Reduced Graphene Oxide: Effect of Reduction on Electrical Conductivity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Graphene Oxide
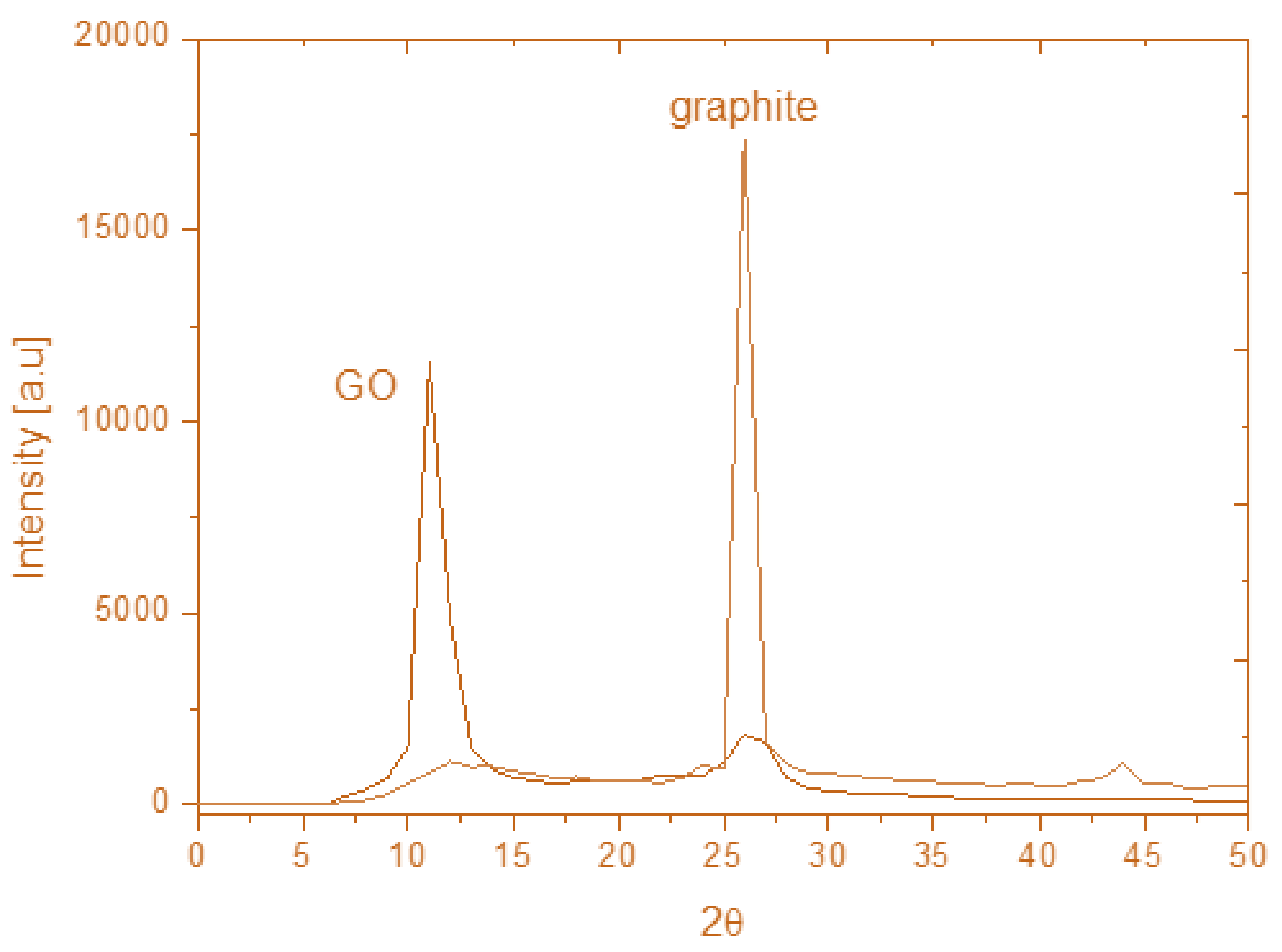
2.2. X-Ray Diffractometry (XRD)
2.3. Design of Experiments
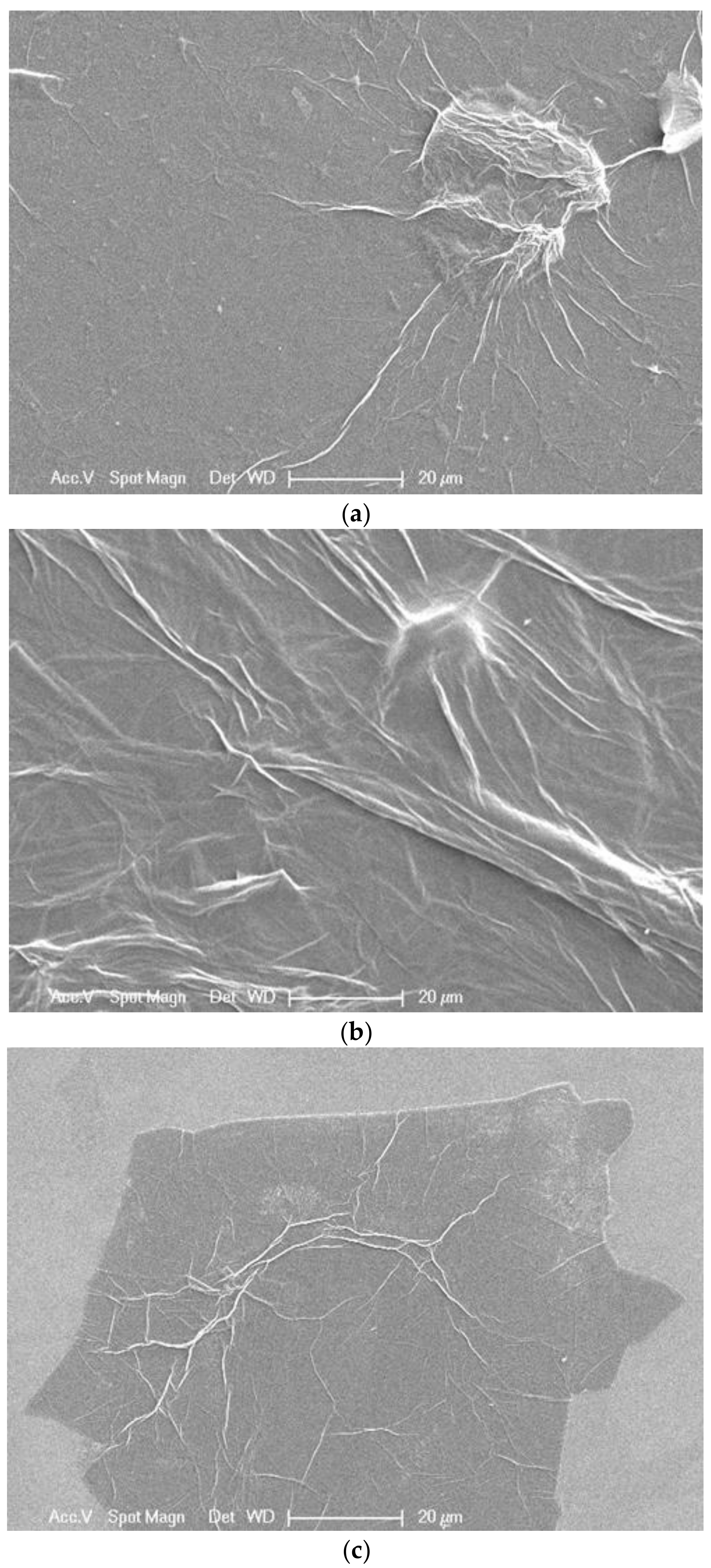
3. Characterization
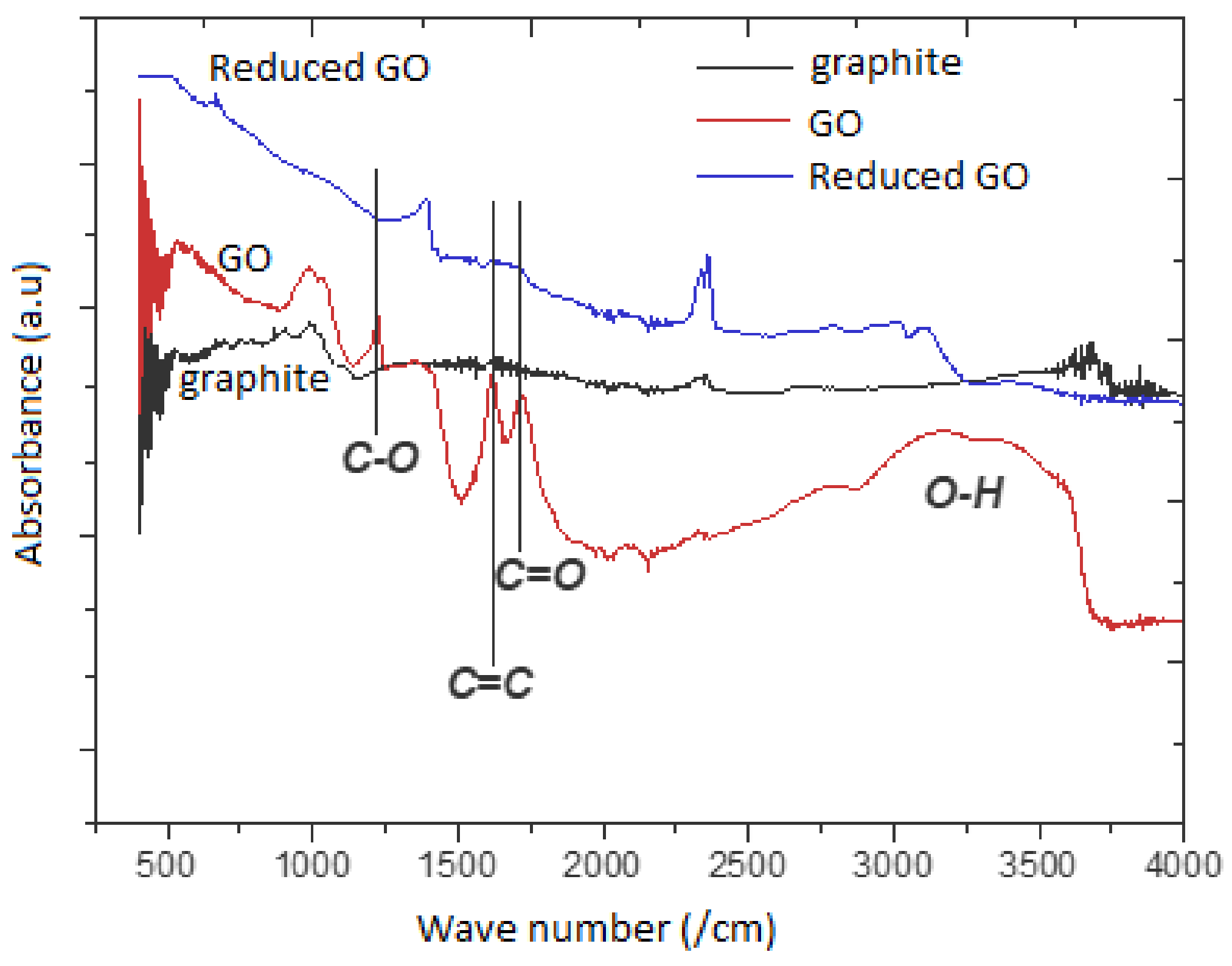
3.1. Fourier Transfer Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.2. Electromagnetic Shielding
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuilla, T.; Bhadra, S.; Yao, D.; Kim, N.H.; Bose, S.; Lee, J.H. Recent Advances in graphene based polymer composites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1350–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y. Electromagnetic interference shielding of graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon 2009, 47, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, G.; Unalan, H.E.; Rupensinghe, N.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; Manish, C. Field Emission from graphene based composite thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 233502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senguptaa, R.; Bhattacharyaa, M.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Bhomicka, A.K. A Review on the Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Graphite and Modified Graphite Reinforced Polymer Composites; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Miura, Y.; Macosko, C.W. Graphene/Polyurethane Nanocomposites for Improved Gas Barrier and Electrical Conductivity. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 3441–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, O.C.; Kim, S.; Pierre, C.; Torkelson, J.M.; Nguyen, S.T. Crumpled Graphene Nanosheets as Highly Effective Barrier Property Enhancers. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4759–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.; Lahiri, I.; Seelaboyina, R.; Kang, Y.S. Synthesis of Graphene and Its Applications: A Review. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2010, 35, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wei, T.; Shao, B.; Fan, Z.; Qian, W.; Zhang, M.; Wei, F. Preparation of a graphene nanosheet/polyaniline composite with high specific capacitance. Carbon 2010, 48, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, J.R.; Dreyer, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-Based Polymer Nanocomposites; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.-X.; Wang, S.; Tang, D.Y.; Jose, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Lim, C.T.; Loh, K.P. Graphene-Polymer Nanofiber membrane for ultrafast photonics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Giannelis, E.P. Functionalized Graphene Sheet—Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Conductive Nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. 2009, 47, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Kolhaas, K.M.; Zimney, E.J.; Stach, E.A.; Piner, R.D.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 2006, 442, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vovchenko, L.L.; Matzui, L.Y.; Oliynyk, V.V.; Launetz, V.L. The Effect of Filler Morphology and Distribution on Electrical and Shielding Properties of Graphite-Epoxy Composites. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 535, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.-S.; Song, W.-L.; Hou, Z.-L.; Wen, B.; Yuan, J. The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites. Carbon 2010, 48, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Gupta, M.C. Novel carbon nanotube-polystyrene foam composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2131–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, R.C.; Peng, L.M.; Duan, X.F.; Chen, Q.; Liang, X.L. Microwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of Fe encapsulated within carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Ruoff, R.S. Chemical methods for the production of graphenes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Mueller, M.B.; Gilje, S.; Kaner, R.B.; Wallace, G.G. Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Kaner, R.B. Materials science—Graphene-based materials. Science 2008, 320, 1170–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerf, A.; He, H.Y.; Forster, M.; Klinowski, J. Structure of graphite oxide revisited. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 4477–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Zhao, H. Exfoliated Graphite Oxide Decorated by PDMAEMA Chains and Polymer Particles. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11808–11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Yao, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wong, C.-P. Solvent-Assisted Thermal Reduction of Graphite Oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 14819–14825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Inoue, T. Light and X-Ray Scatterings. In Polymer Characterisation Techniques and Their Application to Blends; Simon, G.P., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 313–345. [Google Scholar]
- Dikin, D.A.; Stankovich, S.; Zimney, E.J.; Piner, R.D.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Evmenenko, G.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide paper. Nature 2007, 448, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Kulkarni, A.; Stankovich, S.; Ruoff, R.S.; Baik, S. Restoring electrical conductivity of dielectrophoretically assembled graphite oxide sheets by thermal and chemical reduction techniques. Carbon 2009, 47, 1520–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. The chemistry of Graphene Oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Jeong, H.M.; Shin, C.M. Graphite oxide/poly(methyl methacrylate) nanocomposites prepared by a novel method utilizing macroazoinitiator. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, A.; Oruc, F.; Demir, A. Effects of polarity on electrospinning process. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preperation of Graphitic Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D. Elements of X-Ray Diffraction; Addison-Wesley Pub. Co.: Reading, MA, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Tesche, F.M.; Ianoz, M.V.; Karlsson, T. EMC Analysis Methods and Computational Models; John-Wiley & Sons. Inc.: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.P.; Pan, C.Y. Preparation and characterization of poly(methyl methacrylate)-intercalated graphite oxide/poly(methyl methacrylate) nanocomposite. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2004, 44, 2335–2339. [Google Scholar]
- Pande, S.; Singh, B.P.; Mathur, R.B.; Dhami, T.L.; Saini, P.; Dhawan, S.K. Improved Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties of MWCNT-PMMA Composites Using Layered Structures. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saleh, M.H.; Sundararaj, U. Electromagnetic interference shielding mechanisms of CNT/polymer composites. Carbon 2009, 47, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.Y.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, C.G.; Han, J.H. Fabrication and electromagnetic characteristics of electromagnetic wave absorbing sandwich structures. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Kim, K.; Lee, C.Y.; Joo, J.; Cho, S.J.; Yoon, H.S.; Pejaković, D.A.; Yoo, J.W.; Epstein, A.J. Electrical conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding of multiwalled carbon nanotube composites containing Fe catalyst. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 589–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

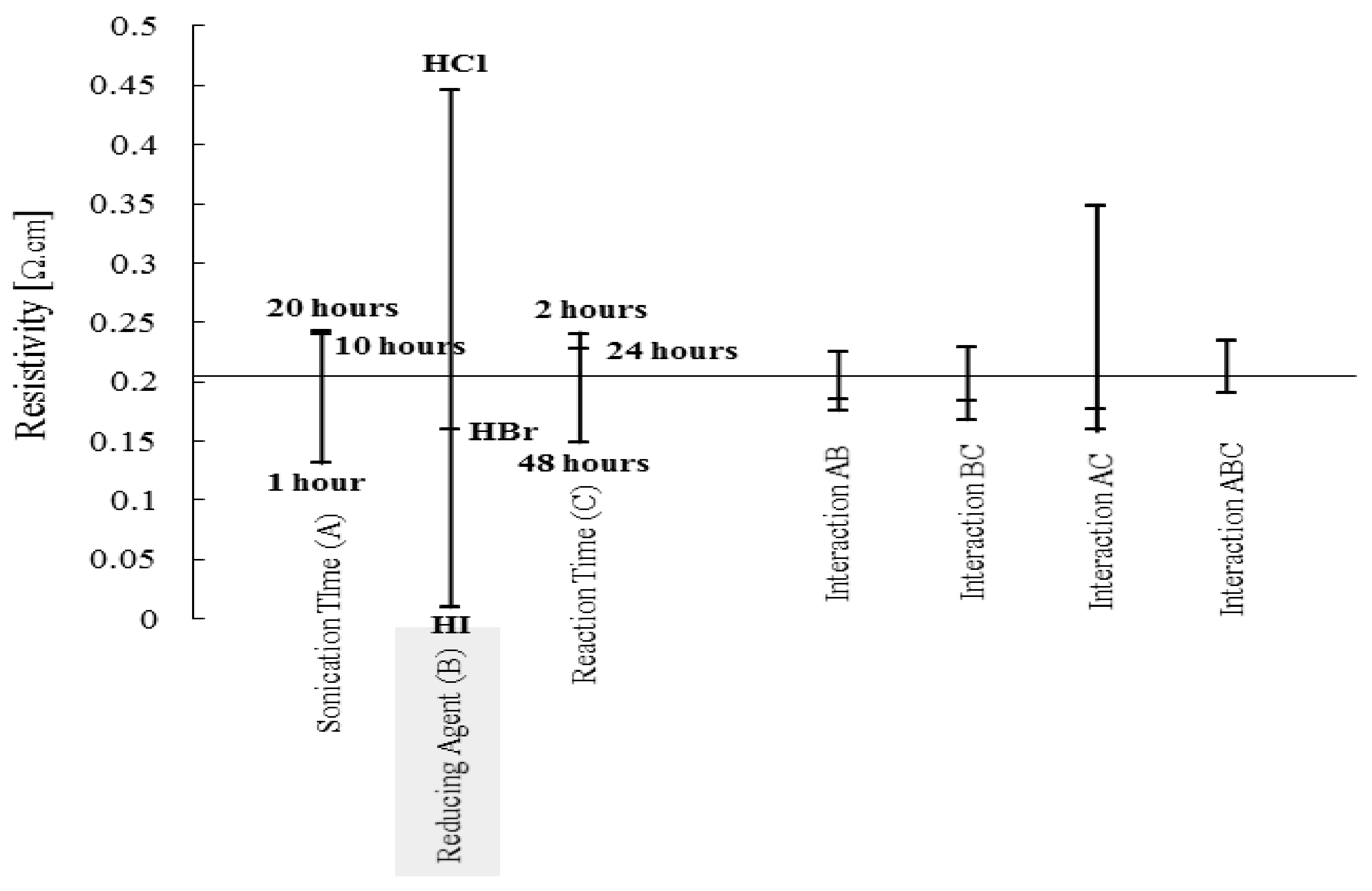
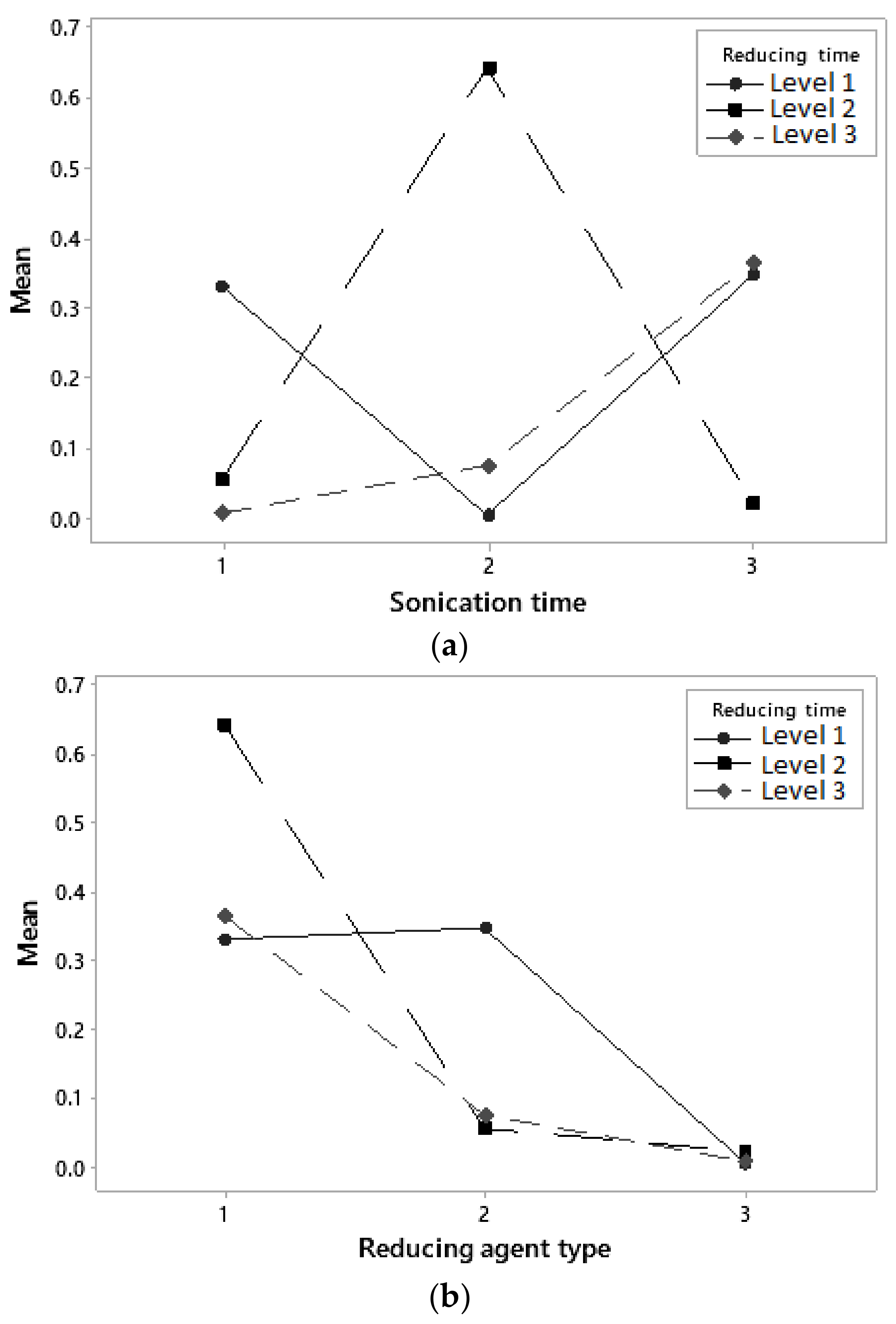

| Factor | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sonication Time (A) | 1 h | 10 h | 20 h |
| Reducing Agent (B) | Hydrochloric acid | Hydrobromic Acid | Hydroiodic Acid |
| Reaction Time (C) | 2 h | 24 h | 48 h |
| Standard Order No. | A | B | C | Resistivity (Ω·cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.330 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.560 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0.006 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.641 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0.076 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0.003 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 0.365 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.347 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0.022 |
| Sr. No. | Electrical Conductivity (S/m) | Frequency (GHz) | EMI Shielding Effectiveness, dB (SEa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 39,000 | 8 | 4.13 |
| 2 | 39,000 | 9 | 4.38 |
| 3 | 39,000 | 10 | 4.62 |
| 4 | 39,000 | 11 | 4.84 |
| 5 | 39,000 | 12 | 5.06 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, S.; Upadhyay, J.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Umer, R.; Das, R. Reduced Graphene Oxide: Effect of Reduction on Electrical Conductivity. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020025
Rao S, Upadhyay J, Polychronopoulou K, Umer R, Das R. Reduced Graphene Oxide: Effect of Reduction on Electrical Conductivity. Journal of Composites Science. 2018; 2(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Sanjeev, Jahnavee Upadhyay, Kyriaki Polychronopoulou, Rehan Umer, and Raj Das. 2018. "Reduced Graphene Oxide: Effect of Reduction on Electrical Conductivity" Journal of Composites Science 2, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020025
APA StyleRao, S., Upadhyay, J., Polychronopoulou, K., Umer, R., & Das, R. (2018). Reduced Graphene Oxide: Effect of Reduction on Electrical Conductivity. Journal of Composites Science, 2(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020025






