Smart Thermomechanochemical Composite Materials Driven by Different Forms of Electromagnetic Radiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Polyaniline Solutions
2.2. Polyaniline Copolymer: Polyaniline-b-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PANI-b-PNIPAM)
2.3. Synthesis of Crosslinked Thermosensitive Hydrogels of Poly(N-isopropyacrylamide) (cPNIPAM)
2.3.1. Nanoporous Hydrogel (NPHG)
2.3.2. Macroporous Hydrogel (MPHG)
2.4. Synthesis of Conducting Polymer (Polyaniline and Polypyrrole) Nanoparticles
2.4.1. Polyaniline Nanospheres (PANI-NS)
2.4.2. Polyaniline Nanofibers (PANI-NF)
2.4.3. Polypyrrole Nanospheres (PPy-NS)
2.5. Synthetic Methods of Composite Materials
2.5.1. In Situ Polymerization of Aniline or Pyrrole Inside a Nanoporous Hydrogel (PH)
2.5.2. In Situ Formation of cPNIPAM around Conducting Polymer Nanoparticles (GAN)
2.5.3. Absorption of Conducting Polymers Nanoparticles into Macroporous Hydrogels (INH)
2.5.4. Loading of Polyanilines from Solution into Nanoporous Hydrogels (AMH)
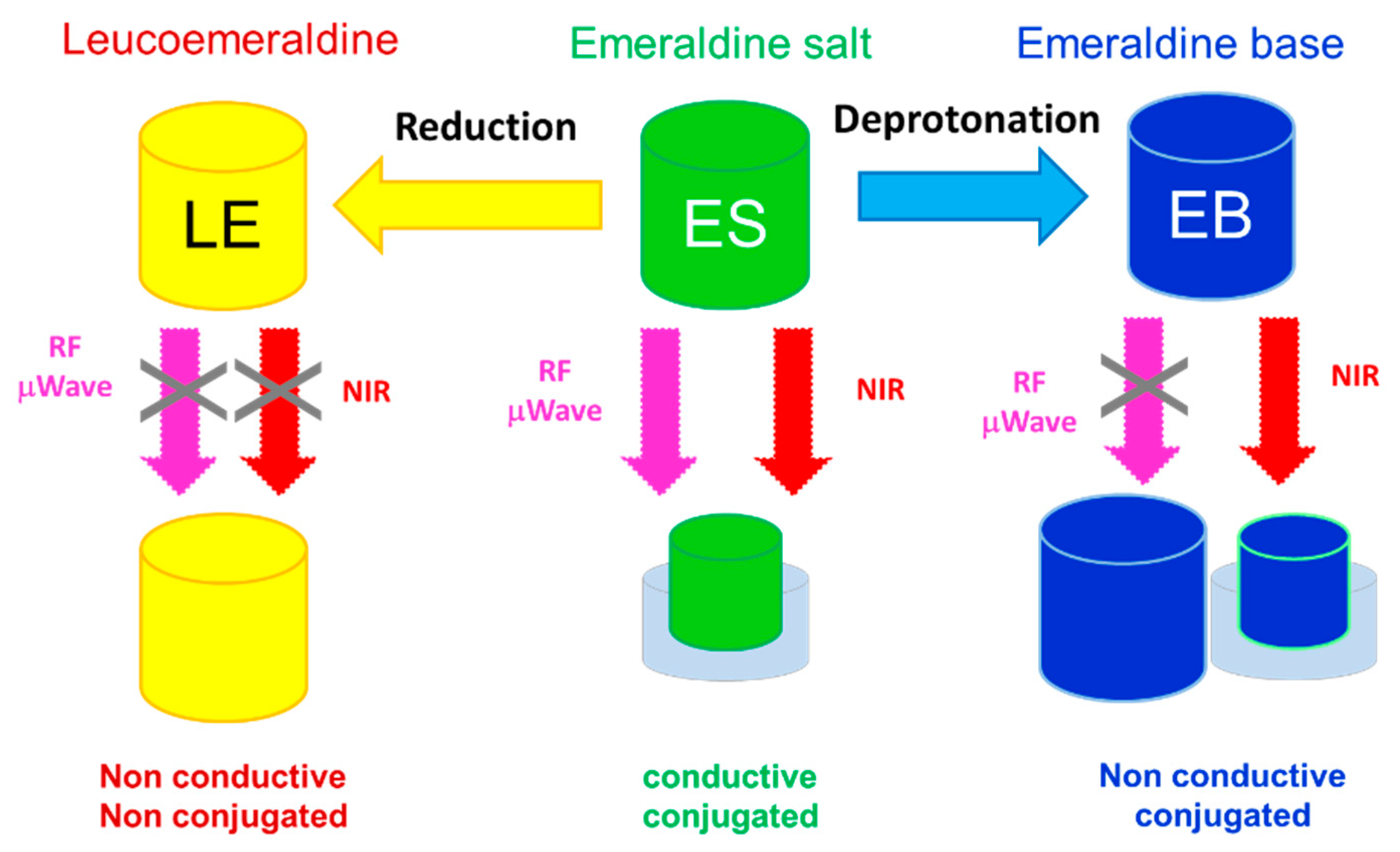
2.6. Modulating the Doping State of the Conducting Polymer
2.6.1. By Protonation/Deprotonation
2.6.2. By Oxidation/Reduction
2.7. Electromagnetic Radiation Form Used as Input
2.7.1. Microwave Irradiation
2.7.2. Near Infrared (NIR I) Light Irradiation
2.7.3. Radiofrequency Irradiation
2.7.4. Characterization
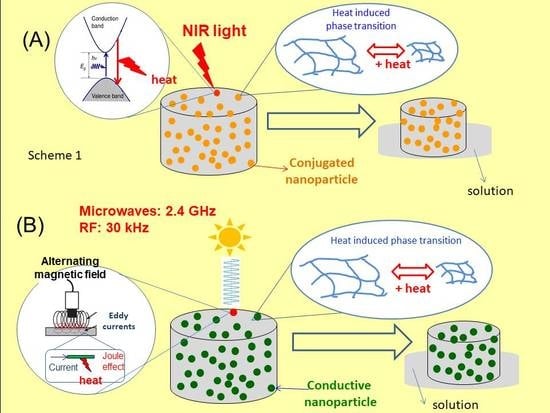
3. Results
3.1. Product Property of the Nanocomposites
3.1.1. Electromagnetic Radiation Absorption (ERA)
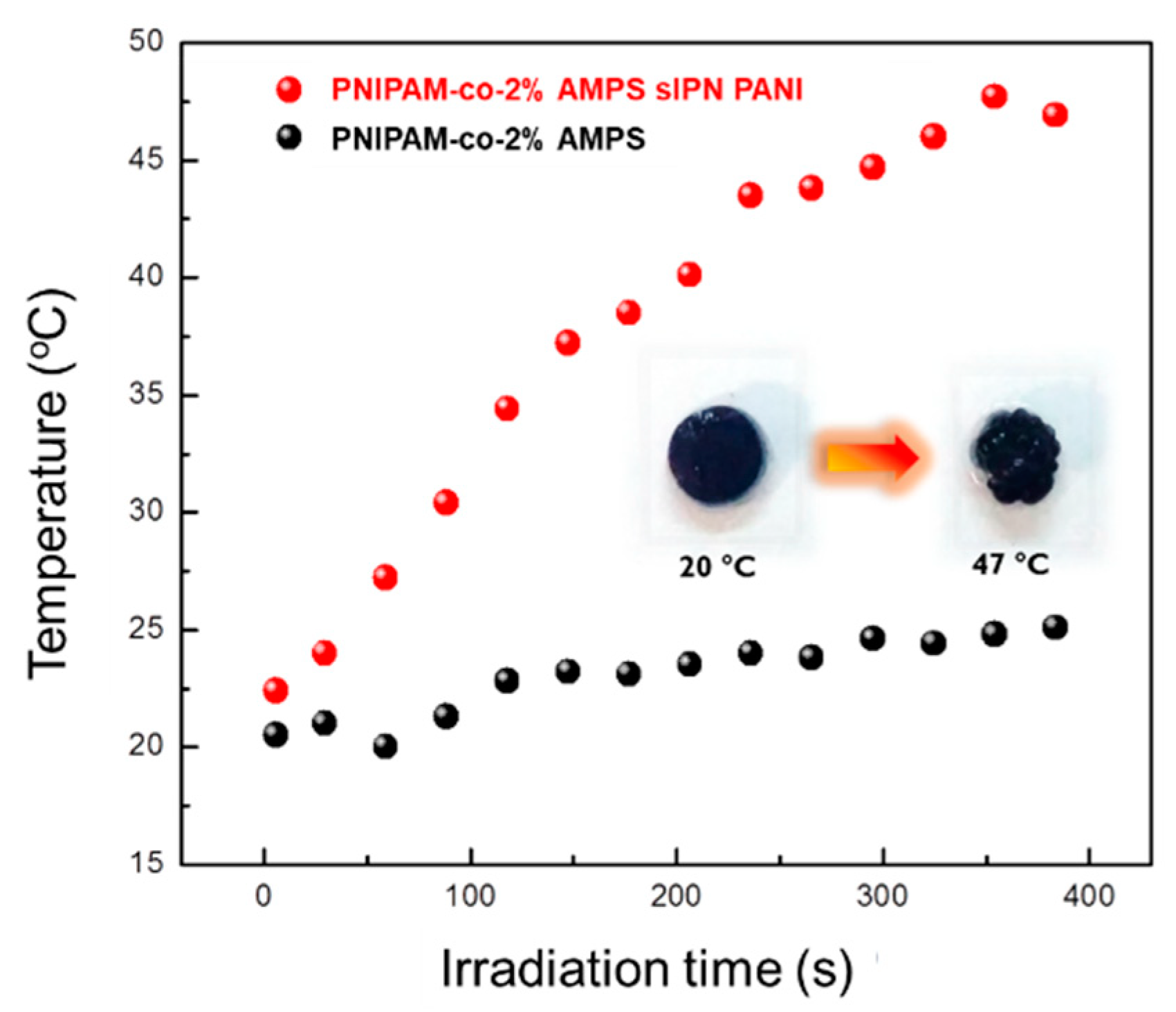
3.1.2. Heat-Induced Phase Transition (HIPT)
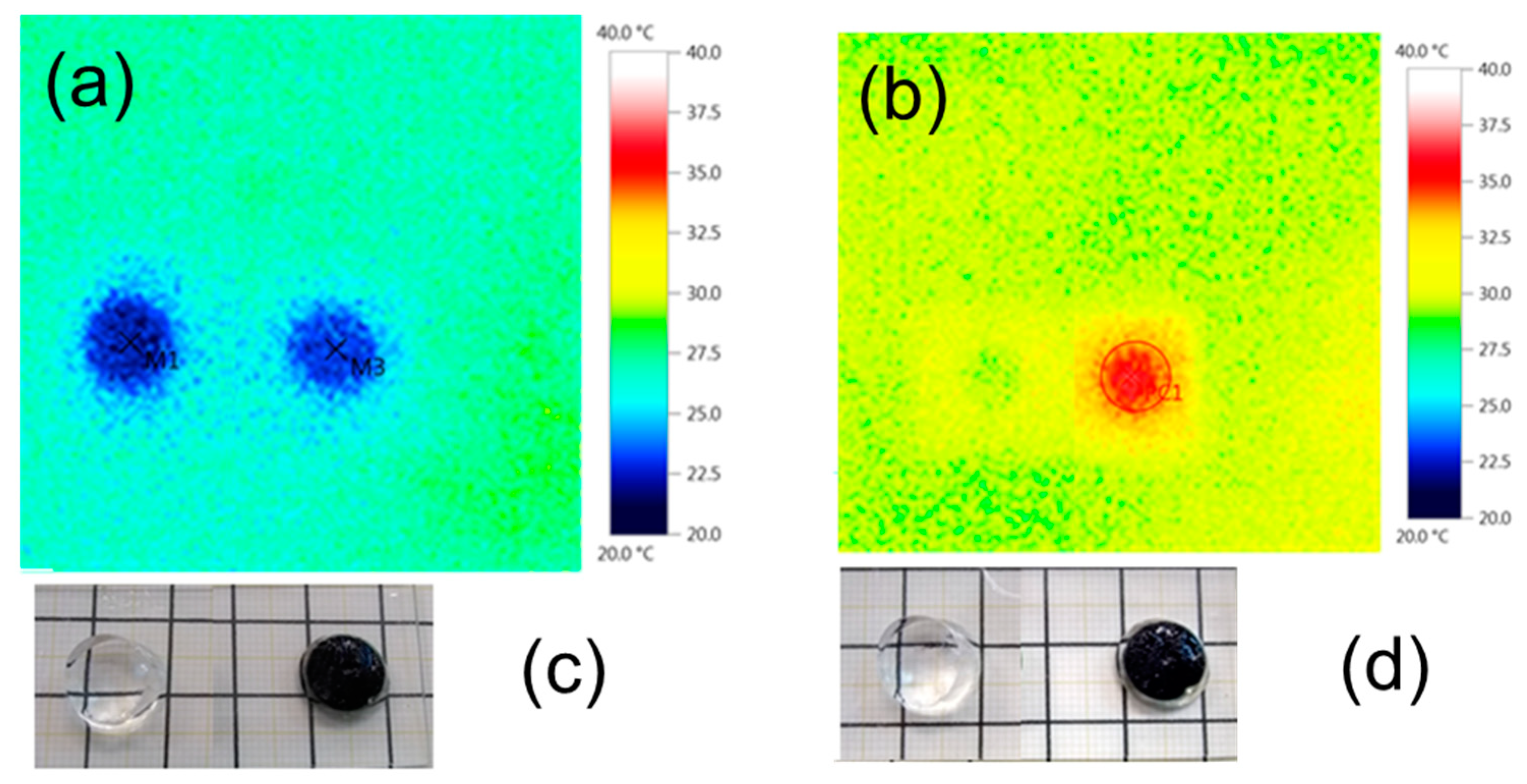
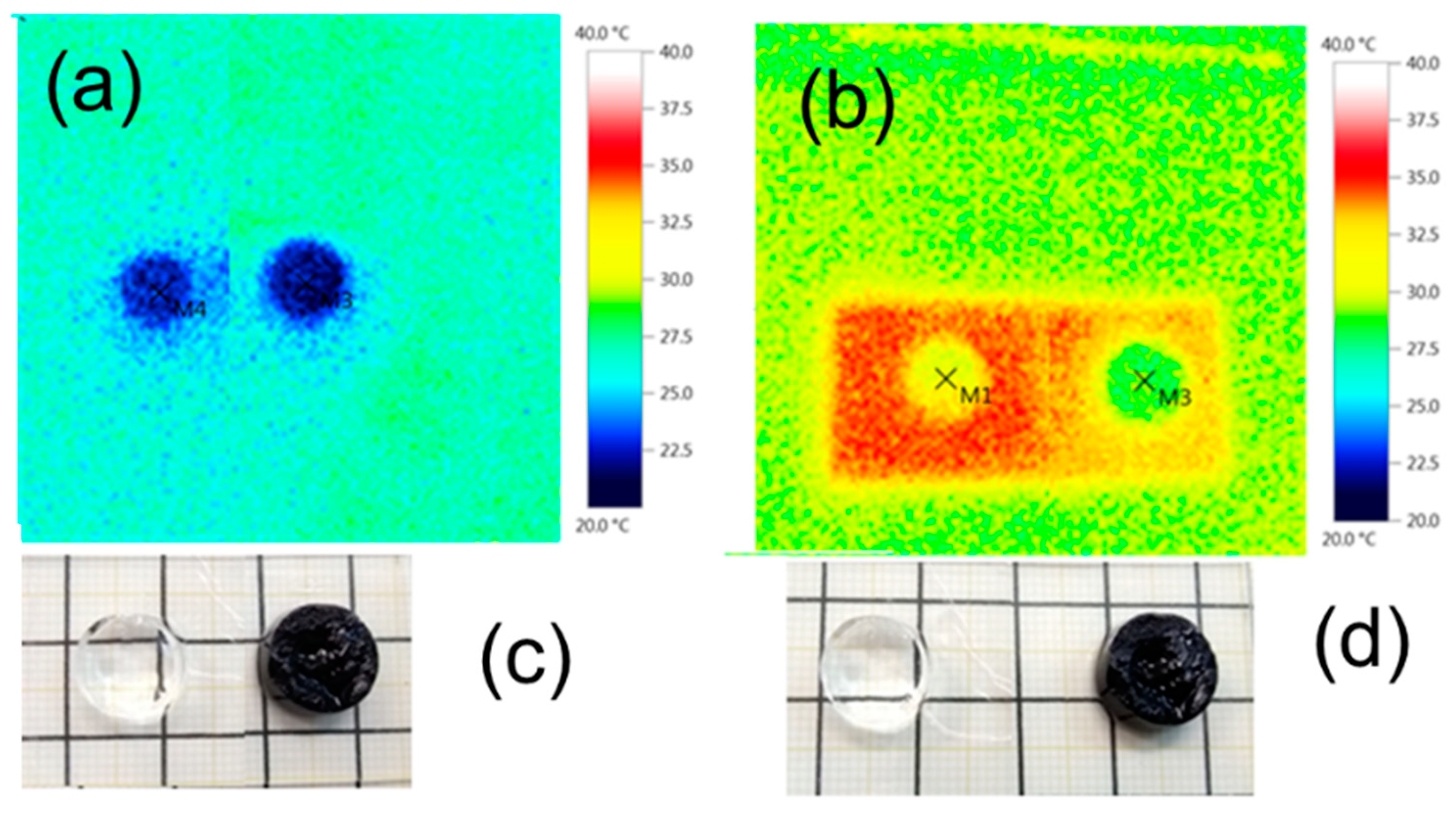
3.2. INH: Loading Preformed Conducting Polymer Nanoparticles inside Macroporous Hydrogels
3.3. GAN: In Situ Polymerization of the Smart Hydrogel Matrix around the Dispersion of Conductive Polymer Nanoparticles
3.4. PIH: In Situ Polymerization of the Conductive Polymer inside The Smart Hydrogel Matrix
3.4.1. Semi-Interpenetrated Network or Nanocomposite?
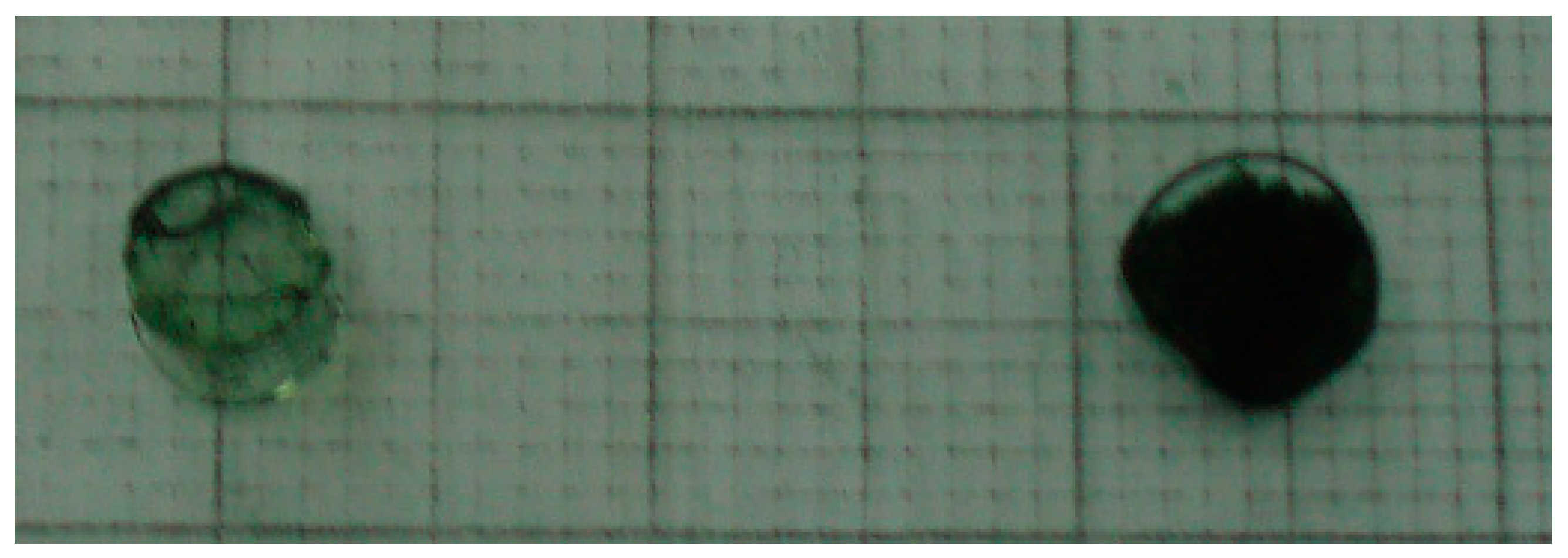
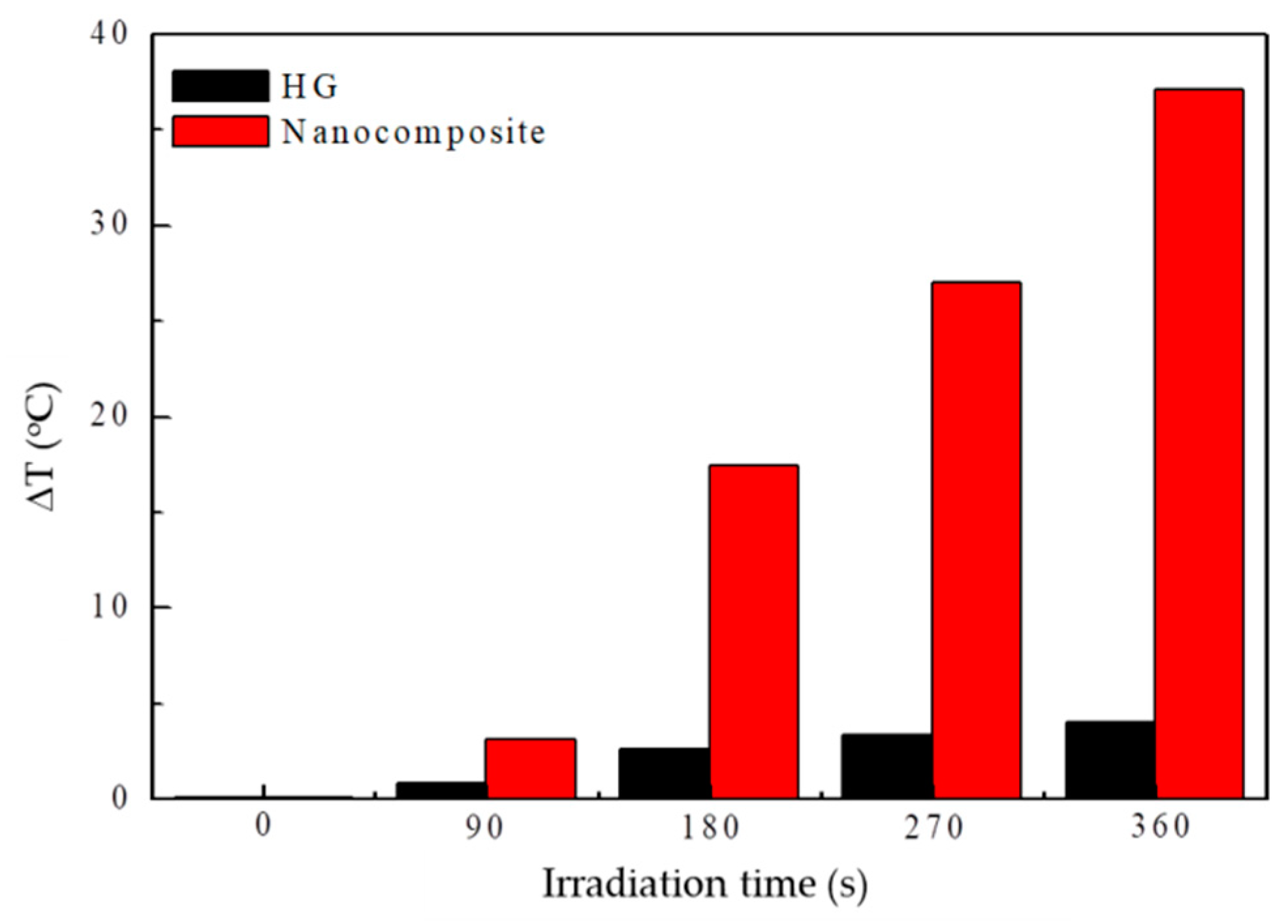
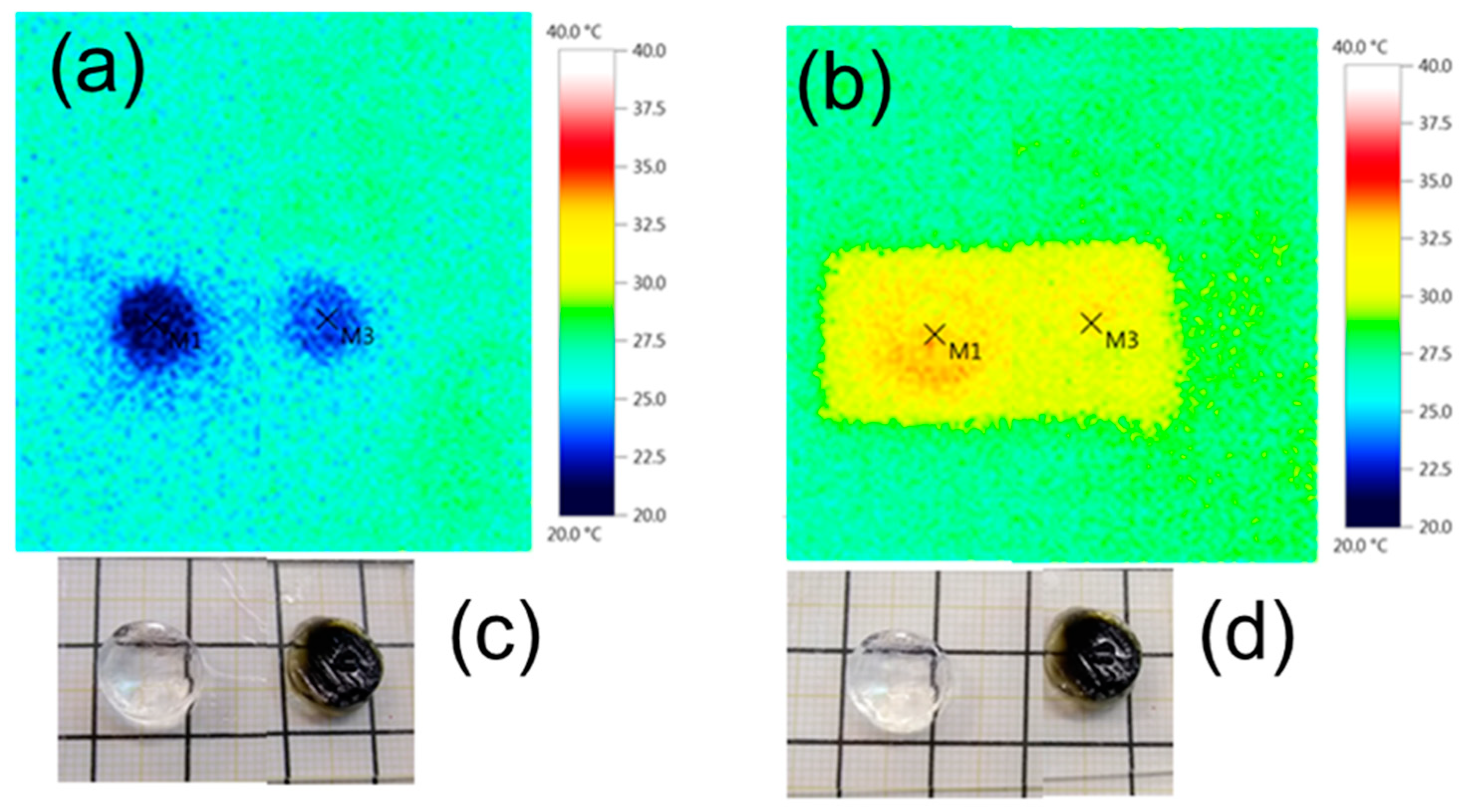
3.4.2. “Smart” Behavior: Effect of Electromagnetic Irradiation (microwaves) on the Conductive Nanocomposites
3.4.3. Effect of Electromagnetic Irradiation (Microwaves) on the Non-Conductive (Deprotonated) Nanocomposite
3.4.4. Effect of Electromagnetic Irradiation (Microwaves) on the Non-Conductive (Reduced) Nanocomposite
3.5. AMH: Loading Conducting Macromolecules inside the Smart Hydrogel Matrix
3.6. Comparison between Composite Materials Made Using Different Synthetic Methods
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbero, E.J. Introduction to Composite Materials Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, N.; Kurian, T.; Yu, Y.; Parameswaranpillai, J. Nanocomposite Materials: Synthesis, Properties and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barbero, E.J. (Ed.) Multifunctional Composites; CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform: Scottsdale Valley, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gurses, A. Introduction to Polymer-Clay Nanocomposites; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van Suchtelen, J. Product properties: A new application of composite materials. Philips Res. Rep. 1972, 27, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Zhou, S. Volume Phase Transition of Swollen Gels: Discontinuous or Continuous? Macromolecules 1997, 30, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischofberger, I.; Calzolari, D.C.E.; De Los Rios, P.; Jelezarov, I.; Trappe, V. Hydrophobic hydration of poly-N-isopropyl acrylamide: A matter of the mean energetic state of water. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umapathi, R.; Reddy, P.M.; Rani, A.; Venkatesu, P. Influence of additives on thermoresponsive polymers in aqueous media: A case study of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 9717–9744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, M.; Guo, M.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Lei, J.; Guo, C.; Qin, C. Agar/gelatin bilayer gel matrix fabricated by simple thermo-responsive sol-gel transition method. Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2017, 77, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shao, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Gold nanorods and their plasmonic properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2679–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. A near-infrared light-responsive hybrid hydrogel based on UCST triblock copolymer and gold nanorods. Polymers 2017, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehl, C.L.; Grady, N.K.; Goodrich, G.P.; Tam, F.; Halas, N.J.; Hafner, J.H. Scattering Spectra of Single Gold Nanoshells. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 122355–122359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messersmith, R.E.; Nusz, G.J.; Reed, S.M. Using the localized surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles to monitor lipid membrane assembly and protein binding. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 26725–26733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yamauchi, Y.; Araoka, F.; Kim, Y.S.; Bergueiro, J.; Ishida, Y.; Ebina, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Hikima, T.; Aida, T. An Anisotropic Hydrogel Actuator Enabling Earthworm-Like Directed Peristaltic Crawling. Angew. Chem. 2018, 57, 15772–15776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lin, X.; Zou, X.; Sun, J.; He, Q. Biodegradable protein-based rockets for drug transportation and light-triggered release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, R.; Larrea, A.; Sebastian, M.S.; Sebastian, V.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Synthesis and size dependent magnetostrictive response of ferrite nanoparticles and their application in magnetoelectric polymer-based multiferroic sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 10701–10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.; Yoon, J. Photothermally driven fast responding photo-actuators fabricated with comb-type hydrogels and magnetite nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, K.; Wu, W.; Xia, M.; Zhu, M. A novel NIR laser switched nanocomposite hydrogel as remote stimuli smart valve. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Kajiura, H.; Maruyama, R.; Kadono, K.; Noda, K. Relative optical absorption of metallic and semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4686–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Ji, Y.; Jiao, X.; Chen, Q.; Hou, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Near-infrared-triggered in situ hybrid hydrogel system for synergistic cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6310–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, E.; Lee, H.S.; Yoon, J. Energy efficient glazing for adaptive solar control fabricated with photothermotropic hydrogels containing graphene oxide. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Du, P.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Peng, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X. Near-infrared responsive MoS2/Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels for remote light-controlled microvalves. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4526–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, P. Simultaneous exfoliation and functionalization of MoSe2 nanosheets to prepare “Smart” nanocomposite hydrogels with tunable dual stimuli-responsive behavior. Small 2016, 12, 3112–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Deng, L.; Ouyang, J.; Wen, M.; Zeng, K.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.-N. A NIR-II light responsive hydrogel based on 2D engineered tungsten nitride nanosheets for multimode chemo/photothermal therapy. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 9471–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Ling, G.; Peng, F.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, S.; He, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, P. Black phosphorus nanosheets and gemcitabine encapsulated thermo-sensitive hydrogel for synergistic photothermal-chemotherapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 232–238. [Google Scholar]
- Fabian, J.; Nakazumi, H.; Matsuoka, M. Near-infrared absorbing dyes. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92, 1197–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, P.T.M.; Jhon, H.; In, I.; Park, S.Y. Photothermal-modulated reversible volume transition of wireless hydrogels embedded with redox-responsive carbon dots. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 4800–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robby, A.I.; Lee, G.; Park, S.Y. NIR-induced pH-reversible self-healing monitoring with smartphone by wireless hydrogel sensor. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 297, 126783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fu, L.; Ai, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J. Design and fabrication of temperature-sensitive nanogels with controlled drug release properties for enhanced photothermal sterilization. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 18180–18186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ruan, C.; Shi, R.; Jiang, B.-P.; Ji, S.; Shen, X.-C. A near infrared-modulated thermosensitive hydrogel for stabilization of indocyanine green and combinatorial anticancer phototherapy. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.-W.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.-J.; Wang, W.; Chen, Q.; Chu, L.-Y. Nano-structured smart hydrogels with rapid response and high elasticity. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Choi, J.; Bang, D.; Kim, E.; Lim, E.-K.; Park, H.; Suh, J.-S.; Lee, K.; Yoo, K.-H.; Kim, E.-K.; et al. Convertible organic nanoparticles for near-infrared photothermalablation of cancer cells angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdebenito, A.; Encinas, M.V. Thiophenols as chain transfer agents in the polymerization of vinyl monomers. Polymer 2005, 46, 10658–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Riberi, K.; Rivarola, C.R.; Molina, M.; Barbero, C.A. Synthesis of a smart conductive block copolymer responsive to heat and near infrared light. Polymers 2019, 1, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Sapurina, I. Polyaniline: Thin films and colloidal dispersions (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2005, 77, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kaner, R.B. A general chemical route to polyaniline nanofibers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.-Y.; Jung, W.-G.; Ihm, D.-W.; Kim, J.-Y. Synthesis and dispersion of polypyrrole nanoparticles in polyvinylpyrrolidone emulsion. Synth. Met. 2010, 160, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashkatov, A.N.; Genina, E.A.; Kochubey, V.I.; Tuchin, V.V. Optical properties of human skin, subcutaneous and mucous tissues in the wavelength range from 400 to 2000 nm. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Huang, Y. Usage of conductive polymer composite as the object film of eddy current gap sensor. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 3202–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsman, A.W.; Hart, C.M.; Gelinck, G.H.; Geuns, T.C.T.; de Leeuw, D.M. Doped polyaniline polymer fuses: Electrically programmable read-only-memory elements. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 2057–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pei, Q.; Qian, E. Protonation and deprotonation of polypyrrole chain in aqueous solutions. Synth. Met. 1991, 45, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Wu, P. A infrared spectroscopic study on the mechanism of temperature-induced phase transition of concentrated aqueous solutions of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) and N-isopropylpropionamide. Polymer 2010, 51, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Park, H.-K.; Park, H.; Lee, S.-H. Snapshot of phase transition in thermoresponsive hydrogel PNIPAM: Role in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Macromol. Res. 2016, 24, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.B.; Molina, M.A.; Rivarola, C.R.; Kogan, M.J.; Barbero, C.A. Smart polyaniline nanoparticles with thermal and photothermal sensitivity. Nanotechnology. 2014, 25, 495602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mishra, R.; Reinwald, Y.; Bhat, S. Cryogels: Freezing unveiled by thawing. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.A.; Rivarola, C.R.; Miras, M.C.; Lescano, D.; Barbero, C.A. Nanocomposite synthesis by absorption of nanoparticles into macroporous hydrogels. Building a chemomechanical actuator driven by electromagnetic radiation. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Molina, M.; Rivarola, C.R.; Barbero, C.A. A novel method to generate nanocomposites containing polypyrrole or polyaniline nanoparticles dispersed in a thermosensitive hydrogel matrix. Evidence of photothermal collapse under radiofrequency or microwave irradiation. Polym. Chem. 2019. in review. [Google Scholar]
- Lira, L.M.; Córdoba de Torresi, S.I. Conducting polymer–hydrogel composites for electrochemical release devices: Synthesis and characterization of semi-interpenetrating polyaniline–polyacrylamide networks. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddhanta, S.K.; Gangopadhyay, R. Conducting polymer gel: Formation of a novel semi-IPN from polyaniline and crosslinked poly (2-acrylamido-2-methyl propanesulphonicacid). Polymer 2005, 46, 2993–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.A.; Rivarola, C.R.; Barbero, C.A. Study on partition and release of molecules in superabsorbent thermosensitive nanocomposites. Polymer 2012, 53, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbil, C.; Saraç, A.S. Description of the turbidity measurements near the phase transition temperature of poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide) copolymers: The effect of pH, concentration, hydrophilic and hydrophobic content on the turbidity. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stile, R.A.; Healy, K.E. Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Semi-interpenetrating Polymer Networks for Tissue Engineering Applications. 1. Effects of Linear Poly (acrylic acid) Chains on Phase Behavior. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Yu, G.; Zhai, D.; Lee, H.R.; Zhao, W.; Liu, N.; Wang, H.; Tee, B.C.K.; Shi, Y.; Cui, Y.; et al. Hierarchical nanostructured conducting polymer hydrogel with high electrochemical activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 10, 9287–9292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ma, C.; Peng, L.; Yu, G. Conductive “Smart” Hybrid Hydrogels with PNIPAM and Nanostructured Conductive Polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; MacDiarmid, A.G. Optical properties of polyaniline. Polymer 1993, 34, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zhao, J.X.; Wu, C.X. Polyacrylamide hydrogels with trapped sulfonated polyaniline. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.V.; Molina, M.; Barbero, C.A. Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) Crosslinked Gels as Intrinsic Amphiphilic Materials. Swelling Properties Used to Build Novel Interphases. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 9038–9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzalaco, S.; Armelin, E. Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) and Copolymers: A Review on Recent Progresses in Biomedical Applications. Gels 2017, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.V.; Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Rivero, R.; Miras, M.C.; Rivarola, C.R.; Barbero, C.A. Polymeric nanocomposites made of a conductive polymer and a thermosensitive hydrogel: Strong effect of the preparation procedure on the properties. Polymer 2015, 78, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reghu, M.; Cao, Y.; Moses, D.; Heeger, A.J. Counterion-induced processibility of polyaniline: Transport at the metal-insulator boundary. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.V.; Molina, M.A.; Abel, S.B.; Barbero, C.A. Large Swelling Capacities of Crosslinked Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) Gels in Organic Solvents. MRS Adv. 2018, 3, 3735–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, D.; Guo, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Yu, J.; et al. Thickness-Gradient Films for High Gauge Factor Stretchable Strain Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6230–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.; Asadian-Birjand, M.; Balach, J.; Bergueiro, J.; Miceli, E.; Calderon, M. Stimuli-responsive nanogel composites and their application in nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6161–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, R.E.; Alustiza, F.; Rodríguez, N.; Bosch, P.; Miras, M.C.; Rivarola, C.R.; Barbero, C.A. Effect of functional groups on physicochemical and mechanical behavior of biocompatible macroporous hydrogels. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 97, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Kurokawa, T.; Gong, J.P. Super tough double network hydrogels and their application as biomaterials. Polymer 2012, 53, 1805–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Synthetic Method | State of Polyaniline (PANI) | Electromagnetic Radiation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Near Infrared Light (NIR I) (3 W, 850 nm) | Microwaves (70 W, 2.4 GHz) | Radiofrequency (RF) (1000 W, 30 kHz) | ||
| INH * | Protonated | ON | ON | ON |
| GAN # | Protonated | OFF | ON | ON |
| PIH * | Protonated | ON | ON | ON |
| PIH * | Deprotonated | ON | OFF | OFF |
| PIH * | Reduced | OFF | OFF | OFF |
| AMH * | Protonated | ON | ON | ON |
| Synthetic Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| INH |
|
|
| GAN |
|
|
| PIH |
|
|
| AMH |
|
|
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riberi, K.; Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Martinez, M.V.; Molina, M.A.; Rivarola, C.R.; Acevedo, D.F.; Rivero, R.; Cuello, E.A.; Gramaglia, R.; Barbero, C.A. Smart Thermomechanochemical Composite Materials Driven by Different Forms of Electromagnetic Radiation. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4010003
Riberi K, Bongiovanni Abel S, Martinez MV, Molina MA, Rivarola CR, Acevedo DF, Rivero R, Cuello EA, Gramaglia R, Barbero CA. Smart Thermomechanochemical Composite Materials Driven by Different Forms of Electromagnetic Radiation. Journal of Composites Science. 2020; 4(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiberi, Kevin, Silvestre Bongiovanni Abel, María V. Martinez, María A. Molina, Claudia R. Rivarola, Diego F. Acevedo, Rebeca Rivero, Emma Antonia Cuello, Romina Gramaglia, and Cesar A. Barbero. 2020. "Smart Thermomechanochemical Composite Materials Driven by Different Forms of Electromagnetic Radiation" Journal of Composites Science 4, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4010003
APA StyleRiberi, K., Bongiovanni Abel, S., Martinez, M. V., Molina, M. A., Rivarola, C. R., Acevedo, D. F., Rivero, R., Cuello, E. A., Gramaglia, R., & Barbero, C. A. (2020). Smart Thermomechanochemical Composite Materials Driven by Different Forms of Electromagnetic Radiation. Journal of Composites Science, 4(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4010003