Effect of Structural Parameters on the Deformational Behaviors of Multiply 3D Layer-by-Layer Angle-Interlock Para-Aramid Fabric for Fiber-Reinforcement Composite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials and Preform Preparations
2.1.1. Materials
2.1.2. Preform Preparations
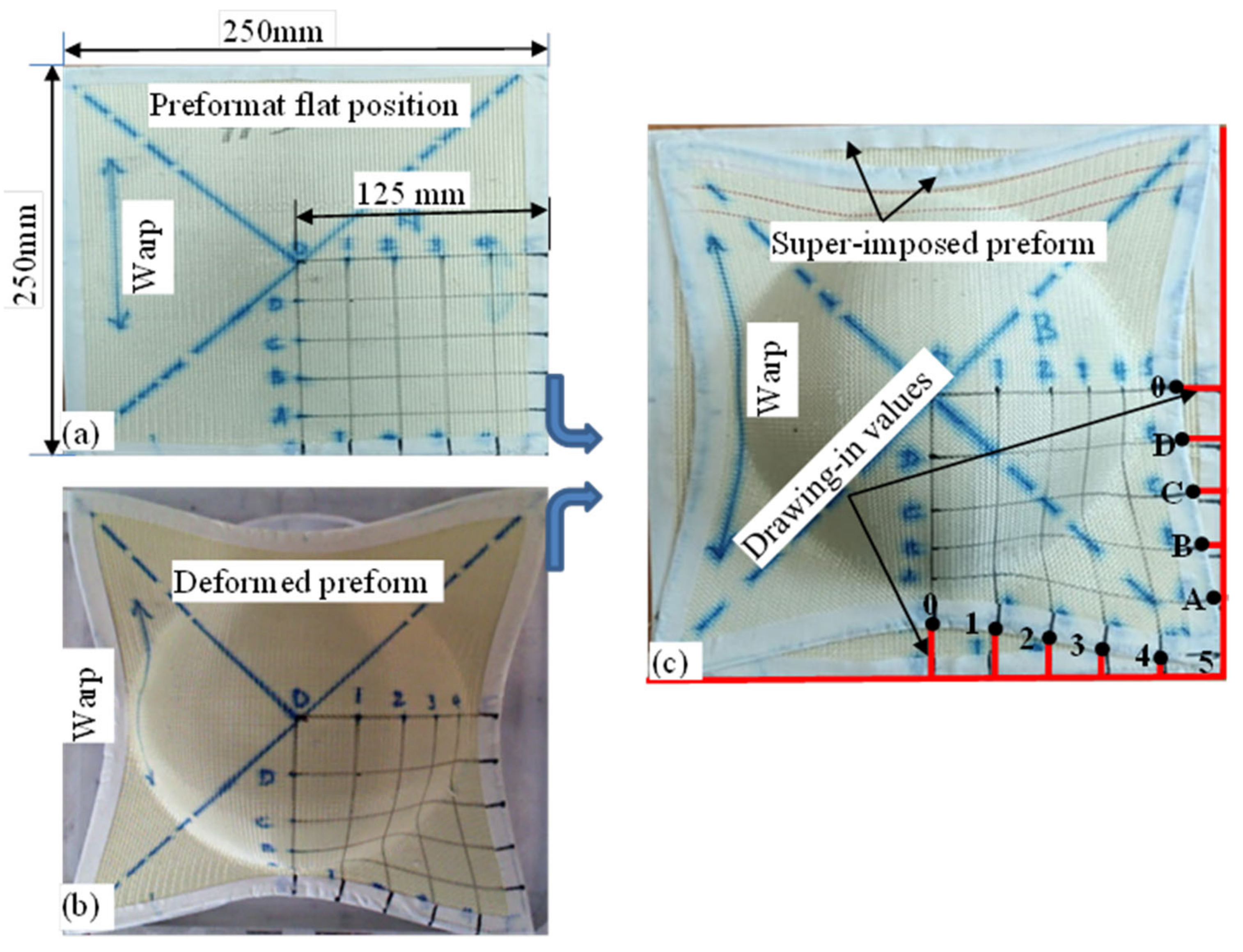
2.2. Formability Testing Device and the Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Formability Behaviors of 3D Warp Interlock Fabrics
3.1.1. Influence of Warp Yarn System on the Punch Force of 3D Warp Interlock Fabric
3.1.2. Influence of Warp Yarn System on the In-Plane Shear Angle
- δ is the in-plane shear angle
- θ is the initial angle measured between the yarns (mostly 90°), is the angle measured between the weft and warp yarns after immediate deformation.
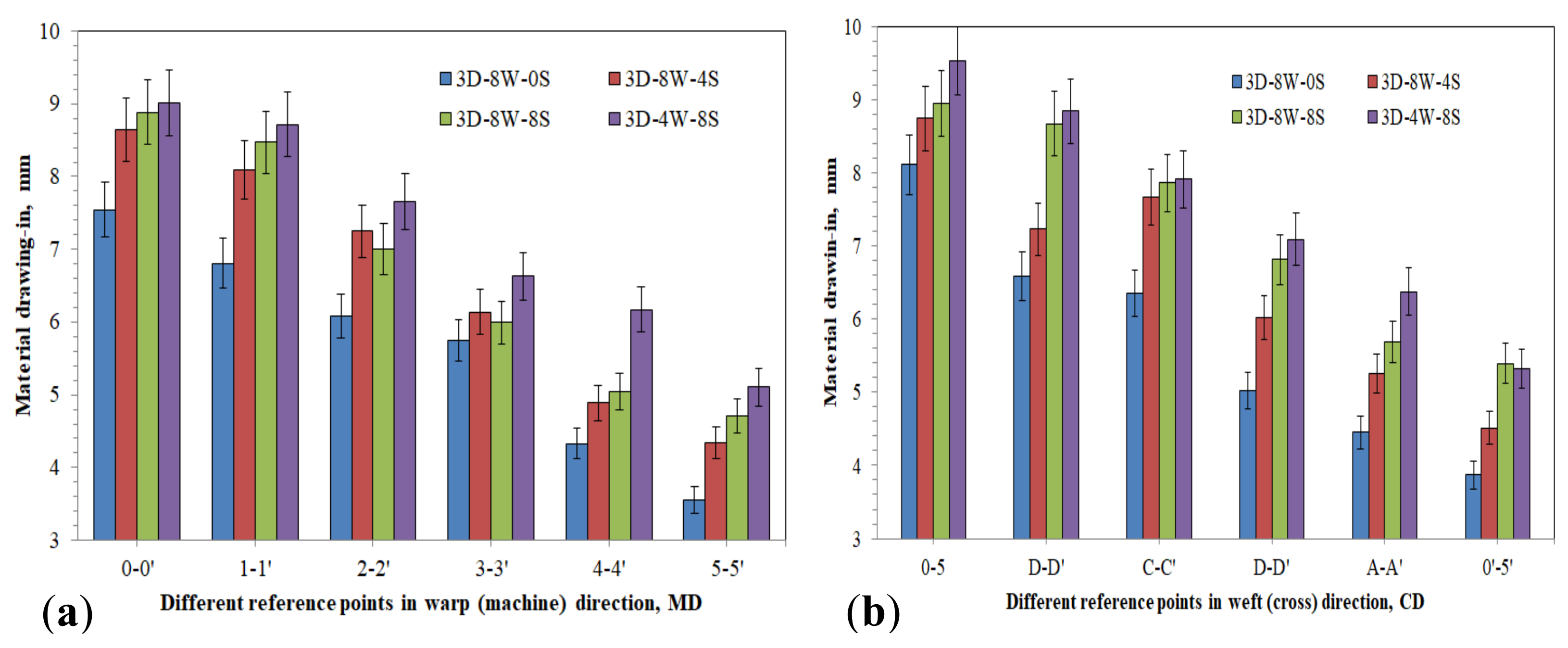
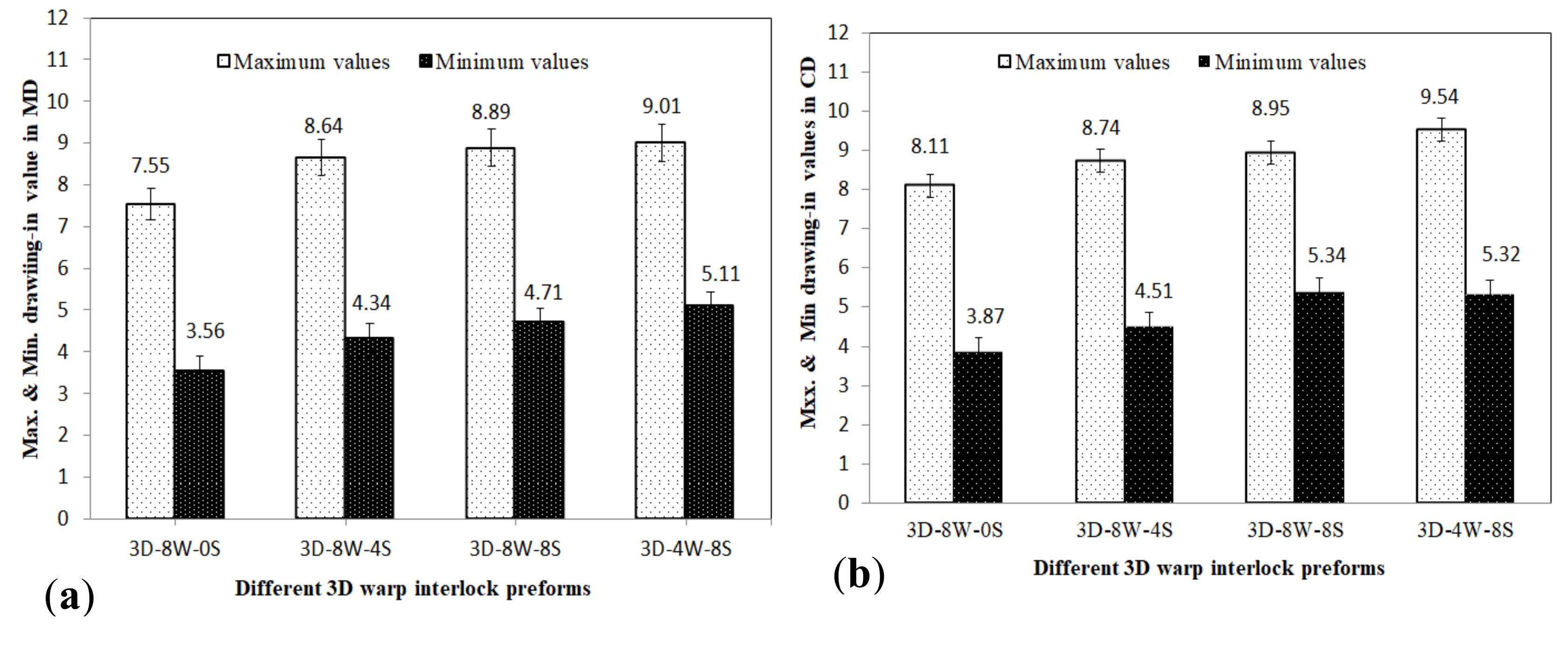
3.1.3. Influence of Warp Yarn in Material Drawing-In Values
3.2. Material Forming Recovery Characteristics
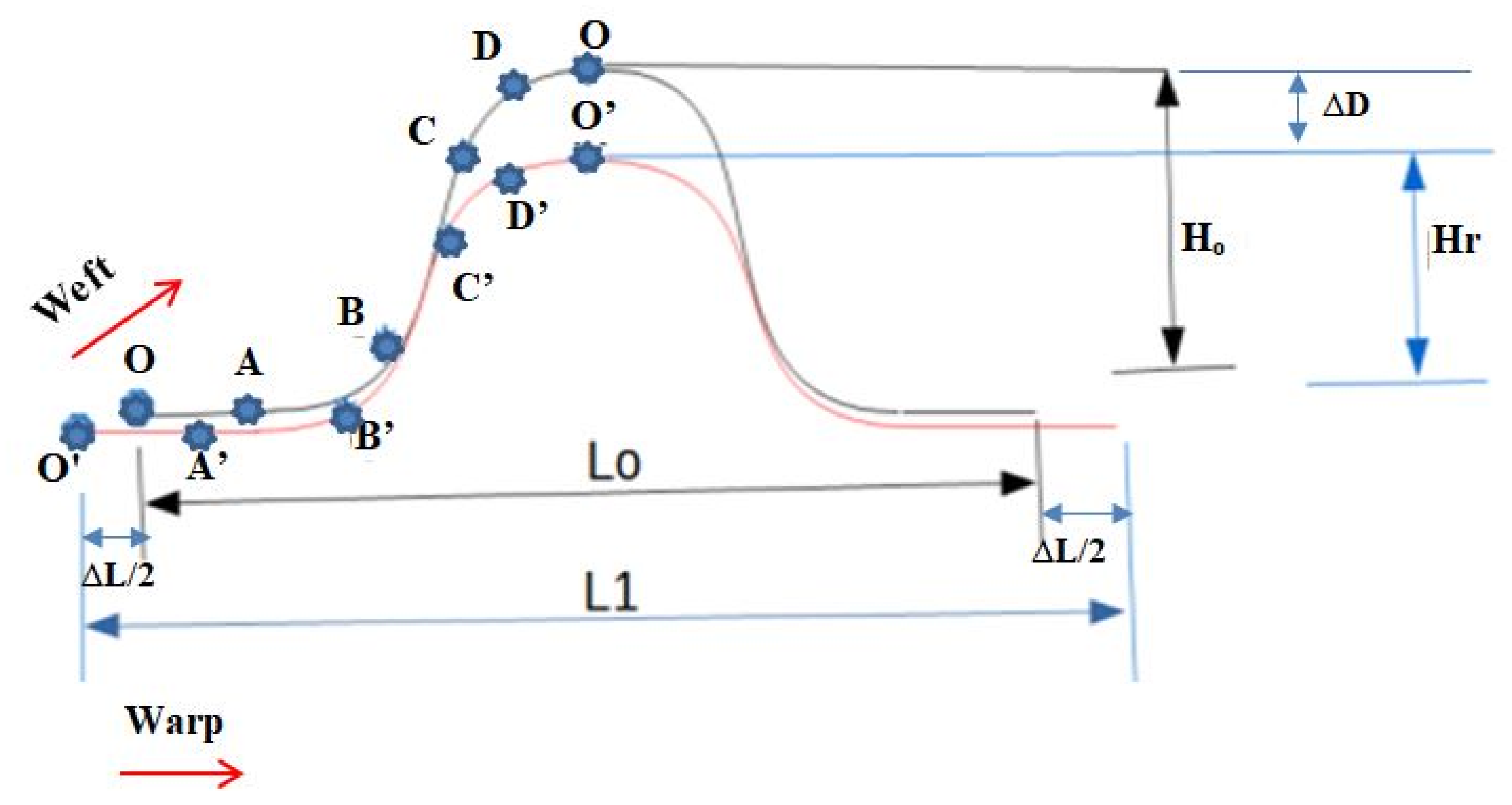
3.2.1. Influence of Warp Yarn System on Maximum Deformed Height Recovery
- ΔD is the deformational recovery in percentage at maximum central depth toward the punching load;
- H0—Deformational recovery at maximum central depth while forming;
- Hr—Deformational recovery at maximum central depth after recovery.
3.2.2. Influence of Warp Yarn System on Drawing-In Recovery
- Do—drawing-in values at the initial;
- Di—drawing-in values after recovery;
- Dr—the recovered drawing-in values after removing the load and waiting 48 h.
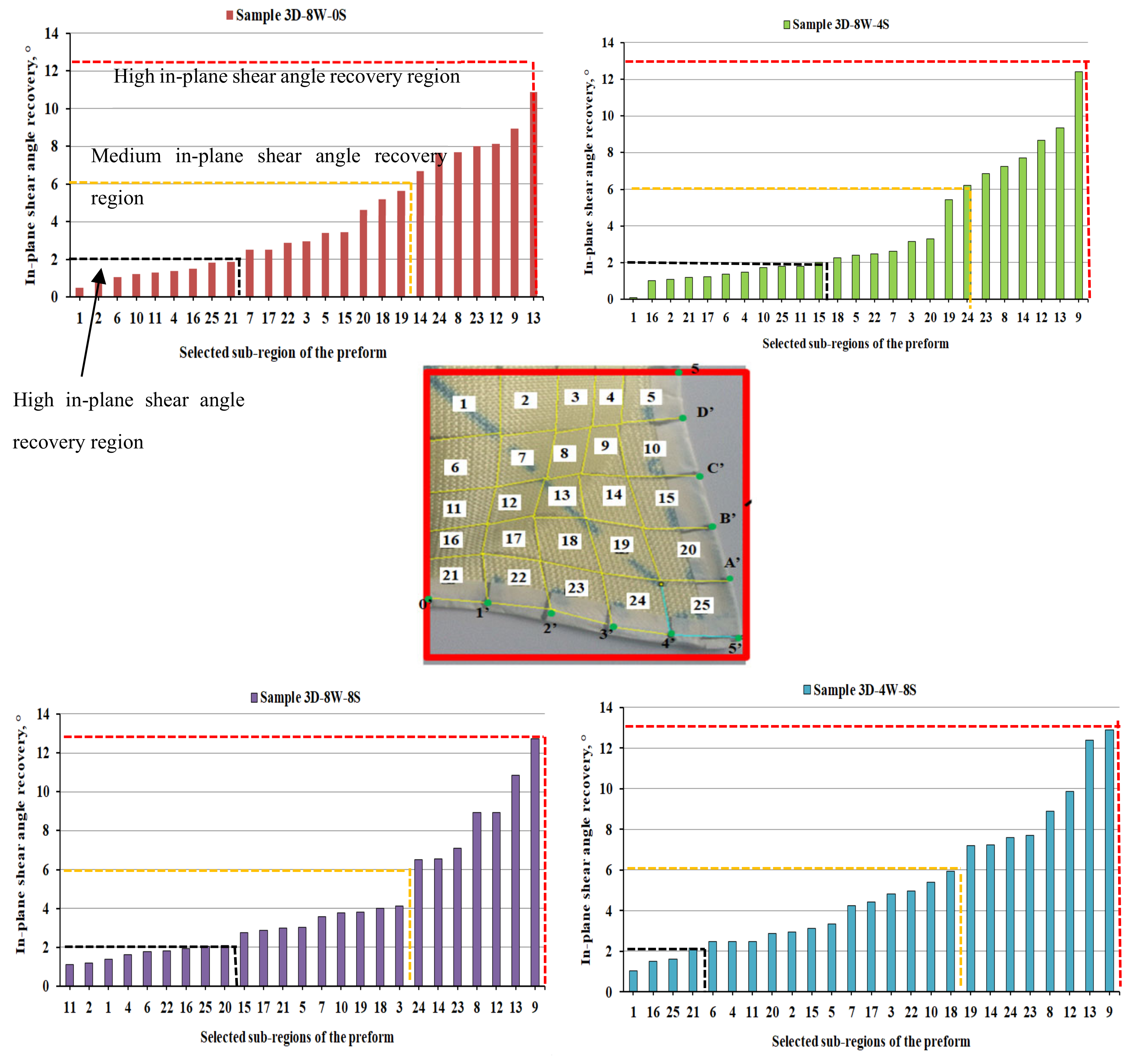
3.2.3. Influence of Warp Yarn System on In-Plane Shear Angle Recovery
4. Conclusions
- In general, the different forming characteristics of 3D warp interlock fabrics were greatly influenced by the warp yarn interchange ratio. For example, the increments of the stuffer warp yarns interchange ratio exhibit an impact, and directly proportional to the stamping force while forming. Sample with higher stuffer warp yarns ratio possesses less yarn undulation in the warp direction which in turn needs a higher amount of punching loads to deform the preforms to its maximum deformational depth.
- The in-plane shear angles were also observed higher in the majority of the region for preform with lower binding warp yarns in the 3D warp interlock fabric.
- The preforms having higher stuffer yarn ratio revealed higher drawing-in values than preforms with no or less stuffer warp yarns.
- The warp yarns interchange ratio also revealed a great influence on the forming recovery properties of 3D warp interlock fabric. The involvement of a higher stuffer warp yarns interchange ratio possesses a higher deformational recovery percentage at maximum depth as compared to the fabric with a lower stuffer warp yarn interchange ratio. For example, preform 3D-8W-0S exhibited a maximum deformational height recovery percentage of 5.1%, whereas 3D-4W-8S recorded only 0.72%. Moreover, preform 3D-8W-4S and 3D-8W-8S revealed 1.45% and 4.35% recovery percentages toward the deformational height at maximum position.
- The drawing-in recovery percentages of the preforms were found higher at the top center of the preforms and decrease as it goes toward the peripheral edges of the preform. Specifically, Sample 3D-4S-8W revealed the maximum drawing-in recovery percentage of 43.13% and 46.98% in the machine and cross direction respectively around the preform peripheral edges. On the contrary, samples with higher binding warp yarns as 3D-8W-0S show the maximum drawing-in recovery percentages values of 31.21% and 34.99% in the machine and cross directions respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Chen, X. Investigation on energy absorption efficiency of each layer in ballistic armour panel for applications in hybrid design. Compos. Struct. 2017, 164, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abtew, M.A.; Boussu, F.; Bruniaux, P.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I. Engineering of 3D warp interlock p-aramid fabric structure and its energy absorption capabilities against ballistic impact for body armour applications. Compos. Struct. 2019, 225, 111179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.A.; Boussu, F.; Bruniaux, P.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Ballistic impact performance and surface failure mechanisms of two-dimensional and three-dimensional woven p-aramid multi-layer fabrics for lightweight women ballistic vest applications. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekampienė, P.; Domskienė, J. Influence of Stitching Pattern on Deformation Behaviour of Woven Fabric during Forming. Mater. Sci. 2010, 16, 1392–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Nawab, Y.; Legrand, X.; Koncar, V. Study of changes in 3D-woven multilayer interlock fabric preforms while forming. J. Text. Inst. 2012, 103, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanwan, A.; Allaoui, S. Different experimental ways to minimize the preforming defects of multi-layered interlock dry fabric. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2018, 12, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Yang, D. Use of 3D Angle-Interlock Woven Fabric for Seamless Female Body Armour: Part 1: Ballistic Evaluation. Text. Res. J. 2010, 80, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Chen, X.; Chai, Y.; Lowe, T. Effect of reinforcement continuity on the ballistic performance of composites reinforced with multiply plain weave fabric. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 90, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.A.; Boussu, F.; Bruniaux, P.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Forming characteristics and surface damages of stitched multi-layered para-aramid fabrics with various stitching parameters for soft body armour design. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 109, 517–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedel, C.; Chen, X. Innovation and Analysis of Police Riot Helmets with Continuous Textile Reinforcement for Improved Protection. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2007, 2, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zahid, B.; Chen, X. Manufacturing of single-piece textile reinforced riot helmet shell from vacuum bagging. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 47, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, D. Use of Three-dimensional Angle-interlock Woven Fabric for Seamless Female Body Armor: Part II: Mathematical Modeling. Text. Res. J. 2010, 80, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.A.; Bruniaux, P.; Boussu, F.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I.; Chen, Y. Development of comfortable and well-fitted bra pattern for customized female soft body armor through 3D design process of adaptive bust on virtual mannequin. Comput. Ind. 2018, 100, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.A.; Bruniaux, P.; Boussu, F.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. A systematic pattern generation system for manufacturing customized seamless multi-layer female soft body armour through dome-formation (moulding) techniques using 3D warp interlock fabrics. J. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 49, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.A.; Bruniaux, P.; Boussu, F.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Female seamless soft body armor pattern design system with innovative reverse engineering approaches. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 2271–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboktakin, A. 3D textile preforms and composites for aircraft strcutures: A review. Int. J. Aviat. Aeronaut. Aerosp. 2019, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddika, A.; Al Mamun, M.A.; Ferdous, W.; Alyousef, R. Performances, challenges and opportunities in strengthening reinforced concrete structures by using FRPs—A state-of-the-art review. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 111, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, V.; Behera, B.K.; Manjunath, R.N. Textile structural composites for automotive leaf spring application. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 182, 107662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.H.; Geraldi, N.R.; Stafford, J.L.; Spicer, A.; Hall, J.; Bradley, C.; Newton, M.I. Woven Natural Fibre Reinforced Composite Materials for Medical Imaging. Materials 2020, 13, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mouritz, A.; Bannister, M.; Falzon, P.; Leong, K. Review of applications for advanced three-dimensional fibre textile composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1999, 30, 1445–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussu, F.; Provost, B.; Lefebvre, M.; Coutellier, D. New Textile Composite Solutions for Armouring of Vehicles. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zunic, B.; Peter, S. Textile Reinforced Structural Composites for Advanced Applications. In Textiles for Advanced Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 88–133. [Google Scholar]
- de Luycker, E.; Morestin, F.; Boisse, P.; Marsal, D. Simulation of 3D interlock composite preforming. Compos. Struct. 2009, 88, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khokar, N. 3D-Weaving: Theory and Practice. J. Text. Inst. 2001, 92, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokarneshan, N.; Alagirusamy, R. Weaving of 3D fabrics: A critical appreciation of the developments. Text. Prog. 2009, 41, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussu, F.; Cristian, I.; Nauman, S. General definition of 3D warp interlock fabric architecture. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 81, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilisik, K. Two-dimensional (2D) fabrics and three-dimensional (3D) preforms for ballistic and stabbing protection: A review. Text. Res. J. 2016, 87, 2275–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chen, X. Multi-layer pattern creation for seamless front female body armor panel using angle-interlock woven fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2017, 87, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha-Minh, C.; Boussu, F.; Kanit, T.; Crépin, D.; Imad, A. Effect of frictions on the ballistic performance of a 3D warp interlock fabric: Numerical analysis. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2012, 19, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lo, W.-Y.; Tayyar, A.E. Mouldability of Angle-Interlock Woven Fabrics for Technical Applications. Text. Res. J. 2002, 72, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, B.; Chen, X. Impact performance of single-piece continuously textile reinforced riot helmet shells. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 48, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, B.; Chen, X. Development of a Helmet Test Rig for Continuously Textile Reinforced Riot Helmets. Int. J. Text. Sci. 2013, 2, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Min, S.; Roedel, C.; Zahid, B.; Chen, X. Moulding of single-piece woven fabrics for protective helmets—A review and future work. In Moulding of Single-Piece Woven Fabrics for Protective Helmets—A Review and Future Work; TexEng/RWTH Aachen: Aachen, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dufour, C.; Wang, P.; Boussu, F.; Soulat, D. Experimental Investigation About Stamping Behaviour of 3D Warp Interlock Composite Preforms. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2014, 21, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, C.; Boussu, F.; Wang, P.; Soulat, D. Local strain measurements of yarns inside of 3D warp interlock fabric during forming process. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2017, 11, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.A.; Boussu, F.; Bruniaux, P.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Influences of fabric density on mechanical and moulding behaviours of 3D warp interlock para-aramid fabrics for soft body armour application. Compos. Struct. 2018, 204, 402–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.Z.; van Hoa, S. Composite Materials Modeling of 3D Angle Interlock Woven Fabric Composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2003, 16, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, M.; Xinwei, W.; Chouwei, Z. Modeling strategies of 3D woven composites: A review. Compos. Struct. 2011, 93, 1947–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.S.; Fang, J.; Lin, H.W. Failure behavior of 3D woven composites under transverse shear. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2003, 34, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Chen, X. Three-dimensional textiles for protective clothing. In Advances in 3D Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 341–360. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y. 2D/3D Woven Fabrics for Ballistic Protection. In Proceedings of the 4th World Conference on 3D Fabrics and Their Applications, Aachen, Germany, 10–11 September 2012; TexEng/RWTH Aachen: Manchester, UK, 2012; pp. 1–12.
- Lefebvre, M.; Boussu, F. High energy absorption of warp interlock fabrics: Application to high speed impact of fragments. In DYMAT International Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2009; pp. 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Najjar, W.; Xavier, L.; Santo, P.D.; Soulat, D.; Boude, S. Analysis of the blank holder force effect on the preforming process using a simple discrete approach. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 554, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Najjar, W.; Legrand, X.; Pupin, C.; Santo, P.D.; Boude, S. A simple discrete method for the simulation of the preforming of woven fabric reinforcement. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 504, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangana, S.; Epaarachchi, J.; Ferdous, W.; Leng, J. A novel hybridised composite sandwich core with Glass, Kevlar and Zylon fibres—Investigation under low-velocity impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2020, 137, 103430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, C.; Boussu, F.; Wang, P.; Soulat, D. Experimental Forming Studies on 3D Warp Interlock Fabrics. In Proceedings of the ECCM16—16th European Conference on Composite Materials, Seville, Spain, 22–26 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Abtew, M.A.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I.; Boussu, F.; Bruniaux, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Mouldability and its recovery properties of 2D plain woven para-aramid fabric for soft body armour applications. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2019, 27, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Skelton, J. Textile materials: Recovery from imposed deformation. Science 1972, 177, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Wang, P.; Legrand, X.; Liu, L. Characterisation and optimisation of wrinkling during the forming of tufted three-dimensional composite preforms. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 127, 105651. [Google Scholar]
- Boisse, P.; Guzman-Maldonado, E.; Wang, P.; Hamila, N.; Colmars, J. Wrinkling and bending during forming of multi-layered textile composite. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.A.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I.; Boussu, F.; Bruniaux, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Two Dimensional (2D) P-Aramid Dry Multi-Layered Woven Fabrics Deformational Behaviour for Technical Applications. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 374, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Abtew, M.A.; Boussu, F.; Bruniaux, P.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Experimental investigation of effects of stitching orientation on forming behaviors of 2D P-aramid multilayer woven preform. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, X.; Boussu, F.; Nauman, S.; Cristian, I.; Lapeyronnie, P.; le Grognec, P.; Binétruy, C. Forming behaviour of warp interlock composite. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2009, 2, 177–180. [Google Scholar]
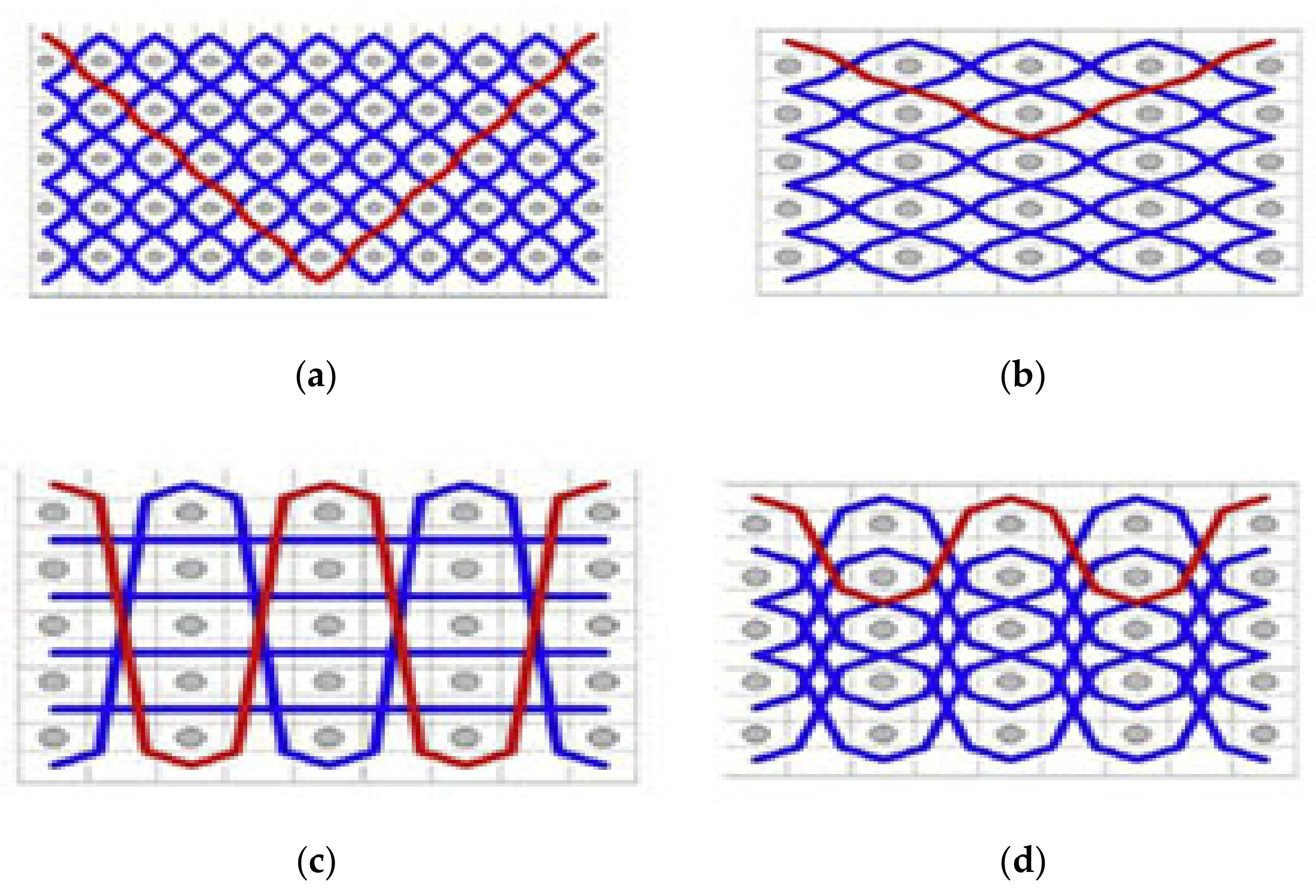













| Fabric Designations | Fiber Linear Density (dtex) | Fiber Strength at Break [N/mm2] | Warp Yarn (Binder: Stuffer) Interchange Ratio | Actual Fabric Density (g/m2) | Fabric Density (Warp/Weft) [yarn/cm] | Average Fabric Thickness [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D-8W-0S | 930 | 225 | 8:0 | 900 | 48/50 | 1.42 |
| 3D-8W-4S | 930 | 225 | 8:4 | 920 | 48/50 | 1.44 |
| 3D-8W-8S | 930 | 225 | 8:8 | 952 | 48/50 | 1.52 |
| 3D-4W-8S | 930 | 225 | 4:8 | 944 | 48/50 | 1.63 |
| Forming Parameters | Parameter Values |
|---|---|
| Punch shape | Hemispherical |
| Punch diameter | 150 mm |
| Stamping velocity | 45 mm/s |
| Blank-holder pressure | 0.4MPa |
| Max. Punching depth | 65 mm |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abtew, M.A.; Boussu, F.; Bruniaux, P.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I. Effect of Structural Parameters on the Deformational Behaviors of Multiply 3D Layer-by-Layer Angle-Interlock Para-Aramid Fabric for Fiber-Reinforcement Composite. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4040145
Abtew MA, Boussu F, Bruniaux P, Loghin C, Cristian I. Effect of Structural Parameters on the Deformational Behaviors of Multiply 3D Layer-by-Layer Angle-Interlock Para-Aramid Fabric for Fiber-Reinforcement Composite. Journal of Composites Science. 2020; 4(4):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4040145
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbtew, Mulat Alubel, Francois Boussu, Pascal Bruniaux, Carmen Loghin, and Irina Cristian. 2020. "Effect of Structural Parameters on the Deformational Behaviors of Multiply 3D Layer-by-Layer Angle-Interlock Para-Aramid Fabric for Fiber-Reinforcement Composite" Journal of Composites Science 4, no. 4: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4040145
APA StyleAbtew, M. A., Boussu, F., Bruniaux, P., Loghin, C., & Cristian, I. (2020). Effect of Structural Parameters on the Deformational Behaviors of Multiply 3D Layer-by-Layer Angle-Interlock Para-Aramid Fabric for Fiber-Reinforcement Composite. Journal of Composites Science, 4(4), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4040145







