Abstract
In this work, the first shear deformation theory (FSDT) is used for the thermo-mechanical analysis of a simply supported five-layer functionally Graded (FG) sandwich plate resting on a Winkler elastic foundation. The sandwich plate consists of five layers (two functionally graded face sheets (), with aluminum (Al) as the metal and Alumina () as ceramic phases. Two vinyl ester adhesive layers bond the face sheets to an Elastollan core. The governing equations are obtained using the principle of virtual displacements. A uniform distributed load q with constant magnitude is applied on the top face sheet while all layers experience a steady temperature equal to T. We adapted layerwise theory (LT) to solve each layer’s stress distribution. Navier solution is employed to produce the semi-analytical solution results, which are compared with those of three-dimensional finite element analysis obtained by ABAQUS software. A parametric study is presented to observe the effect of the material gradation, variation in plate dimensions, variation in the thermo-mechanical load, and elastic foundation on the deflections and stresses in the functionally graded sandwich plate. For a composite sandwich plate with mechanical load, in the absence of thermal load, results of the first-order shear layer theory obtained by using the Navire method are relatively good in comparison to the normal stresses obtained for investigated points, which are obtained by finite element.
1. Introduction
Functionally graded materials (FGMs) were discovered by researchers in Japan to analyze thermal materials and then developed speedily [1]. FGMs often consist of two or more materials whose volume fractions change continuously along certain structure dimensions. The volume fractions of FGM materials are based on functions best describing the material properties in certain directions (i.e., thickness); furthermore, FGMs are capable of withstanding high temperatures [2].
In order to delineate the interactions between the sandwich plate and its bottom elastic foundation, different models are proposed. The simplest model for the elastic foundation is the Winkler model, which considers the foundation as a series of vertical springs without shear effects [3,4]. Mantari and Granados [5] evaluated the stress distribution in an FG sandwich plate under bi-sinusoidal load using first shear deformation theory (FSDT), and the Navier solution was used to solve the problem. The accuracy of the presented theory was determined by comparison with different available solutions in the other papers. Zenkour [6] carried out research on the thermomechanical bending behavior of functionally graded plates (FGPs) resting on an elastic foundation. Thai et al. [7] investigated the FG sandwich plates formed of FG face sheets and an isotropic homogeneous core by using a new first-order shear deformation theory (FSDT), and the results corroborated that the theory was exact, also comparable with the higher-order shear deformation theories. Thai and Choi [8] worked on a first-order shear deformation theory (FSDT) for the free vibrational and mechanical analysis of FG plates, and the results revealed that their theory could achieve the same accuracy as the conventional first-order shear deformation theory possessing more unknowns. Natarajan and Manicam [9] conducted research into the bending and free vibrational behavior of FGM material sandwich plates using flexible shear elements, and the exaction of the results was demonstrated. Xu et al. [10] investigated the steady heat conduction analysis of an FGM flat plate under temperature load on its upper surface. Ferreira et al. [11] researched the static and free vibrational analysis of shear flexible composite plates, and the layerwise theory was applied for the study of sandwich composite plates, and precise results were obtained. Kapuria and Achary [12] carried out a study with a higher-order zig-zag theory for the thermal study of sandwich plates and the results revealed that the efficiency of the presented higher-order zigzag theory was generally more than the previous zig-zag theory. Shodja et al. [13] evaluated an exact thermos-elastic solution for a two-dimensional thick FGM that is composed of homogeneous FG layers. The results confirmed that the effects of concentration stress are removed and the interfacial shear stress is lowered when an FG coating is used. Garg et al. [14] researched the static analysis of symmetric and anti-symmetric composite sandwich plates by trigonometric zig-zag theory and the obtained results were supported by those available in the existing literature. Mechab et al. [15] presented the analytical solutions of cross-ply laminated plates subjected to thermal and mechanical load based on higher-order shear deformation theory. The obtained results were in good agreement with those obtained by other studies. Moleiro et al. [16] examined a new layerwise model for the thermo-mechanical analysis of composite plates with FGM layers. The accuracy of the results was approved by comparison with three-dimensional (3D) exact solutions. Raissi et al. [17] used first order and higher-order layerwise theory (LT) to show the stress and deflection distribution for five layers simply supported square sandwich plate with FG face sheets and elastomeric core while two adhesive layers were used to join the core to the face sheets. Findings revealed that the finite element analysis and LT based on the first and higher-order shear deformation theories give. Kardooni et al. [18] studied the free vibration of five layes composite sandwich plate resting on Winkler elastic foundation. The layerwise theory in conjunction with the third-order and hyperbolic shear deformation (HSDT) theories were used in [19] to determine the analytical and finite element (FE) solutions for stress distribution in the adhesive layer of a circular sandwich plate subjected to a uniformly distributed load. Results indicated that FEA findings give almost similar estimations on the planar stresses compared to analytical solutions based on TSDT and HSDT. However, the out-of-plane shear stresses predicted by HSDT were closer to FEA data.
Presented A refined trigonometric shear deformation theory (RTSDT) was used by Tounsi et al. [20] to take into account the transverse shear deformation effects on the thermos-elastic bending of functionally graded sandwich plates. Unlike any other theory, the number of unknown functions involved was only four, as against five in the case of other shear deformation theories. From numerical results, it was concluded that the proposed theory was accurate and simple in solving the thermos-elastic bending behavior of functionally graded plates. Mahmoudi et al. [21] indicated a theory for the thermo-mechanical analysis of functionally graded sandwich plates resting on a Pasternak elastic foundation. As a result, in contrast to similar studies, the number of unknowns and governing equations in their analysis was only four against six or more in other studies. Wenbin Zhou et al. [22] studied thermomechanical analysis in threads of porous metal–ceramic functionally graded composite joints by ABAQUS codes. Adelina Miteva et al. [23] reviewed some aerospace applications of functionally graded materials, and their paper is motivated by the huge interest in the rapidly developing field of material science, namely, functionally graded (or functionally gradient) materials (FGMs). In order to continue the work presented in [18], our research focuses on the effect of thermo-mechanical loading on the bending stresses developed in a five-layer sandwich plate with FG cover sheets, subjected to a uniformly distributed load applied to the top surface. The presented work in [18], was focused on free vibration of Five Layers Composite Sandwich Plate but this research is focused on the thermo-mechanical analysis of FG sandwich plate and the effect of the mechanical load (uniform distributed load on the top face sheet) and thermal load (all layers are experiencing a steady temperature ΔT) is studied. We assumed that the sandwich plate is resting on Winkler elastic foundation. One of the particle applications for the developed solution is in the body of automobile industry, body of ships, body of plane and the structures that are rested on the vibrated basement in the thermal environmental.
2. Problem Formulation
Figure 1 illustrates an FG sandwich plate subjected to a thermo-mechanical load and resting on Winkler elastic foundation. The face sheets have functional properties, and their exterior surfaces are of pure ceramic. Since the local coordinate in each layer is positioned at the corner of each constituent along the edges of the sandwich plate, then the variations in material properties of the face sheets are in the z-direction (thickness direction) (), namely Young’s modulus and coefficient of thermal expansion , can be defined by Equation (1).
where and are the corresponding material properties of the metal (aluminum (Al)) and the ceramic (Alumina ()) phases, respectively. In Equation (1), is defined as the volume fraction of the ceramic phase within the face sheet. Equation (2) expresses the variation in this parameter along the non-dimensional thickness (), as shown in Figure 1 for different values of power index n [2]. Note that the volume fraction of the ceramic phase is highest at the free surfaces of the sandwich plate, and the metal phase is the highest at the cover sheet interfaces with the core.
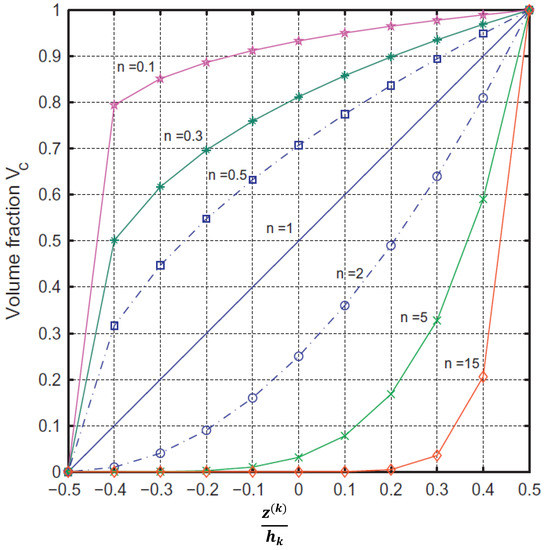
Figure 1.
Variation of volume fraction against the non-dimensional thickness [2].
The analysis was based on LT along with FSDT and the expansion of energy equation with the imposition of displacement continuity at the layer’s interfaces [24]. Assuming a continuous displacement across the layers, the displacement fields in each layer were obtained and presented in Appendix A.
Here, we assumed that u and v are the displacement components in the x and y directions at the core middle plane (z = 0), respectively. Additionally,, , and indicate the displacement components associated with the kth layer. For more information on the layer arrangement, the reader can refer to Figure 2. Furthermore, we assumed that the out-of-plane displacements,, for each layer were only a function of x and y directions. A perfect bond was assumed between any two neighboring layers at their interface.
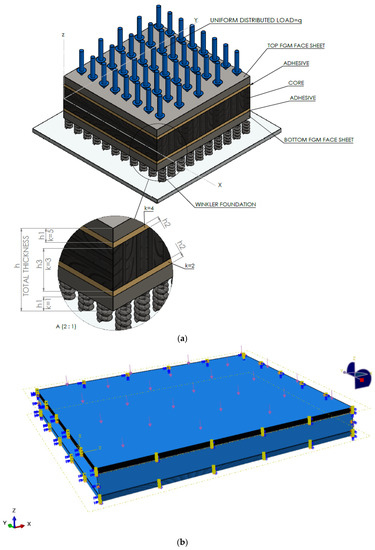
Figure 2.
(a) The geometry of the functionally graded material (FGM) sandwich plate resting on an elastic foundation. (b) Simply supported boundary conditions are imposed on four edges. (c) Meshed model of the sandwiched plate showing the subdivisions in the FGM cover plates.
Based on the linear elasticity and finite deformation, the strain components in the kth layer () are given by Equation (3) [24].
Substituting for displacement components from Appendix A in Equation (3), the strain vector in the kth layer () of the composite sandwich plate is:
In Equation (4), is the temperature change. The superscript “p” and “0” correspond to the total strains and middle-plane strains for the elastic and isotropic FGMs, respectively, and are the bending components. Neglecting for each layer, the linear constitutive relations in the isotropic FGMs can be expressed as in Equation (5) [24].
where (, ) and () are the stress and strain components, respectively. Using the material properties defined in Equation (1), the stiffness coefficients can be calculated easily (as in [24]).
Note that due to the variation of the effective properties of the FG plate along the thickness direction (based on Equation (1)) the elements will be a function of z. Considering the static version of the principle of virtual work, the following expressions can be obtained as in Equation (6).
where and are the material volume, and virtual strain energy, respectively; q is the distributed transverse load and is the density of reaction force of the foundation. For the Winkler foundation model, we have Equation (7):
Additionally, the force and moment components in the kth layer are related to the strain components in terms of Equation (8).
Furthermore, the total in-plane force resultants, the total moment resultants, the transverse force resultants, and the elements of matrices A, B, and D, namely, the , , and (k = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5), can be calculated as in [24]. According to [25], a value of 0.616 was used for the shear correction factor K.
On using Equation (6), one can show that the equilibrium equations for the kth layer are:
where
The displacement components and curvatures are defined in Equation (11). In this equation , , , , and are the Fourier series constants that can be easily determined.
In Equation (11), (m = 1, 2,…) and (n = 1, 2,…). The transvers load and thermal moments are also expanded in double sine series. For this purpose, q(x,y) is expanded as in Equation (12).
The temperature increment is also expanded as in [24] such that:
Additionally, one can write:
3. Numerical Results and Discussions
3.1. Three-Layers Sandwich Plate
For validation of the proposed model in the first step, we verify the formulation and FE modeling. For this reason, we studied the layerwise theory for a three layers sandwich plate (simply supported square with a layer sequence of [0/90/0]) under a uniform distributed transverse load using the analytical solution in Ref. [26]. The proposed layer-wise model was compared with those based on 3D FE modeling in ABAQUS software, and close agreements between the results indicate the validity of the present formulation. In the next step, stress distributions in a five-layer sandwich plate with FG face sheets subject to thermo-mechanical load and resting on Winkler elastic foundation are explored. Results of LT theory are compared with those of FE finding using ABAQUS.3.1. Three-Layer Sandwich Plate under Uniform Load.
To verify the formulation and FE modeling, we studied a simply supported square sandwich plate (with a layer sequence of [0/90/0]) under a uniform distributed transverse load using the same properties in [26]. In the prepared model, using the TIE constraint, we bonded perfectly the core to the face sheets to neutralize the effect of delamination on the final results. Reference [27] presents a complete solution to this problem where the material properties of the core and the face sheets are expressed in Equation (15).
Additionally, skins material properties were related to core properties by a factor R as follows [27]:
Furthermore, the transverse displacements and stresses were normalized according to the following relations [27]:
The findings on transverse displacements, normal stresses, and shear stresses are presented in Table 1. These results reveal that FE modeling in ABAQUS software predicts the values of normalized displacement (), and normalized sstress components , , and with good accuracy compared to those in [26,27].

Table 1.
Comparison of the results based on FE and those of analytical solution from Refs. [26,27].
3.2. Five-Layer FGM Sandwich Plate
Now consider a five–layer square FGM sandwich plate, composed of a core and two adhesive layers bonding the core to the two face sheets, resting on the Winkler foundation, as shown in Figure 2. The simply supported plate was assumed symmetry concerning its middle layer, and its top surface was exposed to a uniformly distributed transverse load q and a steady temperature load T. Each face sheet was composed of (), with aluminum (Al) as the metal phase and Alumina () as the ceramic phase. The vinyl ester (VE) based structural adhesive was used to bond the face sheets to an elastomeric core (Ellastollan R3000).
In the study performed in [28], the behavior of vinyl-ester polymer at strain rates 0.001/s and a wide range of temperatures (from room temperature (RT) to 100 °C) was investigated. Table 2 shows the results of this study over modules of elasticity for this adhesive. It is worth mentioning that the selected 100 °C is close to the glass transition temperature of vinyl-ester. However, although for temperatures close to Tg and high strains, visco-plasticity behavior dominates the material properties yet, in the present study, its effect on deformation was not considered in the standard linear solid model for the material.

Table 2.
Modules of vinyl-ester at different temperatures [28].
Additionally, Table 3 presents the modulus of elasticity of the Elastollan-R3000 core at four different temperatures (RT to 100 C) [29]. Other mechanical properties of the five-layer sandwich plate used in this simulation are given in Table 4.

Table 3.
Modules of elasticity of Elastollan-R3000 at different temperatures [29].

Table 4.
The mechanical properties of the five-layer sandwich plate.
In order to obtain the results on defections and stress components, different points were selected at different locations in the sandwich plate, as shown in Figure 3. The location of these points is expressed in Table 5.
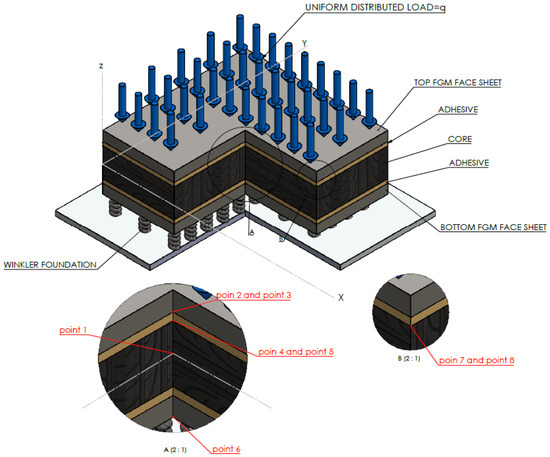
Figure 3.
The geometric position of different points selected in the postulated model.

Table 5.
The geometric positions for 8 points are defined in tables according to the coordinate system is shown in Figure 3.
For the sake of simplicity and reducing the numerical simulation using the ABAQUS software, due to symmetry, the whole FE model was reduced to one-fourth of its original size. The three-dimensional solid element C3D20R was used for meshing. The simply supported boundary conditions were imposed on the two side edges, while the symmetry conditions were imposed on the remaining two edges. Furthermore, to properly model the FGM face sheets and implement the properties of FG material, the thickness of each face sheet was divided into 30 thin layers with different properties defined according to Equation (1). The whole plate was subjected to thermo-mechanical loading (uniform mechanical load q on its top surface and steady temperature in all layers) and resting on Winkler elastic foundation.
In order to obtain the finite element results, several models were prepared and run based on different mesh qualities until the results converged to specific values given in Table 6, Table 7, Table 8, Table 9, Table 10 and Table 11 and Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9. The geometric positions for all points used in these tables are given in Table 5 and Figure 3.

Table 6.
Comparison of the results based on LT and those of FE findings for different temperature.

Table 7.
Comparison of the results based on LT and those of FE findings.

Table 8.
Comparison of the result based on LT and those FE findings.

Table 9.
Comparison of the result based on LT and those FE findings.

Table 10.
Comparison of the result based on LT and those FE findings.

Table 11.
Comparison of the result based on LT and those FE findings.
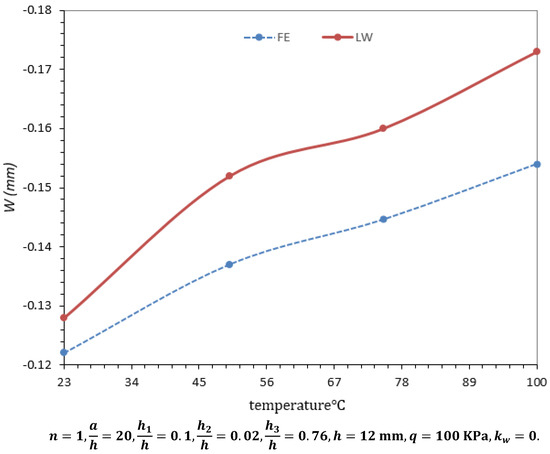
Figure 4.
Effect of the thermal loads on the center deflection of the sandwich (for point 1) plate.
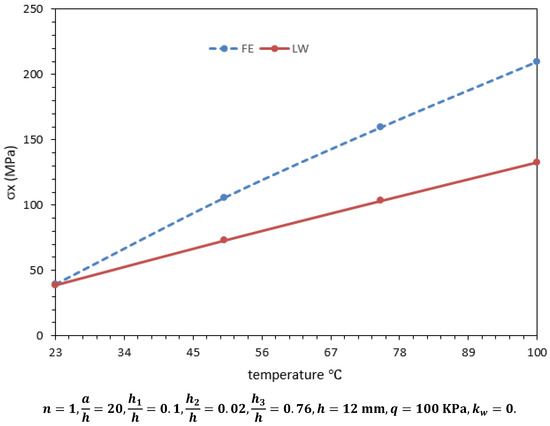
Figure 5.
Effect of the thermal loads on the maximum normal stresses of sandwich plate (for point 6).
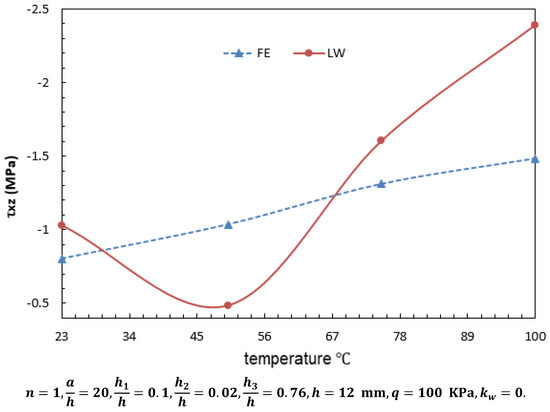
Figure 6.
Effect of the thermal loads on the transverse shear stress of sandwich plate (for point 8).
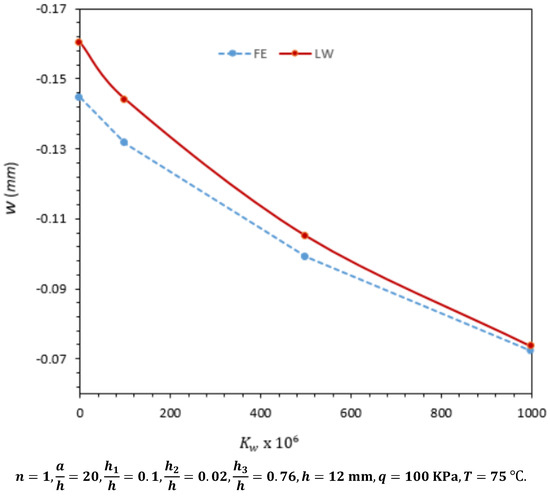
Figure 7.
Effect of the elastic foundation on the center deflection of sandwich plate.
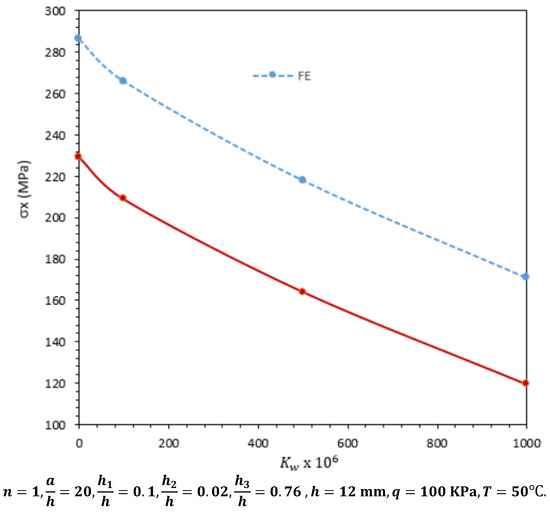
Figure 8.
Effect of the elastic foundation on the maximum normal stresses (point 6) of sandwich plate.
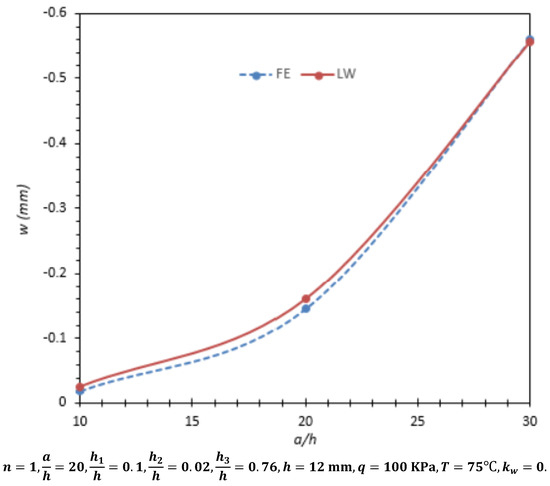
Figure 9.
Effect of the variation of a/h on the center deflection of sandwich plate.
3.3. Numerical Results and Discussions
Now, numerical findings of the analysis of a five-layer FGM sandwich plate subjected to thermo-mechanical load are presented. In order to carry out the accuracy of the general approach that was outlined in the previous sections, the results of LT theory in MATLAB software were compared with those of three-dimensional finite element analysis using the ABAQUS software program. The dimension of the total thickness of the sandwich plate is 12 mm and .
In Table 6, the effect of a distributed load of 100 KPa on the top surface, as well as the increase in temperature of 23 °C, 50 °C, 75 °C, and 100 °C, were investigated on the induced deflections and stresses in the absence of the elastic foundation. As expected, the results in this table show that increasing the temperature increases the normal stresses (), shear stresses (), and the transverse displacements (). Due to a decline in the elastic moduli of the adhesive layer and the core concerning higher temperatures, the overall stiffness of the FG sandwich plate drops, and hence an increase in the transverse displacements of the sandwich plate is observed. According to these results, the maximum stress occurs at the middle and lower points of the bottom face sheet (point 6). The reason for this behavior is that the distributed and the thermal loads both create tensile stresses that add up at point 6.
Table 7 demonstrates the influence of the Winkler elastic foundation from points one to point eight. As expected, results show that the Winkler elastic foundation parameter reduces the center transverse displacements, as well as the maximum normal and shear stresses.
The results in Table 8, Table 9 and Table 10 show the effect of any variation in the plate dimensions as well as any change in the material parameter n on the center transverse displacement (w), normal stress, and shear stress for points one to eight.
The effects of the power-law index on maximum normal stresses, transverse displacement, and shear stress for sandwich plates subjected to thermo-mechanical loads, are presented in Table 8. These results indicate that increasing the value of the power-law index (n) increases the stress component as well as the transverse displacement . This behavior is expected because the sandwich plate with more metal phase (n ) experiences higher defections and hence higher flexural stress .
Results in Table 9 indicate that any increase in the a/h ratio reduces the differences between finite element findings and those of the current solution (for points one to six), which are based on LT and FSDT. This can be interpreted as for thinner sandwich composite plates, the LT in conjunction with FSDT is more applicable compared to thicker plates.
In order to seek the thickness effect of face sheets on the behavior of the square sandwich plate, the core thickness, as well as the adhesive layers, were considered to be fixed while the thickness of the face sheets was increased.
According to the results in Table 10, increasing the thickness of the FGM cover sheets causes high differences in the results for and the in-plane shear stress at some critical locations (points). This difference is higher for the in-plane shear stress for a thicker composite sheet. Results indicate that LT does seem to be able to predict good results for these stresses at the selected critical points in thick composite sheets in the presence of the adhesive layer.
In addition, according to Table 11, with the increase in load and a decrease in temperature, the results of the first-order shear theory have better agreement with the results of the finite element method. However, at high temperatures, using FSDT, the results obtained based on LT do not seem to be reliable.
Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 show a comparison between finite element results and those of semi-analytical solution based on LT for variations in the center deflection (point 1), the maximum normal stresses (at point 6), and the transverse shear stress (at point 8), respectively in the sandwich plate under thermo-mechanical loading for different values of the temperatures. As observed, the layerwise theory predicts more accurate results on w and at lower temperatures. However, for the out-of-plane this is not the case.
In Figure 7 and Figure 8, the effects of elastic foundation on the maximum center deflection and the normal stresses are shown for a square sandwich plate under thermo-mechanical loads, respectively. These results are generated at a temperature of 75 °C. Results indicate that the center displacements and maximum normal stresses decline gradually with a rise in the value of foundation stiffness. The percentage difference between the finite element results and those of the LT diminishes with an increase in the foundation stiffness.
However, the results in Figure 9 indicate that the percentage difference in the center deflection between the results of both methods in the absence of foundation stiffness is almost zero for thin plates (as the span ratio a/h increases). This indicates that the LT, in conjunction with FSDT, has better applicability in thinner composite five-layer sandwich plates.
4. Conclusions
In this work, LT, along with FSDT, was used to study the stress distribution in a five-layer sandwich composite plate subjected to a thermo-mechanical load. Results showed that the first-order shear layer theory, in conjunction with LT, gives relatively good results on a maximum transverse deflection in the five-layer sandwich plate. Moreover, for a composite sandwich plate with mechanical load, in the absence of thermal load, results of the first-order shear layer theory obtained by using the Navire method are relatively good in comparison to the normal stresses obtained for points two to six, which are obtained by finite element. Further results showed that the first-order shear deformation theory, in combination with LT, is not well suited for the determination of in-plane and out-of-plane shear stresses and as well as the normal flexural stresses in thes presence of thermo-mechanical loads. It was also observed that with increasing the temperature, the difference between the finite element and LT also increases. However, the LT, in conjunction with FSDT, had better applicability in predicting flexural, and shear stresses in thinner five-layer sandwich composite plates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R.K.: Data curation, software, Formal analysis, validation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. M.S.: Data curation, visualization, validation, Formal analysis, writing—review and editing. R.M.: visualization, Writing—review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All datasets used in the present study are available in the MSc thesis submitted by M. R. Kardooni in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in Mechanical Engineering at Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, 2020.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest regarding the presented work submitted for possible publication.
Nomenclature
| Width of the plate | |
| elements of matrices for the kth layer | |
| Length of the plate | |
| , | Elastic modules of the metal and ceramic phases, respectively. |
| Density of foundation reaction force | |
| Shear Modulus | |
| Total thickens of the sandwich plate | |
| Cover sheet thickness | |
| Adhesive thickness | |
| Core thickness | |
| Layer number | |
| elastic foundation stiffness | |
| Moment resultants for the kth layer | |
| Force resultants for the kth layer | |
| n | Power law index |
| Material properties of the ceramic phase | |
| Material properties of the metal phase | |
| Uniform distributed load | |
| The elements of the stiffness matrix | |
| stiffness of core | |
| stiffness of skin | |
| Transverse shear stress results for the kth layer | |
| Ratio stiffness of skin to stiffness of the core | |
| T | Surrounding temperature |
| U | Strain energy |
| Displacement component in x-direction | |
| Strain energy of the foundation | |
| Virtual strain energy | |
| Displacement component in the y direction | |
| Volume fraction of the ceramic phase within the face sheet | |
| Displacement component in the z-direction | |
| Dimensionless displacement component in the z-direction | |
| z | Thickness direction |
| Coefficient of expansion thermal for Elastollan R3000 core or vinyl ester | |
| Coefficients of expansion thermal for the metal and ceramic phases, respectively. | |
| Strain components in the kth layer | |
| Shear correction factor | |
| Poisson ratio of Elastollan R3000 core or vinyl ester | |
| Poisson’s ratios of the ceramic and metal phases, respectively. | |
| Stress components in the kth layer | |
| Dimensionless Stress components | |
| Shear Stress components in the kth layer | |
| Dimensionless Shear Stress components | |
| material volume | |
| rotations of the normal lines to the midplane about the y-axis | |
| rotations of the normal lines to the midplane about the x-axis. |
Appendix A
Layer 1:
Layer 2:
Layer 3:
Layer 4:
Layer 5:
References
- Koizumi, M. FGM activities in Japan. Compos. Part B Eng. 1997, 28, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Xuan, H.; Tran, L.V.; Nguyen-Thoi, T.; Vu-Do, H. Analysis of functionally graded plates using an edge-based smoothed finite element method. Compos. Struct. 2011, 93, 3019–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, A.D. Elastic and Viscoelastic Foundation Models. J. Appl. Mech. 1964, 31, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benferhat, R.; Daouadji, T.H.; Mansour, M.S. Free vibration analysis of FG plates resting on an elastic foundation and based on the neutral surface concept using higher-order shear deformation theory. Comptes Rendus Mec. 2016, 344, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantari, J.; Granados, E. A refined FSDT for the static analysis of functionally graded sandwich plates. Thin-Walled Struct. 2015, 90, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenkour, A.M. The refined sinusoidal theory for FGM plates on elastic foundations. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2009, 51, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, H.-T.; Nguyen, T.-K.; Vo, T.P.; Lee, J. Analysis of functionally graded sandwich plates using a new first-order shear deformation theory. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 2014, 45, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, H.-T.; Choi, D.-H. A simple first-order shear deformation theory for the bending and free vibration analysis of functionally graded plates. Compos. Struct. 2013, 101, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Manickam, G. Bending and vibration of functionally graded material sandwich plates using an accurate theory. Finite Elements Anal. Des. 2012, 57, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.J.; Wang, L.L.; Du, H.Y. Analysis of Heating Steady Temperature Field in an Al1100/Ti-6Al-4V/SiC 2D-FGM Plane Plate by FEM. Key Eng. Mater. 2011, 450, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Fasshauer, G.; Batra, R.; Rodrigues, J. Static deformations and vibration analysis of composite and sandwich plates using a layerwise theory and RBF-PS discretizations with optimal shape parameter. Compos. Struct. 2008, 86, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapuria, S.; Achary, G. An efficient higher order zigzag theory for laminated plates subjected to thermal loading. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2004, 41, 4661–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shodja, H.; HaftBaradaran, H.; Asghari, M. A thermoelasticity solution of sandwich structures with functionally graded coating. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 67, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Karkhanis, R.S.; Sahoo, R.; Maiti, P.R.; Singh, B.N. Trigonometric zigzag theory for static analysis of laminated composite and sandwich plates under hygro-thermo-mechanical loading. Compos. Struct. 2018, 209, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechab, B.; Mechab, I.; Benaissa, S. Composites: Part B Analysis of thick orthotropic laminated composite plates based on higher order shear deformation theory by the new function under thermo-mechanical loading. Compos. Part B 2012, 43, 1453–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleiro, F.; Correia, V.F.; Ferreira, A.; Reddy, J. Fully coupled thermo-mechanical analysis of multilayered plates with embedded FGM skins or core layers using a layerwise mixed model. Compos. Struct. 2018, 210, 971–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, H.; Shishesaz, M.; Moradi, S. Applications of higher order shear deformation theories on stress distribution in a five layer sandwich plate. Appl. Comput. Mech. 2017, 48, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardooni, M.R.; Shishesaz, M.; Moradi, S.; Mosalmani, R. Free Vibrational Analysis of a Functionally Graded Five-Layer Sandwich Plate Resting on a Winkler Elastic Foundation in a Thermal Environment. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishehsaz, M.; Raissi, H.; Moradi, S. Stress distribution in a five-layer circular sandwich composite plate based on the third and hyperbolic shear deformation theories. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2019, 27, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounsi, A.; Houari, M.S.A.; Benyoucef, S.; Bedia, E.A.A. A refined trigonometric shear deformation theory for thermoelastic bending of functionally graded sandwich plates. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Benyoucef, S.; Tounsi, A.; Benachour, A.; Bedia, E.A.A.; Mahmoud, S. A refined quasi-3D shear deformation theory for thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded sandwich plates on elastic foundations. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2017, 21, 1906–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, R.; Ai, S.; He, R.; Pei, Y.; Fang, D. Load distribution in threads of porous metal–ceramic functionally graded composite joints subjected to thermomechanical loading. J. Compos. Struct. 2015, 134, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miteva, A.; Bouzekova-Penkova, A. Module for wireless communication in aerospace vehicles. Aerosp. Res. Bulg. 2021, 33, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.N. Mechanics of Laminated Composite Plates and Shells; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birman, V.; Bert, C.W. On the Choice of Shear Correction Factor in Sandwich Structures. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2002, 4, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, S.; Rao, A. Bending, vibration and buckling of simply supported thick orthotropic rectangular plates and laminates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1970, 6, 1463–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A. Analysis of Composite Plates Using a Layerwise Theory and Multiquadrics Discretization. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2005, 12, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaseied, A.; Fatemi, A. Deformation response and constitutive modeling of vinyl ester polymer including strain rate and temperature effects. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elastollan BASF Company, Ellastollan Physical and Mechanical Properties Manual Book of Thermoplastic Polyuerthane Elastomers(TPU), Ellastollan@Product Range. Available online: www.elastollan.de (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Kahya, V.; Turan, M. Vibration and stability analysis of functionally graded sandwich beams by a multi-layer finite element. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 146, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaee, S.; Palmese, G.R. Effects of temperature on cure kinetics and mechanical properties of vinyl-ester resins. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1999, 37, 725–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.-H.; Hung, C.-H.; Ma, C.-C.M.; Yen, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-F.; Weng, C.-C. Preparation and properties of carbon nanotube-reinforced vinyl ester/nanocomposite bipolar plates for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2008, 176, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).