Study of the Physical Behavior of a New Composite Material Based on Fly Ash from the Combustion of Coal in an Ultra-Supercritical Thermal Power Plant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
- Unsaturated polyester resin (UP) thermosetting.
- -
- The accelerator (cobalt octoate) gives the resin a pinkish hue, which partly disappears with the setting.
- -
- The catalyst: methyl ethyl ketone peroxide.
- ·
- Density at 20 °C …… 1.11 g/cm3
- ·
- Viscosities at 25 °C ………………. 5–6 dPa.s approximately.
- ·
- Dry shrinkage ………………………. 64%.
- Mechanical properties
- ISO 527 traction.
- Stress at break............................. 55 MPa
- Elongation at break......................... 2.2%
- Bending ISO 178 40
- Stress at break............................. 117 MPa
- Modulus of elasticity................................... 3800 GPa
- Physical properties at 20 °C
- Freezing time: .............................................. 18 min
- Freezing time at exothermic peak: ............ 15 min
- Exothermic peak: ......................................... 138 °C
- Industrial waste treated:
Preparing Waste Fly Ash (Powder)
2.2. Development of New Composite Material
3. Characterization of Materials
3.1. Thermal Analysis (Thermal Conductivity)
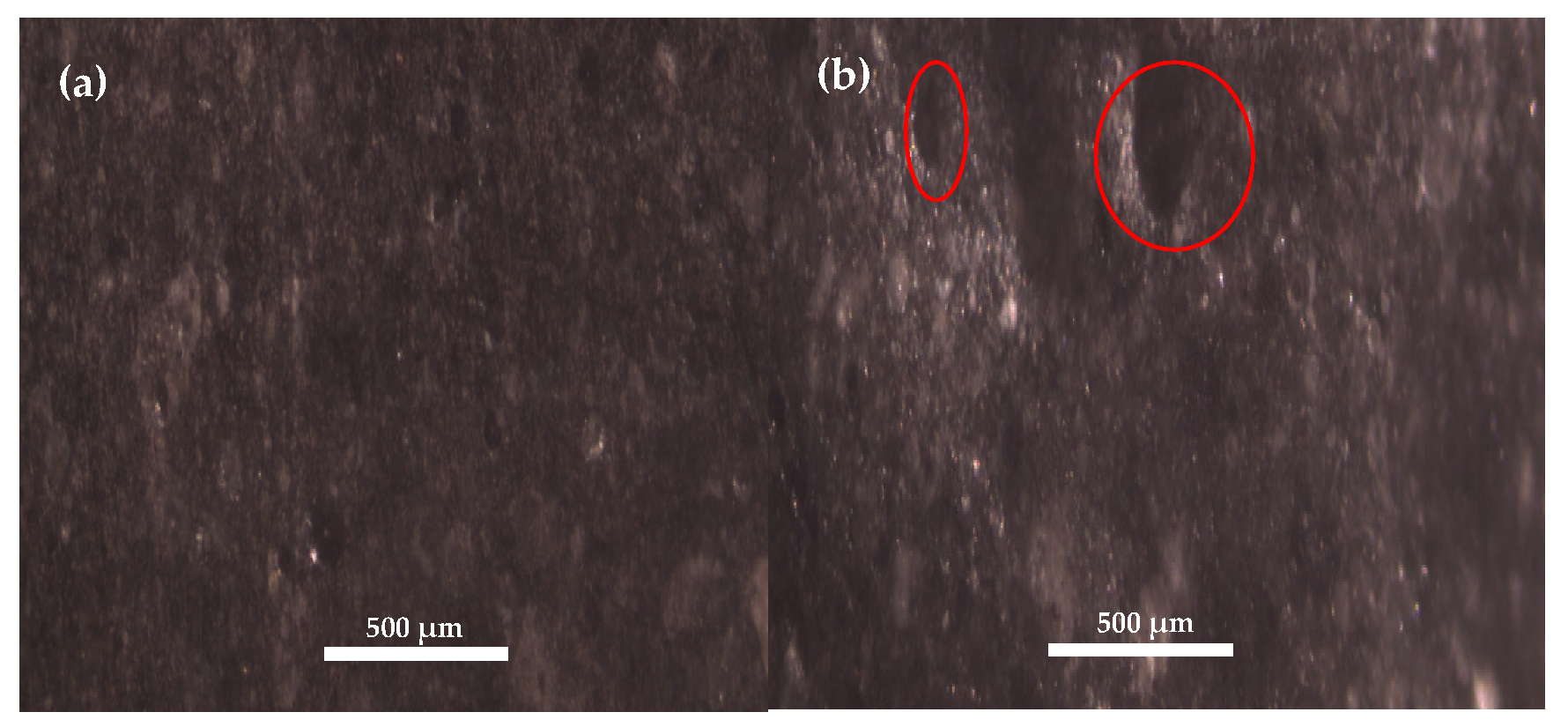
3.2. Behavior to Erosion
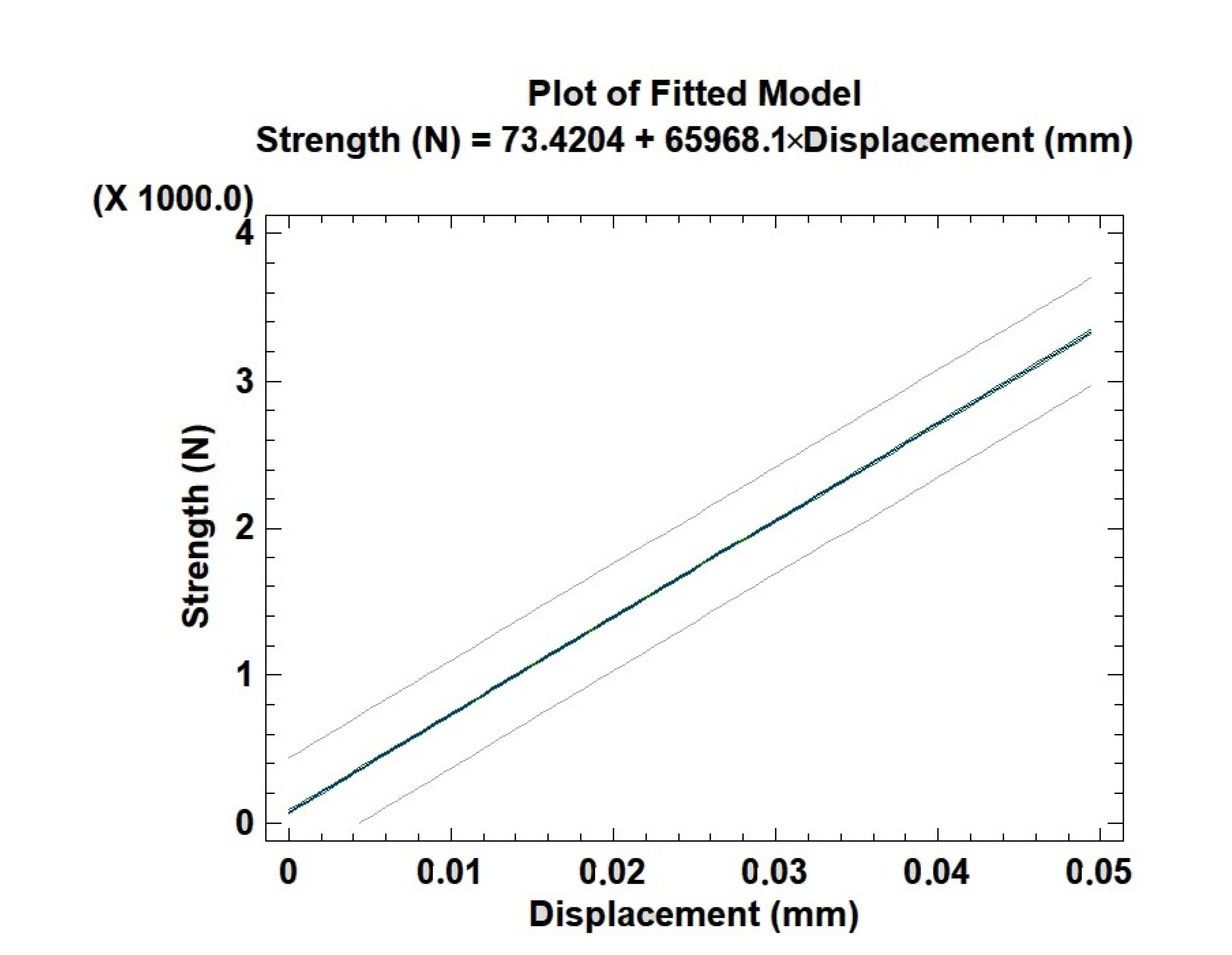
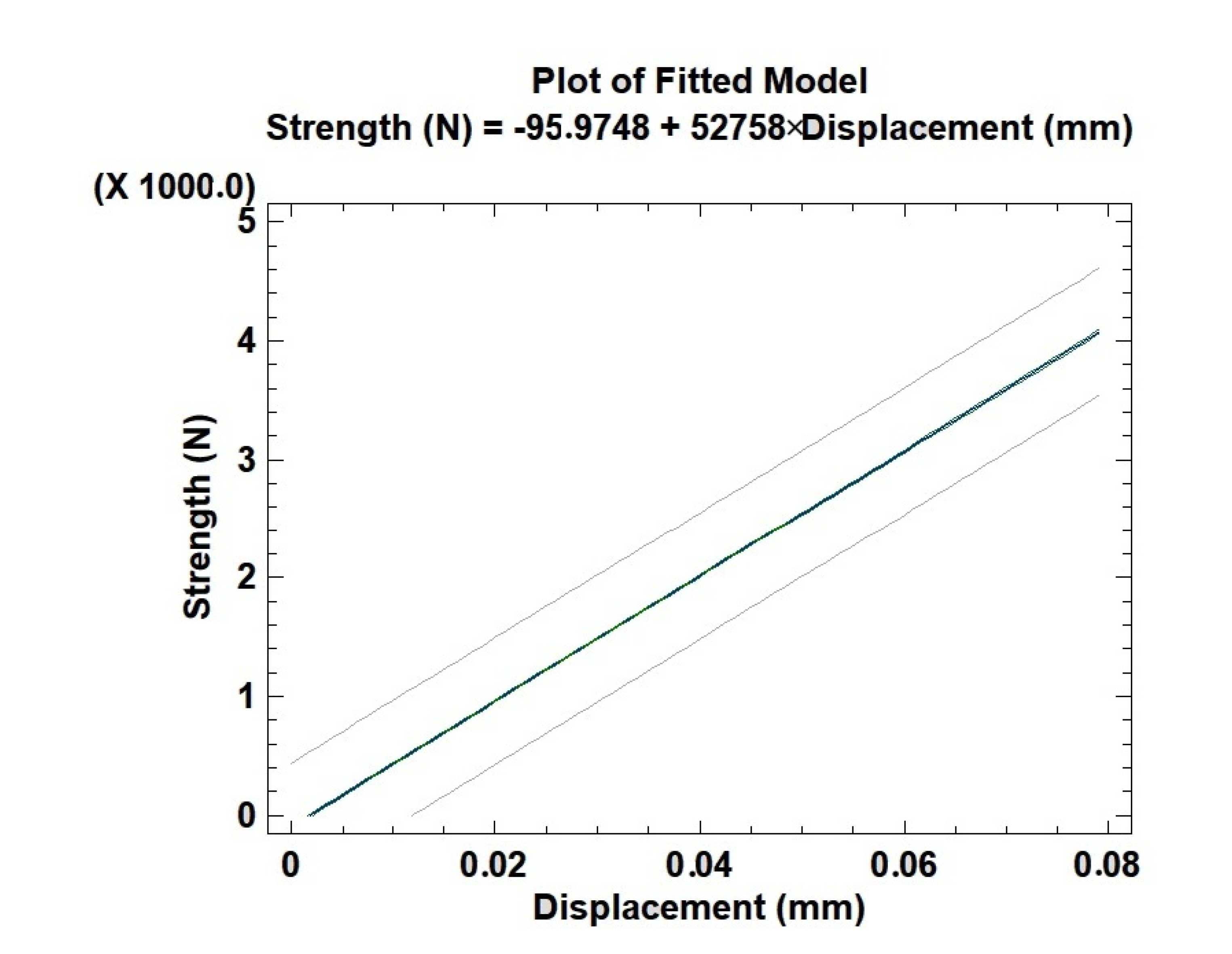
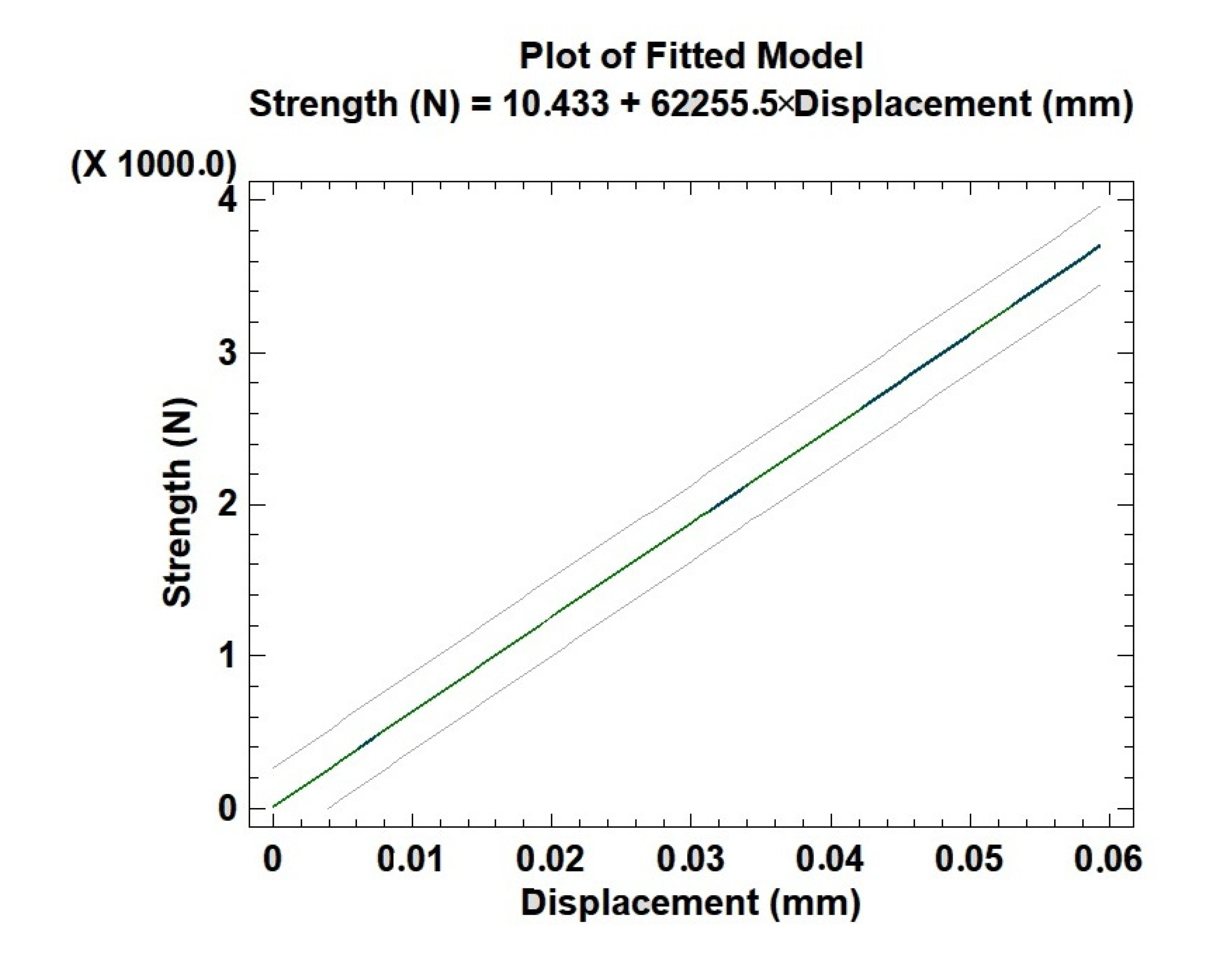
3.3. Young’s Module Compression Test
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.5. Ray Diffraction X (DRX):
- -
- Bragg-Brentano θ–2θ configuration goniometer
- -
- Scintillation detector; NaI type
- -
- Room temperature controller up to 1200 °C
- -
- Acquisition speed 0.05–25°/min (θ)
- -
- Measurement repeatability: 0.001° (2θ)
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Thermal Analysis (Thermal Conductivity)
4.2. Behavior to Erosion
4.3. SEM and DEX Methods
4.4. Young’s Module Compression Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. A review on the utilization of fly ash. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 327–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Cai, C.; Yu, X. Cenospheres from Coal Ash and Their Application; National Defense Press: Beijing, China, 2008; p. 254. [Google Scholar]
- Lighty, J.S.; Veranth, J.M.; Sarofim, A.F. Combustion Aerosols: Factors Governing Their Size and Composition and Implications to Human Health. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2000, 50, 1565–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Xie, Q.; Zhao, C. Technology to Transfer Coal-Based Solid Wastes to Resources; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005; p. 294. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhai, J.; Xu, Y.; Tu, J.; Lin, Y. Study on the characteristics and genetic mechanism of microspheriods in cpfa. Environ. Eng. 1997, 15, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lauf, R.J. Cenospheres in fly ash and conditions favouring their formation. Fuel 1981, 60, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngu, L.-N.; Wu, H.; Zhang, D.-K. Characterization of Ash Cenospheres in Fly Ash from Australian Power Stations. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 3437–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.U.; Xiao-min, C.H.E.N.; Guang-ping, X.U. Study on the Characteristics and Genetic Mechanism of Microspheroids in CPFA from Huaneng Nanjing Electric Power Plant. Geol. J. China Univ. 2000, 1, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Vassileva, C.G. A new approach for the classification of coal fly ashes based on their origin, composition, properties, and behavior. Fuel 2007, 86, 1490–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramme, B.W.; Tharaniyil, M.P. Coal Combustion Products Utilization Handbook, 3rd ed.; Wisconsin Electric Power Company: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- NF EN 197-1. French and European standards for products or uses with coal fly ash: Cement-Part 1: Composition, specifications and conformity criteria for current cements. 2001. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/sist/00e7c857-98b1-4132-b9ec-9cf156a8dfc3/sist-en-197-1-2001-opra2-2006 (accessed on 3 June 2021).
- Tikalsky, P.J.; Carrasquillo, R.L. The Effect of Fly Ash on the Sulfate Resistance of Concrete; Research Report 481-5; Center for Transportation Research: Austin, TX, USA, 1989; pp. 106–118. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, B.; Dorey, S.E.; Cooke, R.G. Strength and Toughness of Fibre Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1988, 31, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, M. Realization of Eco-Cements by the Recovery of Unconventional Coal Fly Ash from Spreader Stoker Thermal Power Plants. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2016; pp. 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Alheyen, S. Synthesis, Characterization, Microstructure and Durability of Fly Ash-based Geopolymers. Doctoral Dissertation, Mohammed University 5, Rabat, Morocco, 2017; pp. 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, G.; Zhao, S.; Xu, C.; Yang, Y. Parametric analysis and process optimization of steam cycle in double reheat ultra-supercritical power plants. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 99, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, M. Realization of Eco-Cements by the Valorization of Non-Conventional Coal Fly Ash from Spreader Stoker Thermal Power Plants. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2016; pp. 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kashif, M.; Awan, M.B.; Nawaz, S.; Amjad, M.; Talib, B.; Farooq, M.; Rehan, M. Untapped renewable energy potential of crop residues in Pakistan: Challenges and future directions. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 256, 109924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, D.G.; Sharples, M.; Lien, L.; Schumacher, G.; Babich, A.; Harris, D.; Carras, J. Future directions toward more efficient and cleaner use of coal. In The Coal Handbook: Towards Cleaner Production; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 497–528. [Google Scholar]
- Afechkar, M.; Nahhass, M. Valorisation des cendres volantes dans le domaine routier (terrassements et couches de chaussées); Laboratoire du CNER; 2004; p. 4. Available online: http://www.ampcr.ma/actes/7eme_congres_national_de_la_route/CONGRE/TH4/TH4_4.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2021).
- 21. Ayrinhac. Recovery of Fly Ash from a Fluidized Bed Boiler Circulating in the Civil Engineering Sector. Doctoral Dissertation, National Institute of Applied Sciences of Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2005; p. 11.
- El Alouani, M.; Alehyen, S.; El Achouri, M.; Taibi, M. Comparative study of the adsorption of micropollutant contained in aqueous phase using coal fly ash and activated coal fly ash: Kinetic and isotherm studies. Chem. Data Collect. 2019, 23, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Chugh, Y. Development of fly ash-based automotive brake lining. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.Y.; Chen, L.; Komarneni, S.; Zhou, C.H.; Tong, D.S.; Yang, H.M.; Yu, W.H.; Wang, H. Fly ash-based geopolymer: Clean production, properties and applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 125, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, R.; Coleman, K.; Rao, U. Materials for ultra-supercritical coal-fired power plant boilers. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2006, 83, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein-Brzozowska, G.; Flórez, D.M.; Maier, J.; Scheffknecht, G. Nickel-base superalloys for ultra-supercritical coal-fired power plants: Fireside corrosion. Laboratory studies and power plant exposures. Fuel 2013, 108, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; Xu, W. China’s R&D of advanced ultra-supercritical coal-fired power generation for addressing climate change. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018, 5, 364–371. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, D.H.; Silva, R.J. Exergoenvironmental analysis of a ultra-supercritical coal-fired power plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.T.; Zhao, Y. Development of ultra-supercritical power generation technology in China. Huadian Technol. 2008, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Castello, P.; Guttmann, V.; Farr, N.; Smith, G. Laboratory-simulated fuel-ash corrosion of superheater tubes in coal-fired ultra-supercritical-boilers. Mater. Corros. 2000, 51, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulaoued, I.; Amara, I.; Mhimid, A. Experimental determination of thermal conductivity and diffusivity of new building insulating materials. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2016, 34, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, M.A. Corrosion et Corrosion-Abrasion d’alliage. Fac. Sci. Rabat 1996, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Guenbour, A.; Faucheu, J.; Bachir, A.B. On the mechanism for improved passivation by addition of molybdenum to austenitic stainless steels in O-phosphoric acid. Corrosion 1998, 44, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skal, S.; Kerroum, Y.; Guenbour, A.; Bellaouchou, A.; Tabyaoui, H.; Idrissi, H.; Zarrouk, A.; García-Antón, J. Effect of abrasive particles on electrochemical behaviour of passive film formed on Alloy 59 in contaminated phosphoric acid. JMES 2017, 8, 3234–3246. [Google Scholar]
- Ennawaoui, C.; Lifi, H.; Hajjaji, A.; Samuel, C.; Rguiti, M.; Touhtouh, S.; Courtois, C. Dielectric and mechanical optimization properties of porous poly (ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) copolymer films for pseudo-piezoelectric effect. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaine, S. Etude des Propriétés Thermiques et Mécaniques des Bétons Isolants Structurels Incorporant des Cénosphères. Doctoral Dissertation, Génie civil. École centrale de Nantes, Nantes, France, 2018; p. 33. (In French). [Google Scholar]
- Kanzaoui, M.E.L.; Boussen, R.; Hajjaji, A.; Guenbour, A. Development and study of mechanical behaviour reinforcing composites by waste BTP. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences on Development and Study of Mechanical Behaviour Reinforcing Compo-sites by Waste BTP, Rabat, Morocco, 22–25 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Long, K.; Du, X.; Xu, S.; Xie, Y.M. Composite Structures, Maximizing the effective Young’s modulus of a composite material by exploiting the Poisson effect. Compos. Struct. 2016, 153, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Element | Mass Percent (%) |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 43–54% |
| Al2O3 | 22–32% |
| Fe2O3 + TiO2 | 4–15% |
| CaO | 1–8% |
| MgO | 1–3% |
| K2O | 2−5% |
| Na2O | 0.5–1% |
| SO3 | 0.2−2% |
| 1st Material | 2nd Material | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ● Paving: 50% Fly Ash Dimensions: 25 × 25 × 1 (cm) | ● Paving: 60% Fly Ash Dimensions: 25 × 25 × 1 (cm) | |||||
| Test number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Thickness (cm) | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Tint (°K) | 320.65 | 320.75 | 320.95 | 315.43 | 316.46 | 315.25 |
| Text (°K) | 301.46 | 299.75 | 301.35 | 300.35 | 300.25 | 301.00 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m.°K) | 0.834 | 0.762 | 0.816 | 1.061 | 0.987 | 1.123 |
| 1st Material | 2nd Material | |
|---|---|---|
| • Paving: 50% Fly Ash Dimensions: (cm) | • Paving: 60% Fly Ash Dimensions: (cm) | |
| 25 × 25 × 1 | 25 × 25 × 1 | |
| Thickness (cm) | 1 | 1 |
| Average Thermal Conductivity (W/m. °K) | 0.804 | 1.057 |
| Standard deviation (σ) | 0.030 | 0.055 |
| Designation | Material | Conductivity Thermal (W/m.K) | Thickness (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Floor | Solid concrete | 2 | 18 |
| Facade veil | concrete or BIS | Variable (0.4 or 0.8) | 15 |
| Insulating | Glass wool | 0.038 | 10 |
| Young’s Modulus in (GPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 |
| Composite | |||
| 50% Fly ash | 14.85 | 13.24 | 14.7 |
| 60% Fly ash | 19.82 | 14.13 | 13.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Kanzaoui, M.; Ennawaoui, C.; Eladaoui, S.; Hajjaji, A.; Guenbour, A.; Boussen, R. Study of the Physical Behavior of a New Composite Material Based on Fly Ash from the Combustion of Coal in an Ultra-Supercritical Thermal Power Plant. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5060151
El Kanzaoui M, Ennawaoui C, Eladaoui S, Hajjaji A, Guenbour A, Boussen R. Study of the Physical Behavior of a New Composite Material Based on Fly Ash from the Combustion of Coal in an Ultra-Supercritical Thermal Power Plant. Journal of Composites Science. 2021; 5(6):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5060151
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Kanzaoui, Mustapha, Chouaib Ennawaoui, Saleh Eladaoui, Abdelowahed Hajjaji, Abdellah Guenbour, and Ratiba Boussen. 2021. "Study of the Physical Behavior of a New Composite Material Based on Fly Ash from the Combustion of Coal in an Ultra-Supercritical Thermal Power Plant" Journal of Composites Science 5, no. 6: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5060151
APA StyleEl Kanzaoui, M., Ennawaoui, C., Eladaoui, S., Hajjaji, A., Guenbour, A., & Boussen, R. (2021). Study of the Physical Behavior of a New Composite Material Based on Fly Ash from the Combustion of Coal in an Ultra-Supercritical Thermal Power Plant. Journal of Composites Science, 5(6), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5060151







