Structural Formation and Properties of Eco-Friendly Foam Concrete Modified with Coal Dust
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- Analysis of the existing research, regulatory, and technological base to manufacture non-autoclaved foam concrete using various types of waste;
- -
- Identification of scientific deficits and prospects from the point of view of theory and practice for the use of coal dust as components of such foam concrete;
- -
- Setting up an experiment, selecting basic components, and determining technological parameters to obtain the most effective foam concrete based on coal dust;
- -
- Conducting pilot experiments and analyzing the results obtained in comparison with existing analogs to determine the effectiveness of the suggested solutions;
- -
- Determination of fundamental relationships between the composition, structure, and properties of the resulting foam concrete;
- -
- Scientific substantiation of the result obtained, determination of the qualitative and quantitative picture of structure formation, and properties of foam concrete using coal dust.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- -
- Portland cement CEM I 52.5N (C) (CEMROS, Stary Oskol, Russia).
- -
- Quartz sand (S) (RostStroyMix, Rostov-on-Don, Russia).
- -
- Coal dust (CD) (IMPEX-GROUP, Krasny Sulin, Russia).
- -
- Synthetic foaming agent Rospena (F) (Rospena, Mordovia, Russia).
2.2. Methods
- -
- Initial materials were dosed under the formulation of the compositions;
- -
- Dry components (sand, cement, and coal dust) were added to water and mixed for 2 min at a speed of 600 rpm on a turbulent laboratory foam concrete mixer CA 400/500 (DSTU, Rostov-on-Don, Russia) with a capacity of 50 L using one-stage technology without the use of a special foam-forming installation;
- -
- A foaming agent was introduced into the resulting mixture and all components were intensively mixed for 4 min;
- -
- The foam concrete mixture, brought to a homogeneous state, was poured into molds and compacted by tapping the metal molds 15 times with the mixture on the concrete surface;
- -
- Foam concrete samples were kept in natural conditions for 3 h and then placed in a steaming chamber;
- -
- Steaming of foam concrete samples was carried out according to the following regime: temperature rise—3 h; exposure—12 h; cooling—2 h. The maximum steaming temperature was 80 °C;
- -
- Before stripping, steamed samples were kept for 2 h in laboratory conditions at a relative air humidity of 55% and an air temperature of 25 °C and then removed from the molds.
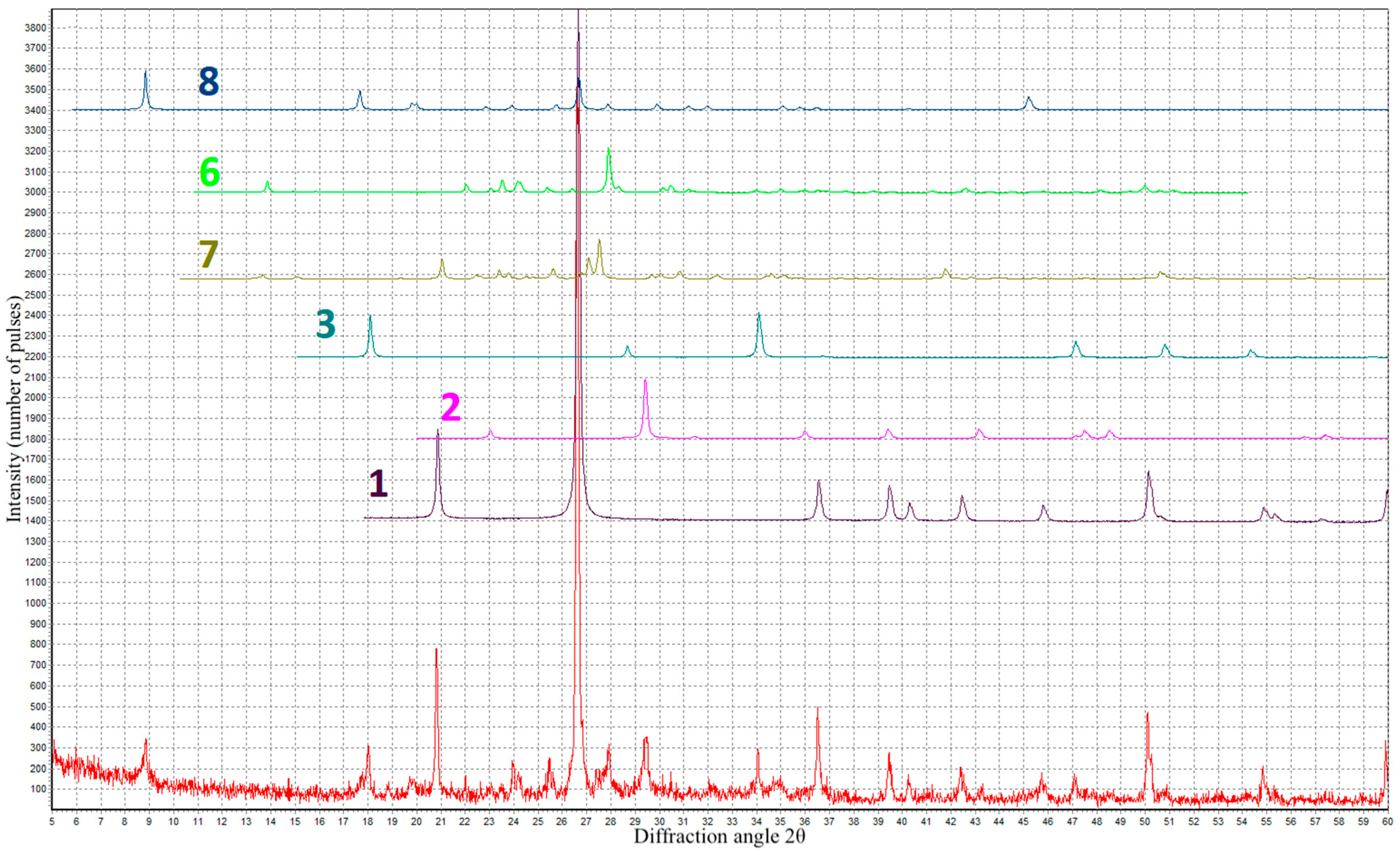
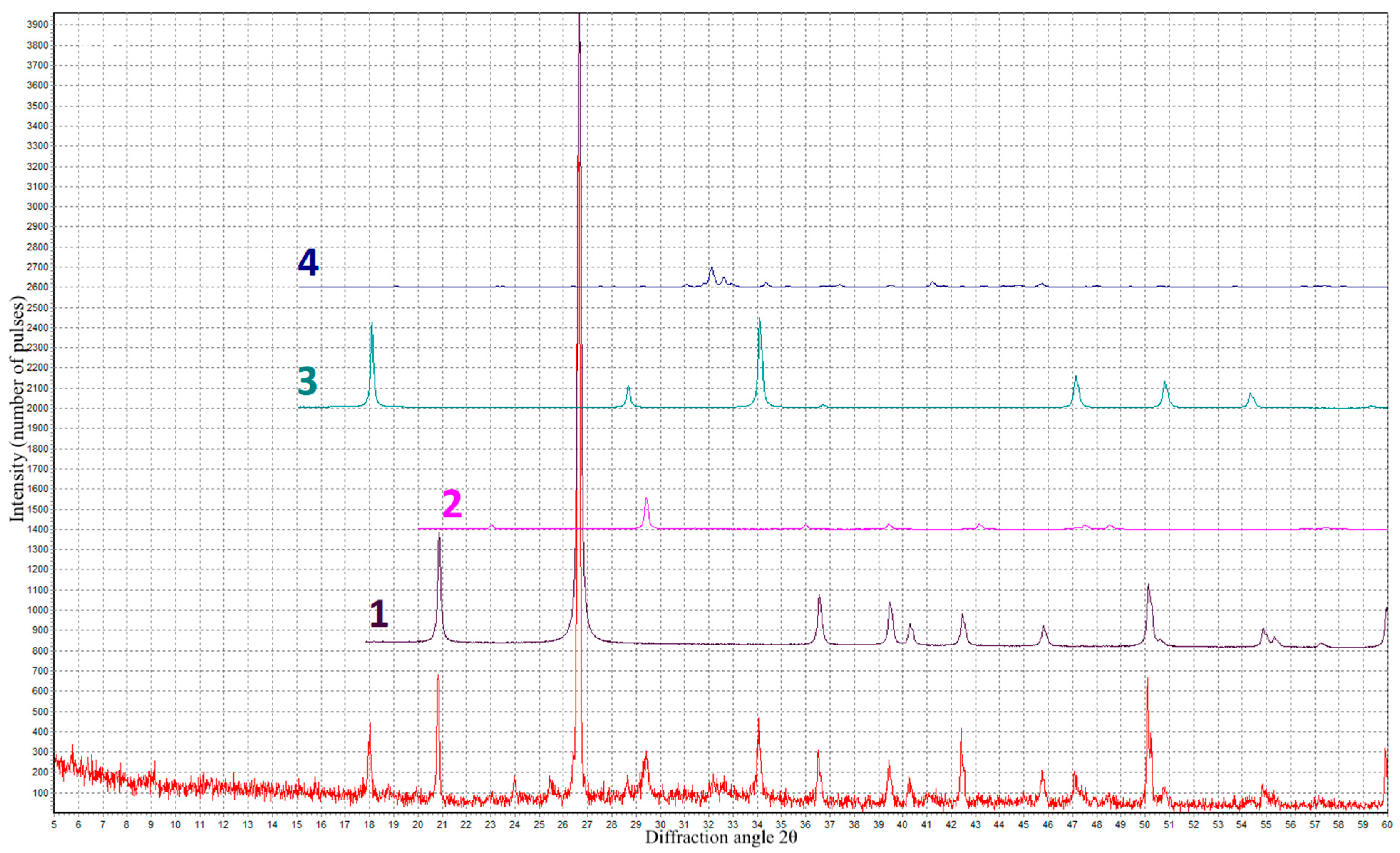
3. Results and Discussion
- -
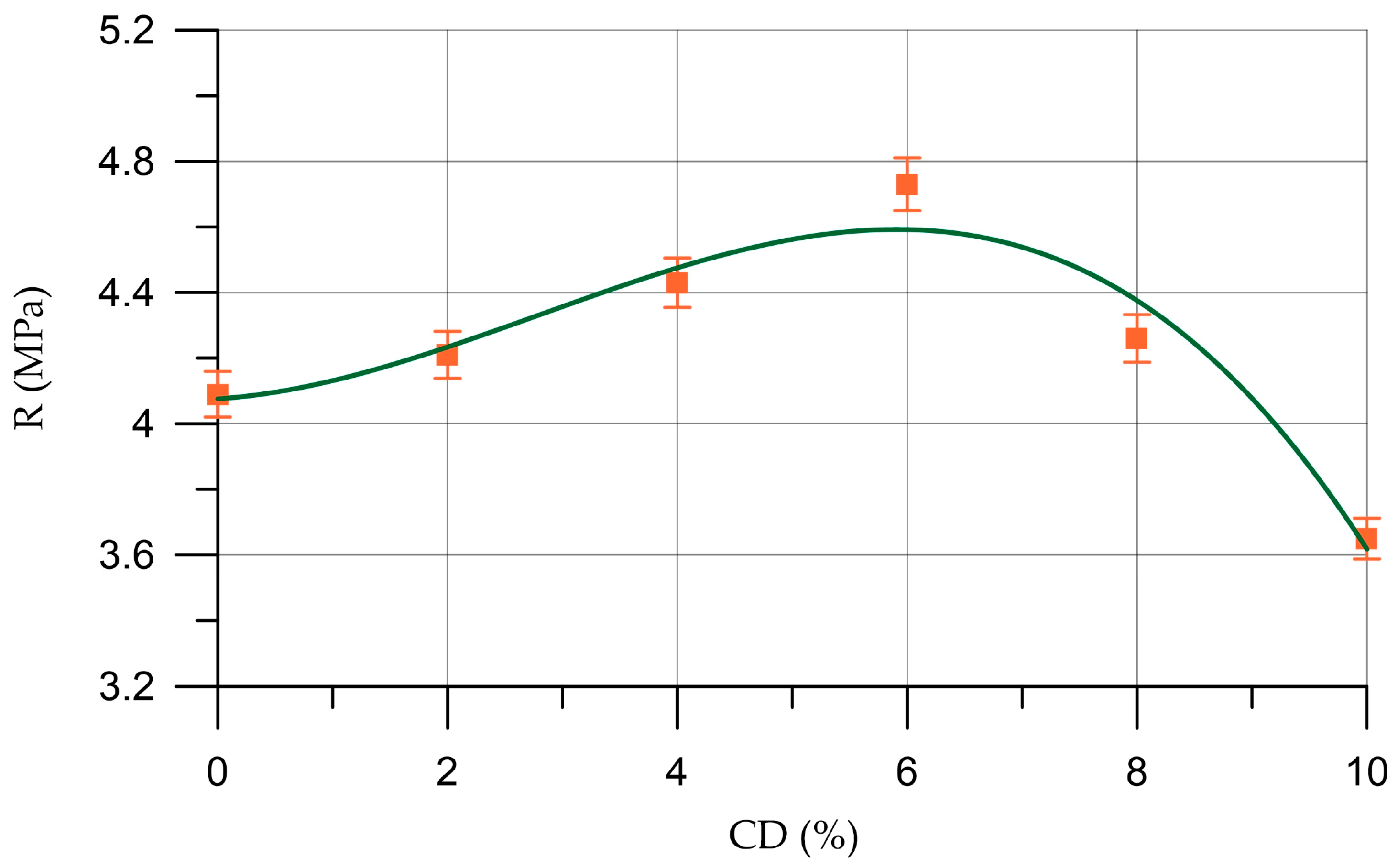
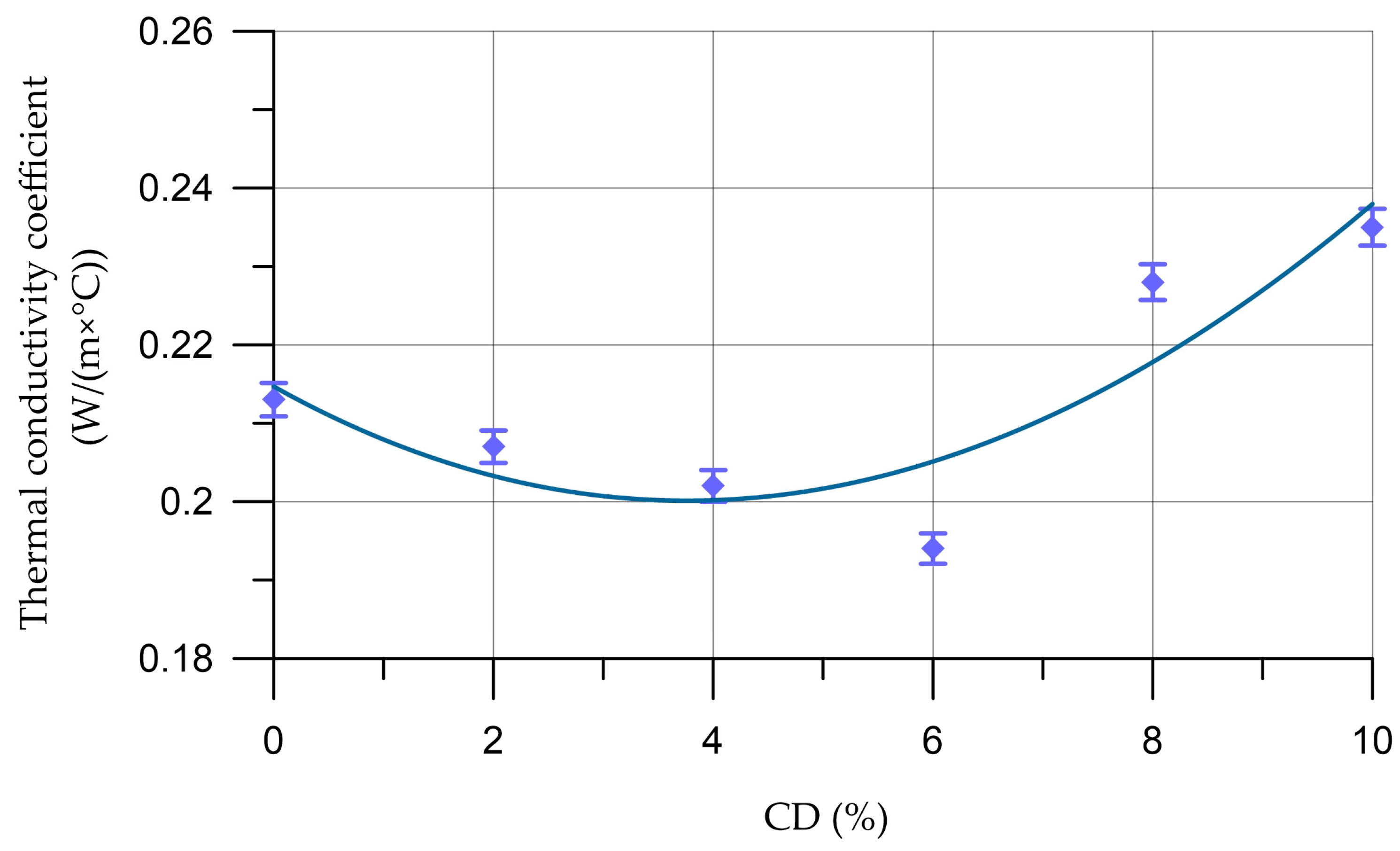
- At an optimal content (2–6%), coal dust introduced into the foam concrete instead of part of the cement acts as a mineral stabilizer and increases the stability of the foam, and due to the presence of silicon dioxide in the CD composition, it promotes the formation of additional hydrosilicates that strengthen the interpore walls;
- -
- When the amount of coal dust increases by more than 6%, a negative effect is observed, expressed in the deterioration of rheological and physical–mechanical characteristics, which is associated with the supersaturation of the foam concrete mixture with too many highly dispersed particles of coal dust, with a high water requirement.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mugahed Amran, Y.H.; Farzadnia, N.; Abang Ali, A.A. Properties and applications of foamed concrete; a review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 990–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyatham, B.P.R.V.S.; Lakshmayya, M.T.S.; Chaitanya, D.V.S.R.K. Review on performance and sustainability of foam concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Su, R.K.L. A Review on Durability of Foam Concrete. Buildings 2023, 13, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencel, O.; Bilir, T.; Bademler, Z.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. A Detailed Review on Foam Concrete Composites: Ingredients, Properties, and Microstructure. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherban’, E.M.; Beskopylny, A.N.; Stel’makh, S.A.; Mailyan, L.R.; Meskhi, B.; Shilov, A.A.; Pimenova, E.; El’shaeva, D. Combined Effect of Ceramic Waste Powder Additives and PVA on the Structure and Properties of Geopolymer Concrete Used for Finishing Facades of Buildings. Materials 2023, 16, 3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beskopylny, A.N.; Stel’makh, S.A.; Shcherban’, E.M.; Mailyan, L.R.; Meskhi, B.; Varavka, V.; Beskopylny, N.; El’shaeva, D. A Study on the Cement Gel Formation Process during the Creation of Nanomodified High-Performance Concrete Based on Nanosilica. Gels 2022, 8, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stel’makh, S.A.; Shcherban’, E.M.; Beskopylny, A.N.; Mailyan, L.R.; Meskhi, B.; Shilov, A.A.; Evtushenko, A.; Chernil’nik, A.; El’shaeva, D.; Karalar, M.; et al. Physical, Mechanical and Structural Characteristics of Sulfur Concrete with Bitumen Modified Sulfur and Fly Ash. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadiel, A.A.M.; Mohammed, N.S.; Abu-Lebdeh, T.; Munteanu, I.S.; Niculae, E.; Petrescu, F.I.T. A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Mechanical Properties of Rubberized Concrete. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoon, A.N.; Hason, M.M.; Sharba, A.A.K.; Abdulhameed, A.A.; Amran, M.; Avudaiappan, S.; Flores, E.S. Sawdust-Based Concrete Composite-Filled Steel Tube Beams: An Experimental and Analytical Investigation. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiela, B.; Brudny, K.; Lin, W.-T.; Korniejenko, K. Investigation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Construction- and Demolition-Waste-Based Geopolymers. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Qu, N.; Li, J. Development and functional characteristics of novel foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskopylny, A.N.; Shcherban’, E.M.; Stel’makh, S.A.; Mailyan, L.R.; Meskhi, B.; Varavka, V.; Chernil’nik, A.; Pogrebnyak, A. Improved Fly Ash Based Structural Foam Concrete with Polypropylene Fiber. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Qi, X.; Guo, S.; Zhang, L.; Ren, J. A systematic research on foamed concrete: The effects of foam content, fly ash, slag, silica fume and water-to-binder ratio. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 339, 127683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencel, O.; Bayraktar, O.Y.; Kaplan, G.; Arslan, O.; Nodehi, M.; Benli, A.; Gholampour, A.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Lightweight foam concrete containing expanded perlite and glass sand: Physico-mechanical, durability, and insulation properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 320, 126187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyuev, A.V.; Kashapov, N.F.; Klyuev, S.V.; Zolotareva, S.V.; Shchekina, N.A.; Shorstova, E.S.; Lesovik, R.V.; Ayubov, N.A. Experimental studies of the processes of structure formation of composite mixtures with technogenic mechanoactivated silica component. Constr. Mater. Prod. 2023, 6, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petukhov, D.S.; Adamov, A.A.; Keller, I.E. Selection and Identification of a Model of Elasto-Viscoplasticity of the Filled Fluorocomposite according to Free and Constrained Compression Tests. Adv. Eng. Res. 2022, 22, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramyan, S.G.; Klyuev, S.V.; Emelyanova, O.E.; Oganesyan, O.V.; Chereshnev, L.I.; Akopyan, G.O.; Petrosian, R.O. Improving reinforced concrete column strengthening techniques for reconstruction projects using composite jacketing formworks. Constr. Mater. Prod. 2023, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, P.; Guo, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, D.; Gao, M.; Peng, C. Experimental Investigation of the Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene-Fiber-Reinforced Foamed Concrete at High Temperatures. Polymers 2023, 15, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Q.S.; Sheikh, M.N.; McCarthy, T.J.; Robati, M.; Allen, M. Experimental investigation on foam concrete without and with recycled glass powder: A sustainable solution for future construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bat-Erdene, P.-E.; Pareek, S.; Koenders, E.; Mankel, C.; Löher, M.; Xiao, P. Evaluation of the Thermal Performance of Fly Ash Foam Concrete Containing Phase Change Materials (PCMs). Buildings 2023, 13, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Ge, Z.; Sun, R.; Xu, X.; Lu, Y.; Ling, Y.; Zhang, H. Drying shrinkage, durability and microstructure of foamed concrete containing high volume lime mud-fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 327, 126990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ding, S.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Q. Preparation and Properties of Foam Concrete Incorporating Fly Ash. Materials 2022, 15, 6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gencel, O.; Oguz, M.; Gholampour, A.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Recycling waste concretes as fine aggregate and fly ash as binder in production of thermal insulating foam concretes. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 38, 102232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencel, O.; Kazmi, S.M.S.; Munir, M.J.; Kaplan, G.; Bayraktar, O.Y.; Yarar, D.O.; Karimipour, A.; Ahmad, M.R. Influence of bottom ash and polypropylene fibers on the physico-mechanical, durability and thermal performance of foam concrete: An experimental investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, C.; Hu, Z.; Wang, L.; Yue, G.; Zheng, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, P. Study on the Performance of Foam Concrete Prepared from Decarburized Fly Ash. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, H.; Qin, L.; Hou, Y.; Shi, Y. Dynamic characteristics and response analysis of a new type of prefabricated fly ash foam concrete structure. Structures 2023, 57, 105074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencel, O.; Bayraktar, O.Y.; Kaplan, G.; Benli, A.; Martínez-Barrera, G.; Brostow, W.; Tek, M.; Bodur, B. Characteristics of hemp fibre reinforced foam concretes with fly ash and Taguchi optimization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 294, 123607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Lv, Y. Strength, Durability, and Microstructure of Foamed Concrete Prepared Using Special Soil and Slag. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, O.Y.; Kaplan, G.; Gencel, O.; Benli, A.; Sutcu, M. Physico-mechanical, durability and thermal properties of basalt fiber reinforced foamed concrete containing waste marble powder and slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 288, 123128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Ning, Y.; Ji, T. Compressive strength, pore structure, and hydration products of slag foam concrete under sulfate and chloride environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, G.; Song, D.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Z. Preparation of Steel Slag Foam Concrete and Fractal Model for Their Thermal Conductivity. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, M.; Qi, S.; Wang, C.; Ruan, M. Laboratory investigation of foamed concrete prepared by recycled waste concrete powder and ground granulated blast furnace slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, G.; Song, D.; Li, H.; Jalal, F.E.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y. Investigation on preparation and compressive strength model of steel slag foam concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 72, 106548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tan, H.; He, X.; Jian, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Deng, X.; Lin, X. Enhancement in compressive strength of foamed concrete by ultra-fine slag. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 138, 104954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencel, O.; Nodehi, M.; Bayraktar, O.Y.; Kaplan, G.; Ahmet, B.; Gholampour, A.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Basalt fiber-reinforced foam concrete containing silica fume: An experimental study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 326, 126861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Dai, S.; Ma, B.; Jiang, Q. Investigation of silica fume as foam cell stabilizer for foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 237, 117514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ma, L.; Deng, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, J.; Banthia, N. Influence of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and silica fume on stability, rheological properties, and printability of 3D printing foam concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 122, 104158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanita, R.; Maizir, H.; Zulapriansyah, R.; Subagiono, Y.; Arshad, M.F. The effect of silica fume admixture on the compressive strength of the cellular lightweight concrete. Results Eng. 2022, 14, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koksal, F.; Sahin, Y.; Gencel, O. Influence of expanded vermiculite powder and silica fume on properties of foam concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskhi, B.; Beskopylny, A.N.; Stel’makh, S.A.; Shcherban’, E.M.; Mailyan, L.R.; Beskopylny, N.; Chernil’nik, A.; El’shaeva, D. Insulation Foam Concrete Nanomodified with Microsilica and Reinforced with Polypropylene Fiber for the Improvement of Characteristics. Polymers 2022, 14, 4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Yin, G.; Shi, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Hao, W.; Feng, J. Investigation on properties of phase change foamed concrete mixed with lauric acid-hexadecanol/fumed silica shape-stabilized composite phase change material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, H.S.; Hatungimana, D.; Ramyar, K. Effect of fly ash and silica fume on hardened properties of foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 194, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Gao, H.; Liao, H.; Fang, L.; Cheng, F. Enhancing the performance of foam concrete containing fly ash and steel slag via a pressure foaming process. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencel, O.; Benli, A.; Bayraktar, O.Y.; Kaplan, G.; Sutcu, M.; Elabade, W.A.T. Effect of waste marble powder and rice husk ash on the microstructural, physico-mechanical and transport properties of foam concretes exposed to high temperatures and freeze–thaw cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 291, 123374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, J.; Yao, X.; Zhang, C.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W. Recent advances in sustainable lightweight foamed concrete incorporating recycled waste and byproducts: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 403, 133083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acordi, J.; Simão, L.; Faraco, M.N.S.; Borgert, C.H.; Olivo, E.; Montedo, O.R.K.; Raupp-Pereira, F. Waste valorization of coal mining waste from a circular economy perspective: A Brazilian case study based on environmental and physicochemical features. Resour. Policy 2023, 80, 103243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseenko, V.A.; Bech, J.; Alekseenko, A.V.; Shvydkaya, N.V.; Roca, N. Environmental impact of disposal of coal mining wastes on soils and plants in Rostov Oblast, Russia. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 184, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOST 12730.1-2020; Concretes. Methods of Determination of Density. Gost Standard: Moscow, Russia, 2020. Available online: https://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200177299 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- EN 12390-7:2019; Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 7: Density of Hardened Concrete. iTeh Standards: Etobicoke, ON, Canada, 2019. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/811a0cf3-55e3-495a-b06e-5c302d5f2806/en-12390-7-2019 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- GOST 10180-2012; Concretes. Methods for Strength Determination Using Reference Specimens. Gost Standard: Moscow, Russia, 2012. Available online: http://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200100908 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- EN 12390-1:2021; Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 1: Shape, Dimensions and Other Requirements of Specimens and Moulds. iTeh Standards: Etobicoke, ON, Canada,, 2021. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/d1c9ccee-2e5a-425e-a964-961da95d2f99/en-12390-1-2021 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- EN 12390-2:2019; Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 2: Making and Curing Specimens for Strength Tests. iTeh Standards: Etobicoke, ON, Canada, 2019. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/ae7e6a86-1cbc-455e-8b2a-8964be9087f9/en-12390-2-2019 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- EN 12390-3:2019; Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 3: Compressive Strength of Test Specimens. iTeh Standards: Etobicoke, ON, Canada, 2019. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/7eb738ef-44af-436c-ab8e-e6561571302c/en-12390-3-2019 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- EN 12390-4:2019; Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 4: Compressive Strength—Specification for Testing Machines. iTeh Standards: Etobicoke, ON, Canada, 2019. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/10b1c613-819b-42d7-8f94-480cd37a666a/en-12390-4-2019 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- GOST 7076-99; Building Materials and Products. Method of Determination of Steady-State Thermal Conductivity and Thermal resistance. Gost Standard: Moscow, Russia, 2000. Available online: https://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200005006 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- Kazumov, A.S.; Velichko, E.G. Development of rational parameters of components of foam concrete composition. Stroit. Nye Mater. 2016, 8, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameau, A.L.; Salonen, A. Effect of particles and aggregated structures on the foam stability and aging. C R Phys. 2014, 15, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tong, S.; Xu, X.; Mao, J.; Kang, X.; Luo, J.; Jiang, L.; Guo, M.Z. Effect of foam stabilization on the properties of foamed concrete modified by expanded polystyrene. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 73, 106822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ge, T.; Wu, Y.; Chen, R. Effect of Sand-to-Cement Ratio on Mechanical Properties of Foam Concrete. Buildings 2022, 12, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Xue, C.; Guo, W.; Wang, S.; Shi, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, Q. Preparation of foam concrete from solid wastes: Physical properties and foam stability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408, 133733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stel’makh, S.A.; Shcherban’, E.M.; Shuiskii, A.I.; Prokopov, A.Y.; Madatyan, S.M.; Parinov, I.A.; Cherpakov, A.V. Effects of the Geometric Parameters of Mixer on the Mixing Process of Foam Concrete Mixture and Its Energy Efficiency. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneda-Martínez, L.; Kunther, W.; Medina, C.; Sánchez de Rojas, M.I.; Frías, M. Exploring sulphate resistance of coal mining waste blended cements through experiments and thermodynamic modelling. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 121, 104086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherban’, E.M.; Stel’makh, S.A.; Beskopylny, A.N.; Mailyan, L.R.; Meskhi, B.; Elshaeva, D.; Chernil’nik, A.; Mailyan, A.L.; Ananova, O. Eco-Friendly Sustainable Concrete and Mortar Using Coal Dust Waste. Materials 2023, 16, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorný, J.; Ševčík, R.; Zárybnická, L.; Podolka, L. The Role of High Carbon Additives on Physical–Mechanical Characteristics and Microstructure of Cement-Based Composites. Buildings 2023, 13, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhaiba, S.; Blanco-Varela, M.T.; Diouri, A.; Bougarrani, S. Characterization and hydration of cements and pastes obtained from raw mix containing Moroccan oil shale and coal waste as a raw material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 189, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskopylny, A.N.; Stel’makh, S.A.; Shcherban’, E.M.; Mailyan, L.R.; Meskhi, B.; El’shaeva, D.; Varavka, V. Developing Environmentally Sustainable and Cost-Effective Geopolymer Concrete with Improved Characteristics. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, Z.; Jian, J.; Chen, S.; Luo, W.; Zhang, C. Experimental study on the physico-mechanical properties and microstructure of foam concrete mixed with coal gangue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 359, 129428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
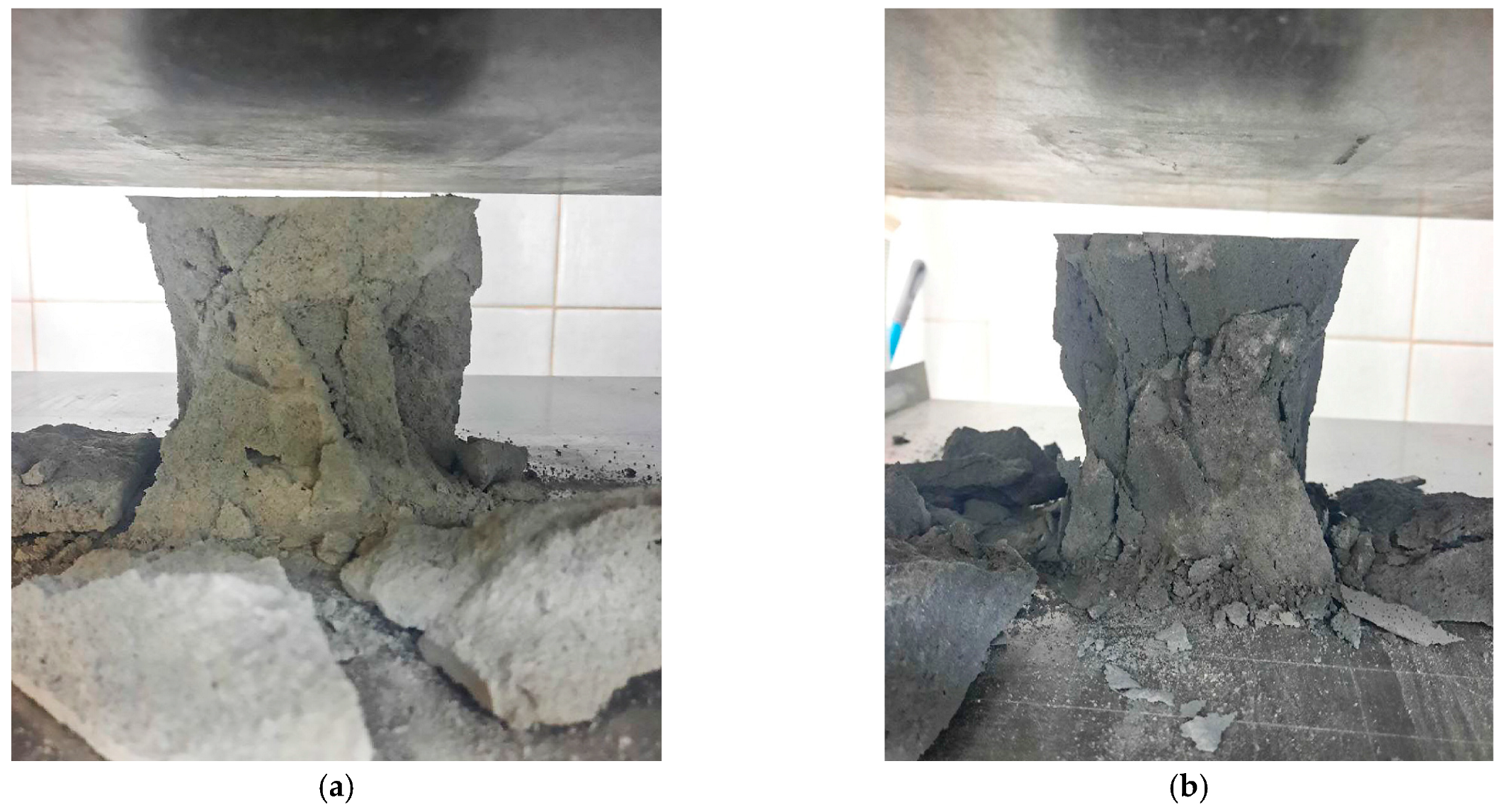
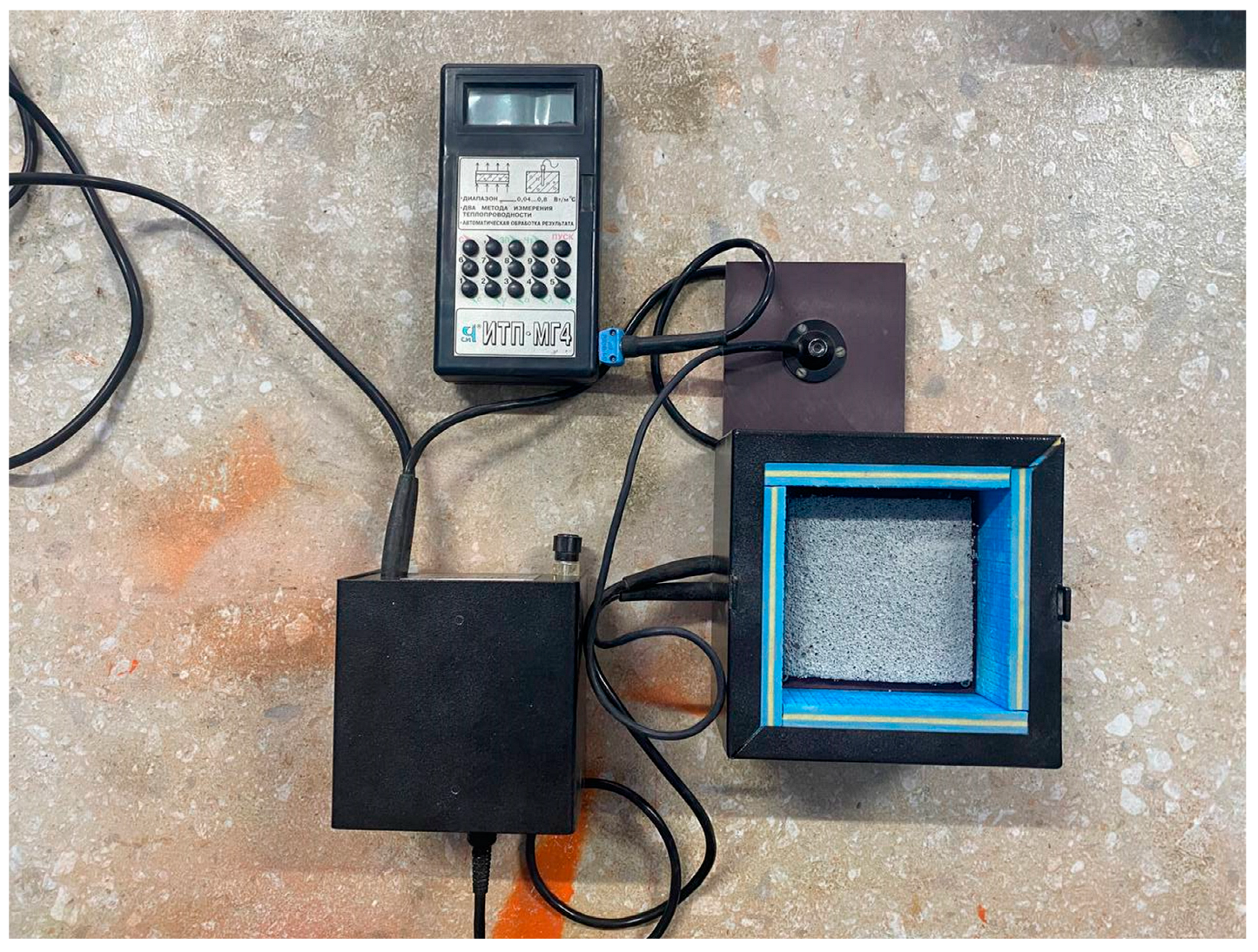
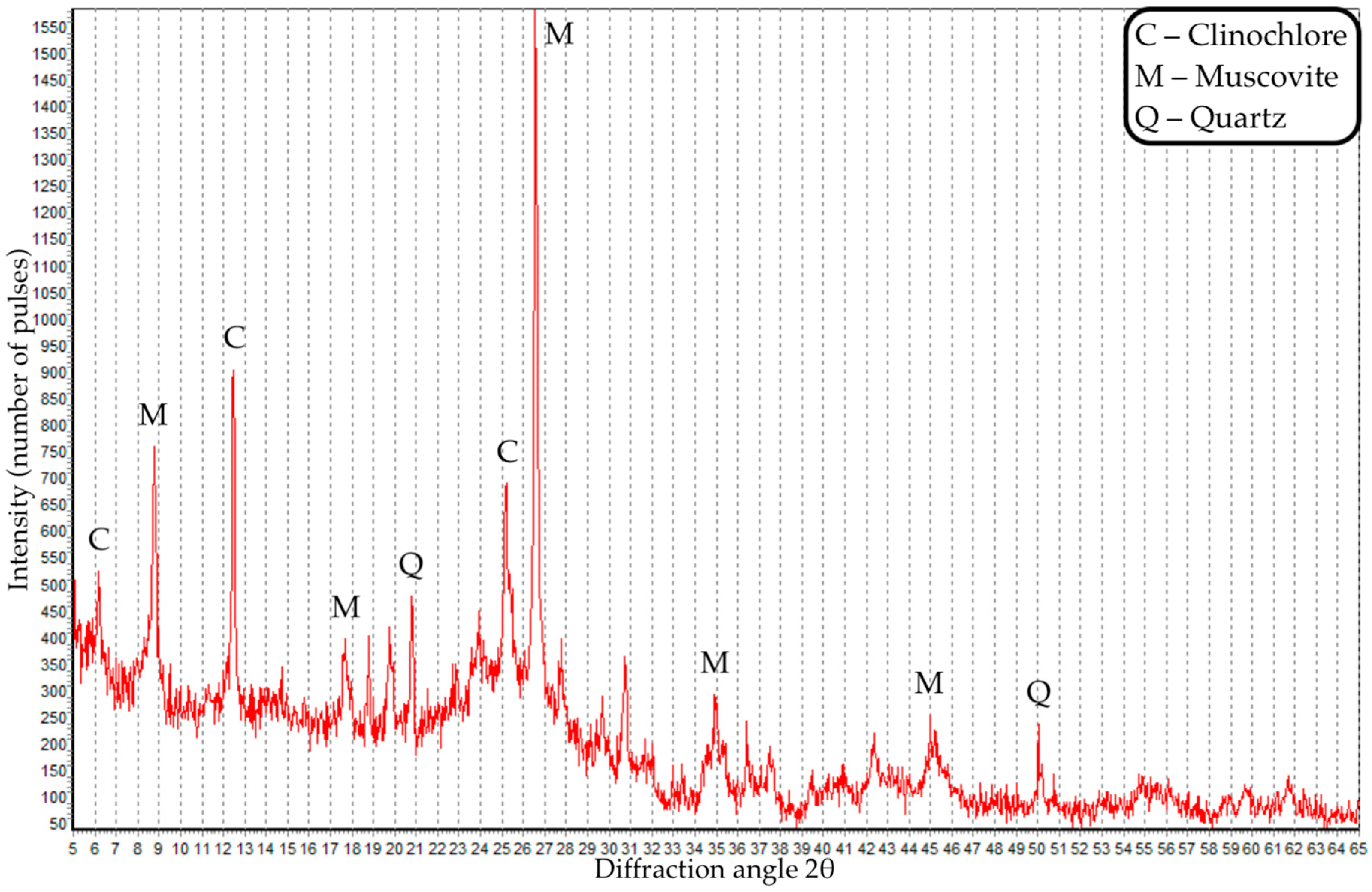








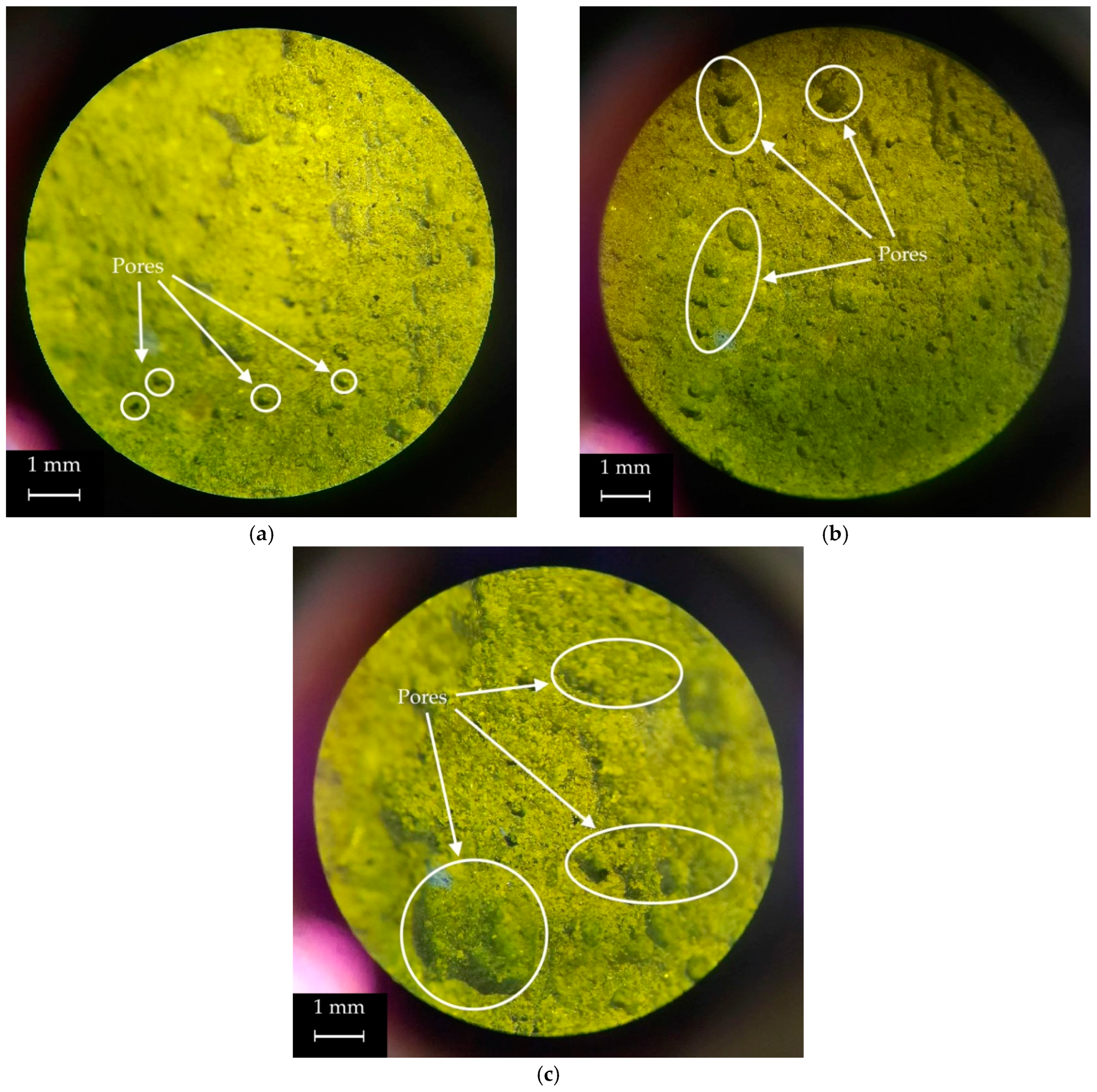
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Specific surface area (m2/kg) | 335 |
| Soundness (mm) | 0.4 |
| Fineness, passing through a sieve No 008 (%) | 98.1 |
Setting times (min)
| 150 240 |
Compressive strength (MPa):
| 24.6 56.1 |
| Sieve Diameter (mm) | Content (% by Weight) of Grains with a Particle Size of Less than 0.16 mm | Fineness Modulus | ||||
| Partial Residues on Sieves (%) | ||||||
| Total Residues on Sieves (%) | ||||||
| 2.5 | 1.25 | 0.63 | 0.315 | 0.16 | ||
| 1.6 | 4.3 | 7.9 | 39.7 | 43.7 | 2.8 | 1.72 |
| 1.6 | 5.9 | 13.8 | 53.5 | 97.8 | ||
| Bulk density (kg/m3) | 1421 | |||||
| The content of dust and clay particles (%) | 0.12 | |||||
| Content of clay in lumps (%) | 0.06 | |||||
| SiO2 (%) | Al2O3 (%) | Fe2O3 (%) | CaO (%) | MgO (%) | TiO2 (%) | P2O5 (%) | SO3 (%) | Loss on Ignition (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30.83 | 15.74 | 6.22 | 2.92 | 3.43 | 0.64 | 0.07 | 2.81 | 37.34 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| General view | Clear liquid |
Composition:
| 25 4 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.10 |
| Stability (h) | 1.5 |
| Multiplicity | 85 |
| Mixture Type | Proportion per 1 м3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (kg/m3) | W (L/m3) | S (kg/m3) | CD (kg/m3) | Foaming Agent (L) | |
| 0CD | 408 | 230 | 326 | 0 | 1 |
| 2CD | 400 | 230 | 326 | 8 | 1 |
| 4CD | 392 | 230 | 326 | 16 | 1 |
| 6CD | 384 | 230 | 326 | 24 | 1 |
| 8CD | 375 | 230 | 326 | 33 | 1 |
| 10CD | 367 | 230 | 326 | 41 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stel’makh, S.A.; Shcherban’, E.M.; Beskopylny, A.N.; Mailyan, L.R.; Meskhi, B.; Shilov, A.A.; Mailyan, A.L.; Zakieva, N.I.; Chernil’nik, A.; El’shaeva, D. Structural Formation and Properties of Eco-Friendly Foam Concrete Modified with Coal Dust. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7120519
Stel’makh SA, Shcherban’ EM, Beskopylny AN, Mailyan LR, Meskhi B, Shilov AA, Mailyan AL, Zakieva NI, Chernil’nik A, El’shaeva D. Structural Formation and Properties of Eco-Friendly Foam Concrete Modified with Coal Dust. Journal of Composites Science. 2023; 7(12):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7120519
Chicago/Turabian StyleStel’makh, Sergey A., Evgenii M. Shcherban’, Alexey N. Beskopylny, Levon R. Mailyan, Besarion Meskhi, Alexandr A. Shilov, Alexander L. Mailyan, Nadezhda I. Zakieva, Andrei Chernil’nik, and Diana El’shaeva. 2023. "Structural Formation and Properties of Eco-Friendly Foam Concrete Modified with Coal Dust" Journal of Composites Science 7, no. 12: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7120519
APA StyleStel’makh, S. A., Shcherban’, E. M., Beskopylny, A. N., Mailyan, L. R., Meskhi, B., Shilov, A. A., Mailyan, A. L., Zakieva, N. I., Chernil’nik, A., & El’shaeva, D. (2023). Structural Formation and Properties of Eco-Friendly Foam Concrete Modified with Coal Dust. Journal of Composites Science, 7(12), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7120519












