Effect of Laser Shock Peening on the Fatigue Performance of Q355D Steel Butt-Welded Joints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
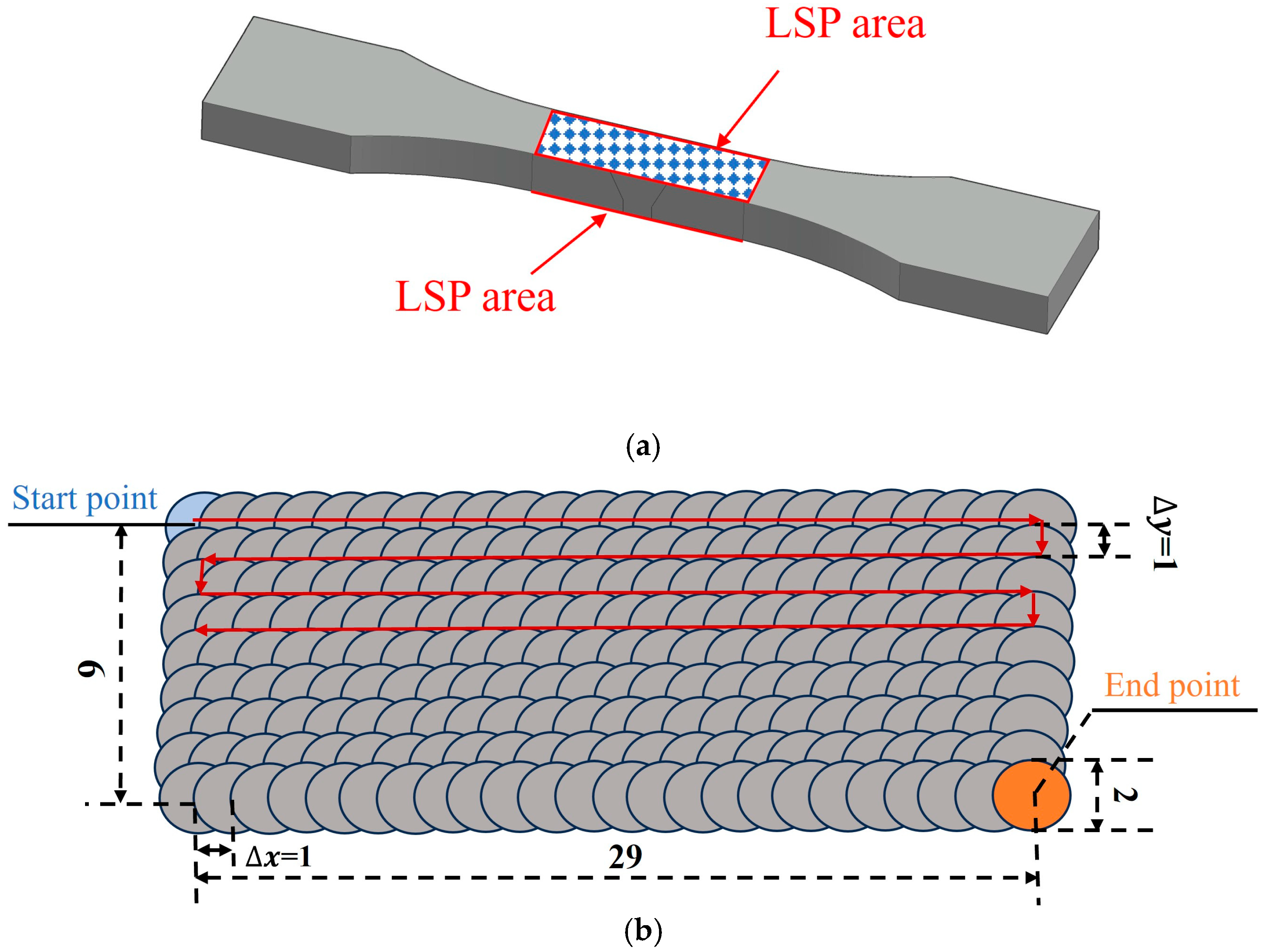
2.1. Specimen Design
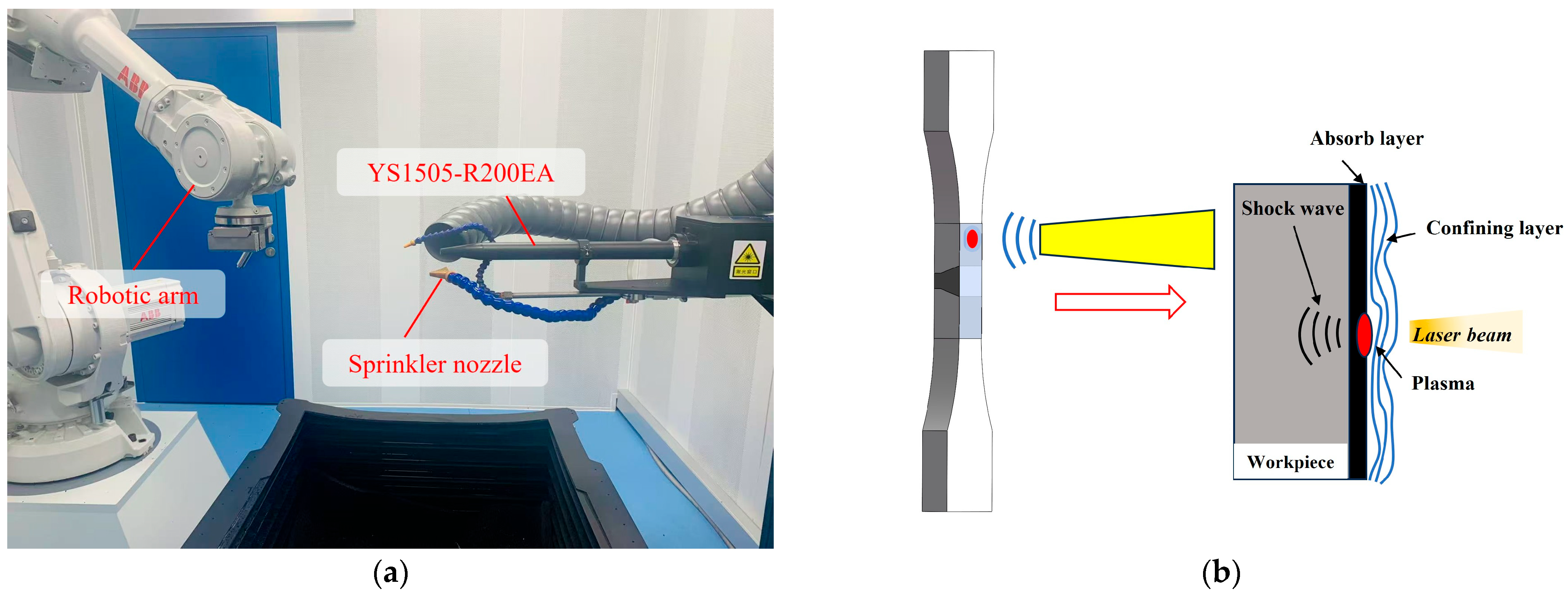
2.2. LSP Experiment and Parameter Determination
2.3. Material Performance Testing and Chanracterization
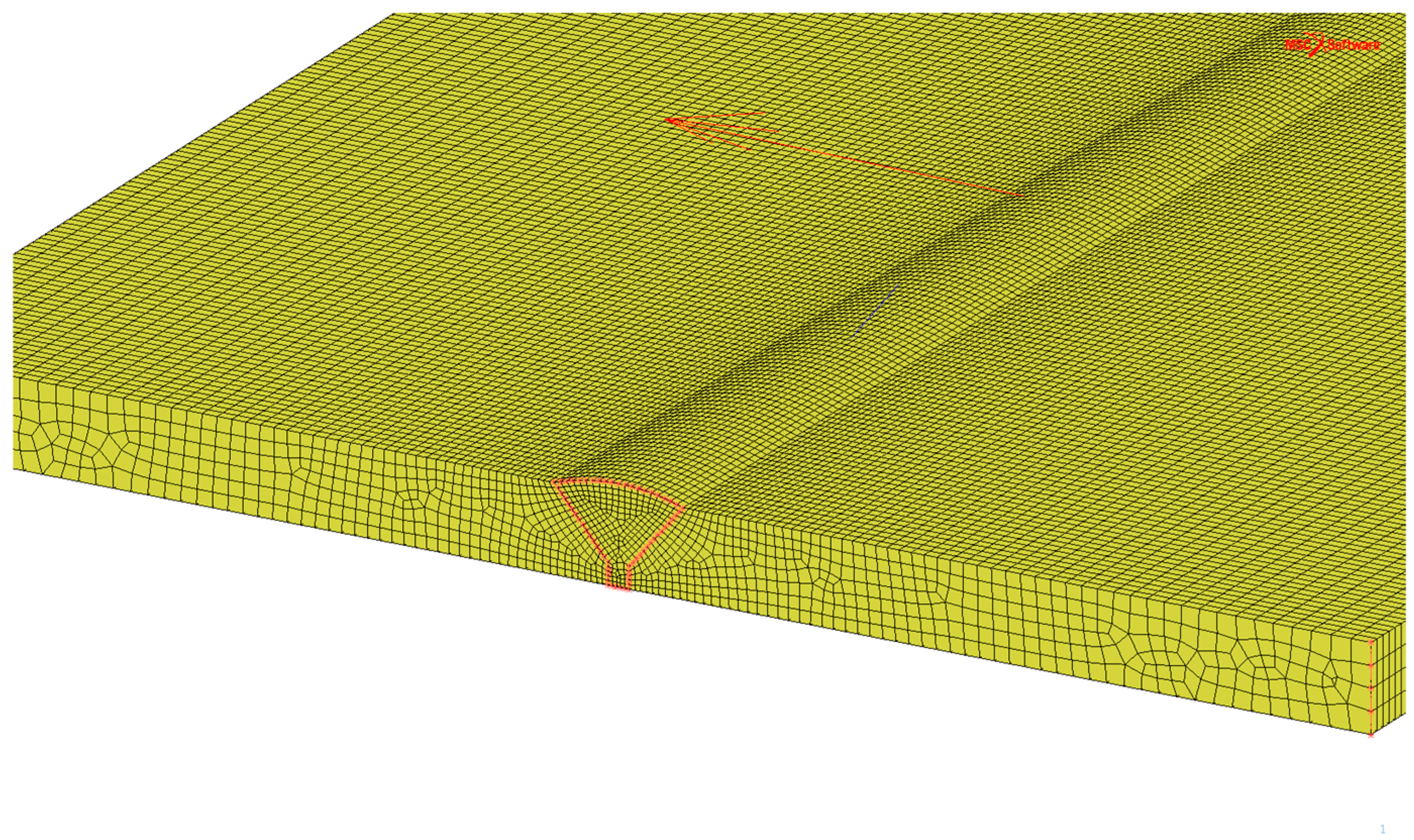
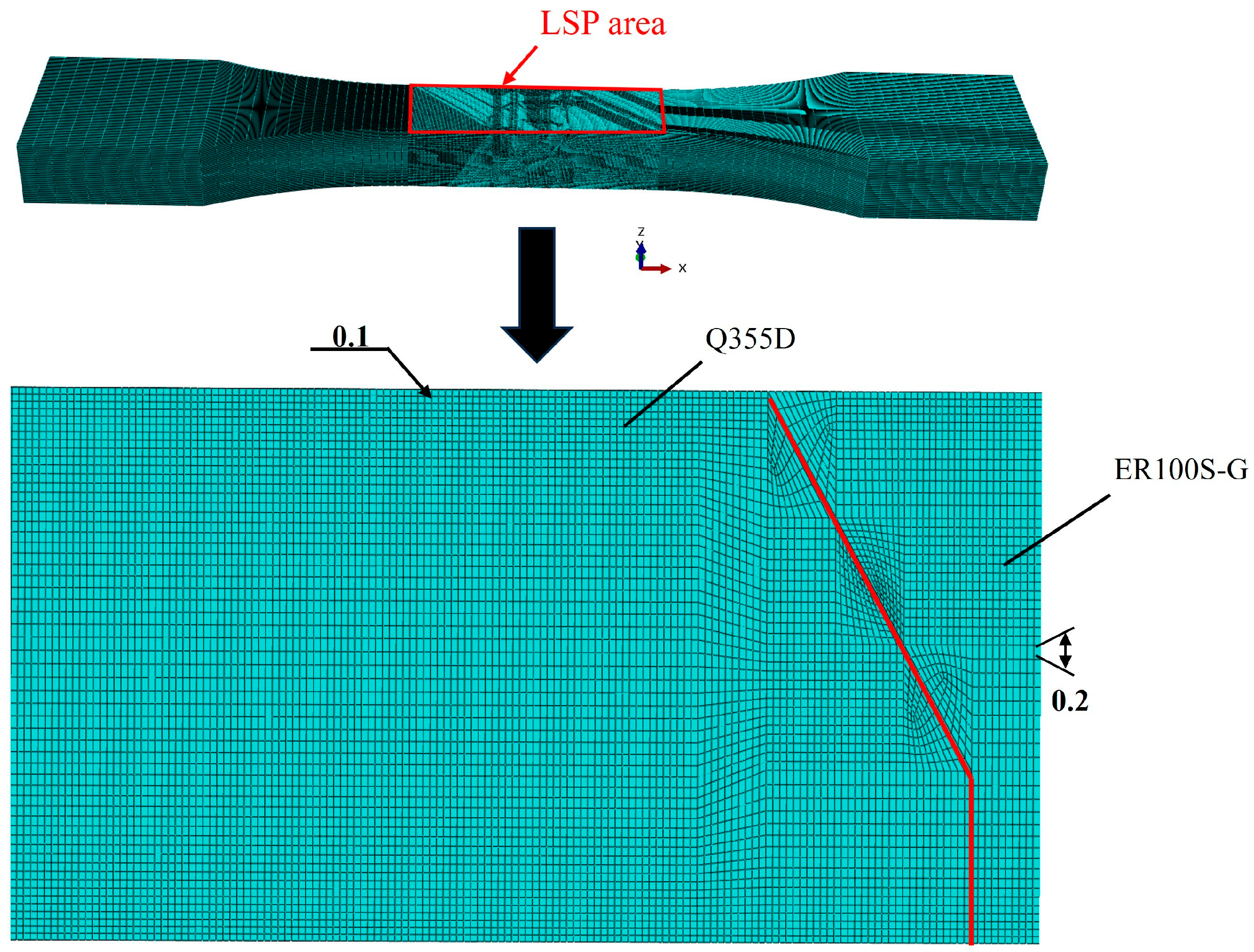
2.4. Finite Element Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Finite Element Modeling
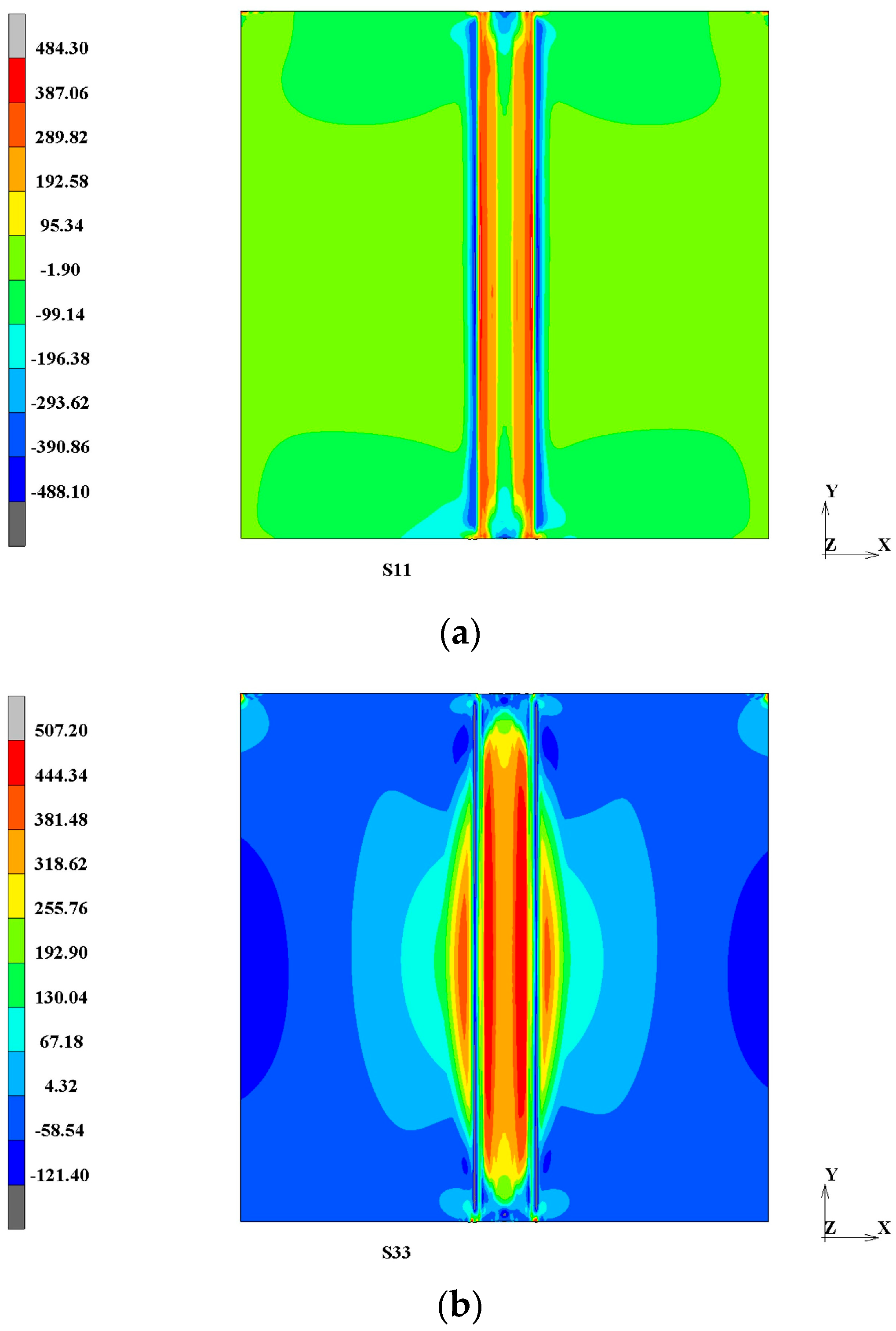
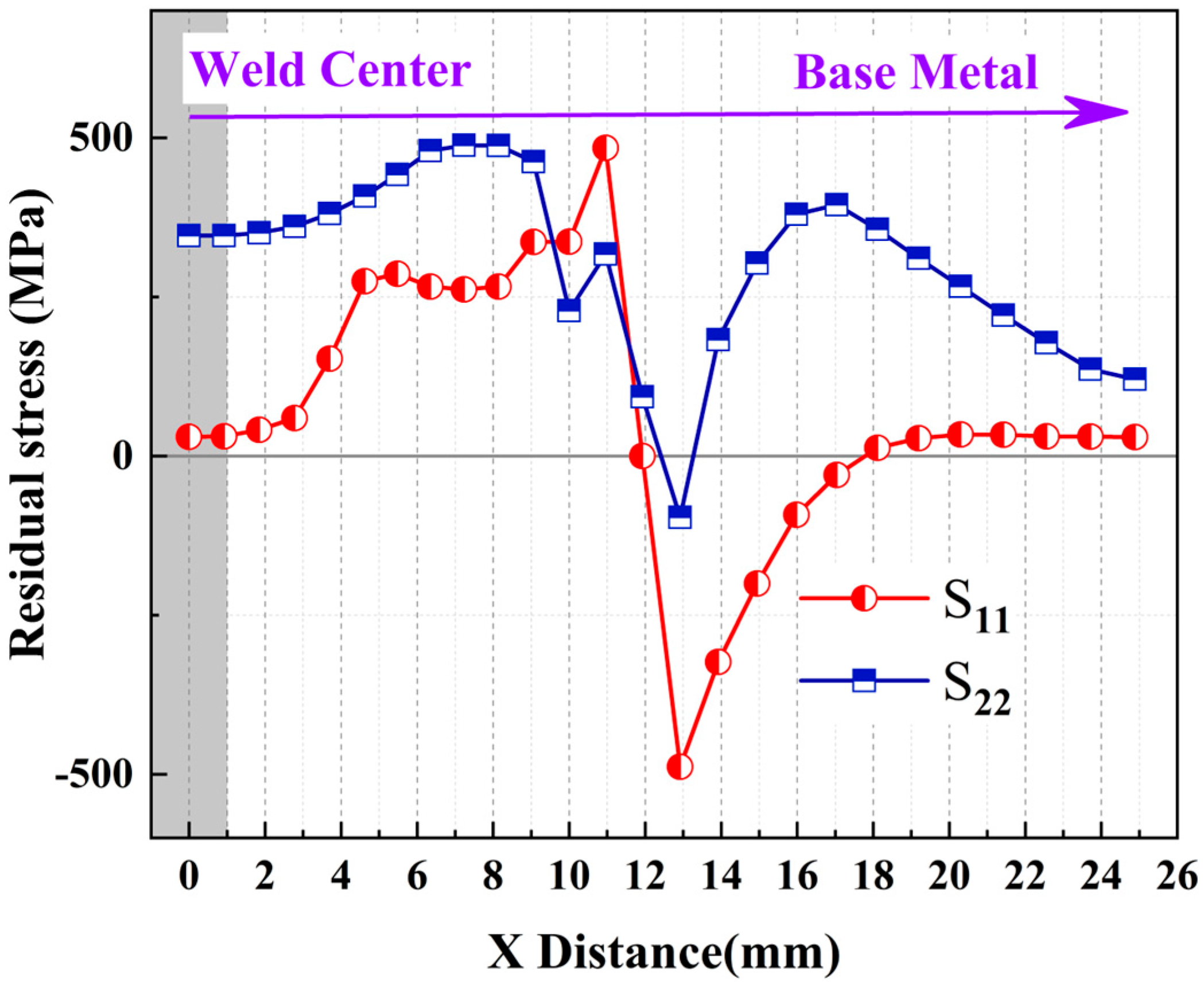
3.1.1. Welding Residual Stress Distribution
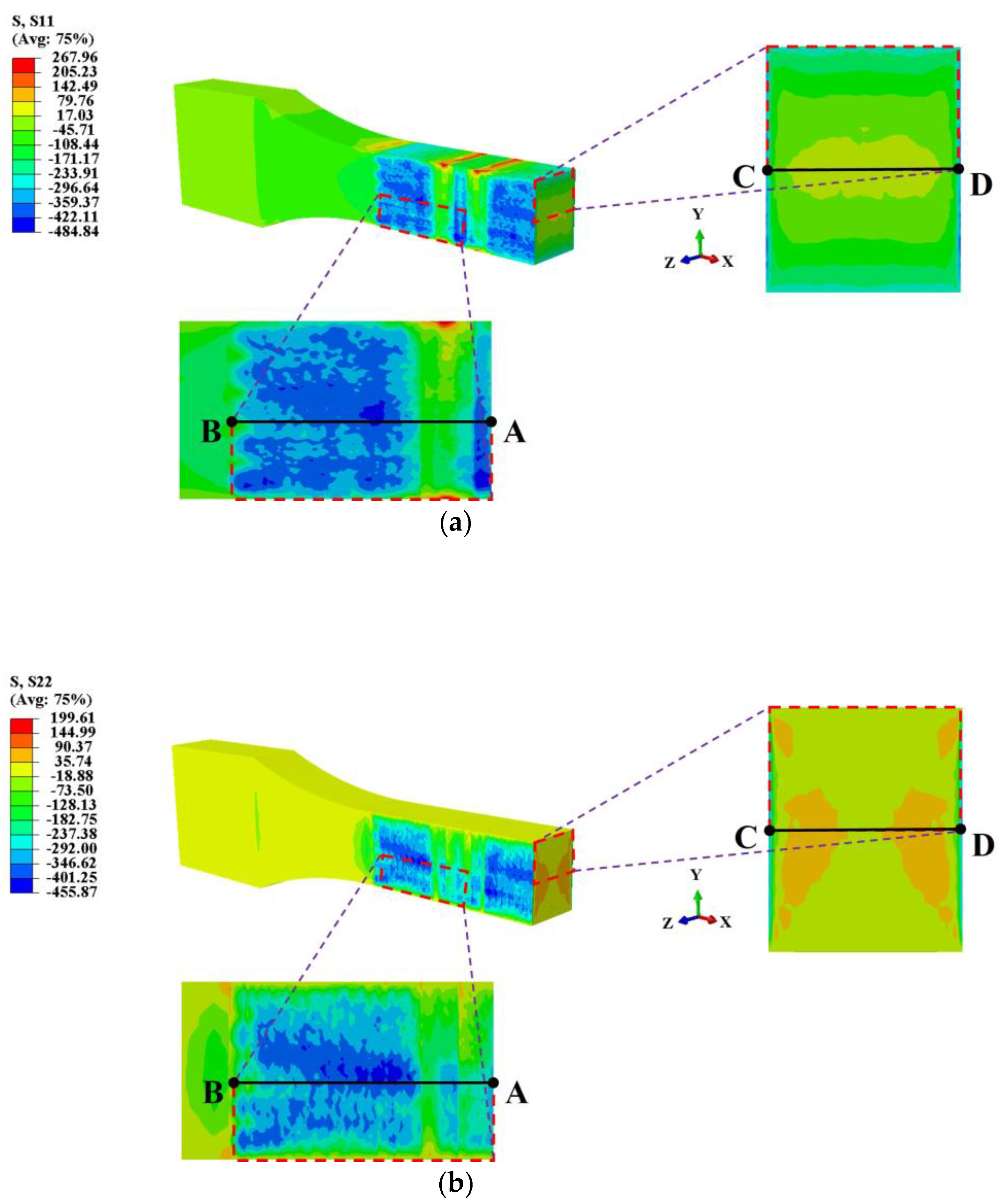
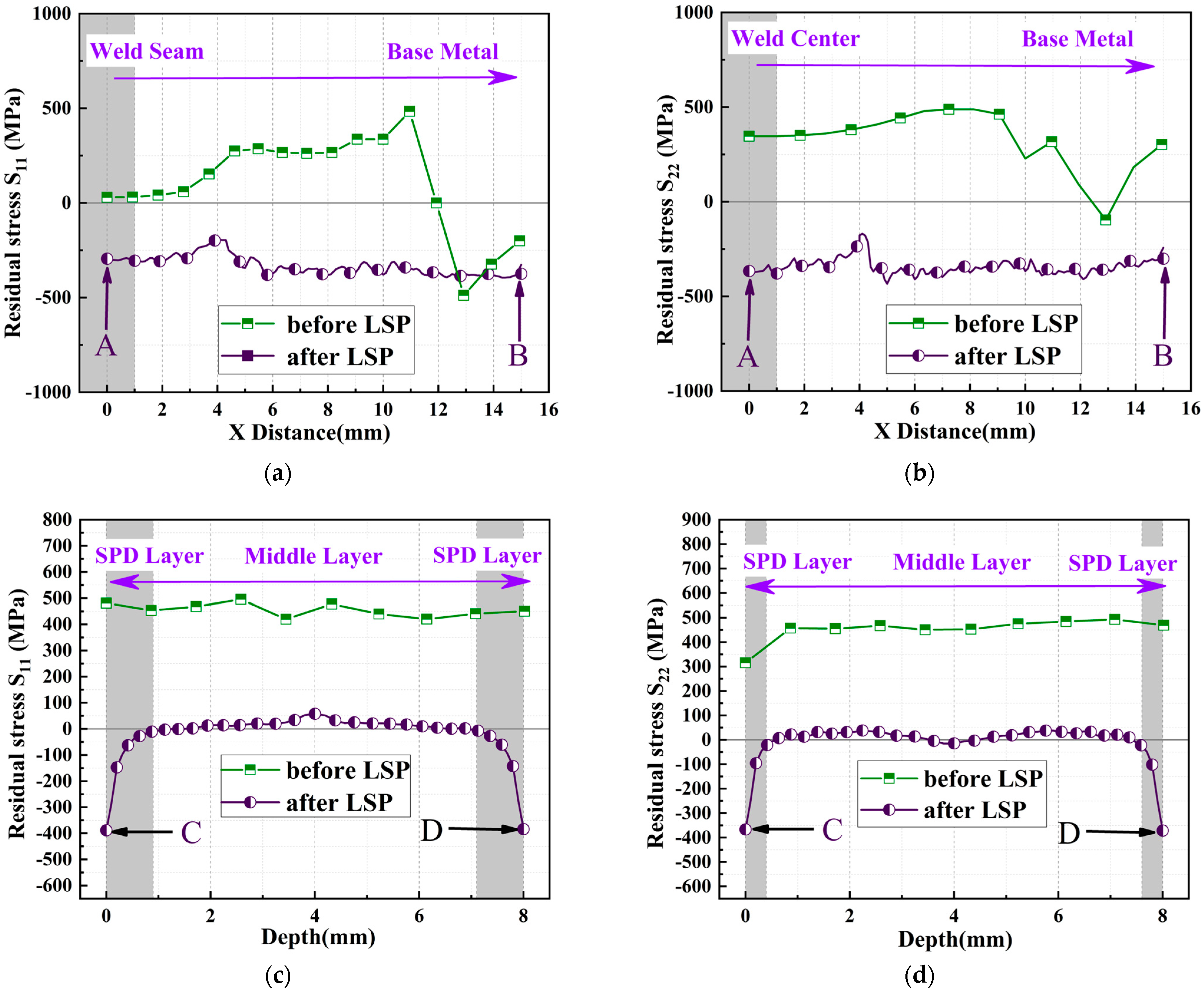
3.1.2. Residual Stress Distribution in LSP-Treated Specimens
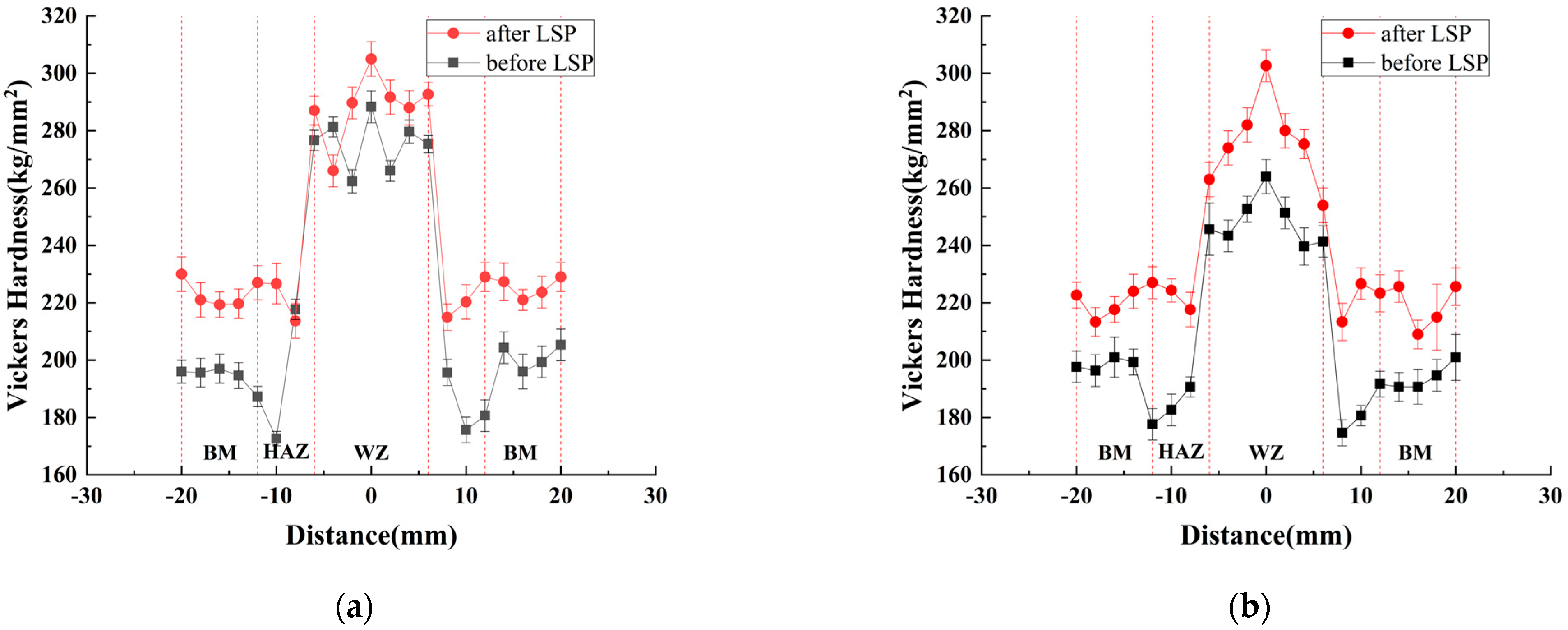
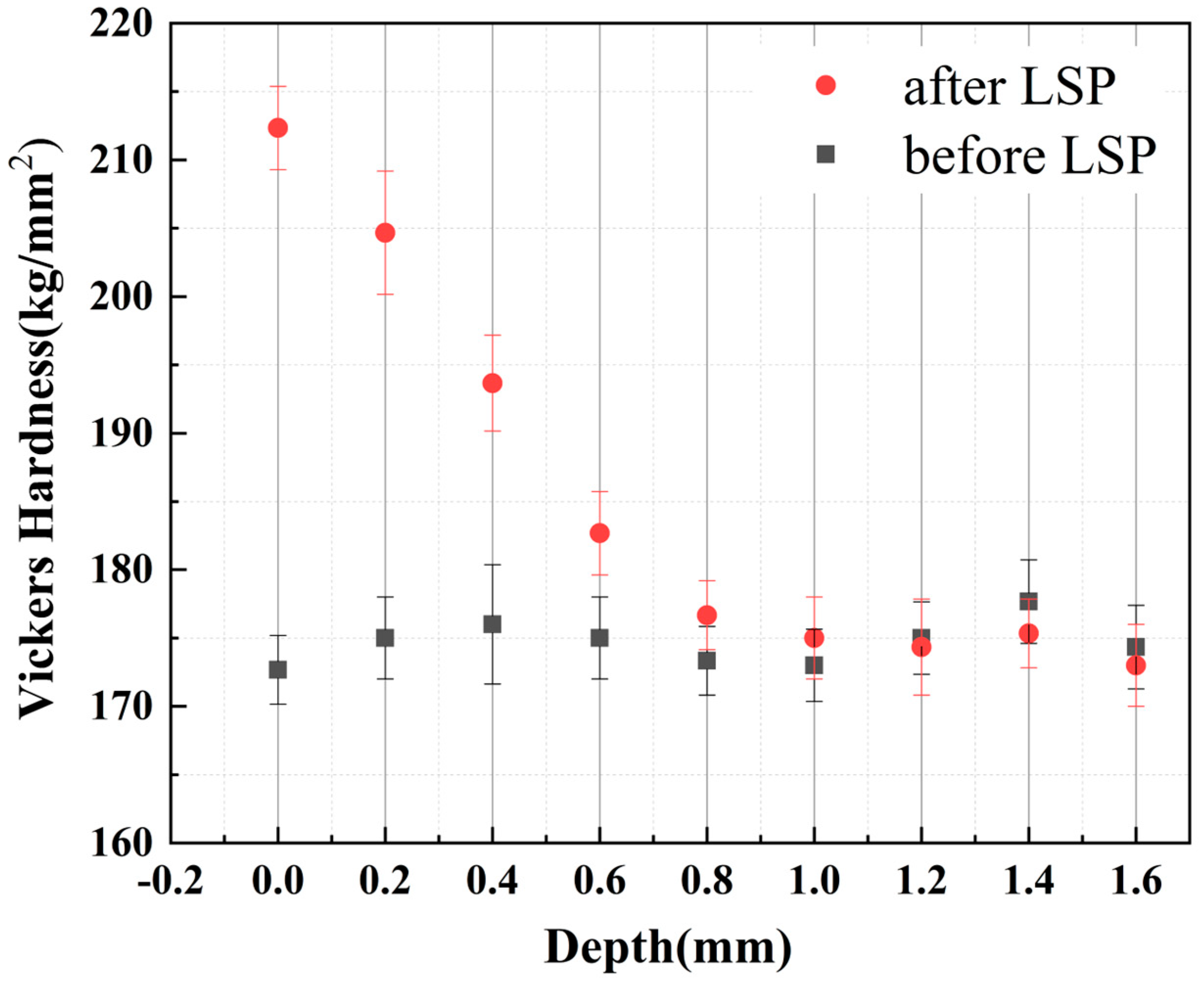
3.2. Hardness Test
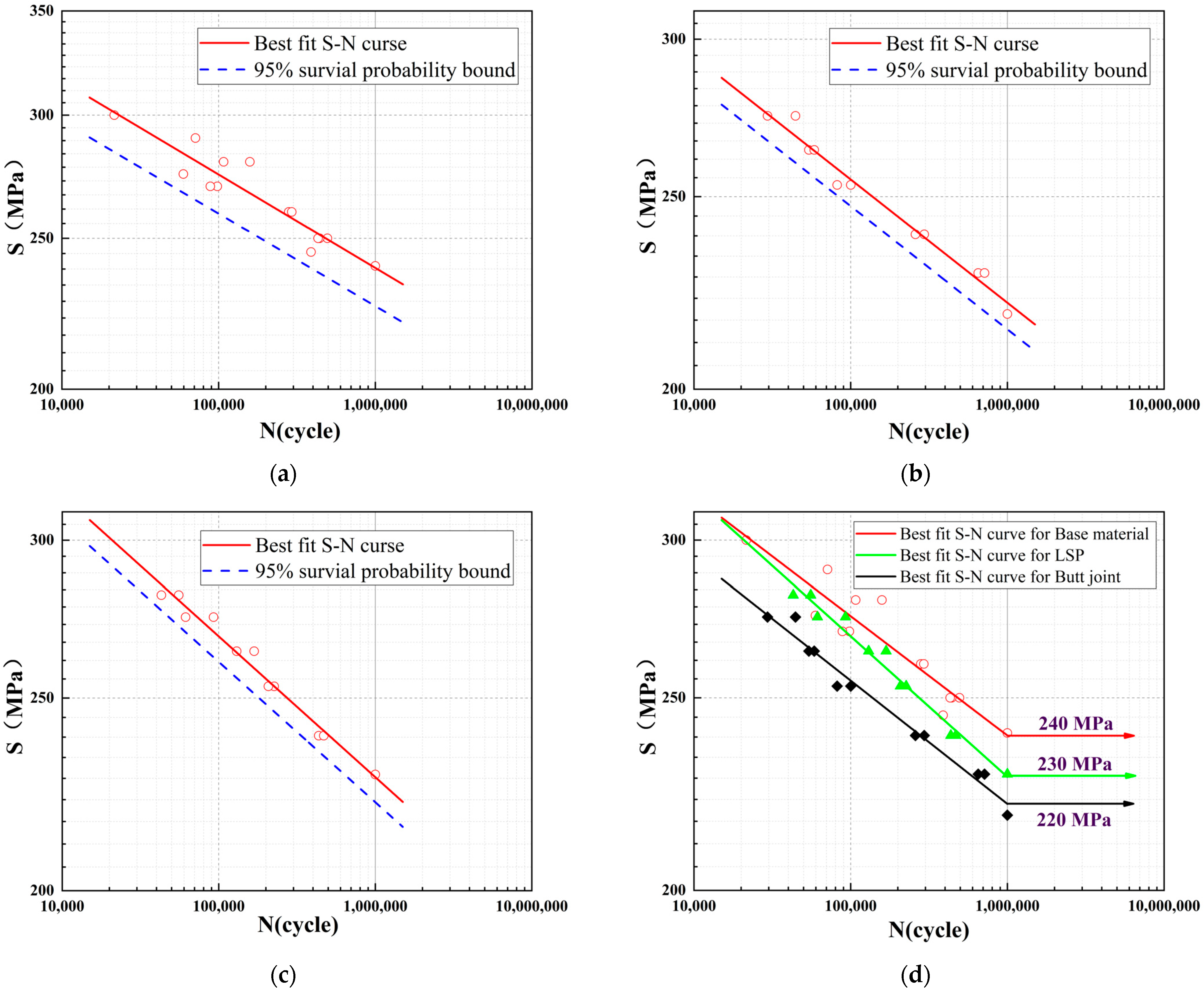
3.3. Fatigue Results
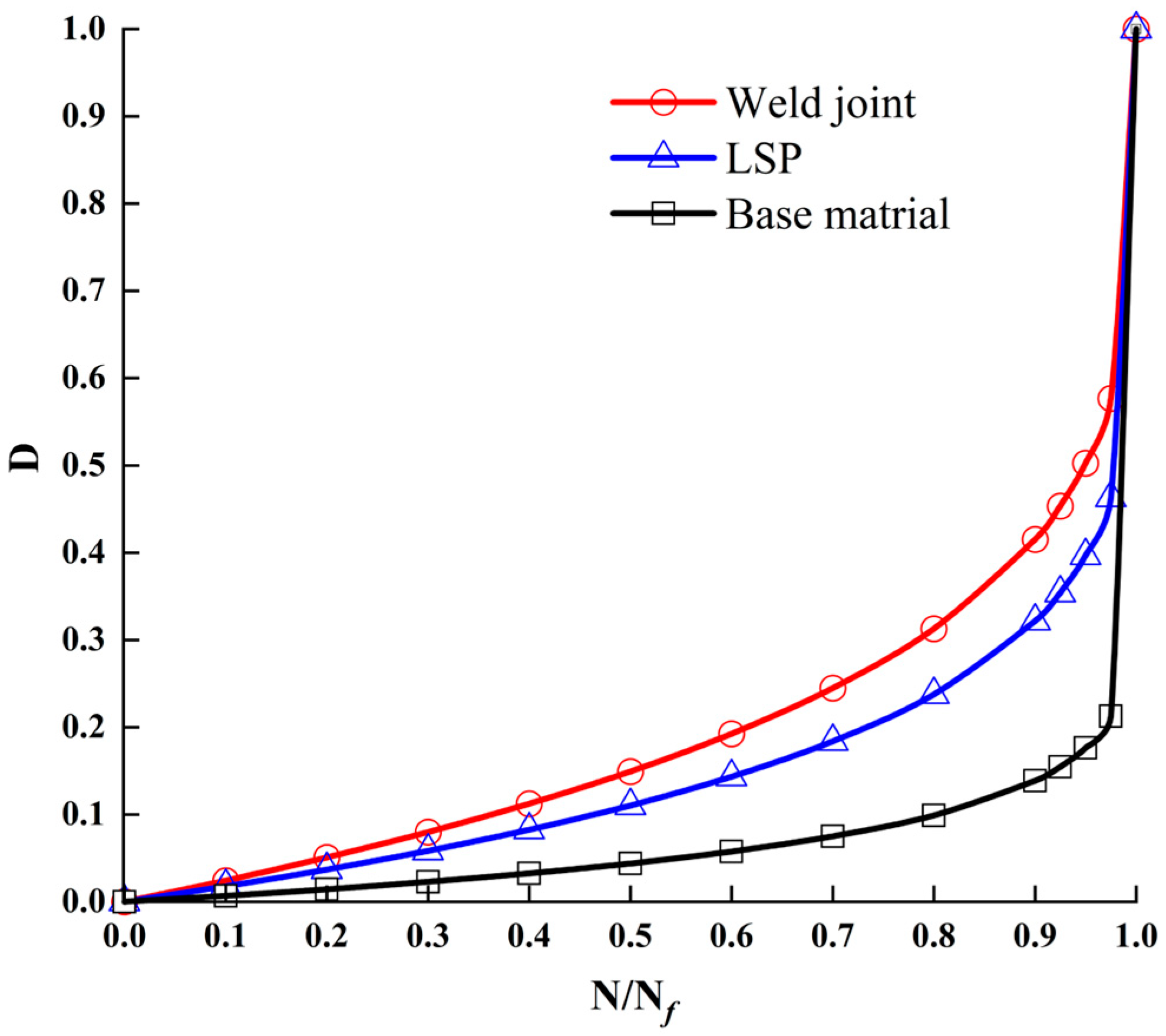
3.4. Fatigue Damage
3.5. Fracture Morphological Analysis
4. Conclusions
- LSP significantly increased microhardness across all joint zones (22.9% improvement in upper-surface HAZ, 11.3% in lower-surface WZ), forming a hardness gradient decaying within approximately 700 m depth from the surface. This gradient hardening establishes a microstructural foundation for enhanced fatigue resistance.
- LSP substantially extended joint fatigue life: by 113–165% in the high-stress region (250–270 MPa) and 46–63% in the medium-low-stress region (230–240 MPa). This indicates exceptional effectiveness in suppressing crack initiation and early propagation under high stresses.
- Finite element analysis revealed significant residual tensile stress concentration (S11 peak ~484 MPa) beyond 11 mm on both sides of the weld. LSP effectively induced surface residual compressive stress, markedly reducing residual tensile stress levels (e.g., S22 peak decreased from ~488 MPa to −397 MPa), effectively lowering tensile stress in critical zones to inhibit crack initiation.
- Fractographic analysis confirmed reduced microcrack density and smaller fatigue striation spacing in LSP-treated specimens. This originates from the synergistic effect of surface residual compressive stress (inducing crack closure) and microstructural refinement/strengthening, collectively retarding crack propagation rates.
- These results validate LSP’s efficacy in enhancing fatigue performance of Q355D welded joints. Future work should evaluate its robustness in engineering applications by increasing sample sizes and optimizing process parameters.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Tong, L.; Niu, L.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, X.-L. Experimental research on fatigue performance of high-strength structural steel series. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 183, 106743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corigliano, P.; Crupi, V. Review of Fatigue Assessment Approaches for Welded Marine Joints and Structures. Metals 2022, 12, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Shi, X.; Wei, S.; Xia, H.; Zhou, G.; Masoudi Nejad, R.; Berto, F. Fatigue performance assessment of thick TIG-Dressing cruciform welded joints made by Q355D structural steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 5977–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knysh, V.V.; Mordyuk, B.N.; Solovei, S.O.; Savitsky, V.V.; Mikhodui, O.L.; Lesyk, D.A.; Motrunich, S.I. HFMI-induced fatigue strength improvement of S355 steel transverse non-load-carrying attachments with lack of fusion in the weld root. Int. J. Fatigue 2024, 181, 108147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qutaba, S.; Asmelash, M.; Saptaji, K.; Azhari, A. A review on peening processes and its effect on surfaces. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 4233–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Wang, D.; Jing, H.; Huo, L. The effects of ultrasonic peening treatment on the ultra-long life fatigue behavior of welded joints. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 3299–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.; Wang, X. A review of fatigue test data on weld toe grinding and weld profiling. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 145, 106073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lai, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, C. Dislocation-based study on the influences of shot peening on fatigue resistance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 383, 125247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z.; Lv, J.; Luo, K.; Lu, J. Progressive developments, challenges and future trends in laser shock peening of metallic materials and alloys: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2023, 191, 104061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangamani, G.; Anand, P.I.; Sahu, A.; Singh, I.; Gianchandani, P.K.; Tamang, S.K. Enhance the microstructure and mechanical properties of directed energy deposition-Arc (DED-Arc) stainless steel 308L using laser shock peening process. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangamani, G.; Tamang, S.K.; Badhai, J.; Karthik, S.; Narayanan, J.A.; Thangaraj, M.; Thirugnanasambandam, A.; Sonawane, A.; Anand, P.I. Elucidating the impact of laser shock peening on the biocompatibility and corrosion behaviour of wire arc additive manufactured SS316L bone staples. Appl. Phys. A-Mater. Sci. Process. 2025, 131, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangamani, G.; Tamang, S.K.; Patel, M.S.; Narayanan, J.A.; Pallagani, J.; Rose, P.; Gianchandani, P.K.; Thirugnanasambandam, A.; Anand, P.I. Post-processing treatment of Wire Arc Additive Manufactured NiTi shape memory alloy using laser shock peening process: A study on tensile behavior and fractography analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 136, 3315–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangamani, G.; Tamang, S.K.; Badhai, J.; Karthik, S.; Narayanan, J.A.; Thirugnanasambandam, A.; Sonawane, A.; Anand, P.I. Post-processing of wire-arc additive manufactured stainless steel 316 l bone staples using laser shock peening: A mechanical and antibacterial study. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 10, 5525–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, T.; Yu, Y.; Liu, P.; Pan, X. Effect of Laser Shock Peening on High-Cycle Fatigue Performance of 1Cr18Ni9Ti/GH1140 Weld. Metals 2022, 12, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, R.; Liu, X.; Lv, Q.; Wang, X.; Tian, Z. Effect of laser shock peening on fatigue properties of U75VG rail flash-butt welding joints. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 149, 107889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangamani, G.; Kumar Tamang, S.; Patel, M.S.; Arackal Narayanan, J.; Thangaraj, M.; Zhang, J.; Kumar Gianchandani, P.; Iyamperumal Anand, P. Studies on the effect of laser shock peening intensity on the mechanical properties of wire arc additive manufactured SS316L. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethapriyan, T.; Palani, I.; Singh, M.K.; Rai, D.K.; Shanmuga Priyan, V.; Subbu, S.K. Post-processing of wire arc additive manufactured stainless steel 308L to enhance compression and corrosion behavior using laser shock peening process. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024, 33, 9267–9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Guo, C.; Sun, M. Experiments and numerical simulations on fatigue properties of laser shock peening for FV520B steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 182, 112198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, Y.; Ye, C. Recent Developments and Novel Applications of Laser Shock Peening: A Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2001216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, C.; Jin, C.; Ji, X.; Han, T. Effects of different forging ratios on microstructure, mechanical properties and friction and wear behaviour of Q355D steel. Can. Metall. Q. 2024, 64, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Yin, Y.; Qin, W.J.; Wang, X.F.; Li, F.K. Characterization of Mechanical Properties of Welds of Q355D Steel by DSI Technique. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 04023617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Han, Q.; Yu, X.; Yu, Z. Experimental investigation on the corrosion and corrosion fatigue behavior of butt weld with G20Mn5QT cast steel and Q355D steel under dry–wet cycle. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 134, 105977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabaki, M.M.; Nikodinovski, M.; Chenier, P.; Ma, J.; Harooni, M.; Kovacevic, R. Welding of aluminum alloys to steels: An overview. J. Manuf. Sci. Prod. 2014, 14, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Q.Q.; Yao, D.D.; Gao, Z.B.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.F.; Li, X.W. Fatigue mechanism of medium-carbon steel welded joint: Competitive impacts of various defects. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 151, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Yin, Y.; Qin, W.J.; Bai, J.H. Thermal Simulation and Fracture Resistance Evaluation of Coarse-Grain Heat-Affected Zone in Welds of Q355D Steel. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, B.; Swaroop, S. Review: Laser shock peening as post welding treatment technique. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 32, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Sun, Y.F.; Yu, X.F.; Su, Y.; Li, C.G. Effect of the Absorption Layer on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of M50 Steel by Laser Shock Peening. JOM 2024, 76, 7247–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yella, P.; Venkateswarlu, P.; Buddu, R.K.; Vidyasagar, D.V.; Rao, K.B.S.; Kiran, P.P.; Rajulapati, K.V. Laser shock peening studies on SS316LN plate with various sacrificial layers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Rohde, R. Dynamic deformation twinning in shock-loaded iron. J. Appl. Phys. 1971, 42, 4171–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Ye, L. Simulation of multiple laser shock peening of a 35CD4 steel alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 178, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, H. Tensile performance of normal and high-strength structural steels at high strain rates. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 184, 110457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyre, P.; Berthe, L.; Scherpereel, X.; Fabbro, R. Laser-shock processing of aluminium-coated 55C1 steel in water-confinement regime, characterization and application to high-cycle fatigue behaviour. J. Mater. Sci. 1998, 33, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Dai, F.; Siddiquee, A.N.; Konovalov, S. Effects of different laser shock processes on the surface morphology and roughness of TC4 titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 325, 118301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, D.; Duan, C.; Luo, X.; Cao, X.; Hao, X. Numerical and Experimental Study on the Fatigue Behavior of X80 Steel Treated by Biomimetic Laser Shock Peening. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024, 33, 13709–13720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, M.; Yu, P.H.; Sun, Y.F.; Su, Y.; Yu, X.F. Effect of laser shock peening overlap rate on microstructure and wear resistance of M50 steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 184, 112548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamundi Azaath, L.; Mohan, E.; Natarajan, U. Effect of rake angle and tool geometry during machining process of AISI 4340 steel in finite element approach. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 3731–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, A.S.; Dabboussi, W.; Nemes, J.A.; Abeyaratne, R.C. An improved multi-objective identification of Johnson-Cook material parameters. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2009, 36, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirigiri, V.K.R.; Gudiga, V.Y.; Gattu, U.S.; Suneesh, G.; Buddaraju, K.M. A review on Johnson Cook material model. Mater. Today-Proc. 2022, 62, 3450–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, M.; Jung, D.W. Johnson Cook Material and Failure Model Parameters Estimation of AISI-1045 Medium Carbon Steel for Metal Forming Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hfaiedh, N.; Peyre, P.; Song, H.; Popa, I.; Ji, V.; Vignal, V. Finite element analysis of laser shock peening of 2050-T8 aluminum alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2015, 70, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoedel, P.; Gkatzogiannis, S.; Ummenhofer, T. Practical aspects of welding residual stress simulation. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 132, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Dong, W.C.; Lu, S.P. Finite element and experiment analysis of welding residual stress in S355J2 steel considering the bainite transformation. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 62, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, W.X.; Dong, H.; Li, T.; Cao, H.Y. Effect of Welding Sequence and Constraint on the Residual Stress and Deformation of Thick Welded Butt Joint Made of Q345qD Steel. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 5966274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, L.; Du, J.G.; Cao, Y.S. Analysis of residual stresses in electron beam welding with filler wire of Ti62A alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D. Influence of deposition sequence on welding residual stress and deformation in an austenitic stainless steel J-groove welded joint. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcis, P.H.P.; Katsumoto, H.; Payares-Asprino, M.C.; Liu, S.; Siewert, T.A. Cruciform fillet welded joint fatigue strength improvements by weld metal phase transformations. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2008, 31, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Z.; Luo, K.Y.; Zhang, Y.K.; Cui, C.Y.; Sun, G.F.; Zhou, J.Z.; Zhang, L.; You, J.; Chen, K.M.; Zhong, J.W. Grain refinement of LY2 aluminum alloy induced by ultra-high plastic strain during multiple laser shock processing impacts. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 3984–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Zhou, J.; Meng, X.; Huang, S. Improvement in Fatigue Performance of Aluminium Alloy Welded Joints by Laser Shock Peening in a Dynamic Strain Aging Temperature Regime. Materials 2016, 9, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Long, Z.; Xing, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, L. The effect of laser shock peening on very high cycle fatigue properties of laser welded 2A60 aluminum alloy joints. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2023, 290, 109537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Pan, X.; He, W.; Liu, P.; An, Z.; Zhou, L. Improving high cycle fatigue performance of gas tungsten arc welded Ti6Al4V titanium alloy by warm laser shock peening. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 149, 106270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeh, S.; Malik, A. Investigation into the effects of laser shock peening as a post treatment to laser impact welding. Mater. Des. 2021, 205, 109701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.Q.; Feng, A.X.; Cao, X.G.; Lin, G.H.; Ronaldo, C.N. Effects of laser non-uniform shock peening on the microstructure and fatigue performance of SUS 304 stainless steel welded joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 2024, 914, 147186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.D.; Guo, W.; Jia, Q.; Chen, G.X.; Chi, J.X.; Zhang, H.Q.; Wu, S.H.; Peng, C.; Peng, P. Effects of laser shock peening on microstructure and mechanical properties of TIG welded alloy 600 joints. Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 2021, 808, 140914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T. Nanoparticles reinforced joints produced using friction stir welding: A review. Eng. Res. Express 2023, 5, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Cui, L.; Luo, S.; Su, H.; Pang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, L.; He, W.; Liang, X. Superior fretting wear resistance of titanium alloys from stable gradient nanostructures induced by laser shock peening. Int. J. Plast. 2025, 188, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Muvvala, G.; Sarkar, S.; Racherla, V.; Nath, A.K. Effect of laser shock peening on microstructural, mechanical and corrosion properties of laser beam welded commercially pure titanium. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 133, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, O.; DeWald, A. An investigation of the peening effects on the residual stresses in friction stir welded 2195 and 7075 aluminum alloy joints. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 4822–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Meng, F.Y.; Lv, X.X.; Liu, H.Y.; Gao, X.X.; Wang, Y.B.; Lu, Y. Improvement of mechanical properties of stainless maraging steel laser weldments by post-weld ageing treatments. Mater. Des. 2012, 40, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.H.; Fisher, J.W.; Prask, H.J.; Gnäupel-Herold, T.; Yen, B.T.; Roy, S. Residual stress modification by post-weld treatment and its beneficial effect on fatigue strength of welded structures. Int. J. Fatigue 2003, 25, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.Y.; Zhang, T.M.; Chen, Y.H.; Lu, J.Z.; Ding, X.Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; Lan, M.; Shen, Y.; Wang, S.L. Effect of laser shock peening on stress corrosion cracking of TC4/2A14 dissimilar metal friction stir welding joints. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.P.; Rigsbee, J.M.; Banas, G.; Elsayed-Ali, H.E. Laser-shock processing effects on surface microstructure and mechanical properties of low carbon steel. Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 1999, 260, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.J.; Huang, Y.J.; Sun, J.F.; Ngan, A.H.W. Strengthening CrFeCoNiMnCu high entropy alloy via laser shock peening. Int. J. Plast. 2022, 154, 103296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashaev, N.; Ushmaev, D.; Ventzke, V.; Klusemann, B.; Fomin, F. On the application of laser shock peening for retardation of surface fatigue cracks in laser beam-welded AA6056. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2020, 43, 1500–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wan, J.; Liu, Y.; Hao, J. Experimental study on fatigue performance of high strength steel welded joints. Thin-Walled Struct. 2018, 131, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



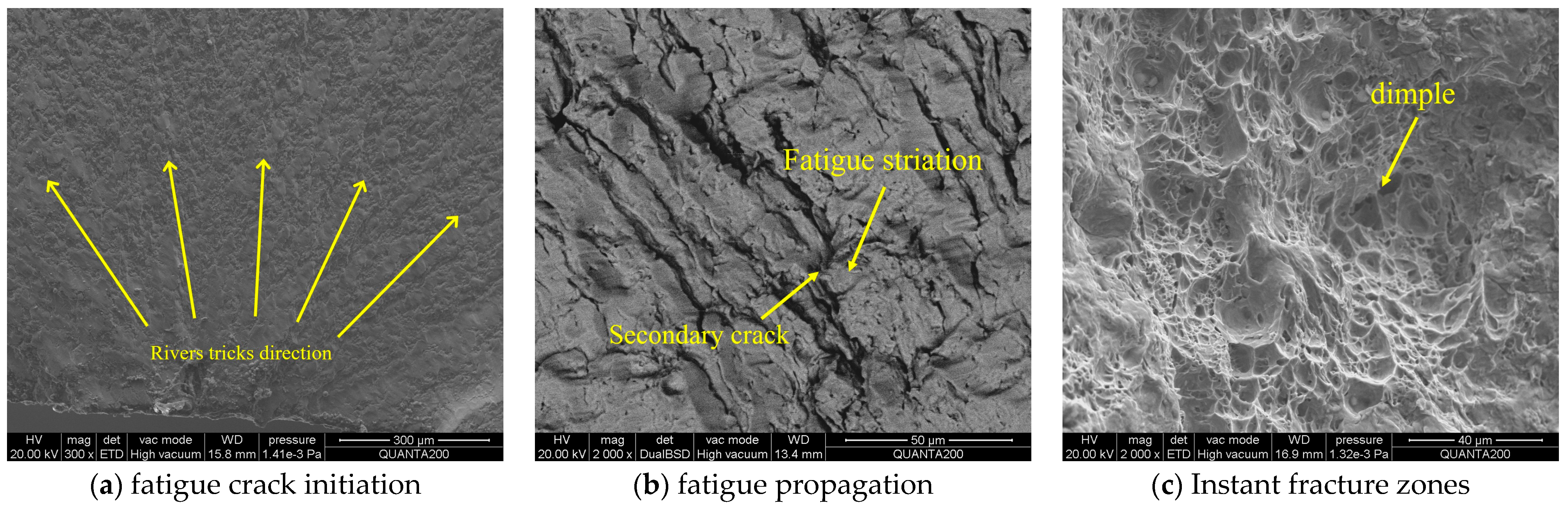
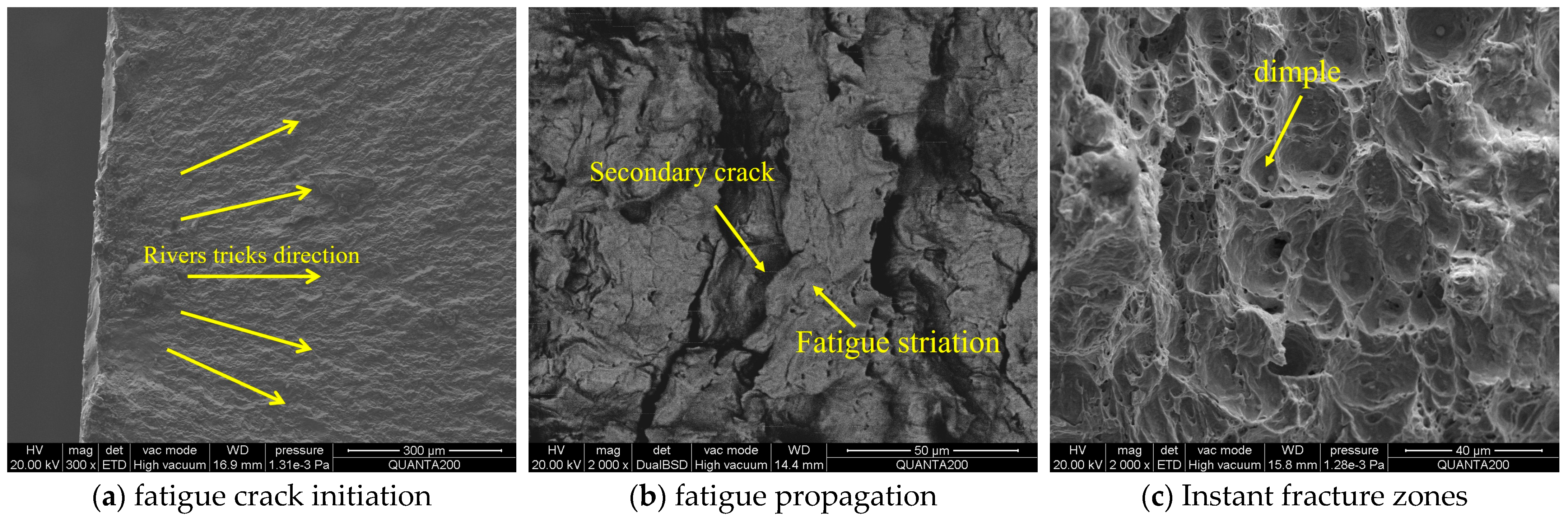
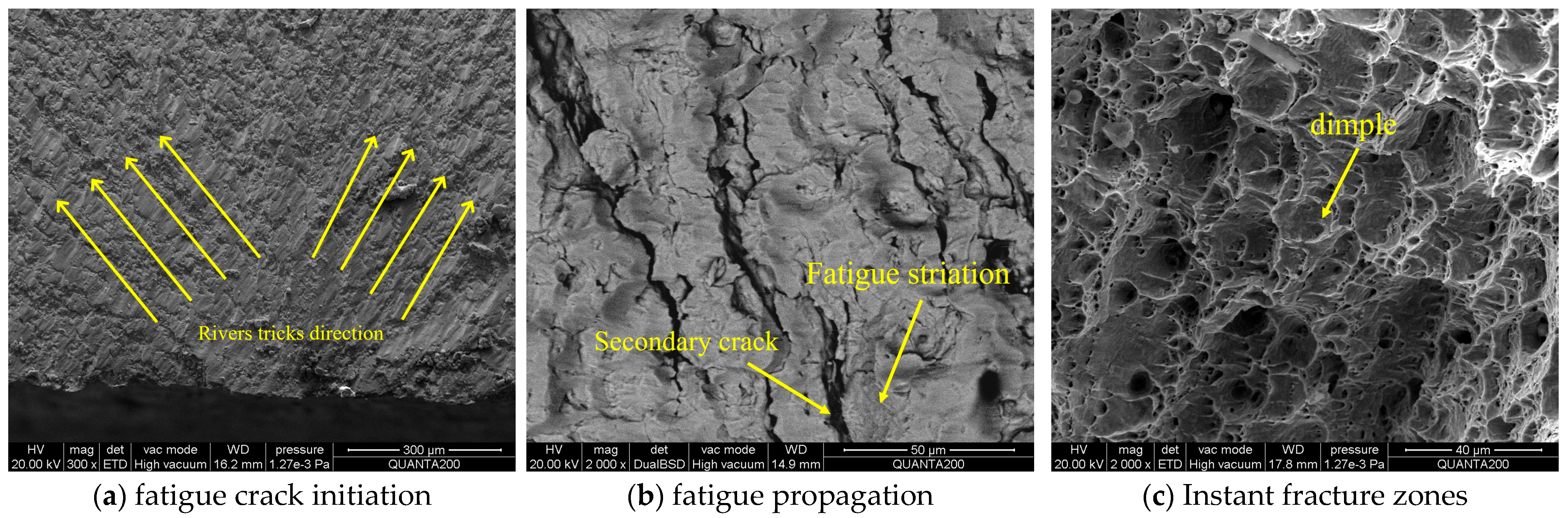
| Steel Grade | Group Type | Specimen Type | Specimen Type | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q355D | A | Base material | 16 | |
| B | Butt joint | ER100S-G | 13 | |
| C | LSP-treated | ER100S-G | 13 |
| Chemical Composition | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Ni | Cr | Mo | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q355D | 0.172 | 1.36 | 0.221 | 0.02 | 0.003 | 0.015 | 0.212 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| ER100S-G | 0.12 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Laser Wavelength (nm) | Laser Energy (J) | Pulse Width (ns) | Repetition Frequency (Hz) | Spot Overlapping Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1064 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 50 |
| Material Type | A (MPa) | B (MPa) | n | C | m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q355D | 304.1 | 771.68 | 0.452 | 0.039 | 1.108 |
| ER100S-G | 720 | 600 | 0.3 | 0.022 | 1.10 |
| Zone | Surface | Before LSP (HV) | After LSP (HV) | Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WZ | Upper | 275 | 290 | 5.45 |
| Lower | 248 | 276 | 11.3 | |
| HAZ | Upper | 175 | 215 | 22.9 |
| Lower | 171 | 206 | 20.5 | |
| BM | Upper | 200 | 223 | 11.5 |
| Lower | 197 | 221 | 12.1 |
| Specimen Number | (MPa) | N (Cycle) | Specimen Number | (MPa) | N (Cycle) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM-1 | 300 | 21,605 | BJ-5 | 250 | 100,213 |
| BM-2 | 290 | 71,149 | BJ-6 | 250 | 81,955 |
| BM-3 | 290 | 107,722 | BJ-7 | 240 | 294,705 |
| BM-4 | 280 | 158,440 | BJ-8 | 240 | 259,075 |
| BM-5 | 275 | 59,549 | BJ-9 | 230 | 651,384 |
| BM-6 | 270 | 98,182 | BJ-10 | 230 | 714,985 |
| BM-7 | 270 | 88,613 | BJ-11 | 220 | 1,000,000 |
| BM-8 | 260 | 293,146 | LSP-1 | 280 | 55,555 |
| BM-9 | 260 | 280,333 | LSP-2 | 280 | 43,008 |
| BM-10 | 250 | 431,595 | LSP-3 | 270 | 92,684 |
| BM-11 | 250 | 441,313 | LSP-4 | 270 | 64,883 |
| BM-12 | 250 | 494,486 | LSP-5 | 260 | 130,271 |
| BM-13 | 245 | 388,979 | LSP-6 | 260 | 168,359 |
| BM-14 | 240 | 1,000,000 | LSP-7 | 250 | 226,085 |
| BJ-1 | 270 | 44,434 | LSP-8 | 250 | 207,562 |
| BJ-2 | 270 | 29,485 | LSP-9 | 240 | 468,575 |
| BJ-3 | 260 | 54,116 | LSP-10 | 240 | 435,489 |
| BJ-4 | 260 | 58,553 | LSP-11 | 230 | 1,000,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, D.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Hou, Y.; Sun, P.; Qu, S. Effect of Laser Shock Peening on the Fatigue Performance of Q355D Steel Butt-Welded Joints. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9080273
You D, Li Y, Li F, Wang J, Hou Y, Sun P, Qu S. Effect of Laser Shock Peening on the Fatigue Performance of Q355D Steel Butt-Welded Joints. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2025; 9(8):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9080273
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Dongdong, Yongkang Li, Fenglei Li, Jianhua Wang, Yi Hou, Pengfei Sun, and Shengguan Qu. 2025. "Effect of Laser Shock Peening on the Fatigue Performance of Q355D Steel Butt-Welded Joints" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 9, no. 8: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9080273
APA StyleYou, D., Li, Y., Li, F., Wang, J., Hou, Y., Sun, P., & Qu, S. (2025). Effect of Laser Shock Peening on the Fatigue Performance of Q355D Steel Butt-Welded Joints. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 9(8), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9080273






