Study of the Law Motion of the Micro-EDM Drilling Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
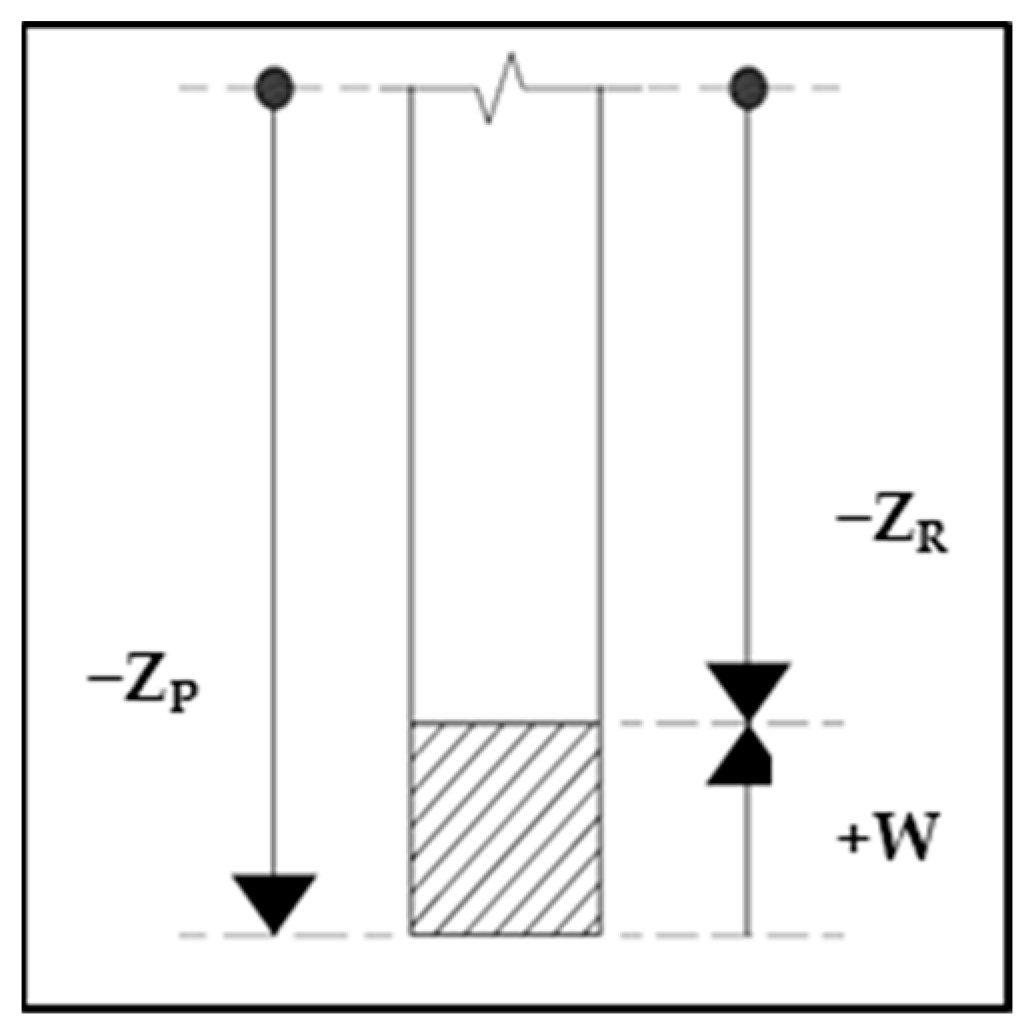
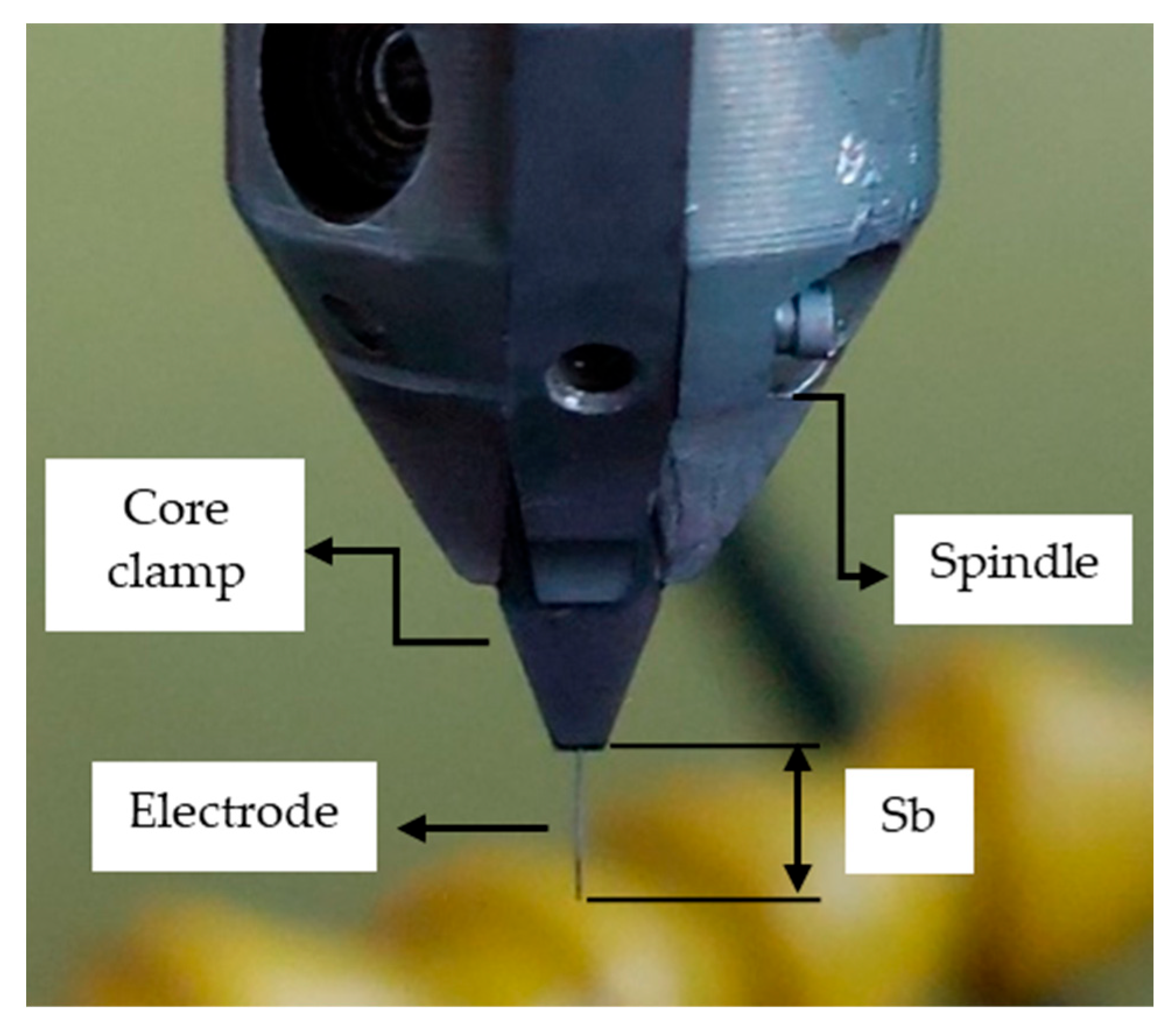
2. Experimental Method
3. Analysis of the Results
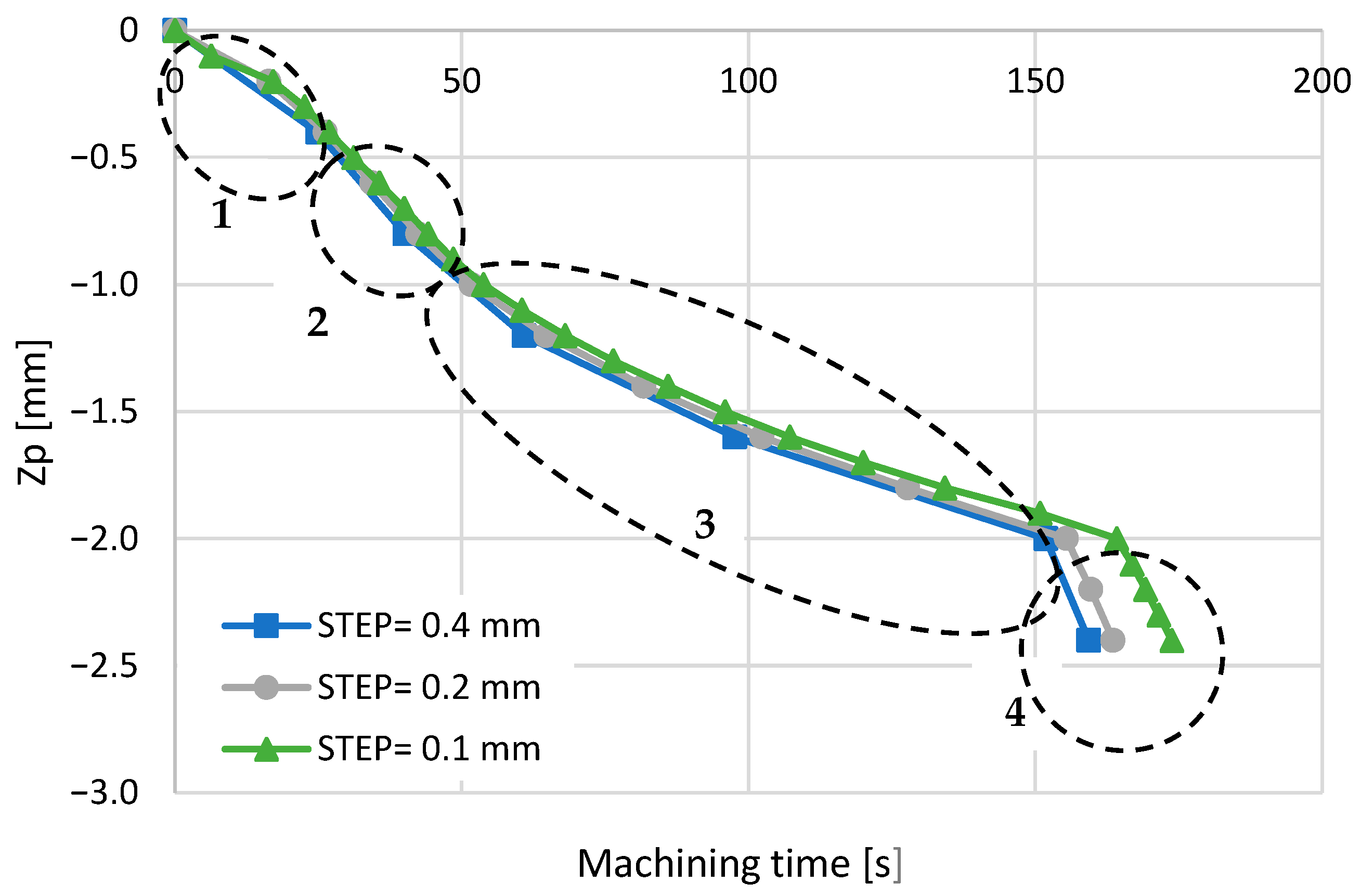
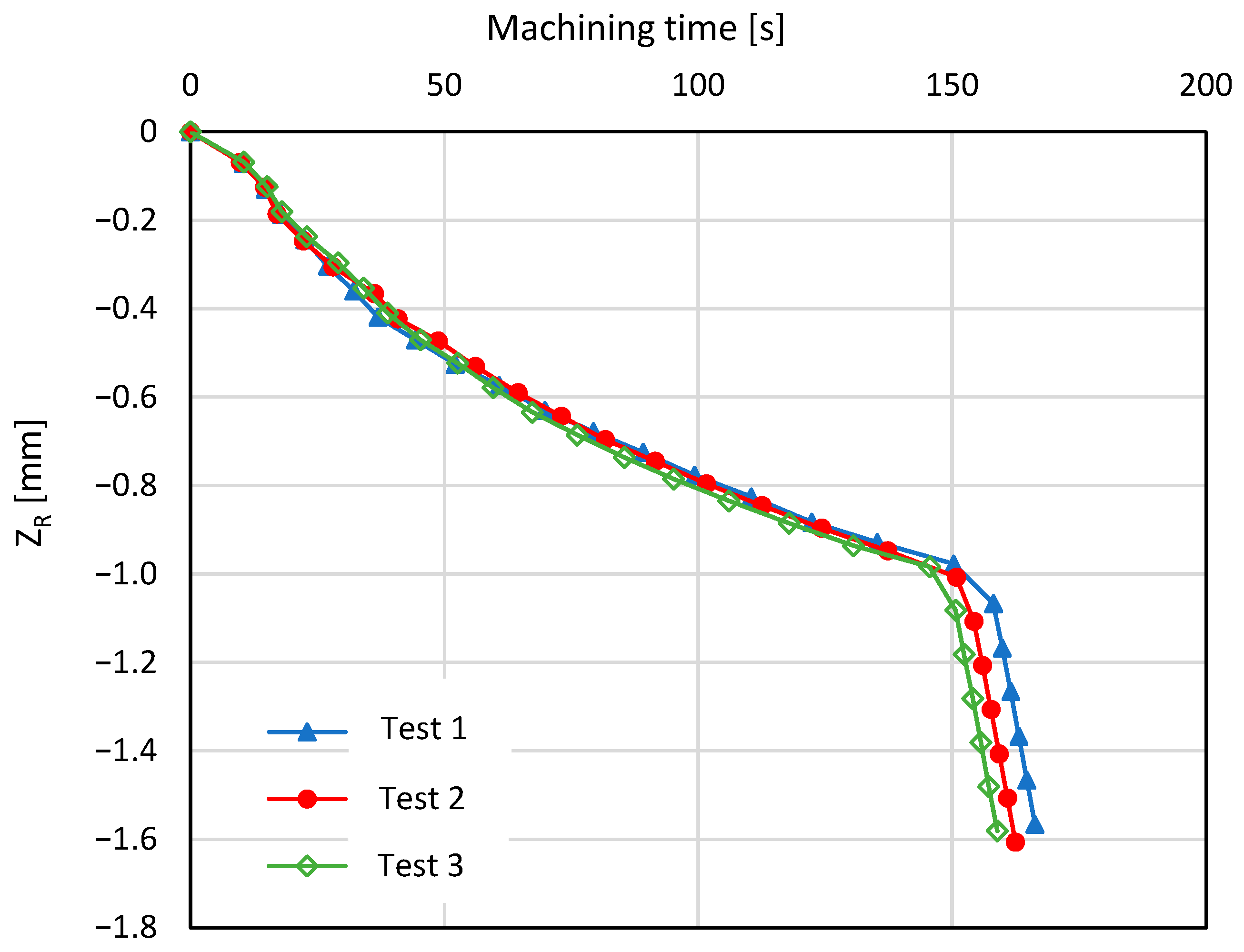
3.1. Validation of the Multistep Procedure
- Initial phase: The electrode undergoes the first stages of erosion of the material, with an almost regular trend of the law of motion.
- Acceleration phase: The process accelerates, probably due to both an increase in the amount of debris in the machining zone and the shape of the tool’s tip, which stabilises after the initial wear.
- Deceleration phase: The machining process decelerates, and the concavity of the curve changes. This deceleration can be attributed to the worsening of the washing conditions using the dielectric with an increase in the depth and an excessive amount of debris in the machining zone.
- Perforation phase: When the electrode erodes, the entire thickness of the plate and the machining time of the steps rapidly decrease because the electrode only performs a finishing action on the sides of the hole. The velocity rapidly increases.
3.2. Analysis of the Case Studies
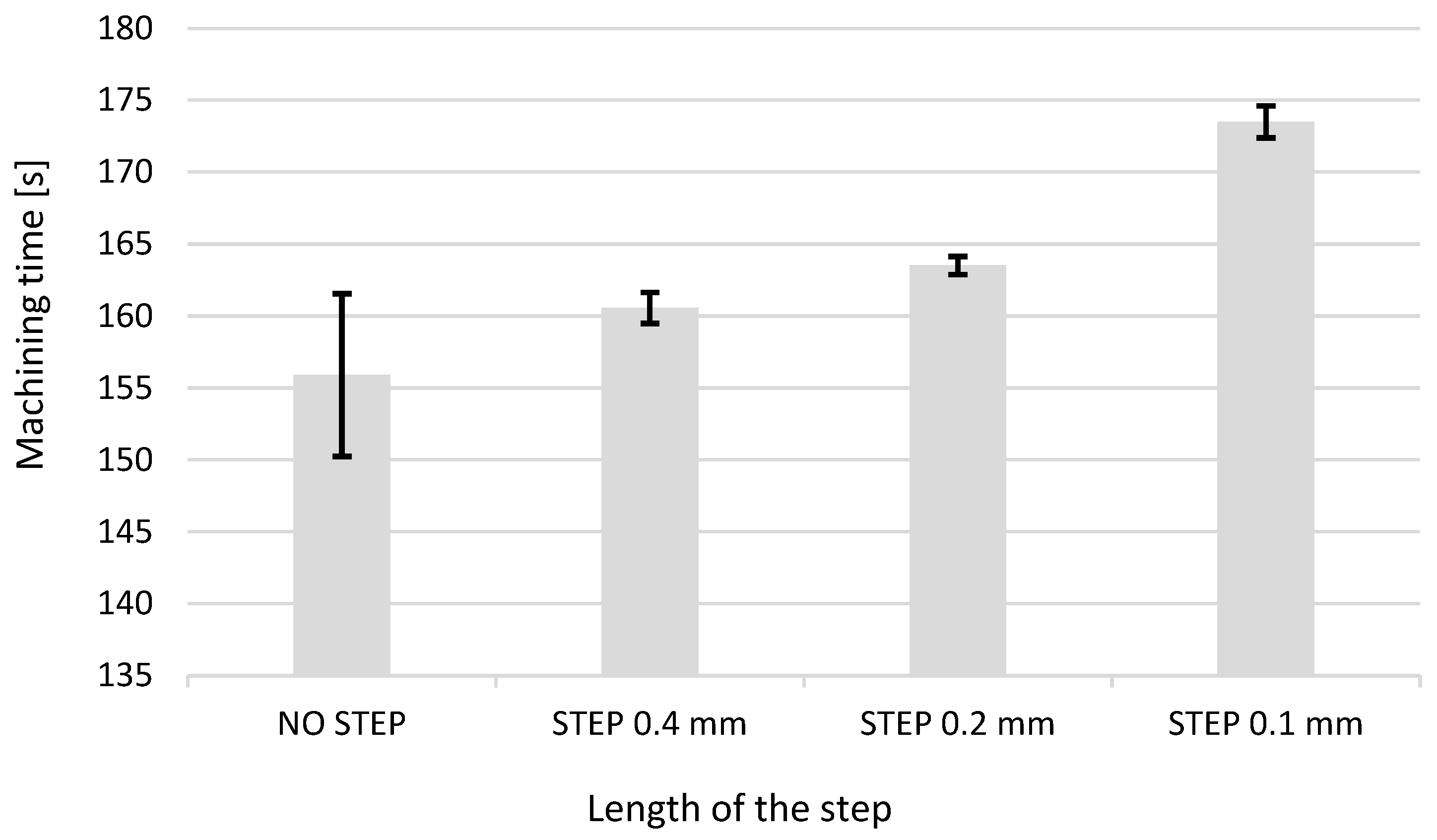
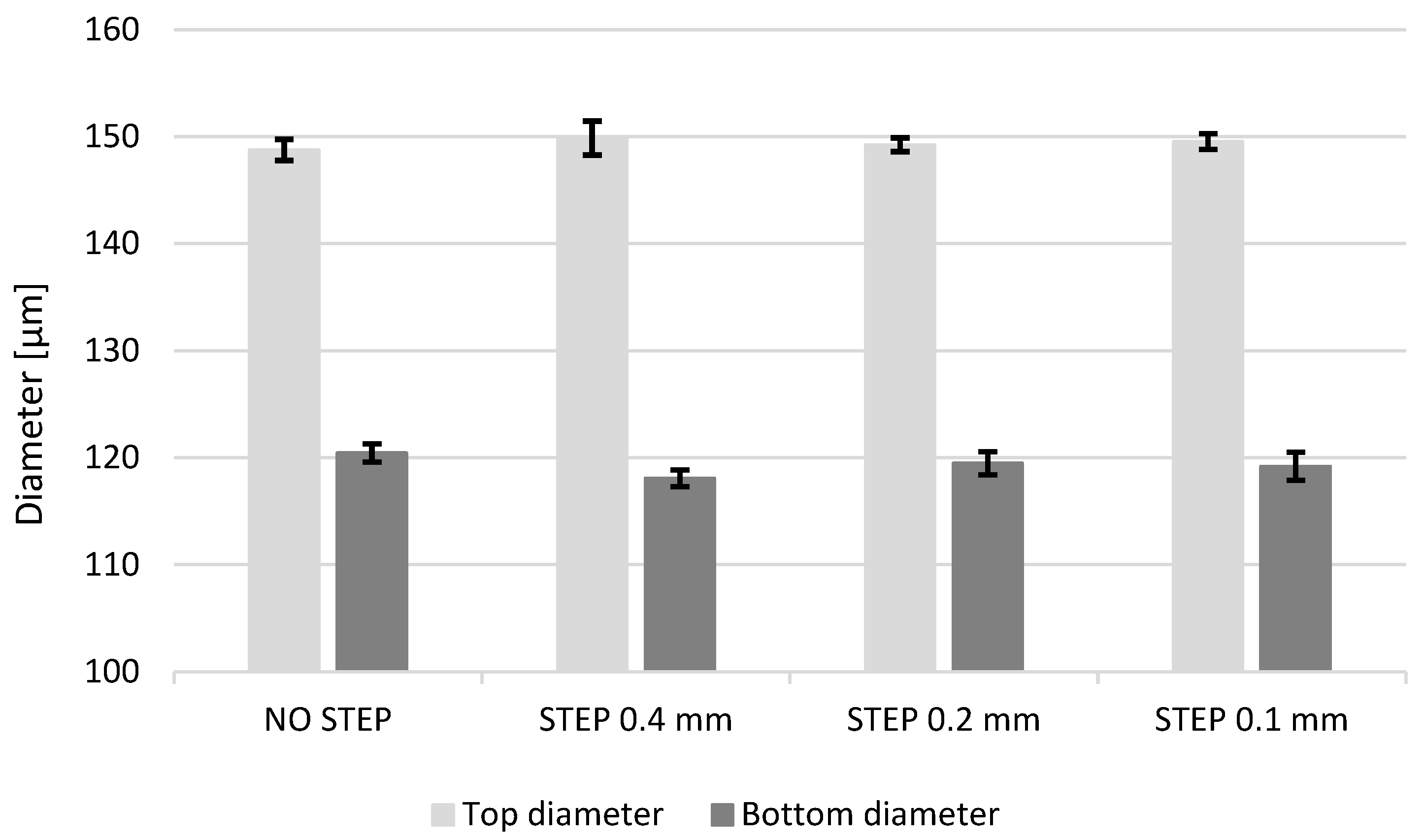
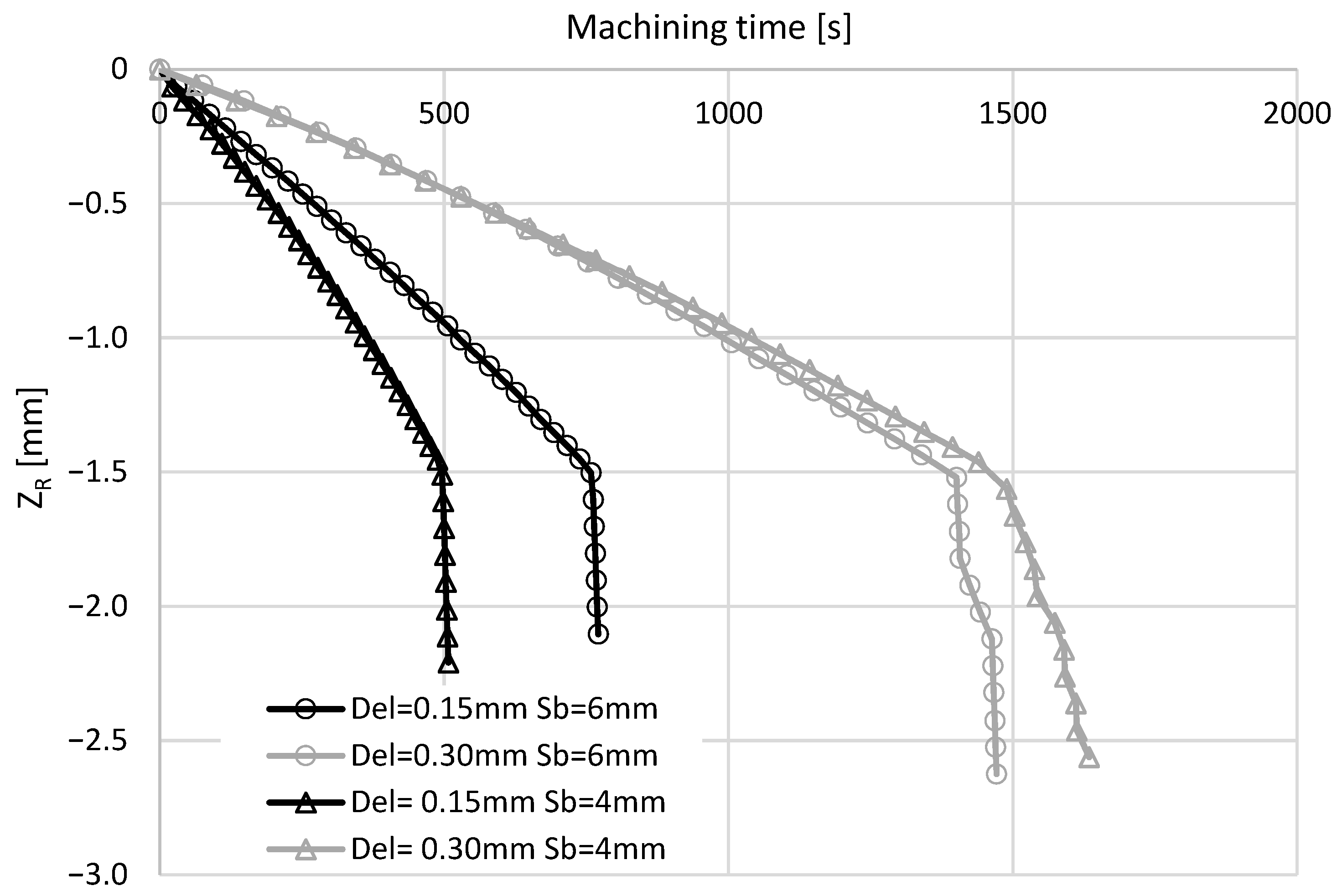
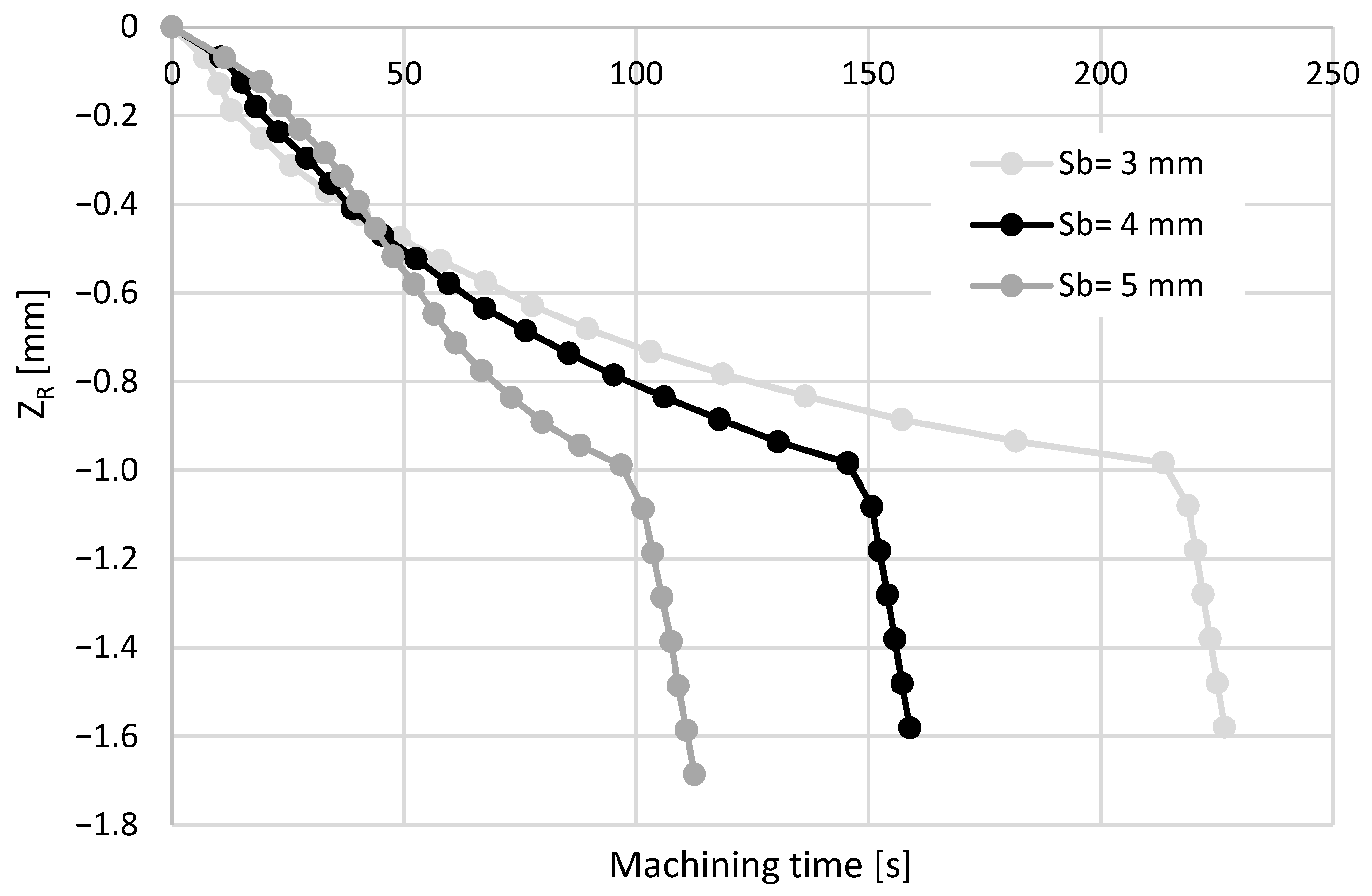
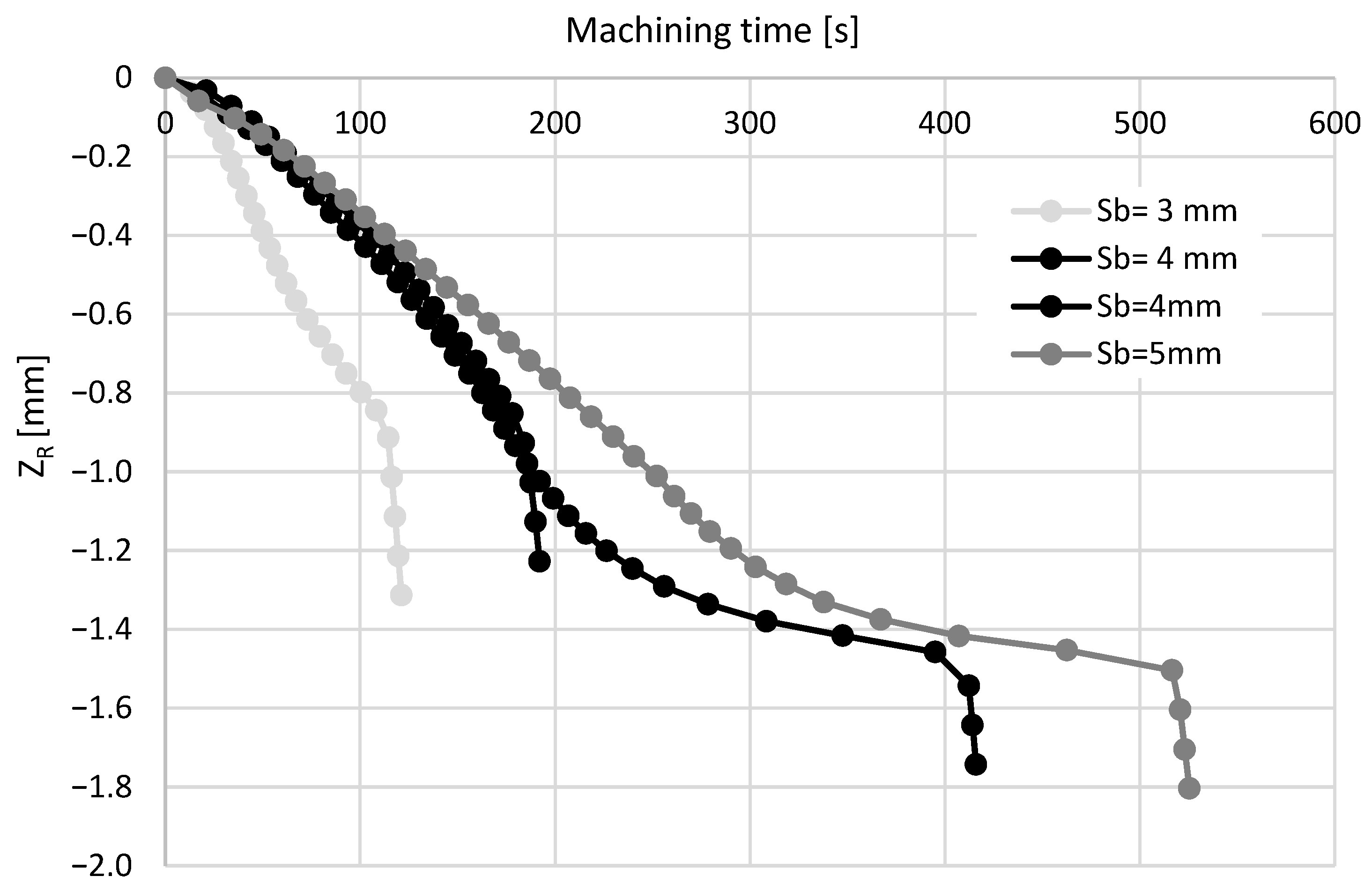
3.2.1. Effects of the Type, Diameter, and Length of the Electrode
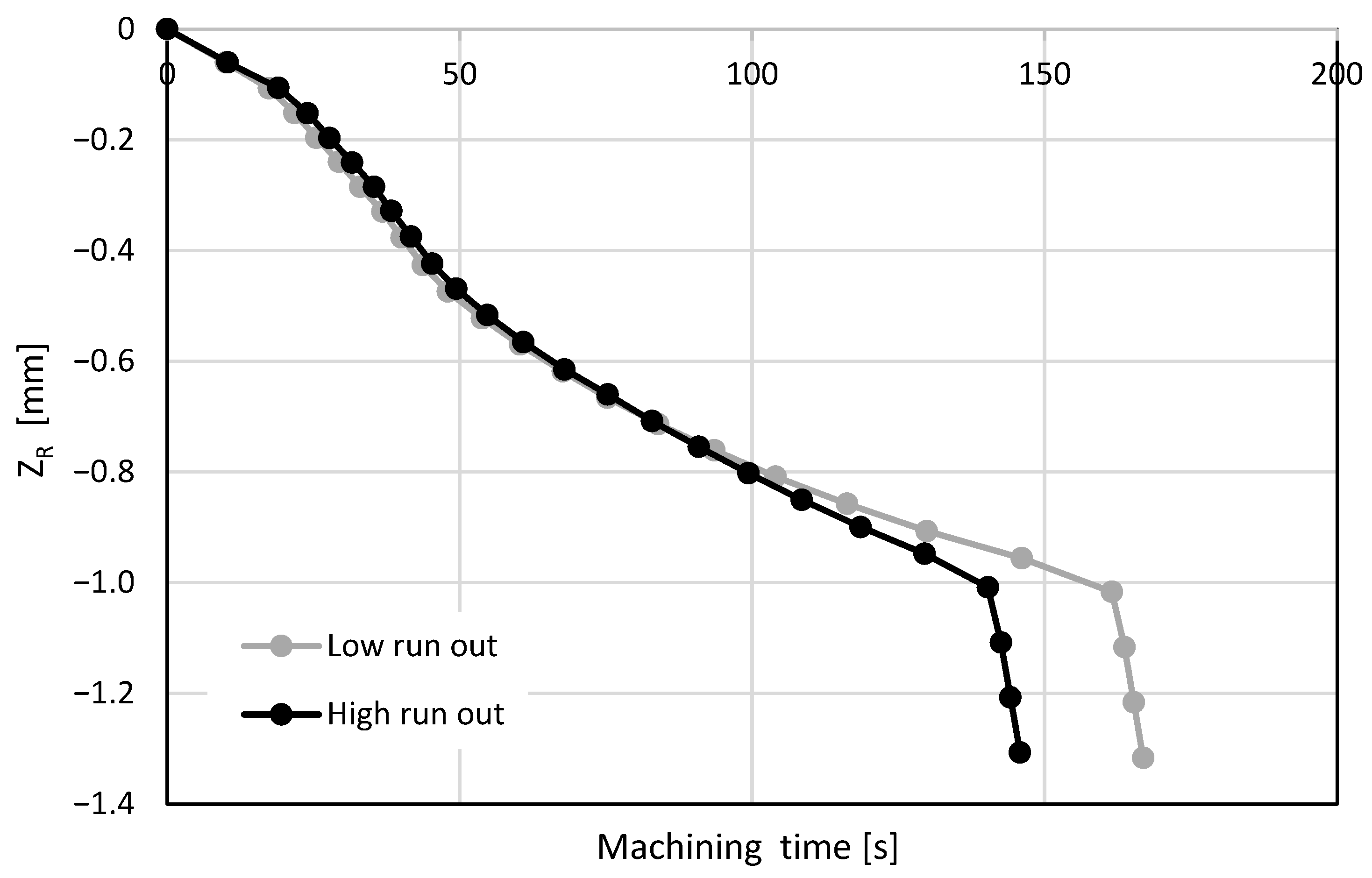
3.2.2. Effect of the Run-Out
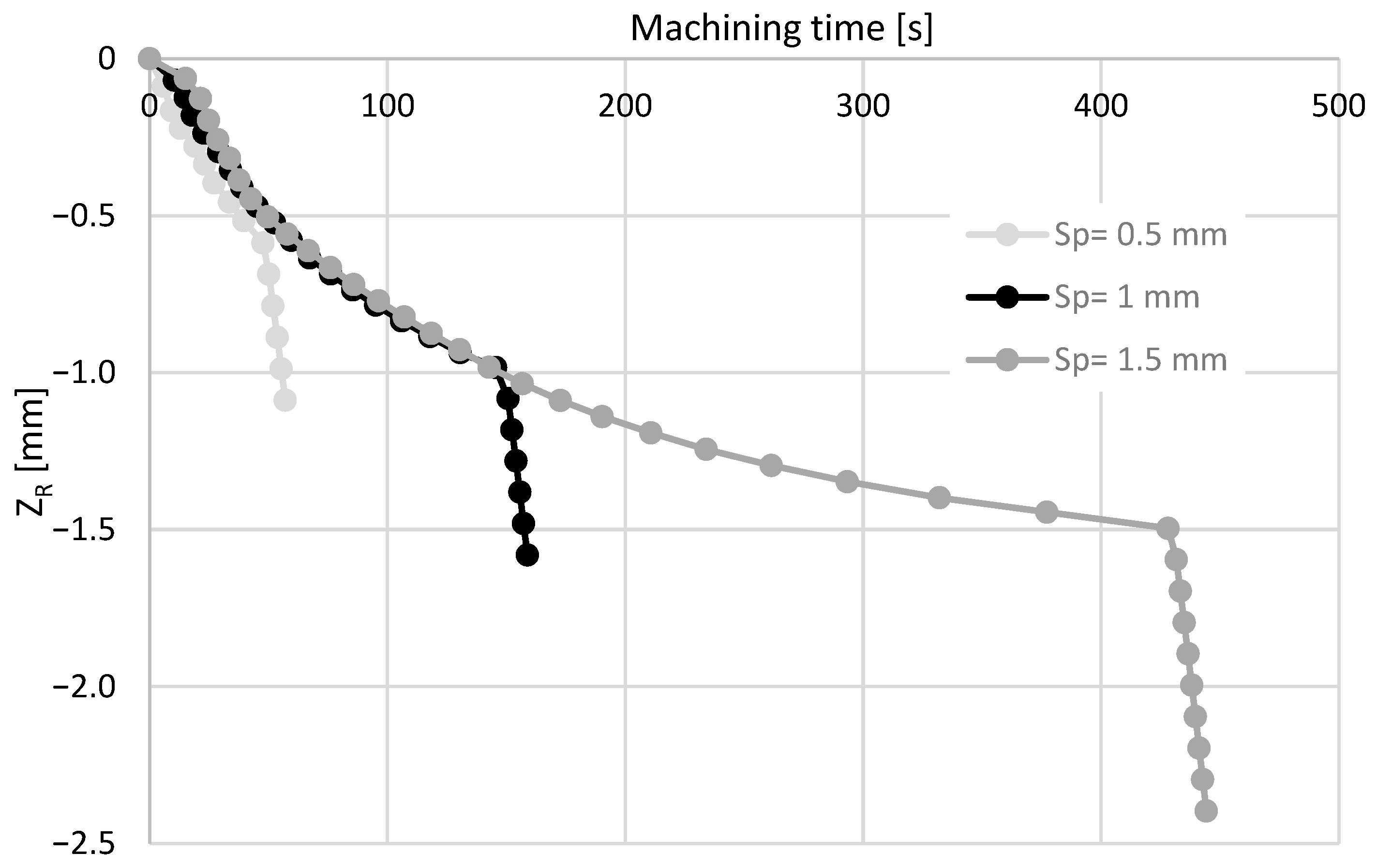
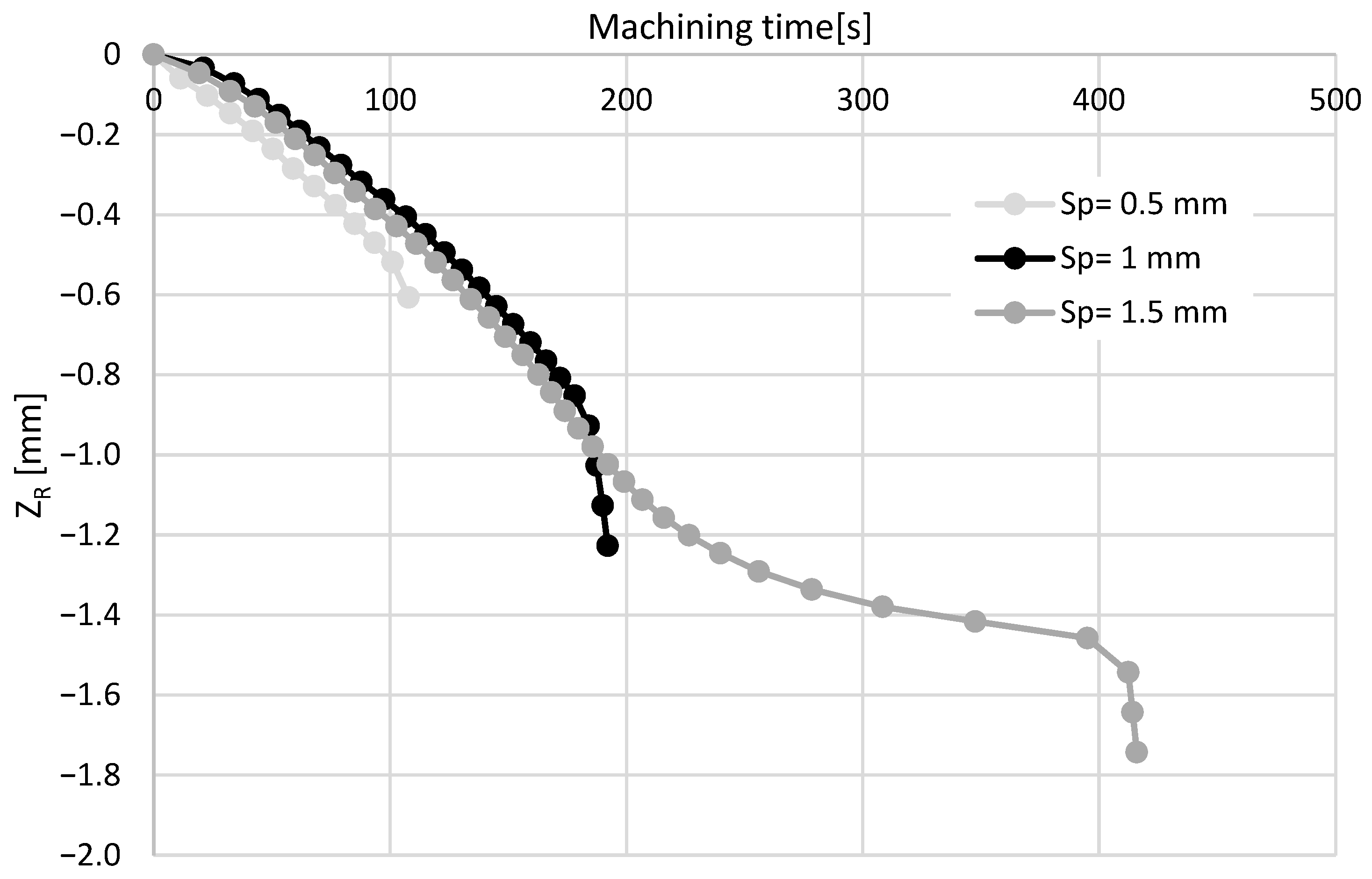
3.2.3. Effect of the Drilling Depth
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, G.; Natsu, W. Realization of micro EDM drilling with high machining speed and accuracy by using mist deionized water jet. Precis. Eng. 2020, 61, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaprasad, P.V.; Panneerselvam, K.; Noorul Haq, A. A comparative assessment in sequential μ drilling of Hastelloy X using laser in combination with μEDM and μECM. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podaný, J.; Tomicek, J. Analysis of small holes manufacturing for optomechanical components. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 20, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.T.; Dimov, S.S.; Bigot, S.; Ivanov, A.; Popov, K. Micro-EDM—Recent developments and research issues. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 149, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.T.; Ivanov, A.; Bigot, S.; Popov, K.; Dimov, S. A study of micro-electro discharge machining electrode wear. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2007, 221, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, G.; Jahan, M.P.; Bhattacharyya, B. Micro-Electrical Discharge Machining Processes Technologies and Applications; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; ISBN 978-981-13-3073-5. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Ambastha, S.; Priyadarshni, N.; Samanta, S. Fabrication of hydrophobic surfaces on Titanium using Micro-EDM ex-hibiting antibacterial properties. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2022, 236, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, F.; Sun, S.; Yang, M.; Shao, J. Surface Integrity of Micro EDM Surface Using Electrodes of Various Diameters. Coatings 2019, 9, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Sharma, A.K.; Goyal, A.; Saxena, K.K.; Negi, P.; Rao, P.C.S. Electric discharge machining performance measures and optimisation: A review. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O.M.; Okka, A. Effect of single and multi-channel electrodes application on EDM fast hole drilling performance. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 51, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niamat, M.; Sarfraz, S.; Aziz, H.; Jahanzaib, M.; Shebab, E.; Ahmad, W.; Hussain, S. Effect of different dielectrics on material removal rate, electrode wear rate and microstructure in EDM. Procedia CIRP 2017, 60, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.H.; Newman, S.T. State of the art electrical discharge machining (EDM). Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2003, 431, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Al Hazza, M.H.F. Performance of electrical discharge machining (EDM) with nickel added dielectric fluid. IIUM Eng. J. 2018, 19, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, N.; Nishant; Mandal, M.C.; Das, S.; Banerjee, T. Comparative study on EDM process parameters optimization using BBO and ACO algorithms. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 6601–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, C.-J.; Chen, R.-Y. Optimization of Electric Discharge Machining Process Using the Response Surface Methodology and Genetic Algorithm Approach. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, R.; Chakraborty, S. Selection of EDM Process Parameters Using Biogeography-Based Optimization Algorithm. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2012, 27, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian, F. Electro discharge machining of Inconel 718 alloy and process optimization. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2020, 35, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouniyar, A.K.; Shandilya, P. Optimization of process parameters in magnetic field assisted powder mixed EDM of aluminium 6061 alloy. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2021, 235, 2998–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, S.; Li, A.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ming, W. Parameters Optimization of Electrical Discharge Machining Process Using Swarm Intelligence: A Review. Metals 2023, 13, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.S.; Rahman, M.; Lim, H.S.; Han, H.; Ravi, N. Investigation of micro-EDM material removal characteristics using single RC-pulse discharges. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 140, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkal, S.U.; Jagtap, P.S. Optimization of Micro EDM Drilling Process Parameters for Titanium Alloy by Rotating Electrode. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 20, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilip, D.G.; Panda, S.; Mathew, J. Characterization and Parametric Optimization of Micro-hole Surfaces in Micro-EDM Drilling on Inconel 718 Superalloy Using Genetic Algorithm. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 5057–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.B.; Masanta, M.; Sarkar, B.R.; Bhattacharyya, B. Investigation of electro-discharge micro-machining of titanium su per alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 41, 1094–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boban, J.; Ahmed, A.; Assam, A. Effect of recirculation zone on debris evacuation during EDM deep hole drilling. Procedia CIRP 2021, 102, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, Y.S.; Song, K.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Chu, C.N. Kerosene Supply Effect on Performance of Aluminum Nitride Micro-Electrical Discharge Machining. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2022, 23, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-W.; Sheu, D.-Y. High aspect ratio of micro hole drilling by Micro-EDM with different cross-section shape micro tools for flushing process. Procedia CIRP 2020, 95, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Luan, J.; Zhao, F.; Guo, D. High aspect ratio micro-hole drilling aided with ultrasonic vibration and planetary movement of electrode by micro-EDM. CIRP Ann. 2009, 58, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yin, Z.; Yu, D.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Dai, C.; Zhang, K. Experimental research and multi-objective optimization of ultrasonic vibration–assisted EDM for Ti6Al4V micro-holes. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 127, 3413–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yin, Z.; Dai, C.; Cao, Z.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, K. The effect of ultrasonic amplitude on the performance of ultrasonic vibration-assisted EDM micro-hole machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 122, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, K.; Sun, Q.; Zhan, Q.; Li, H. A novel EDM method using longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic vibration (LTV) electrodes to improve machining performance for micro-holes. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 102, 31–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Natsu, W.; Yu, Z. Elucidation of gap area phenomenon in micro EDM drilling through direct observation. Procedia CIRP 2020, 95, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Dong, C. Effect of Electrode Size on the Performances of Micro-EDM. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Process Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Polarity | - |
| Width (µs) | 1 |
| Frequency (kHz) | 165 |
| Current | 100 |
| Voltage (V) | 170 |
| Gain | 50 |
| Gap (%) | 70 |
| Energy | 105 |
| Regulation | 01-01 |
| Parameter | |
|---|---|
| Electrode material | Tungsten carbide |
| Workpiece material | Ti-6Al-4V |
| Dielectric | Hydrocarbon oil |
| Internal washing pressure | 30 bar |
| EDM process parameters | Finishing (see Table 1) |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Length of the electrode (Sb) (mm) | 2–3–4–5–6 |
| Run-out (µm) | 5–25 |
| Workpiece thickness (Sp) (mm_ | 0.5–1–1.5 |
| Descent stroke of the electrode (mm) | 1.2–2.4–3.6 |
| Diameter (µm) and type of the electrode | 100 cylinder 150 cylinder and tubular 300 cylinder and tubular |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pellegrini, G.; Ravasio, C. Study of the Law Motion of the Micro-EDM Drilling Process. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7050165
Pellegrini G, Ravasio C. Study of the Law Motion of the Micro-EDM Drilling Process. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2023; 7(5):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7050165
Chicago/Turabian StylePellegrini, Giuseppe, and Chiara Ravasio. 2023. "Study of the Law Motion of the Micro-EDM Drilling Process" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 7, no. 5: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7050165
APA StylePellegrini, G., & Ravasio, C. (2023). Study of the Law Motion of the Micro-EDM Drilling Process. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 7(5), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7050165







