The Magneto-Mechanical Behavior of Active Components in Iron-Elastomer Composite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results
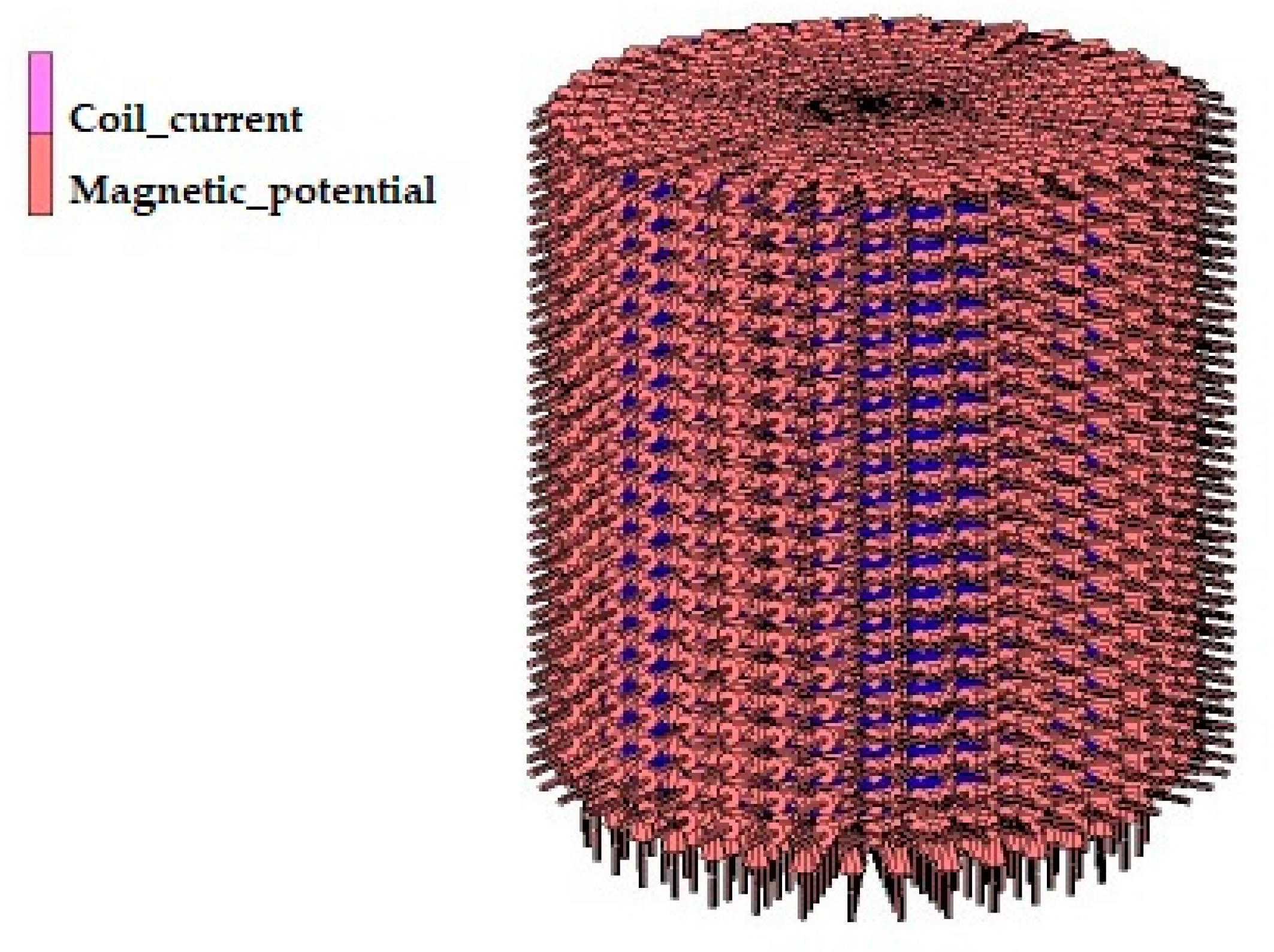
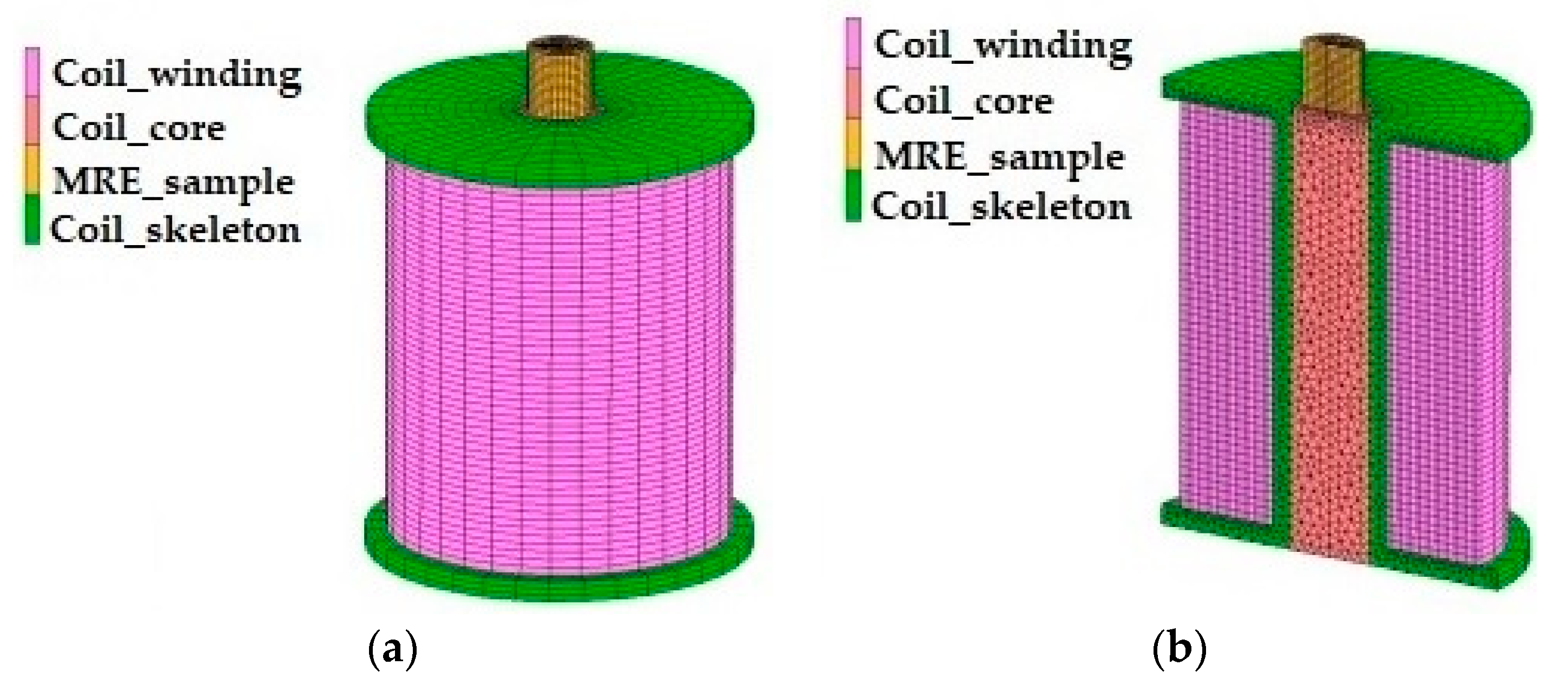
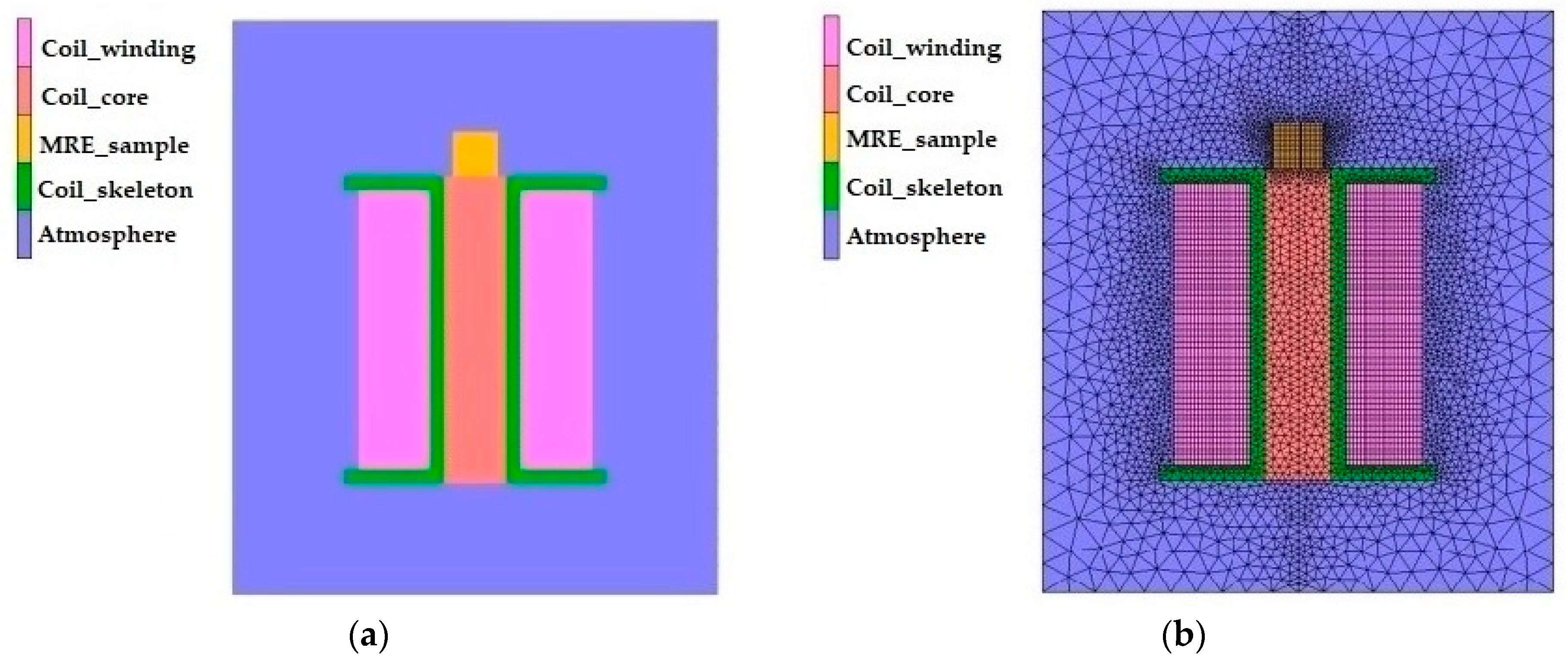
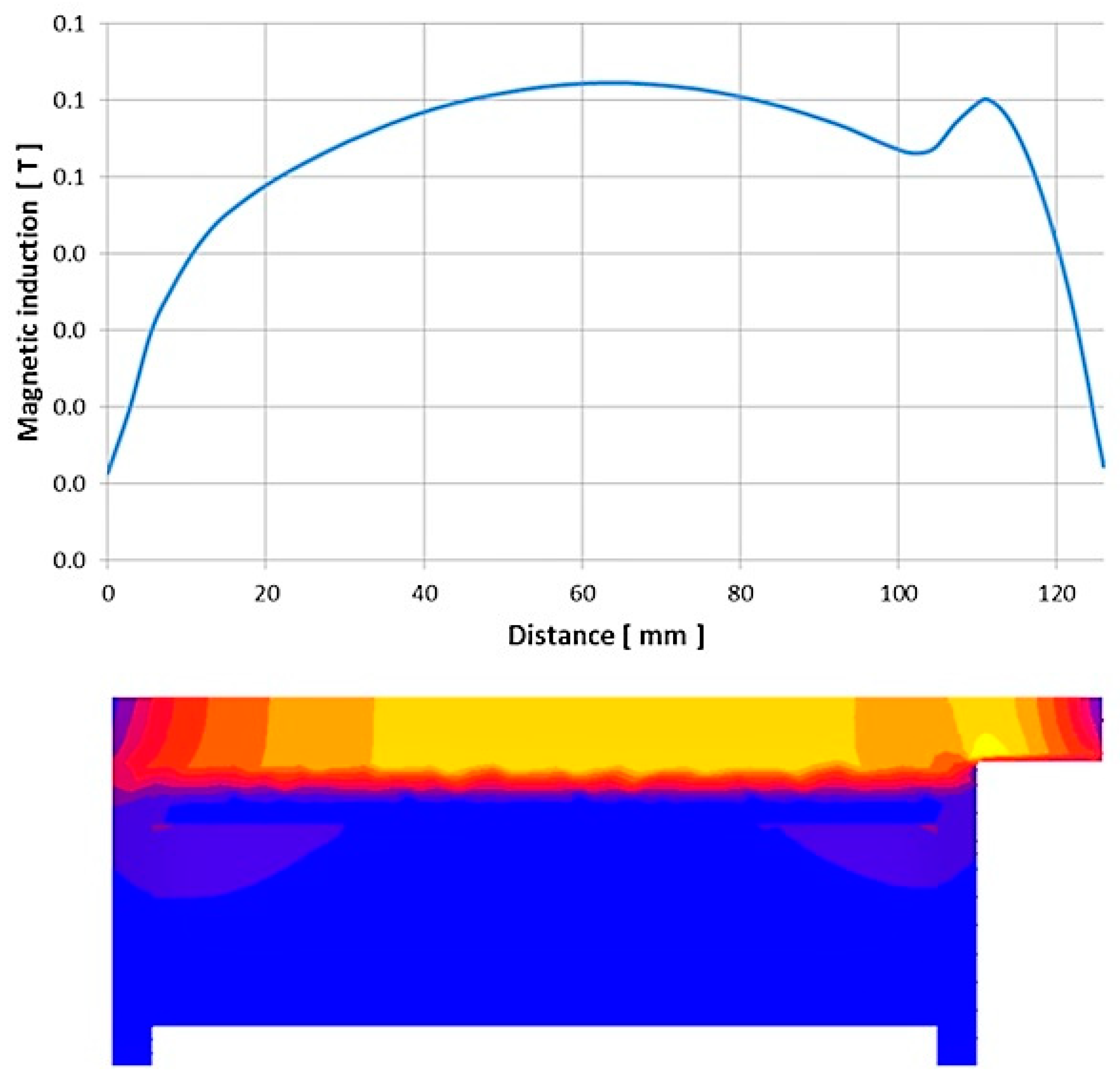
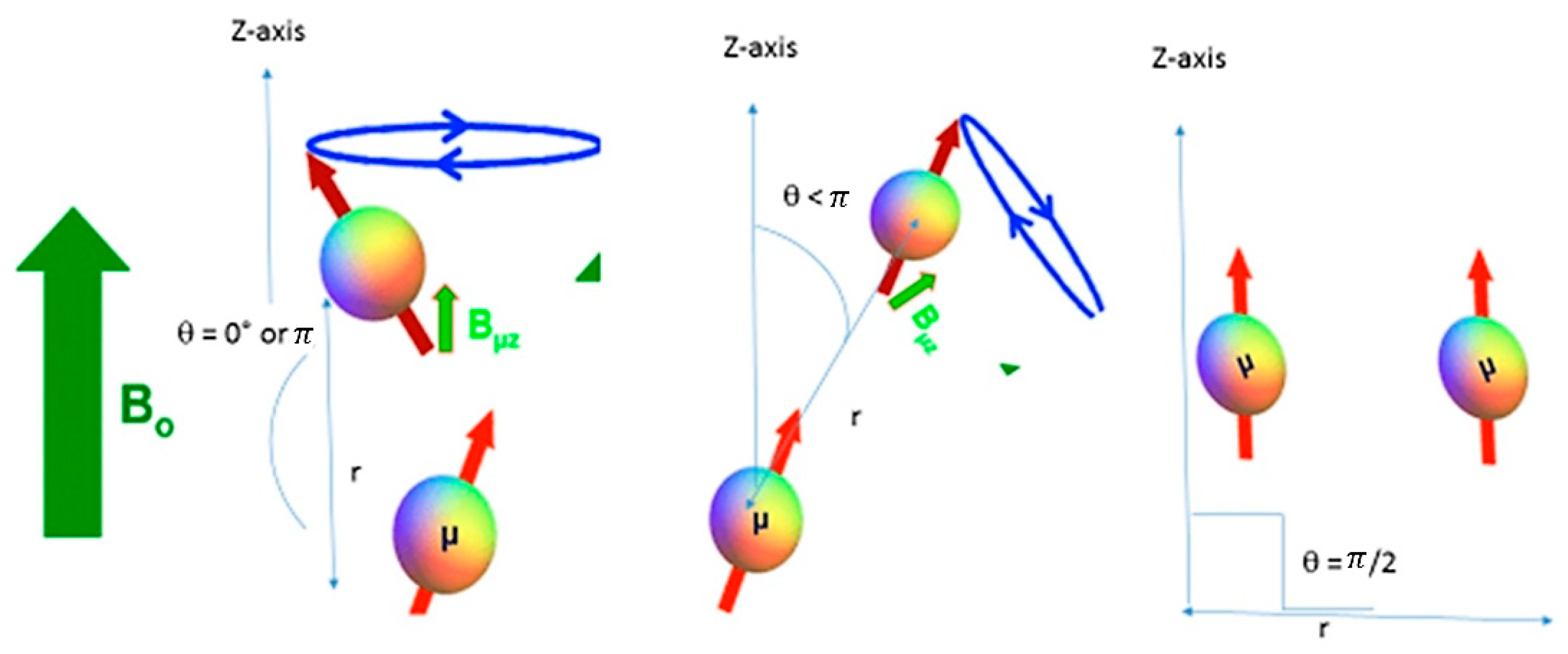
3.1. Simulation Behavior of the Magnet and MRE Samples
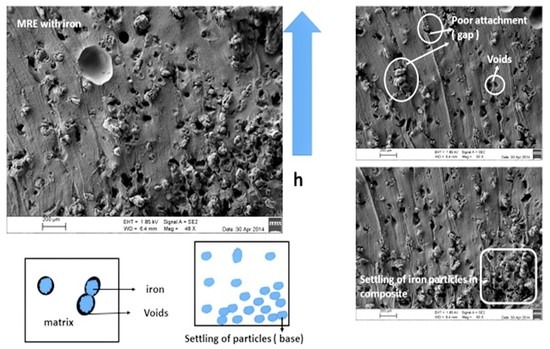
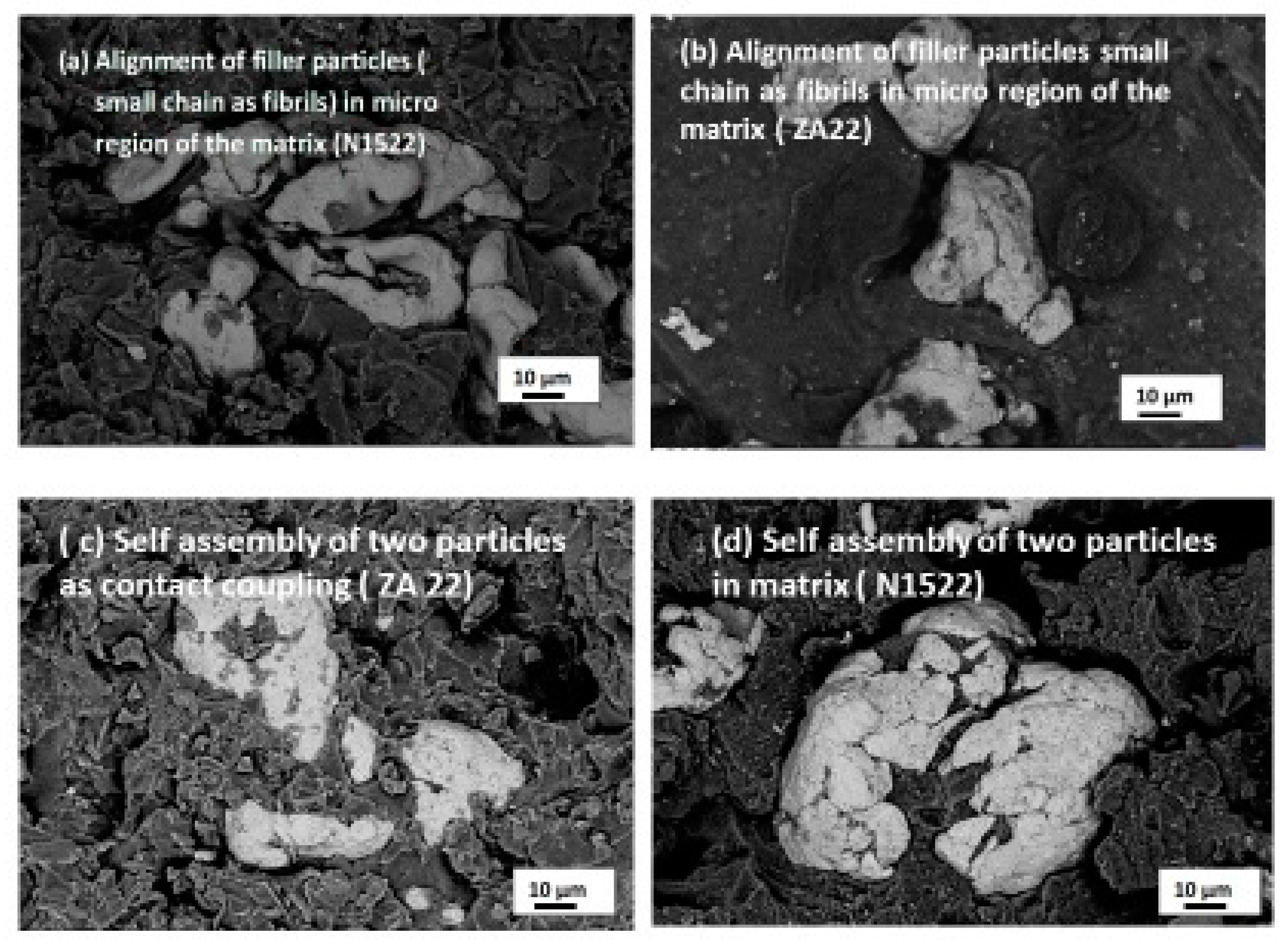
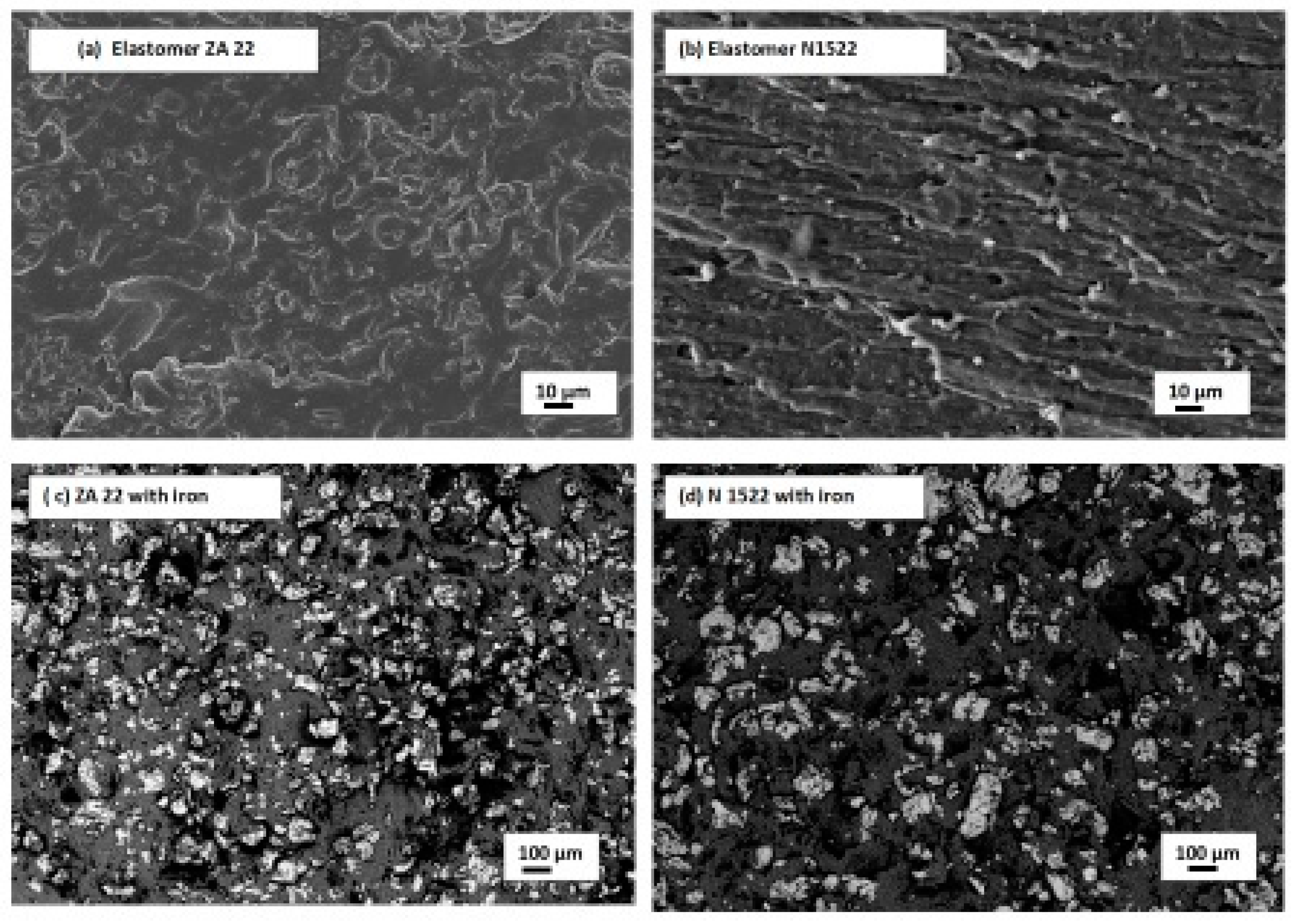
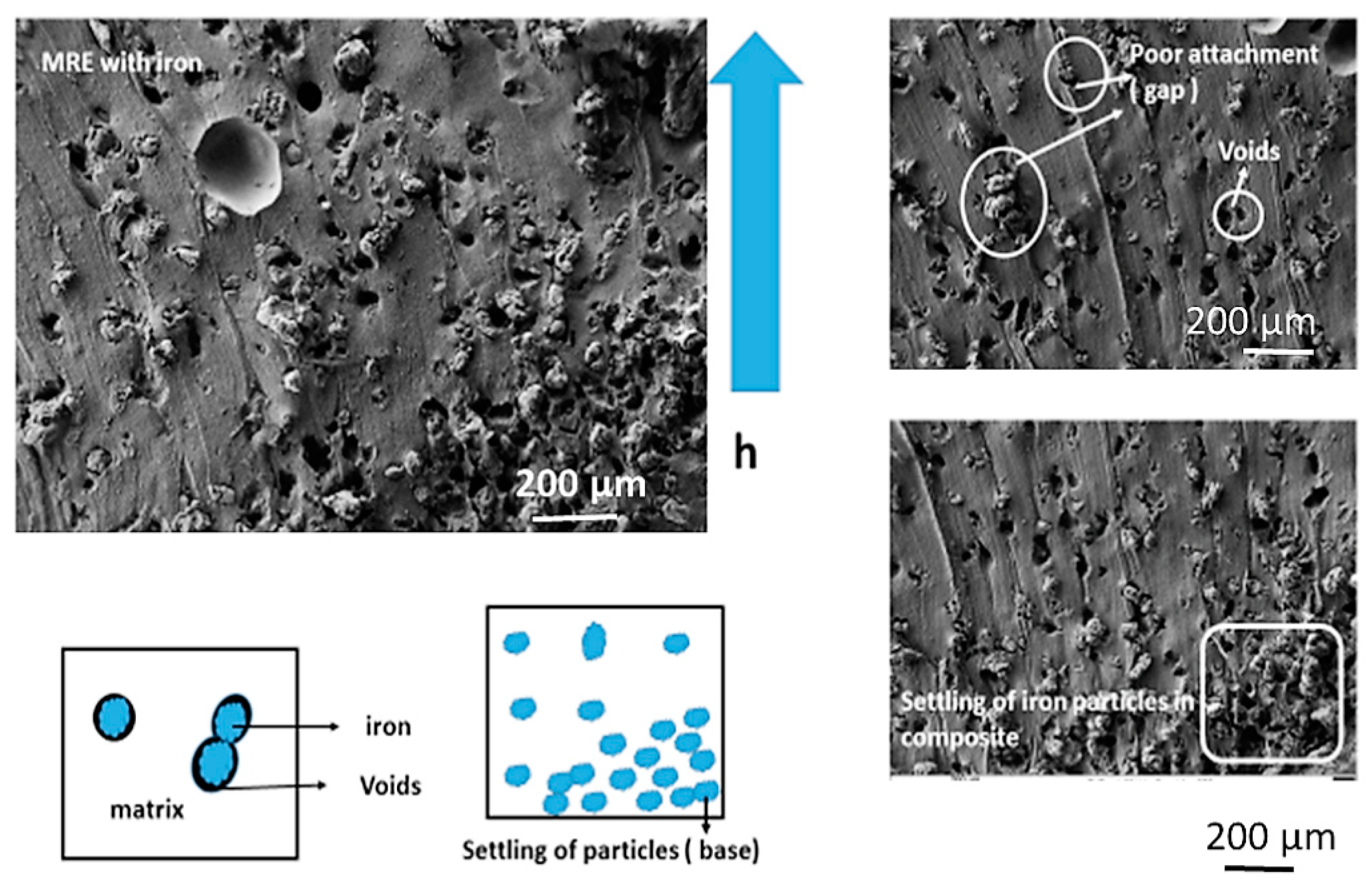
3.2. Microstructural Observation of MRE Composite
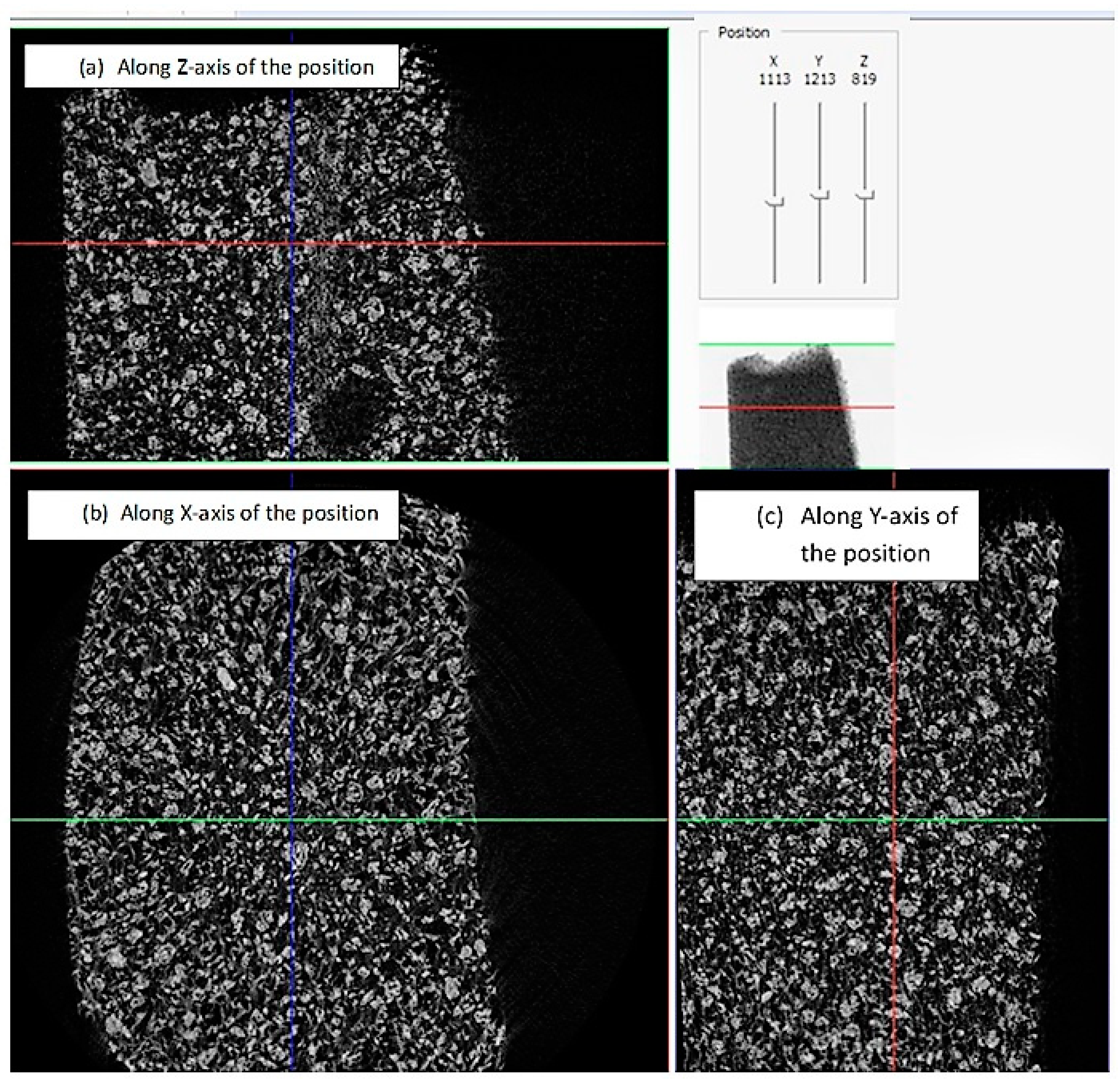
3.3. Micro Computed Tomography of MRE
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samal, S.; Vlacha, J.; Kavana, P. Improved mechanical properties of magneto rheological elastomeric composite with isotropic iron filler distribution. Ciênc. Tecnol. Mater. 2016, 28, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.D.; Jolly, M.R. MR fluid, foam and elastomer devices. Mechatronics 2000, 10, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginder, J.M.; Nichols, M.E.; Elie, L.D.; Tardiff, J.L. Magnetorheological elastomers: Properties and applications. In Proceedings of the 1999 Symposium on Smart Structures and Materials, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 1 March 1999; pp. 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Gong, X.L.; Gong, X.Q.; Zhang, X.Z.; Jiang, W.Q.; Zhang, P.Q.; Chen, Z.Y. New magnetorheological elastomers based on polyurethane/Si-rubber hybrid. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, M.R.; Carlson, J.D.; Munoz, B.C.; Bullions, T.A. The magnetoviscoelastic effect of elastomer composites consisting of ferrous particles embedded in a polymer matrix. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1996, 7, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasoiu, M.; Bica, I. Composite magnetorheological elastomers as dielectrics for plane capacitors: Effects of magnetic field intensity. Results Phys. 2016, 6, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.; Anitas, E.M.; Averis, L.M.E. Tensions and deformations in composites based on polyurethane elastomer and magnetorheological suspension: Effects of the magnetic field. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 28, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunoiu, M.; Bica, I. Magnetorheological elastomer based on silicone rubber, carbonyl iron and Rochelle salt: Effects of alternating electric and static magnetic fields intensities. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 37, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiga, T.; Okada, A.; Kurauchi, T. Magnetroviscoelastic behavior of composite gels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1995, 58, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, G.V.; Borin, D.Y.; Raikher, L.Y.; Melenev, P.V.; Perov, N.S. Motion of ferroparticles inside the polymeric matrix in magnetoactive elastomers. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 204121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petríková, I.; Marvalová, B. Experimental research and numerical simulation of the damping properties of Magnetorheological Elastomers. In Constitutive Models for Rubber X; Lion, A., Johlitz, M., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Samal, S.; Vlach, J.; Kolinova, M.; Kavan, P. Micro-computed tomography characterization of isotropic filler distribution in magnetorheological elastomeric composites. In Advanced Processing and Manufacturing Technologies for Nanostructured and Multifunctional Materials; Ohji, T., Singh, M., Halbig, M., Moon, K., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Ju, B.; Fu, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q. Influence of composition of carbonyl iron particles on dynamic mechanical properties of magnetorheological elastomers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokander, M.; Stenberg, B. Improving the magnetorheological effect in isotropic magnetorheological rubber materials. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.V.; Ecker, E.; Stepanov, G.V.; Shamonin, M.; Monkman, G.J.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlovad, E.A.R. Experimental study of the magnetic field enhanced Payne effect in magnetorheological elastomers. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 8765–8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molchanov, V.; Stepanov, G.; Vasiliev, V.; Kramarenko, E.; Khokhlov, A.; Xu, Z.-D.; Guo, Y.-Q. Viscoelastic properties of magnetorheological elastomers for damping applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaneyko, D.; Toshchevikov, V.; Saphiannikova, M.; Heinrich, G. Mechanical properties of magneto-sensitive elastomers: Unification of the continuum-mechanics and microscopic theoretical approaches. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, T.; Chagnon, G.; Le Cam, J.-B.; Favier, D. Effects of Temperature on the Mechanical Behavior of Filled and Unfilled Silicone Rubbers. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00936536 (accessed on 11 January 2014).
- Taniguchi, T.; Mitsumata, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Koyama, K. Anisotropy in elastic modulus of hydrogel containing magnetic particles. Physica A 2006, 370, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Lu, X.; Gong, X.; Yang, T.; Sun, K.; Chen, X. Effect of carbonyl iron concentration and processing conditions on the structure and properties of the thermoplastic magnetorheological elastomer composites based on poly(styrene-b-ethylene-co-butylene-b-styrene) (SEBS). Polym. Test. 2015, 47, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.V.; Stepanov, G.V.; Shamonin, M.; Monkman, G.J.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Hysteresis of the viscoelastic properties and the normal force in magnetically and mechanically soft magnetoactive elastomers: Effects of filler composition, strain amplitude and magnetic field. Polymer 2015, 76, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, L.; Gong, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Z. Effects of rubber/magnetic particle interactions on the performance of magnetorheological elastomers. Polym. Test. 2006, 25, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Qiao, X.; Watanabe, H.; Gong, X.; Yang, T.; Li, W.; Sun, K.; Li, M.; Yang, K.; Xie, H.; et al. Mechanical and structural investigation of isotropic and anisotropic thermoplastic magnetorheological elastomer composites based on poly(styrene-b-ethylene-co-butylene-b-styrene) (SEBS). Rheol. Acta 2012, 51, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, P.; Hossain, M.; Steinmann, P. A theory of finite deformation magneto-viscoelasticity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 3886–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, P.; Hossain, M.; Steinmann, P. Non-linear magneto-viscoelasticity of transversally isotropic magneto-active polymers. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 2014, 470, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, P.; Pelteret, J.P.; Steinmann, P. Modelling of iron-filled magneto-active polymers with a dispersed chain-like microstructure. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2015, 50, 132–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, M.; Hossain, M.; Steinmann, P. Towards a thermo-magneto-mechanical framework for magneto-rheological elastomers. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2017, 128, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

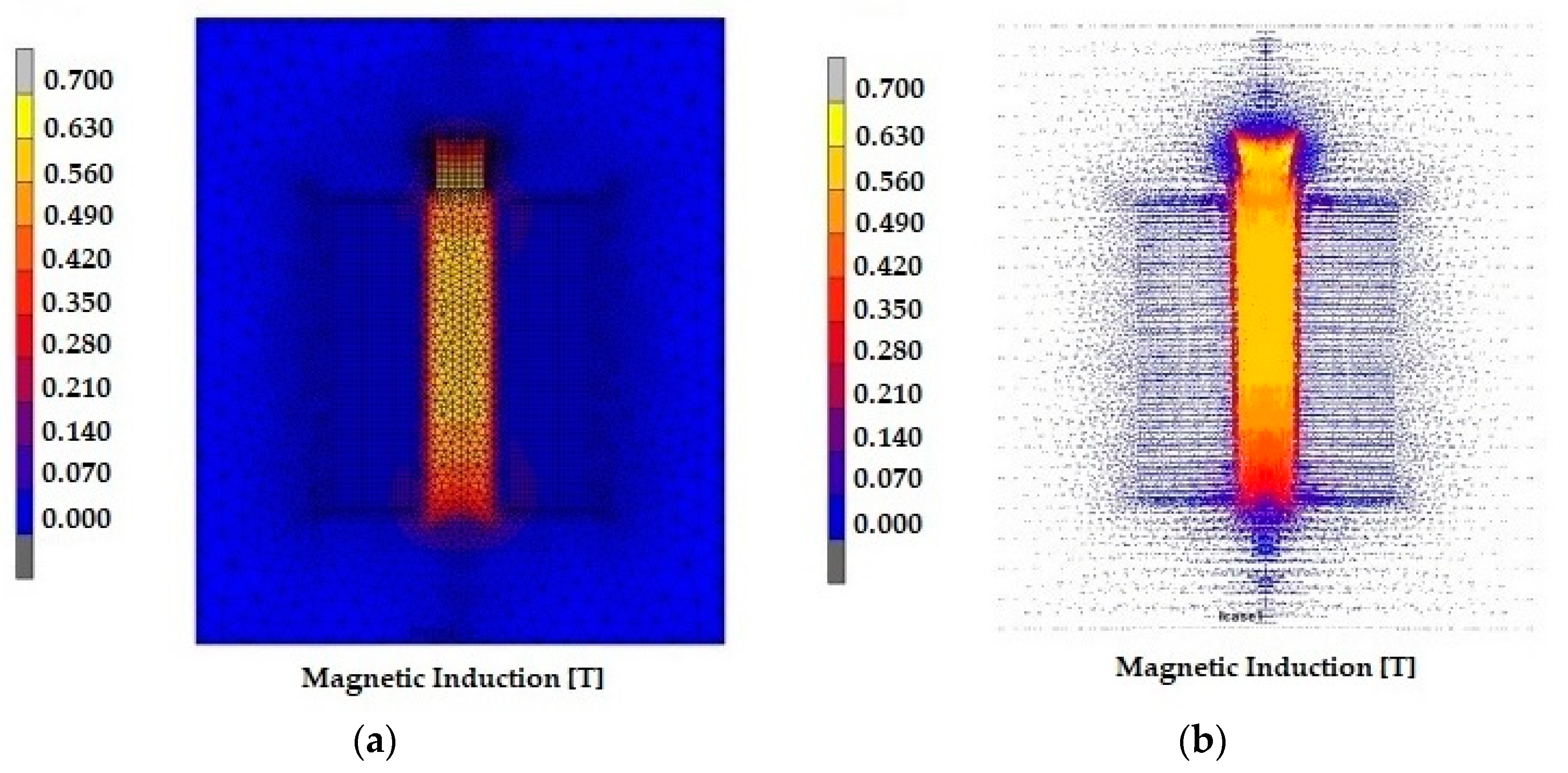
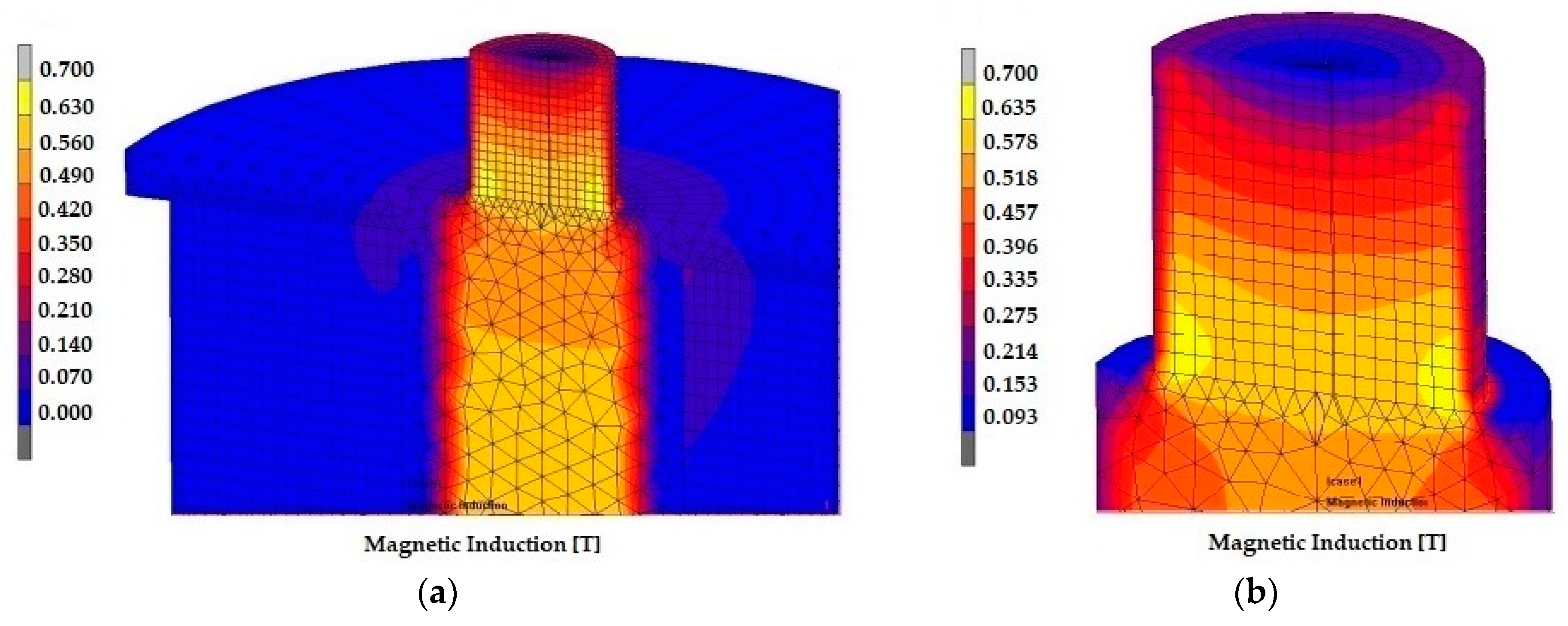
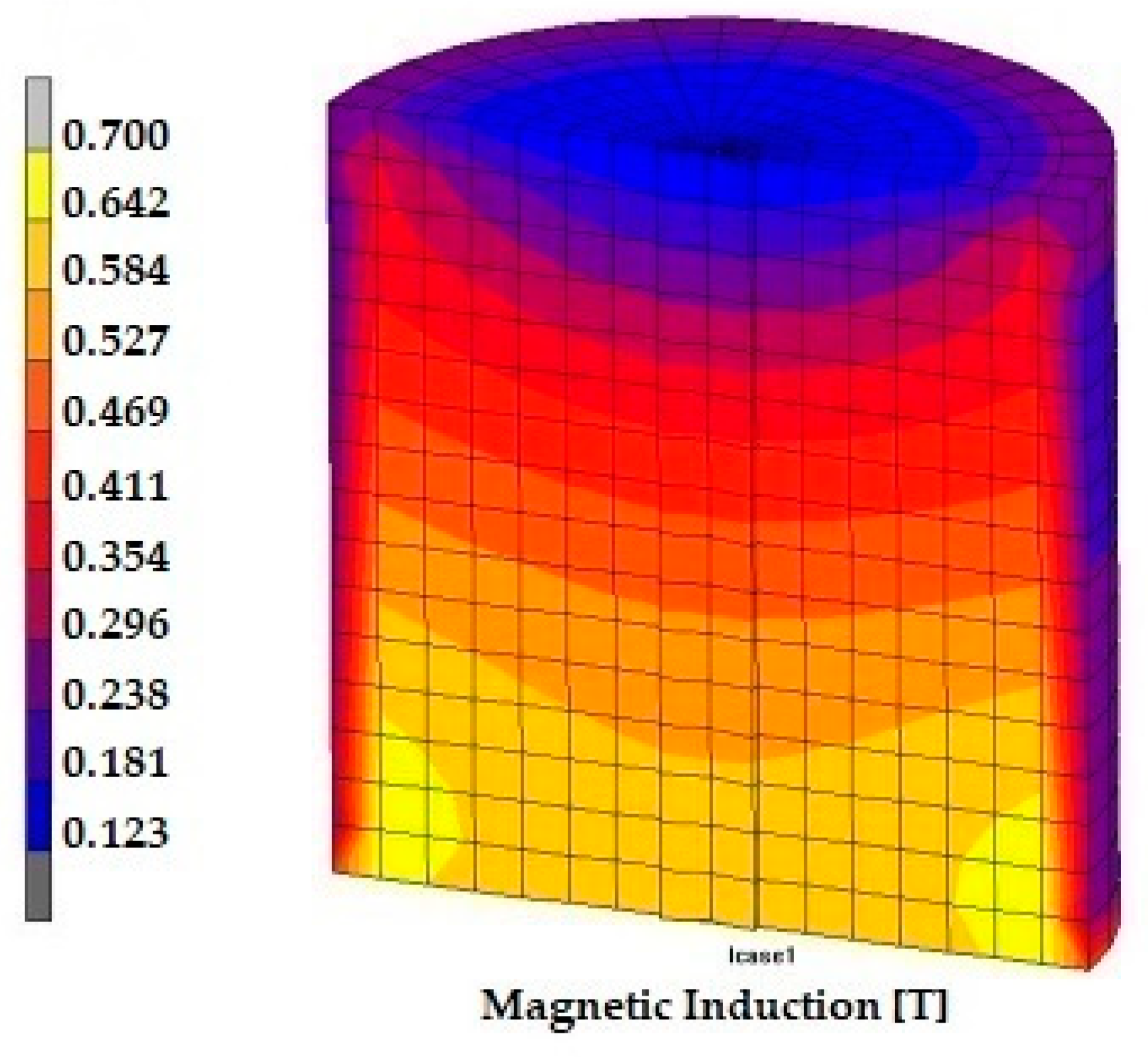
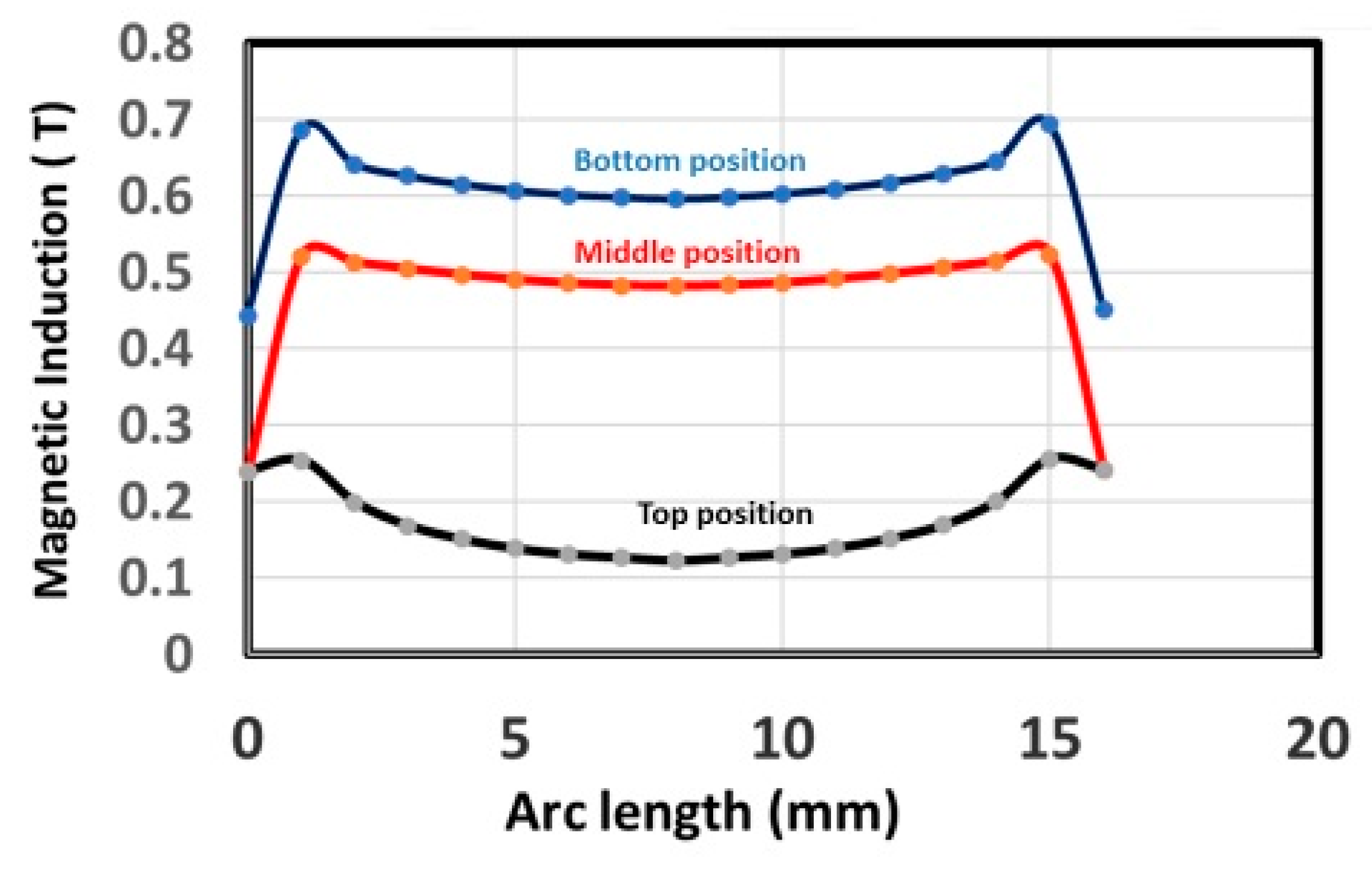



| Number of Layers | 1101 |
| Total VOI Volume | 15.7 mm3 |
| Object Surface Obj.S | 1166.2 mm2 |
| Surface Convexity Index SCv.I | −314.3 mm−1 |
| Structure Separation St.Sp | 0.01 mm |
| Surface of Closed Pores Po.S(cl) | 57.3 mm2 |
| Total Volume of Pore Space Po.V(tot) | 2.7 mm3 |
| Lower Vertical Position | 0.1 mm |
| Object Volume | 12.9 mm3 |
| Intersection Surface i.S | 29.2 mm2 |
| Centroid (x) Crd.X | −0.3 mm |
| Number of Objects Obj.N | 2913 |
| Closed Porosity Po(cl) | 0.6% |
| Total Porosity Po(tot) | 17.4% |
| Upper Vertical Position | 2.3 mm |
| Object Volume Obj.V/TV | 82.5% |
| Object Surface/Volume Ratio Obj.S/Obj.V | 90.0 mm−1 |
| Centroid (y) Crd.Y | 0.02963 mm |
| Number of Closed Pores Po.N | (cl) 82215 |
| Volume of Open Pore Space Po.V (op) | 2.6 mm3 |
| Pixel Size | 2 µm |
| Total VOI Surface (TS) | 38.7 mm2 |
| Object Surface Density Obj.S/TV | 74.2 mm−1 |
| Centroid (z) Crd.Z | 1.2 mm |
| Volume of Closed Pores Po.V(cl) | 0.1 mm3 |
| Open Porosity Po(op) | 16.9% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samal, S.; Kolinova, M.; Blanco, I. The Magneto-Mechanical Behavior of Active Components in Iron-Elastomer Composite. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030054
Samal S, Kolinova M, Blanco I. The Magneto-Mechanical Behavior of Active Components in Iron-Elastomer Composite. Journal of Composites Science. 2018; 2(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamal, Sneha, Marcela Kolinova, and Ignazio Blanco. 2018. "The Magneto-Mechanical Behavior of Active Components in Iron-Elastomer Composite" Journal of Composites Science 2, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030054
APA StyleSamal, S., Kolinova, M., & Blanco, I. (2018). The Magneto-Mechanical Behavior of Active Components in Iron-Elastomer Composite. Journal of Composites Science, 2(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030054