Condition Monitoring in Additive Manufacturing: A Critical Review of Different Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Condition Monitoring Techniques
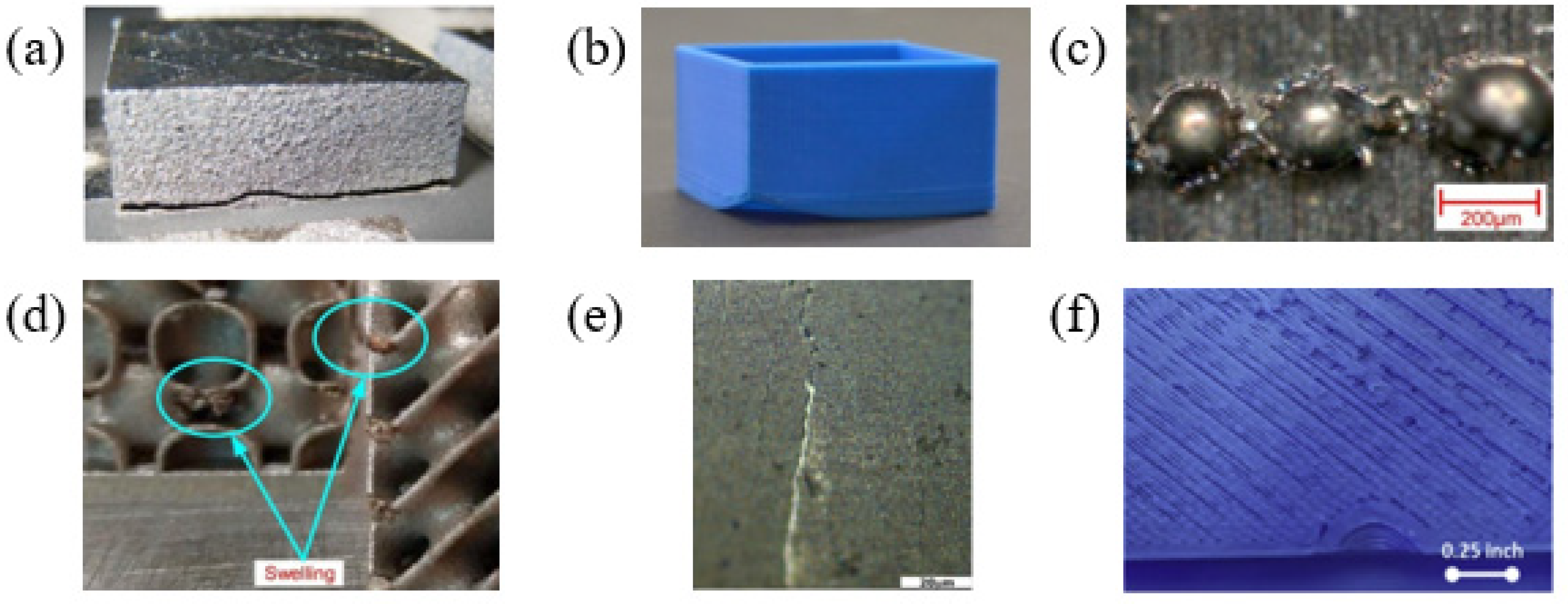
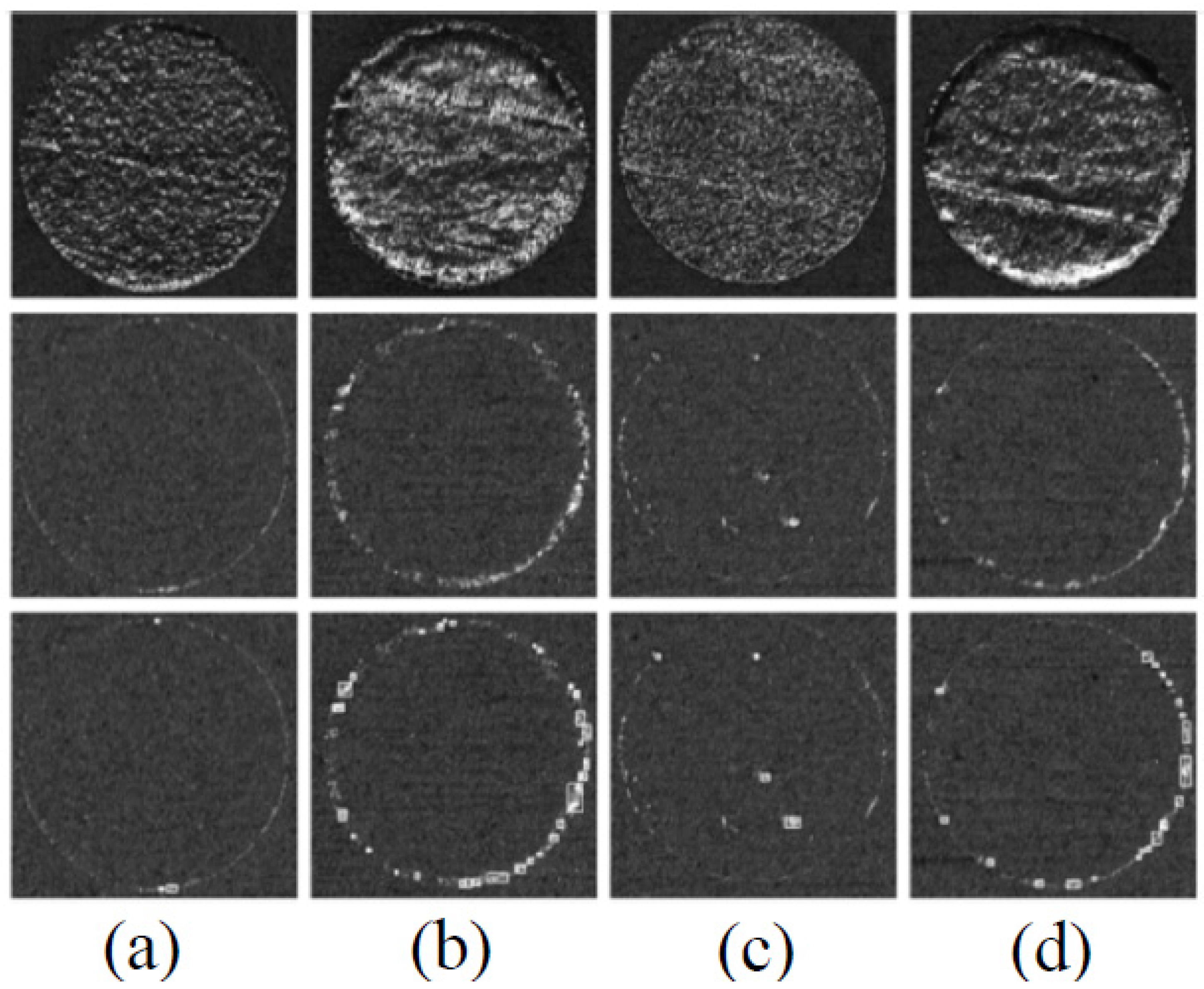
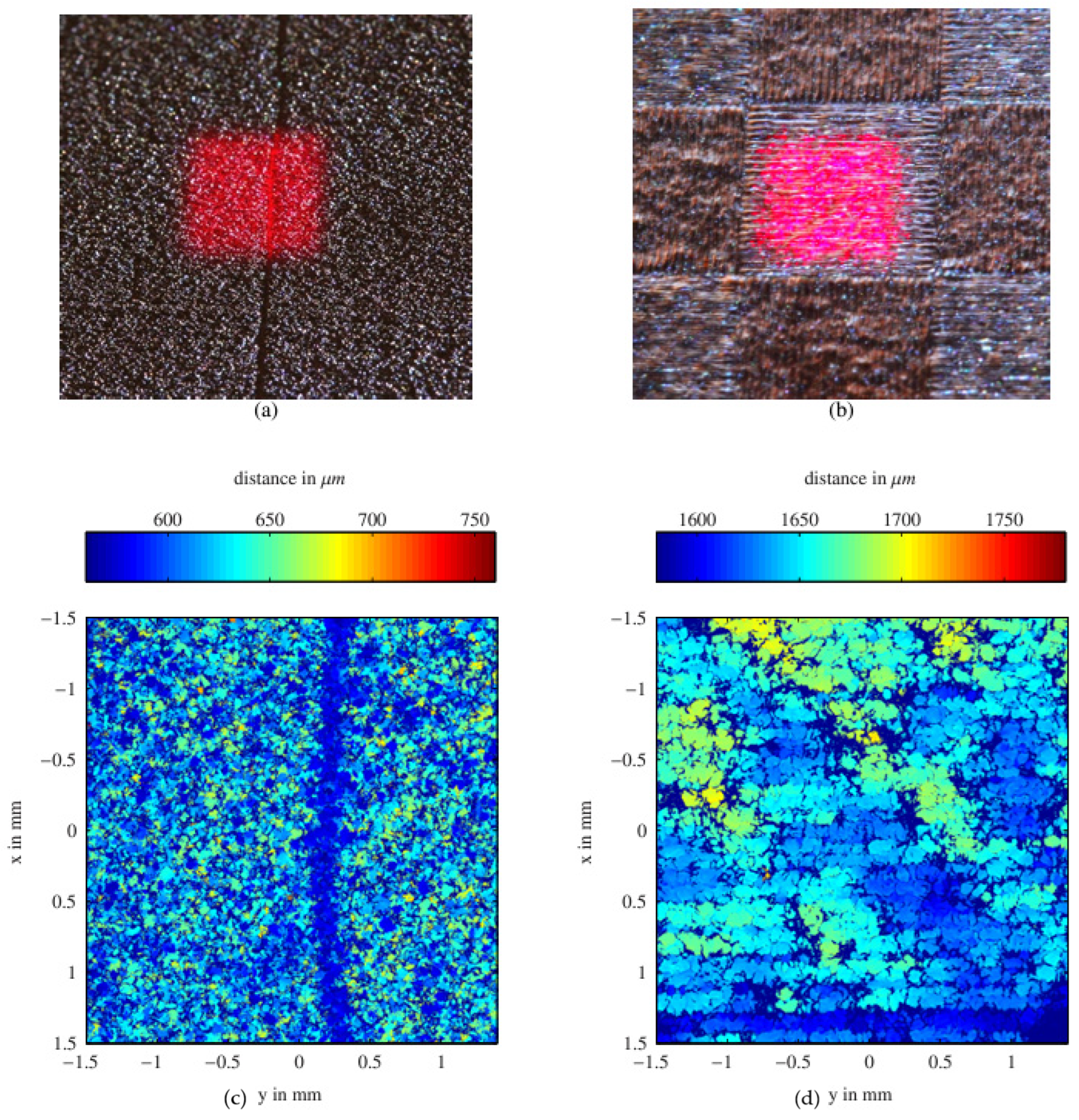
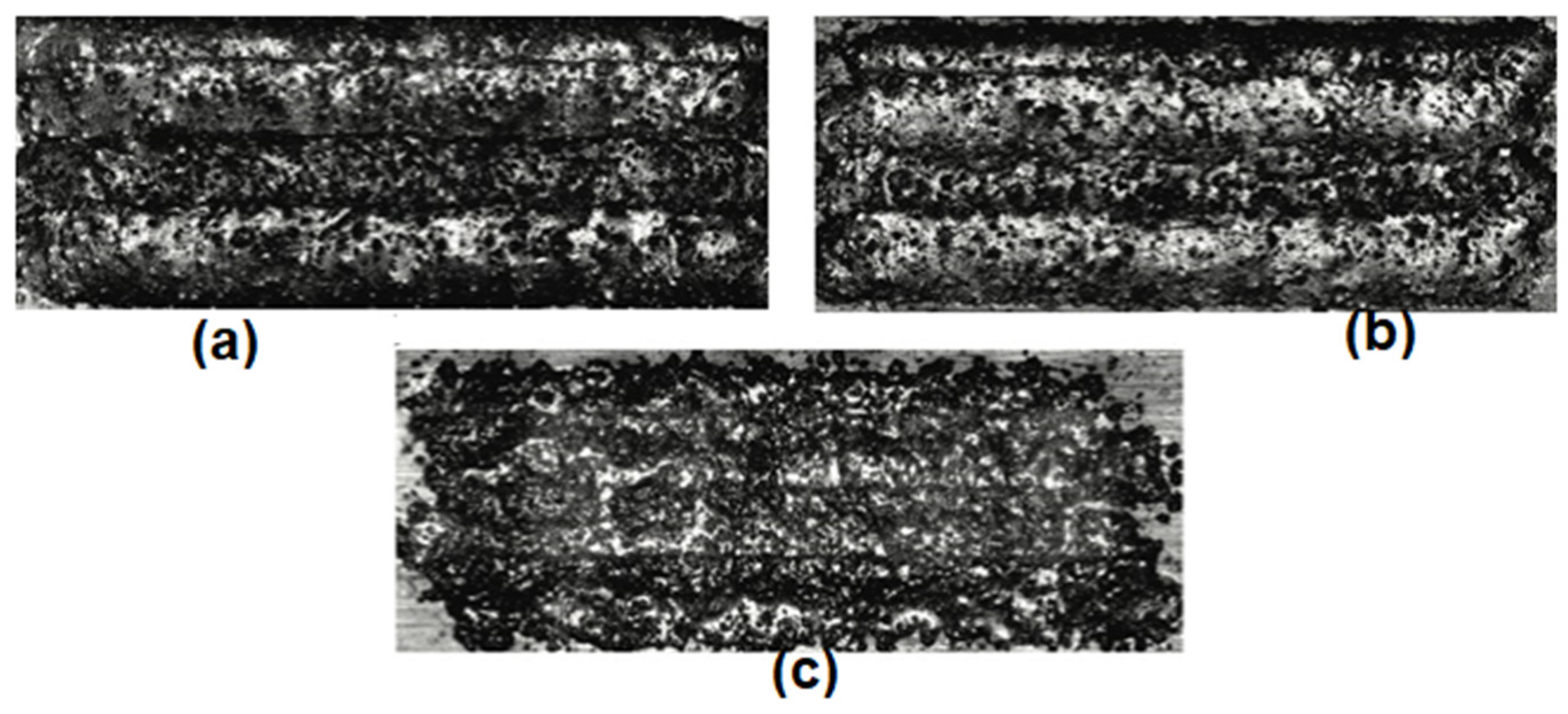
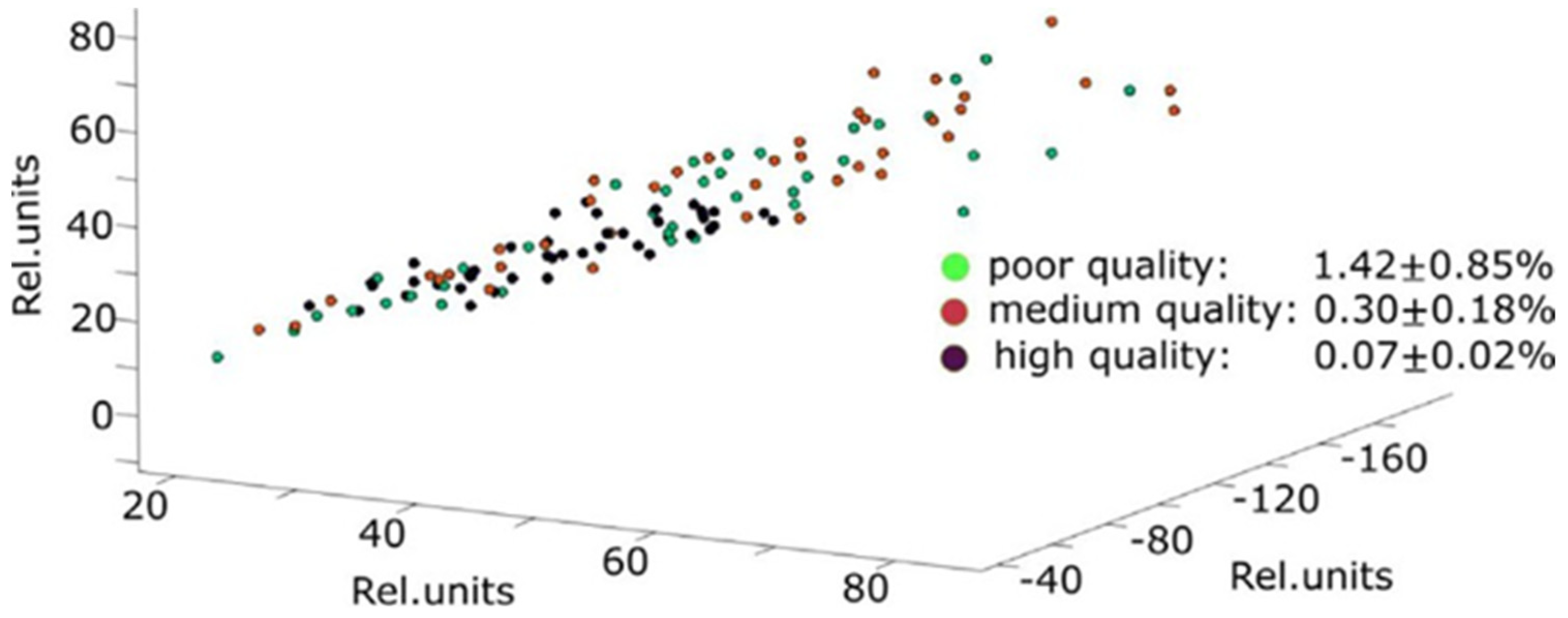
2.1. Optical Techniques
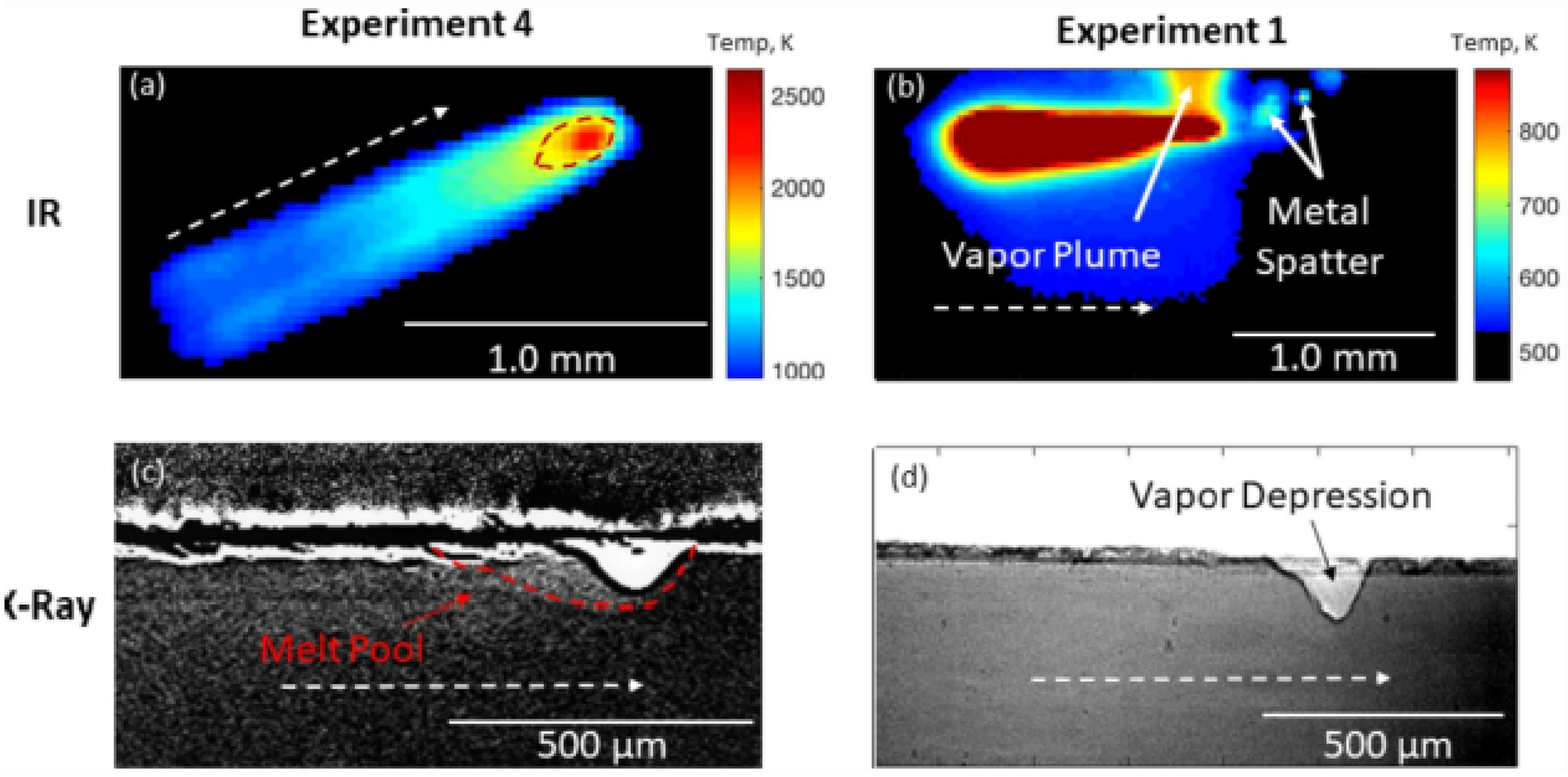
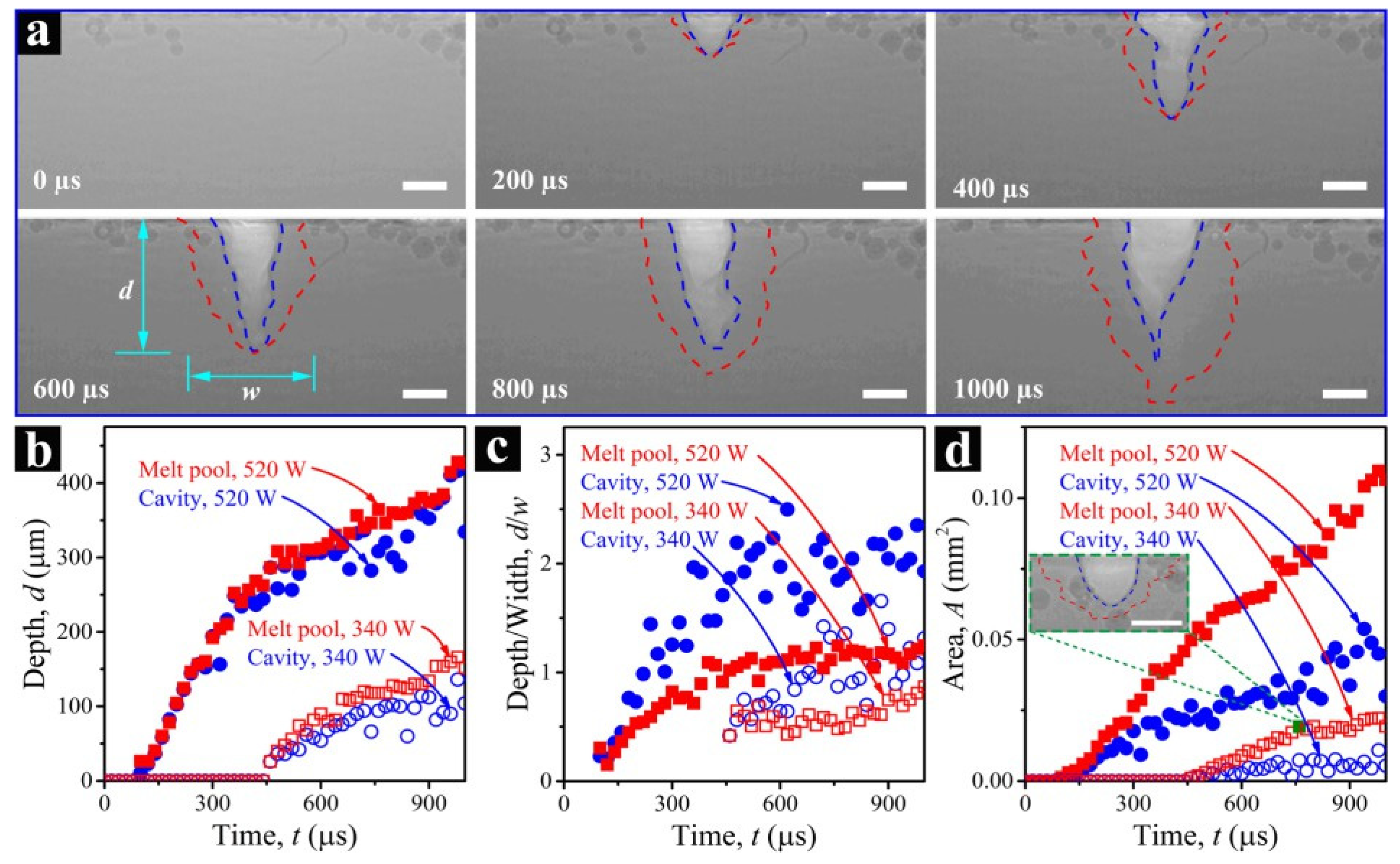
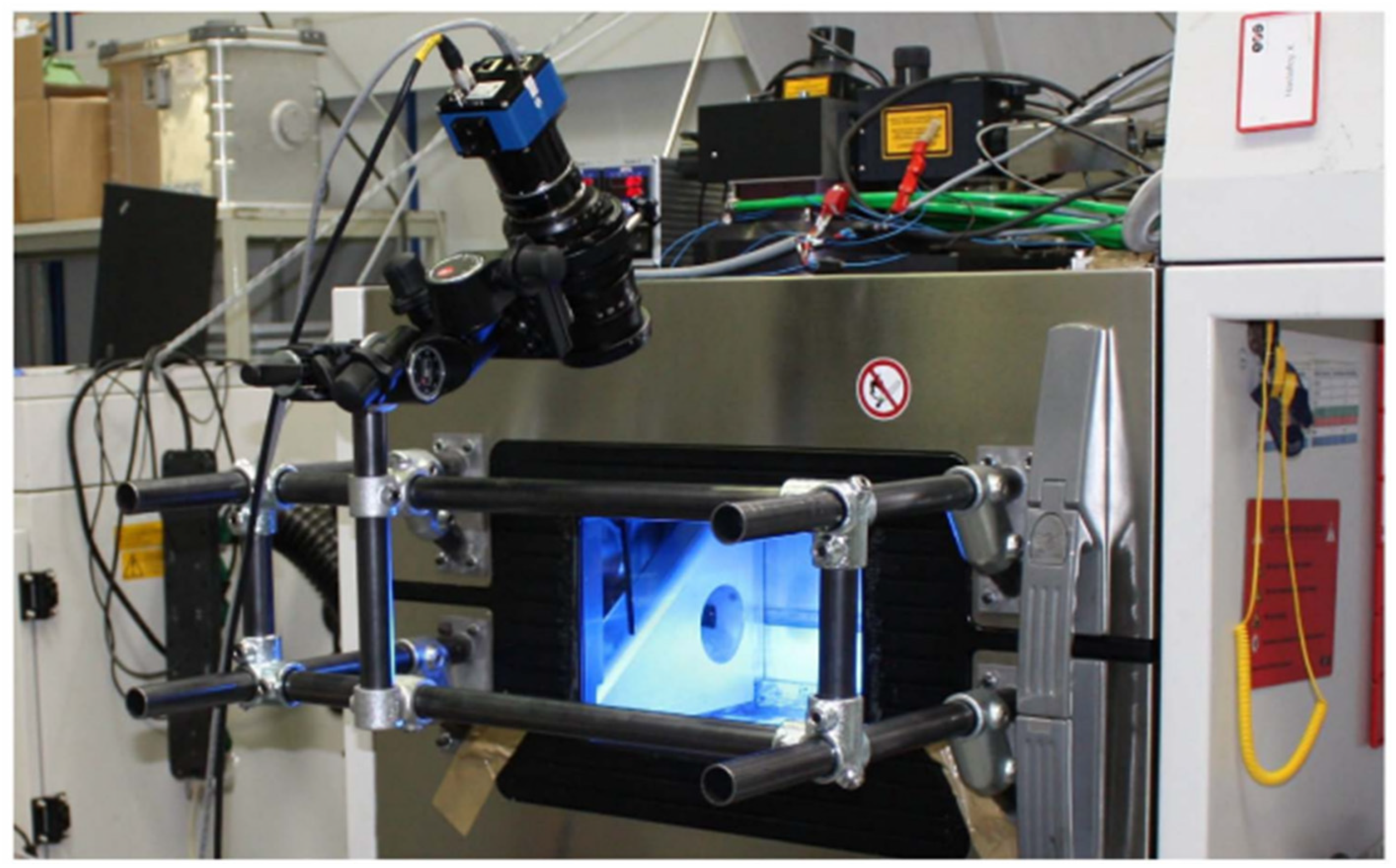
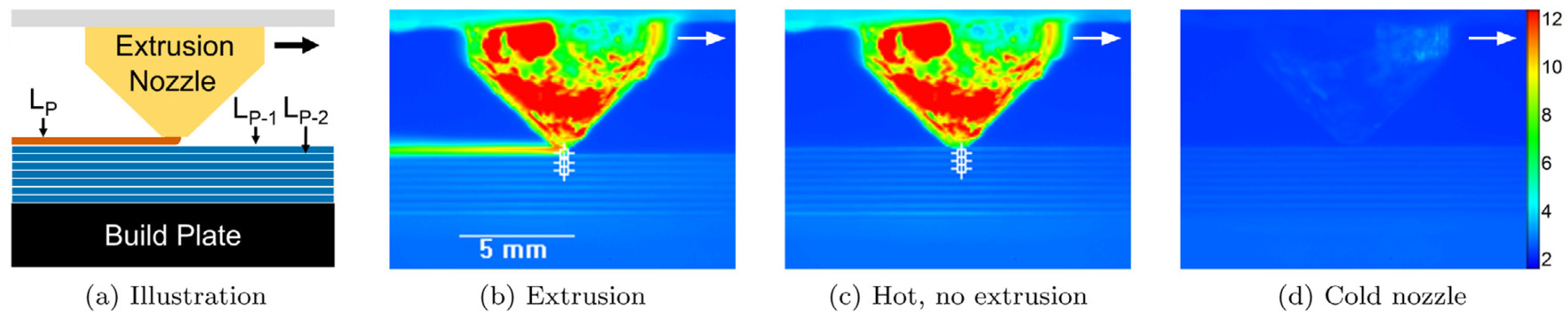
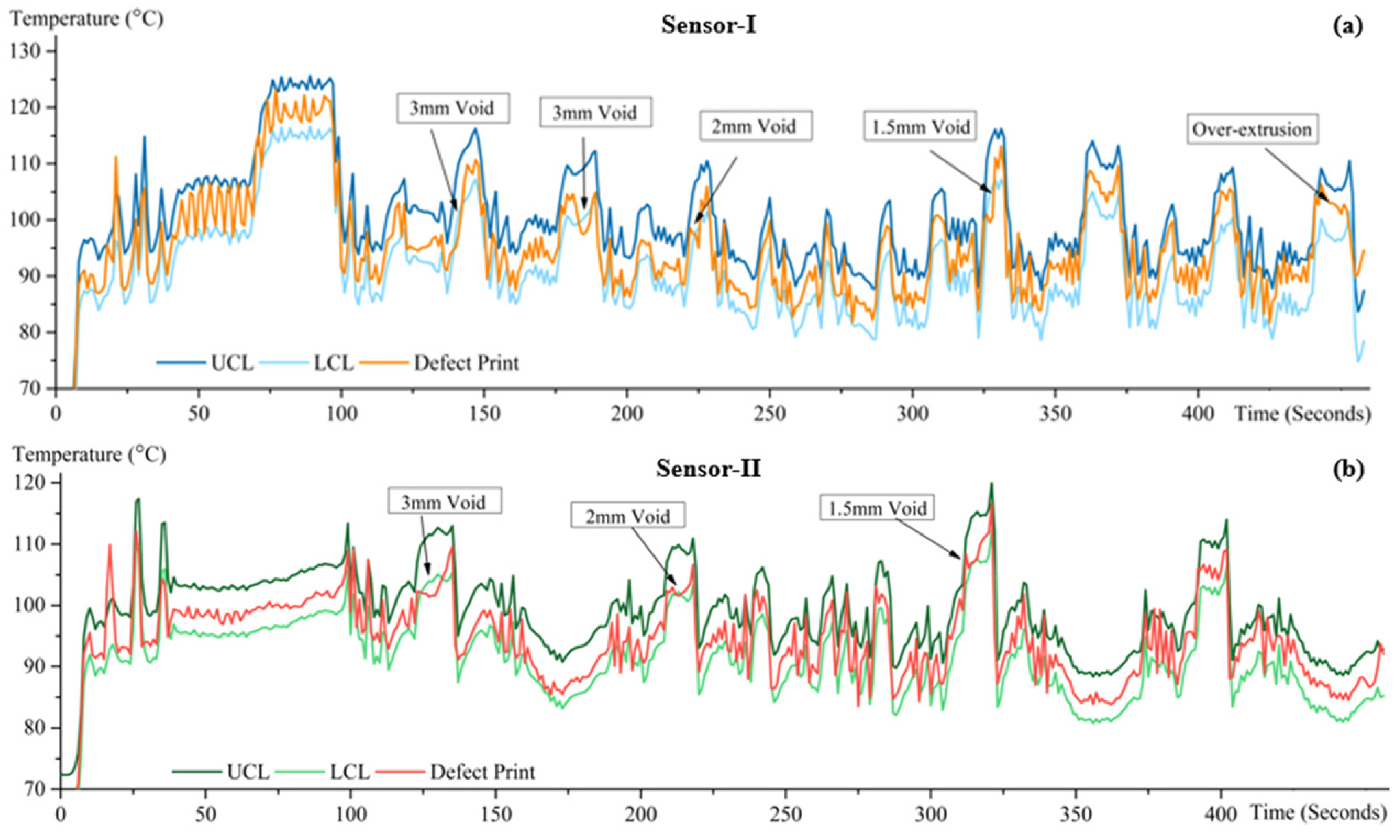
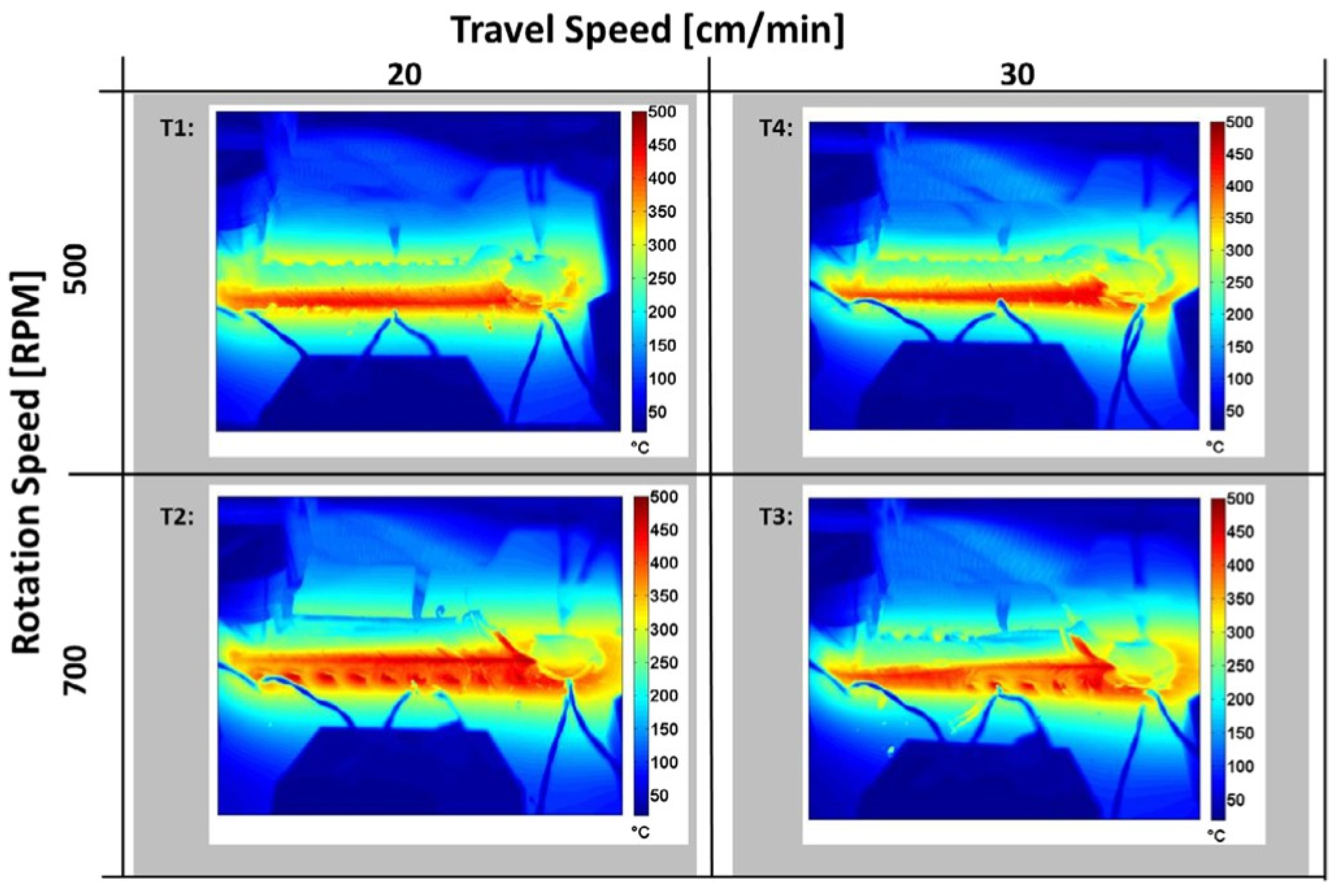
2.2. Thermal Monitoring
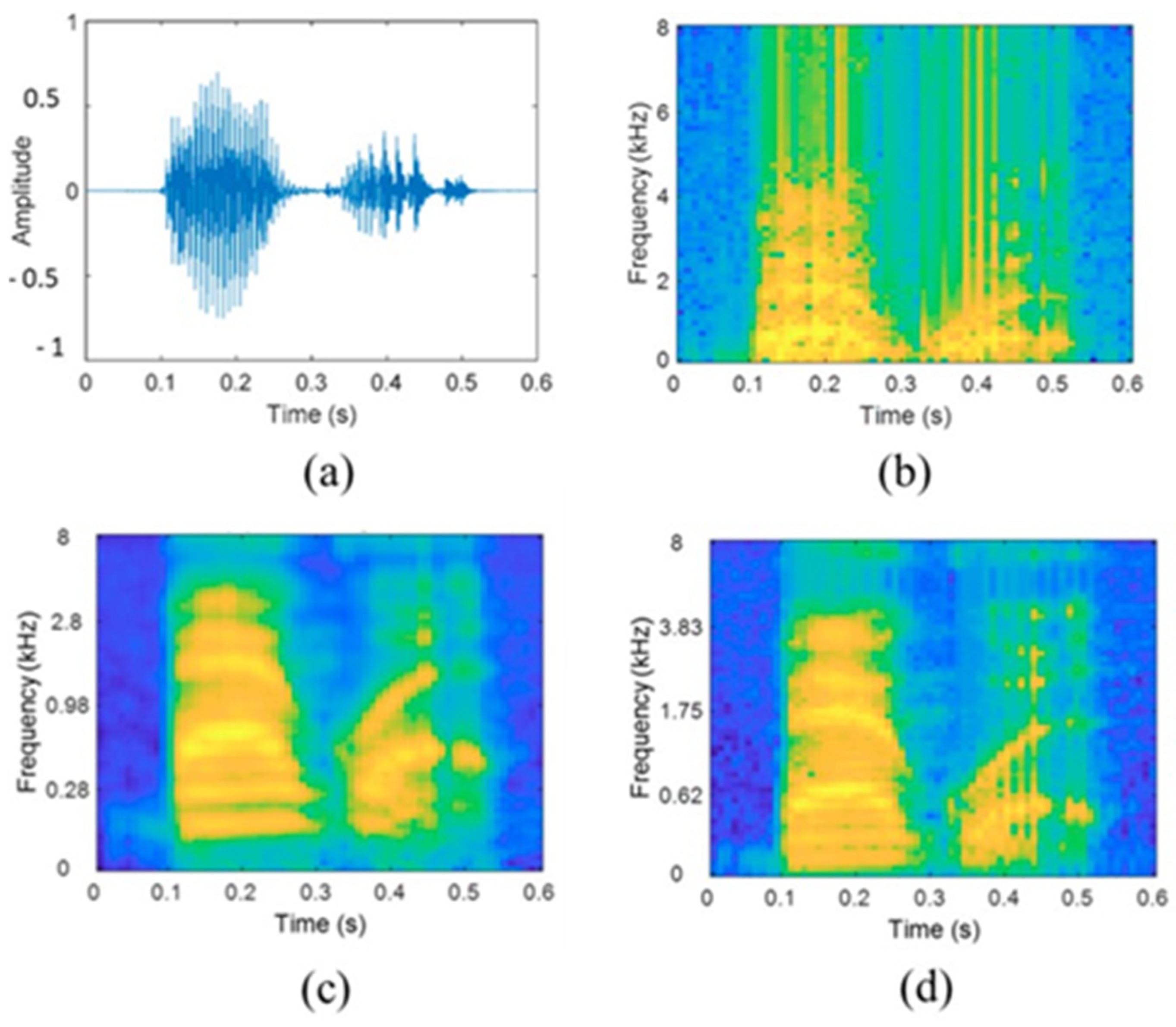
2.3. Acoustics
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Z.; Qin, X.; Li, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wu, Q. Multi-bead overlapping model with varying cross-section profile for robotic game-based additive manufacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 31, 1133–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, G.; Elwany, A. A review on process monitoring and control in metal-based additive manufacturing. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2014, 136, 060801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchik, S.A.; Masinelli, G.; Kenel, C.; Leinenbach, C.; Wasmer, K. Deep learning for in situ and real-time quality monitoring in additive manufacturing using acoustic emission. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 5194–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.W.; Stucker, B. Additive Manufacturing Technologies: 3D Printing, Rapid Prototyping, and Direct Digital Manufacturing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, W.L.; Goh, G.L.; Goh, G.D.; Sheuan, J.T.J.; Yeong, W.Y. Progress and Opportunities for Machine Learning in Materials and Processes of Additive Manufacturing. Adv. Mater. 2024, e2310006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampedro, G.A.R.; Rachmawati, S.M.; Kim, D.-S.; Lee, J.-M. Exploring machine learning-based fault monitoring for polymer-based additive manufacturing: Challenges and opportunities. Sensors 2022, 22, 9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, D.; Magolon, M.; Boer, J.; Elbestawi, M.A.; Mohammadi, M.G. Applications of machine learning in process monitoring and controls of L-PBF additive manufacturing: A review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-C.; Horng, M.-H.; Chang, L.-K.; Hsu, J.-H.; Chang, T.-W.; Hung, J.-C.; Lee, R.-M.; Tsai, M.-C. Deep learning applied to defect detection in powder spreading process of magnetic material additive manufacturing. Materials 2022, 15, 5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Bai, Q. Defect formation mechanisms in selective laser melting: A review. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 30, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Rafi, K.; Gu, H.; Starr, T.; Stucker, B. Analysis of defect generation in Ti–6Al–4V parts made using powder bed fusion additive manufacturing processes. Addit. Manuf. 2014, 1–4, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingarten, C.; Buchbinder, D.; Pirch, N.; Meiners, W.; Wissenbach, K.; Poprawe, R. Formation and reduction of hydrogen porosity during selective laser melting of alsi10mg. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2015, 221, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Pistorius, P.; Beuth, J. Prediction of lack-of-fusion porosity for powder bed fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 14, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuc, L.; Seita, M. A high-resolution and large field-of-view scanner for in-line characterization of powder bed defects during additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 2019, 164, 107562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsmuhlen, J.Z.; Kleszczynski, S.; Witt, G.; Merhof, D. Detection of elevated regions in surface images from laser beam melting processes. In Proceedings of the IECON 2015—41st Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Yokohama, Japan, 9–12 November 2015; p. 15753163. [Google Scholar]
- Mumtaz, K.; Hopkinson, N. Top surface and side roughness of inconel 625 parts processed using selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2009, 15, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, W. Balling behavior of stainless steel and nickel powder during selective laser melting process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 59, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhu, K.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Duan, X. Metal-based additive manu-facturing condition monitoring methods: From measurement to control. ISA Trans. 2022, 120, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Zhao, M.; Di, Y.; Yang, Q.; Lee, J. Assessment of data suitability for machine prognosis using maximum mean discrepancy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 5872–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.; Kim, H.; Ham, M.; Kim, W.; Kim, G.; Cho, J.; Kim, N.; Kim, K. A deep neural network for classification of melt-pool images in metal additive manufacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 31, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Gao, H.; You, Z.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, B. Machine vision-based condition monitoring and fault diagnosis of machine tools using information from machined surface texture: A review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 164, 108068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-C.; Le, M.-Q.; Mogniotte, J.-F.; Capsal, J.-F.; Cottinet, P.-J. Extrusion-based 3D printing of stretchable electronic coating for condition monitoring of suction cups. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, J.; Manoochehri, S. Sensory data fusion using machine learning methods for in-situ defect registration in additive manufacturing: A review. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International IOT, Electronics and Mechatronics Conference (IEMTRONICS), Toronto, ON, Canada, 1–4 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kempen, K.; Thijs, L.; Vrancken, B.; Buls, S.; Humbeeck, J.V.; Kruth, J.-P. Producing crack-free, high density m2 hss parts by selective laser melting: Pre-heating the baseplate. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 12–14 August 2013; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Shen, H.; Fu, J.; Wu, S. Online quality monitoring in mate- rial extrusion additive manufacturing processes based on laser scanning technology. Precis. Eng. 2019, 60, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Zhu, K.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Soon, H.G. The investigation of plume and spatter signatures on melted states in selective laser melting. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 111, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, S.; Tabasi, H.G.; Ivas, T.; Maedar, X.; De Luca, A.; Zweiacker, K.; Wrobel, R.; Jhabvala, J.; Loge, R.E.; Leinenbach, C. Combining alloy and process modification for microcrack mitigation in an additively manufactured ni-base superalloy. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101443. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Law, A.C.C.; Roberson, D.; Kong, Z. Image analysis based closed loop quality control for additive manufacturing with fused filament fabrication. J. Manuf. Syst. 2019, 51, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, B.; Wolff, S.; Parab, N.; Zhao, C.; Lorenzo-Martin, M.C.; Fezzaa, K.; Greco, A.; Sun, T. In situ analysis of laser powder bed fusion using simultaneous high-speed infrared and X-ray imaging. JOM 2021, 73, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Fezzaa, K.; Cunningham, R.W.; Wen, H.; De Carlo, F.; Chen, L.; Rollett, A.D.; Sun, T. Real-time monitoring of laser powder bed fusion process using high-speed X-ray imaging and diffraction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsmühlen, J.Z.; Kleszczynski, S.; Schneider, D.; Witt, G. High resolution imaging for inspection of laser beam melting systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 6–9 May 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neefa, A.; Seyda, V.; Herzog, D.; Emmelmann, C.; Schonleber, M.; Kogel-Hollacher, M. Low coherence interferometry in selective laser melting. Phys. Procedia 2014, 56, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.L.A.; Marussi, S.; Atwood, R.C.; Towrie, M.; Withers, P.J.; Lee, P.D. In situ X-ray imaging of defect and molten pool dynamics in laser additive manufacturing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppala, J.; Migler, K. Infrared thermography of welding zones produced by polymer extrusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. A 2016, 12, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, R.; Lewis, J.; Moore, A. In situ infrared temperature sensing for real-time defect detection in additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 47, 102328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serio, L.; Palumbo, D.; Galietti, U.; Filippis, L.D.; Ludovico, A. Monitoring of the friction stir welding process by means of thermography. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 2016, 31, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombo, G.; Zhang, Y. Acoustic-based machine condition monitoring—Methods and challenges. Eng 2023, 4, 47–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koester, L.W.; Taheri, H.; Bond, L.J.; Faierson, E.J. Acoustic monitoring of additive manufacturing for damage and process condition determination. In AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2102, 020005. [Google Scholar]
- Raffestin, M.; Domashenkov, A.; Bertrand, P.; Faverjon, P.; Courbon, C. Ultrasonic diagnostic for in situ control in metal additive manufacturing. Measurement 2023, 206, 112244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millon, C.; Vanhoye, A.; Obaton, A.-F.; Penot, J.-D. Development of laser ultrasonics inspection for online monitoring of additive manufacturing. Weld. World 2018, 62, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchik, S.; Kenel, C.; Leinenbach, C.; Wasmer, K. Acoustic emission for in situ quality monitoring in additive manufacturing using spectral convolutional neural networks. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 21, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khanafer, K.; Cao, J.; Kokash, H. Condition Monitoring in Additive Manufacturing: A Critical Review of Different Approaches. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8030095
Khanafer K, Cao J, Kokash H. Condition Monitoring in Additive Manufacturing: A Critical Review of Different Approaches. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2024; 8(3):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8030095
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhanafer, Khalil, Junqian Cao, and Hussein Kokash. 2024. "Condition Monitoring in Additive Manufacturing: A Critical Review of Different Approaches" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 8, no. 3: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8030095
APA StyleKhanafer, K., Cao, J., & Kokash, H. (2024). Condition Monitoring in Additive Manufacturing: A Critical Review of Different Approaches. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 8(3), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8030095






