 | 70 | 20 | 10 | |
| Varying the electrode width offset with electrode overlapping | Width offset of 0.2, 0.6, and 1.0 | 70 | 70 | 20 | 10 |
| Varying the electrode width offset, without electrode overlapping | Width offset of 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0 | 70 | 140 | 20 | 10 |
| Varying inner-electrode width in the longitudinal and transverse directions | Short inner electrode | 140 | 140 | 20 | 20 |
| Long inner electrode | 140 | 140 | 20 | 60 |
| Material | Longitudinal Resistivity [Ωmm] | Transverse Resistivity [Ωmm] |
|---|---|---|
| TC33/K51 epoxy a | 0.0425 | 355.7 |
| Copper | 1.68 × 10−5 | |
| Longitudinal (0°) | Transverse (90°) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental (Ω) [CV%] | Analytical (Ω) | Experimental (kΩ) [CV%] | Analytical (kΩ) | |
| Wide sample with wide electrodes | 1.25 [4.64] | 1.21 | 3.65 [10.15] | 3.42 |
| Wide sample with narrow electrodes | 6.63 [1.83] | 6.07 | 3.79 [12.36] | 3.42 |
| Narrow sample with narrow electrodes | 6.39 [8.7] | 6.07 | 7.93 [5.91] | 6.86 |
| Width Offset Ratio (−) | Experimental (Ω) [CV%] | Analytical (Ω) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6.63 [0.87] | 6.07 |
| 0.2 | 6.74 [4.36] | 7.59 |
| 0.6 | 10.5 [1.73] | 15.18 |
| 1 | 48 [8.28] | ∞ |
| 2 | 881.79 [9.23] | 857.14 |
| 3 | 1864.52 [6.82] | 1714.28 |
| 5 | 3656.45 [7.37] | 3428.57 |
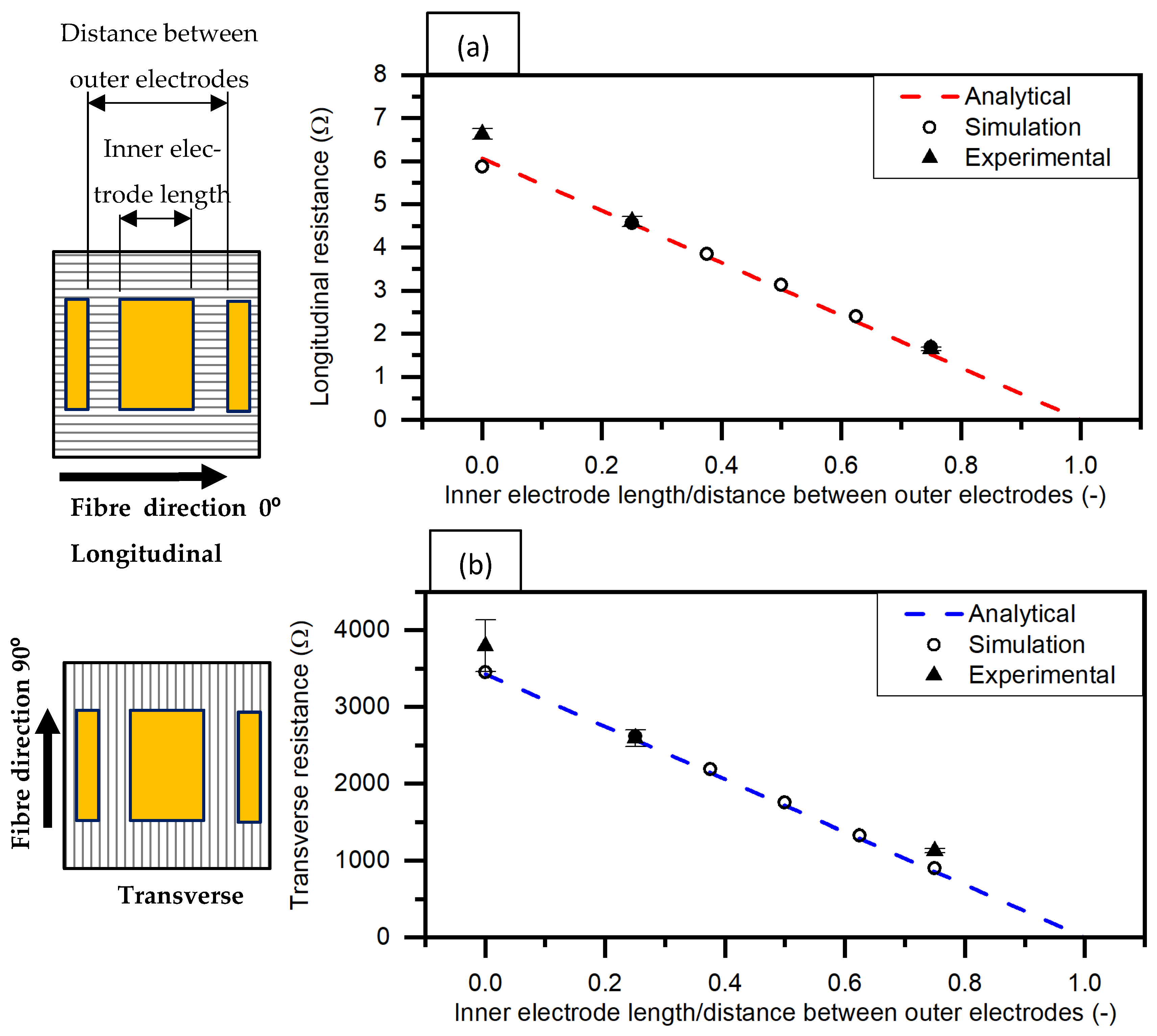
| Inner Electrode Length/Distance Between Outer Electrodes | Longitudinal (0°) | Transverse (90°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental (Ω) [CV%] | Analytical (Ω) | Experimental (Ω) [CV%] | Analytical (Ω) | |
| 0 | 6.63 [1.86] | 6.07 | 3794.4 [8.91] | 3428.57 |
| 0.25 | 4.6 [2.59] | 4.55 | 2589.59 [4.15] | 2571.4 |
| 0.75 | 1.64 [2.19] | 1.51 | 1128.43 [2.21] | 857.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acosta, J.D.; Jalalvand, M.; Malik, S.A.; Hamilton, A. Understanding and Estimating the Electrical Resistance Between Surface Electrodes on a UD Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Composite Layer. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110615
Acosta JD, Jalalvand M, Malik SA, Hamilton A. Understanding and Estimating the Electrical Resistance Between Surface Electrodes on a UD Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Composite Layer. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(11):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110615
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcosta, J. David, Meisam Jalalvand, Sheik Abdul Malik, and Andrew Hamilton. 2025. "Understanding and Estimating the Electrical Resistance Between Surface Electrodes on a UD Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Composite Layer" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 11: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110615
APA StyleAcosta, J. D., Jalalvand, M., Malik, S. A., & Hamilton, A. (2025). Understanding and Estimating the Electrical Resistance Between Surface Electrodes on a UD Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Composite Layer. Journal of Composites Science, 9(11), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110615









