Effect of Selective Z-Pinning on the Static and Fatigue Strength of Step Joints between Composite Adherends
Abstract
1. Introduction
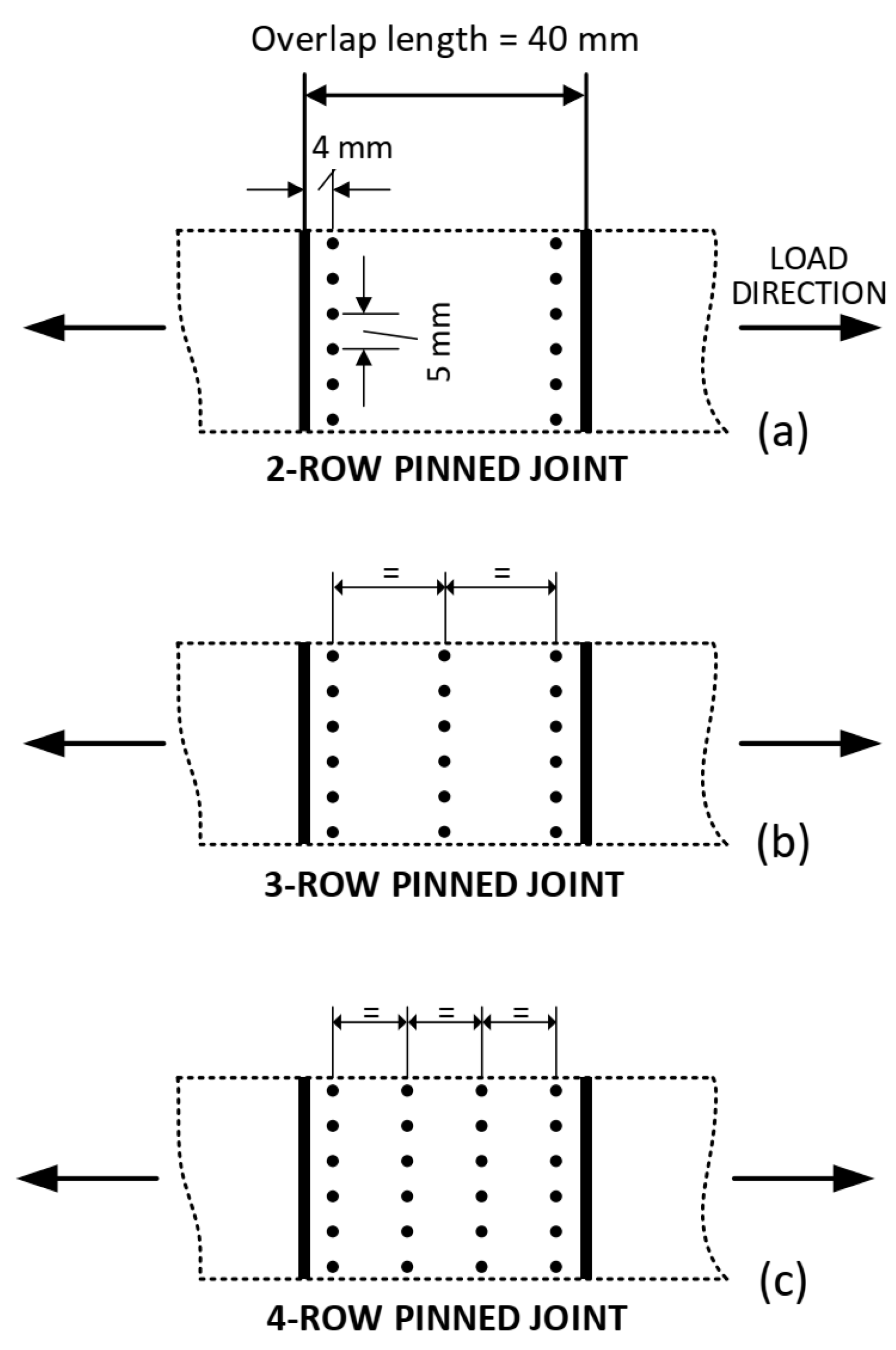
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
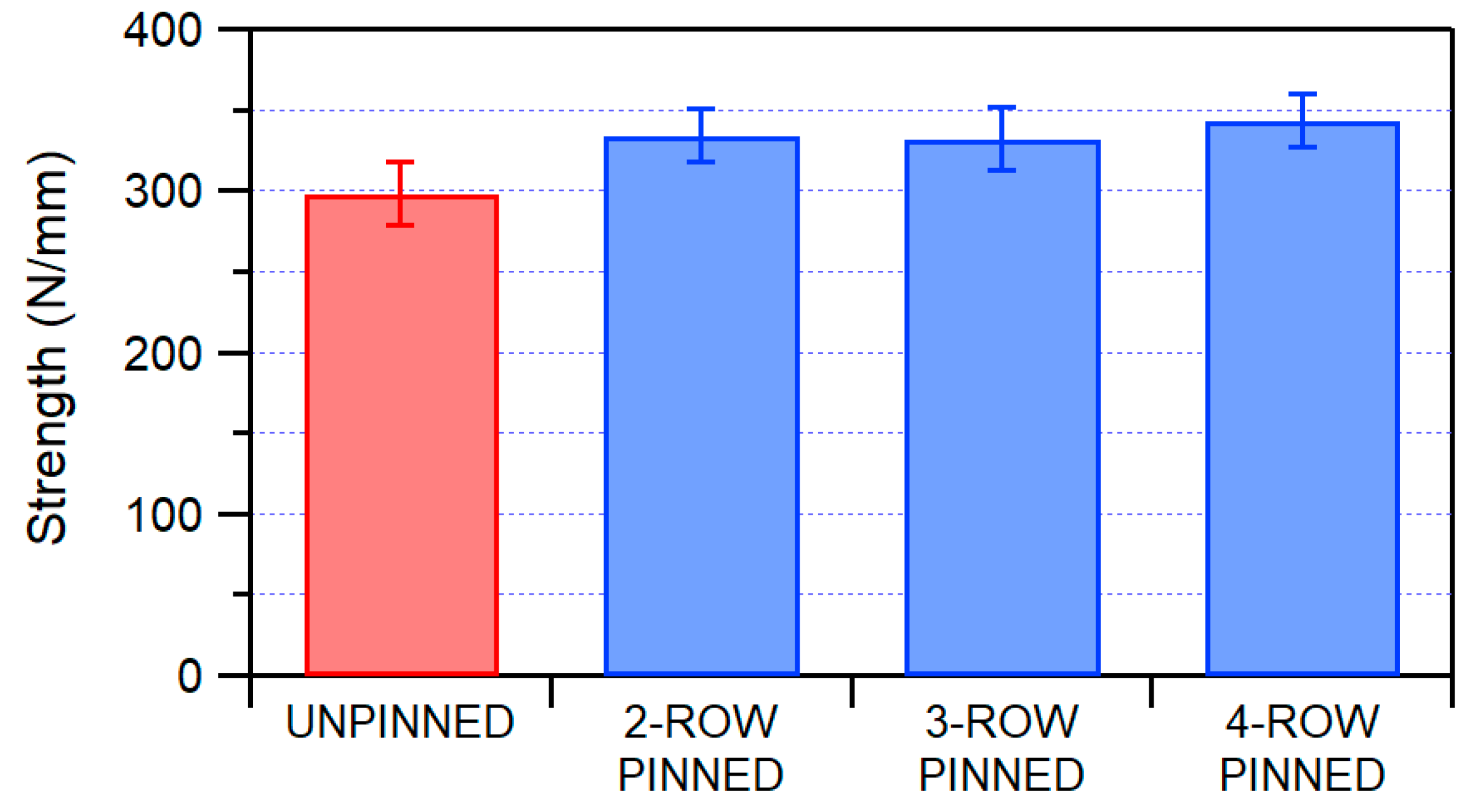
3.1. Static Tests
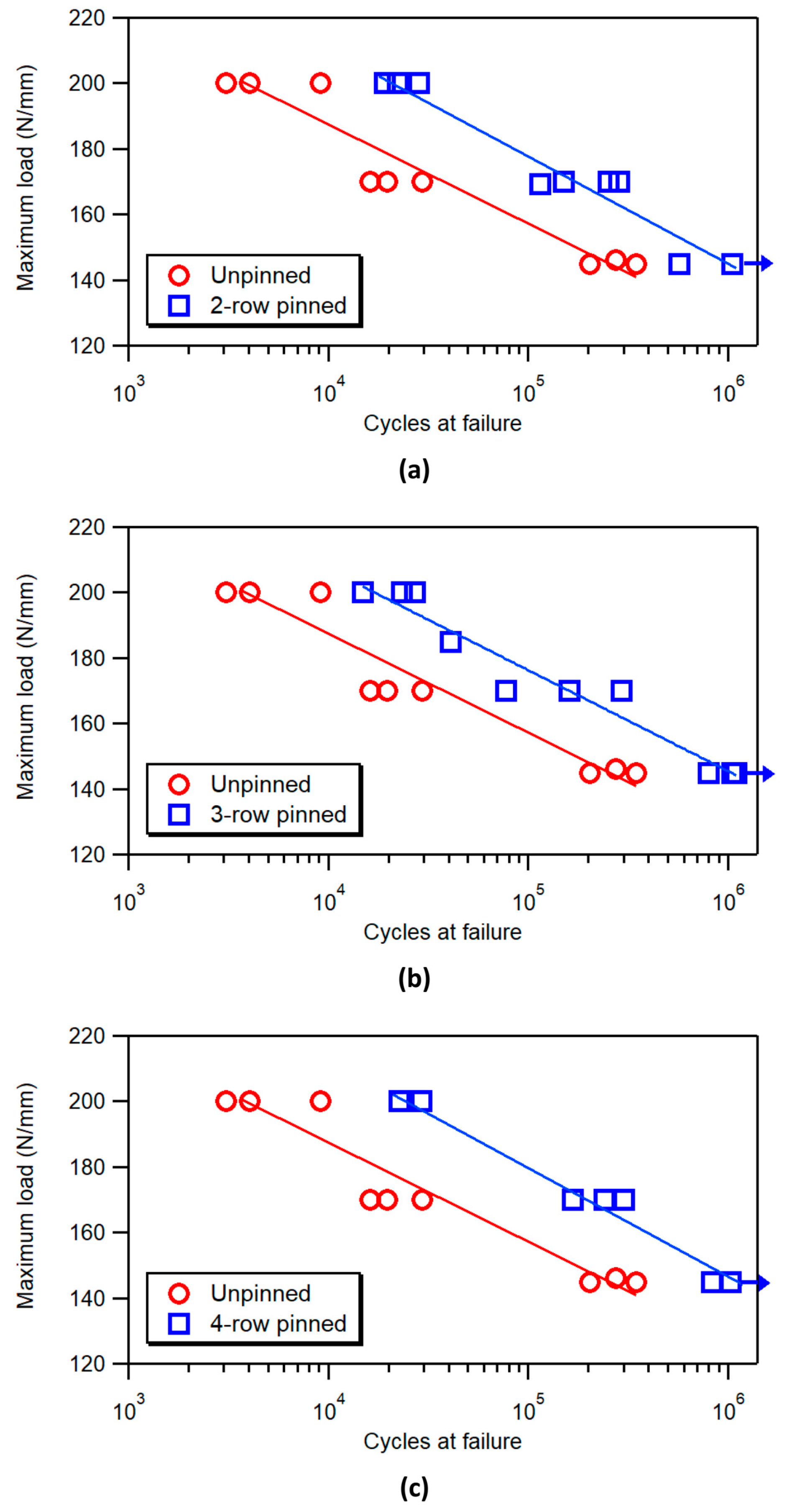
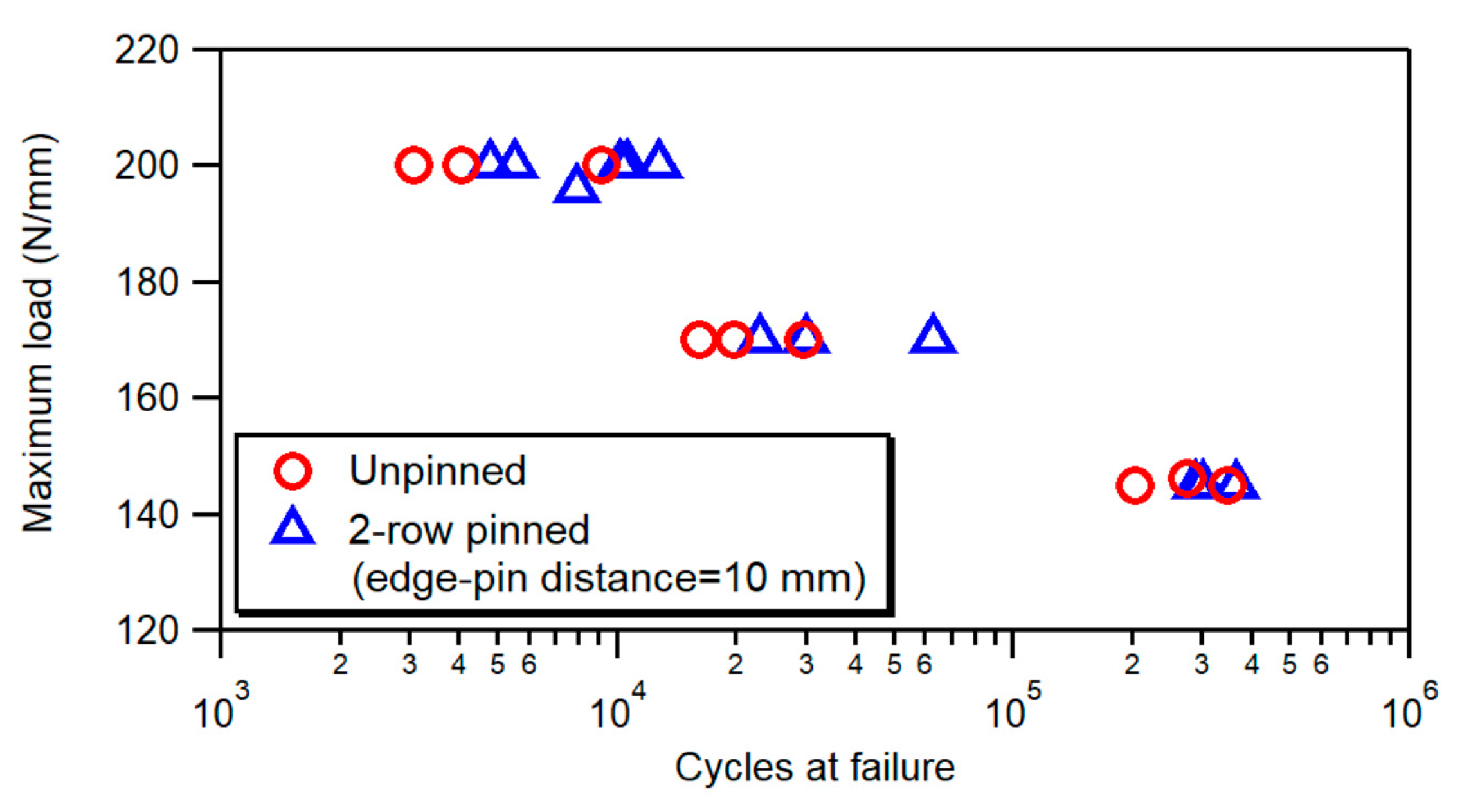
3.2. Fatigue Tests
4. Conclusions
- Z-pinning improves both the static strength and the fatigue lives of the joints.
- The observed increase in static strength (about 15%) and the enhancements in fatigue performance exhibited by z-pinned joints are substantially independent of the number of pin rows.
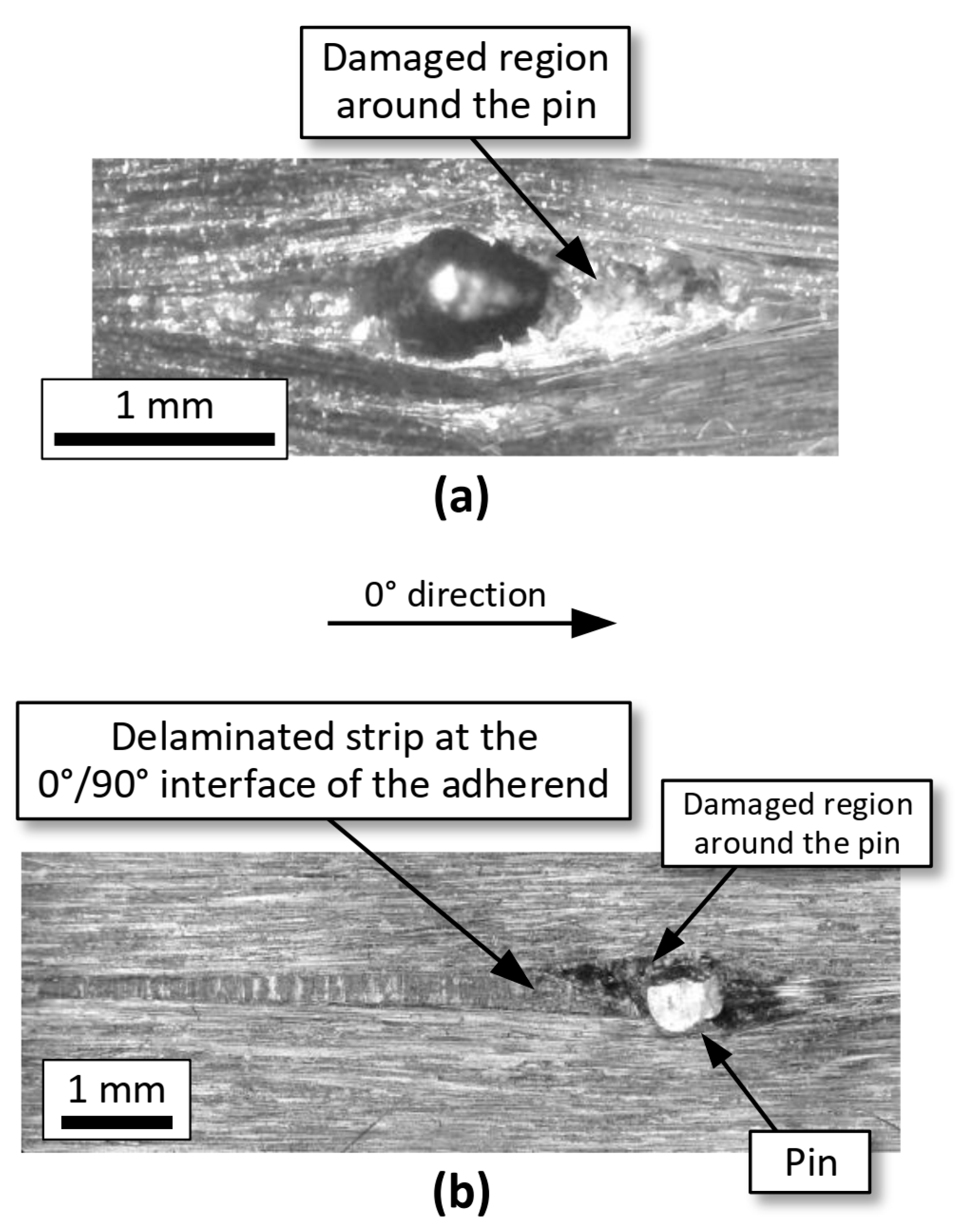
- Similar damage mechanisms occur in the joints under static and fatigue loads. In both unpinned and pinned joints, damage initiates as a matrix crack at the resin-rich regions between the terminations of the adherends. These cracks subsequently grow as delaminations at the joining interface, until they propagate unstably leading to the ultimate failure.
- The improvements in the structural properties of pinned joints are due to the crack-bridging tractions applied by z-pins, which delay the growth of the debonding crack once it reaches the pins adjacent to the joint edges.
- The presence of z-pins introduces additional energy absorbing mechanisms, such as the frictional pullout of pins, resin crushing, and delamination damage within the adherends, which further enhance the load-bearing capacity and damage tolerance of the joints.
- The fatigue and strength improvements achieved by z-pinning are essentially due to the pins close to the overlap edges.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banea, M.D.; da Silva, L.F.M. Adhesively bonded joints in composite materials: An overview. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2009, 223, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoppul, S.D.; Finegan, J.; Gibson, R.F. Mechanics of mechanically fastened joints in polymer–matrix composite structures—A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 301–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhe, S.; Banea, M.D.; de Barros, S.; da Silva, L.F.M. An updated review of adhesively bonded joints in composite materials. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 72, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisnom, M.R. The role of delamination in failure of fibre-reinforced composites. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2012, 370, 1850–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.; Marques, E.A.S.; Machado, J.J.M.; Carbas, R.J.C.; Jiang, D.; da Silva, L.F.M. Review on techniques to improve the strength of adhesive joints with composite adherends. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 177, 107363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Bobyr, M. A review of delamination damage of composite materials. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekinejad, H.; Carbas, R.J.C.; Akhavan-Safar, A.; Marques, E.A.S.; Castro Sousa, F.; da Silva, L.F.M. Enhancing fatigue life and strength of adhesively bonded composite joints: A comprehensive review. Materials 2023, 16, 6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.-G.; Sun, C.T. Novel design of a bonded lap joint. AIAA J. 2001, 39, 1991–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessel, G.; Broughton, J.; Fellows, N.; Durodola, J.; Hutchinson, A. A numerical and experimental study on reverse-bent joints for composite substrates. In Proceedings of the 48th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–26 April 2007; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, T.P.; Mallick, P.K. Effect of spew geometry on stresses in single lap adhesive joints. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 1998, 18, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresimin, M.; Ricotta, M. Fatigue behaviour and damage evolution of single lap bonded joints in composite material. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, B.J.; Han, Y.W. Evaluation of fatigue characteristics for adhesively-bonded composite stepped lap joint. Compos. Struct. 2004, 66, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymerich, F. Effect of stitching on the static and fatigue performance of co-cured composite single-lap joints. J. Compos. Mater. 2004, 38, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Mouritz, A.P.; Cox, B.N. Properties and failure mechanisms of pinned composite lap joints in monotonic and cyclic tension. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2163–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymerich, F.; Onnis, R.; Priolo, P. Analysis of the effect of stitching on the fatigue strength of single-lap composite joints. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Mouritz, A.P.; Cox, B.N. Elevated temperature properties of pinned composite lap joints. J. Compos. Mater. 2008, 42, 741–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, T.; Isa, M.; Chang, P.; Mouritz, A. Improving the structural properties and damage tolerance of bonded composite joints using z-pins. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 46, 3255–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingkarawat, K.; Mouritz, A.P. Comparative study of metal and composite z-pins for delamination fracture and fatigue strengthening of composites. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 154, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.-G.; Park, Y.-B.; Kweon, J.-H.; Choi, J.-H. Fatigue behaviour of metal pin-reinforced composite single-lap joints in a hygrothermal environment. Compos. Struct. 2014, 108, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, M.-G.; Kweon, J.-H.; Choi, J.-H. Fatigue Characteristics of jagged pin-reinforced composite single-lap joints in hygrothermal environments. Compos. Struct. 2015, 119, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, M.; Růžek, R.; Bělský, P. Concurrent use of z-pins for crack arrest and structural health monitoring in adhesive-bonded composite lap joints. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 188, 107967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, A.R.; Ladani, R.B.; Wang, C.H.; Mouritz, A.P. Design considerations in the strengthening of composite lap joints using metal z-pins. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 160, 107031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritz, A.P. Review of z-pinned composite laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 2383–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarantinos, N.; Tsantzalis, S.; Ucsnik, S.; Kostopoulos, V. Review of through-the-thickness reinforced composites in joints. Compos. Struct. 2019, 229, 111404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritz, A.P. Review of z-pinned laminates and sandwich composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 139, 106128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulos, V.; Sarantinos, N.; Tsantzalis, S. Review of through-the-thickness reinforced z-pinned composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugg, K.L.; Cox, B.N.; Ward, K.E.; Sherrick, G.O. Damage Review of z-pinned laminates and sandwich composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1998, 29, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartié, D.D.R.; Cox, B.N.; Fleck, N.A. Mechanisms of crack bridging by composite and metallic rods. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’membe, B.; Yasaee, M.; Hallett, S.R.; Partridge, I.K. Effective use of metallic z-pins for composites through-thickness reinforcement. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 175, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’membe, B.; Gannon, S.; Yasaee, M.; Hallett, S.R.; Partridge, I.K. Mode II delamination resistance of composites reinforced with inclined z-pins. Mater. Des. 2016, 94, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, A.C.; Drechsler, K.; Hombergsmeier, E. Analysis of the static and fatigue strength of a damage tolerant 3d-reinforced joining technology on composite single lap joints. In Proceedings of the 53rd AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–26 April 2012; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Juergens, M.; Nogueira, A.C.; Lang, H.; Hombergsmeier, E.; Drechsler, K. Influence of an optimized 3d-reinforcement layout on the structural mechanics of co-bonded CFRP joints. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Composite Materials, Seville, Spain, 22–26 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Juergens, M.; Kurtovic, A.; Mertens, T.; Kolb, M.; Greitemeier, D.; Lang, H.; Hombergsmeier, E.; Drechsler, K. Influence of surface treatment and design of 3D-reinforcements on delamination resistance and mechanical properties of CFRP/CFRP joints under static and fatigue loading. In Proceedings of the 20th Internation Conference on Composite Materials, Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stelzer, S.; Ucsnik, S.; Pinter, G. Fatigue behaviour of composite–composite joints reinforced with cold metal transfer welded pins. Int. J. Fatigue 2015, 81, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, S.; Ucsnik, S.; Pinter, G. Strength and damage tolerance of composite–composite joints with steel and titanium through the thickness reinforcements. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 88, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisagni, C.; Furfari, D.; Pacchione, M. Experimental investigation of reinforced bonded joints for composite laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 2018, 52, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.; Mouritz, A.P.; Cox, B.N. Properties and failure mechanisms of z-pinned laminates in monotonic and cyclic tension. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Scharr, G. Pull-out performance of rectangular z-pins in hot-cured carbon fiber reinforced laminates. Compos. Struct. 2018, 186, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, G.; Aymerich, F. Effect of stitching on the static and fatigue properties of fibre-dominated and matrix-dominated composite laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2023, 173, 107648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritz, A.P. A simple fatigue life model for three-dimensional fiber-polymer composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2006, 40, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loi, G.; Buonadonna, P.; El Mohtadi, R.; Carta, M.; Lai, D.; El Mehtedi, M.; Aymerich, F. Effect of Selective Z-Pinning on the Static and Fatigue Strength of Step Joints between Composite Adherends. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs8030084
Loi G, Buonadonna P, El Mohtadi R, Carta M, Lai D, El Mehtedi M, Aymerich F. Effect of Selective Z-Pinning on the Static and Fatigue Strength of Step Joints between Composite Adherends. Journal of Composites Science. 2024; 8(3):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs8030084
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoi, Gabriela, Pasquale Buonadonna, Rayane El Mohtadi, Mauro Carta, Daniele Lai, Mohamad El Mehtedi, and Francesco Aymerich. 2024. "Effect of Selective Z-Pinning on the Static and Fatigue Strength of Step Joints between Composite Adherends" Journal of Composites Science 8, no. 3: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs8030084
APA StyleLoi, G., Buonadonna, P., El Mohtadi, R., Carta, M., Lai, D., El Mehtedi, M., & Aymerich, F. (2024). Effect of Selective Z-Pinning on the Static and Fatigue Strength of Step Joints between Composite Adherends. Journal of Composites Science, 8(3), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs8030084







