Experimental Investigation on the Cutting of Additively Manufactured Ti6Al4V with Wire-EDM and the Analytical Modelling of Cutting Speed and Surface Roughness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Artefacts and Production
2.2. Design of Experiment (DoE)
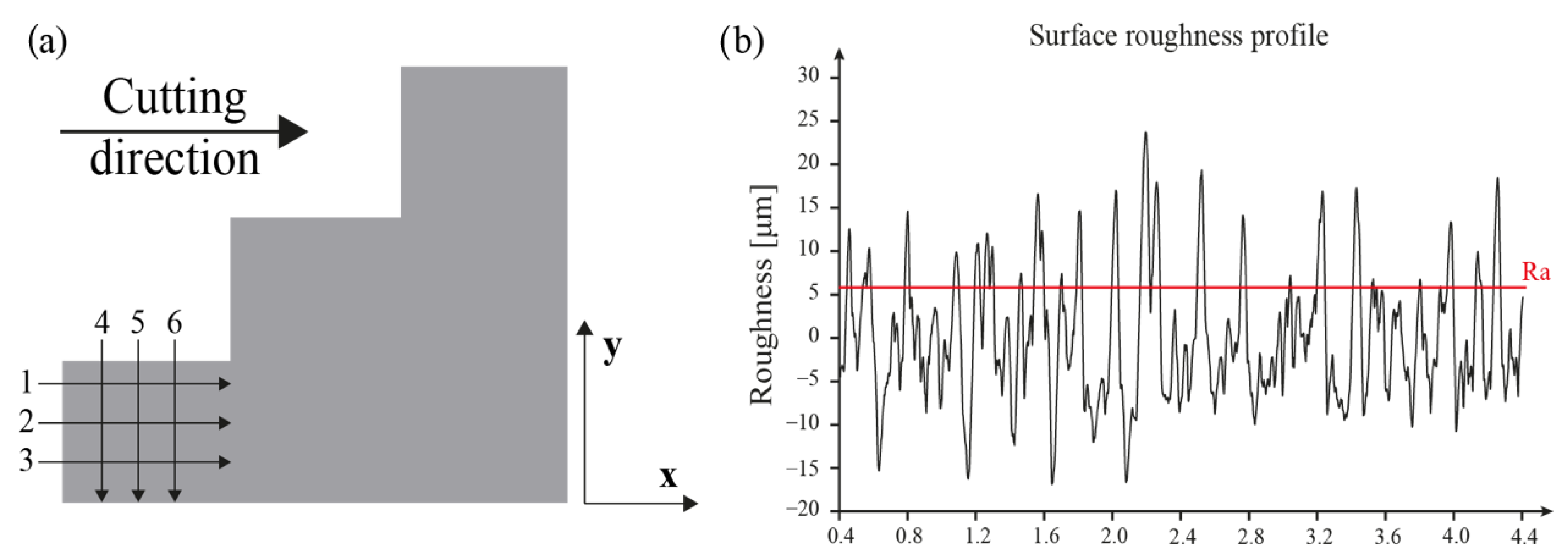
2.3. Performance Indexes Calculation
- Workpiece positioning and clamping on W-EDM machine guides;
- Wire electrode positioning and axis resetting;
- Setting process parameters and wire linear path;
- Machining the workpiece from the thinner to the thicker thickness;
- Measuring the time necessary to perform the cut for each thickness.
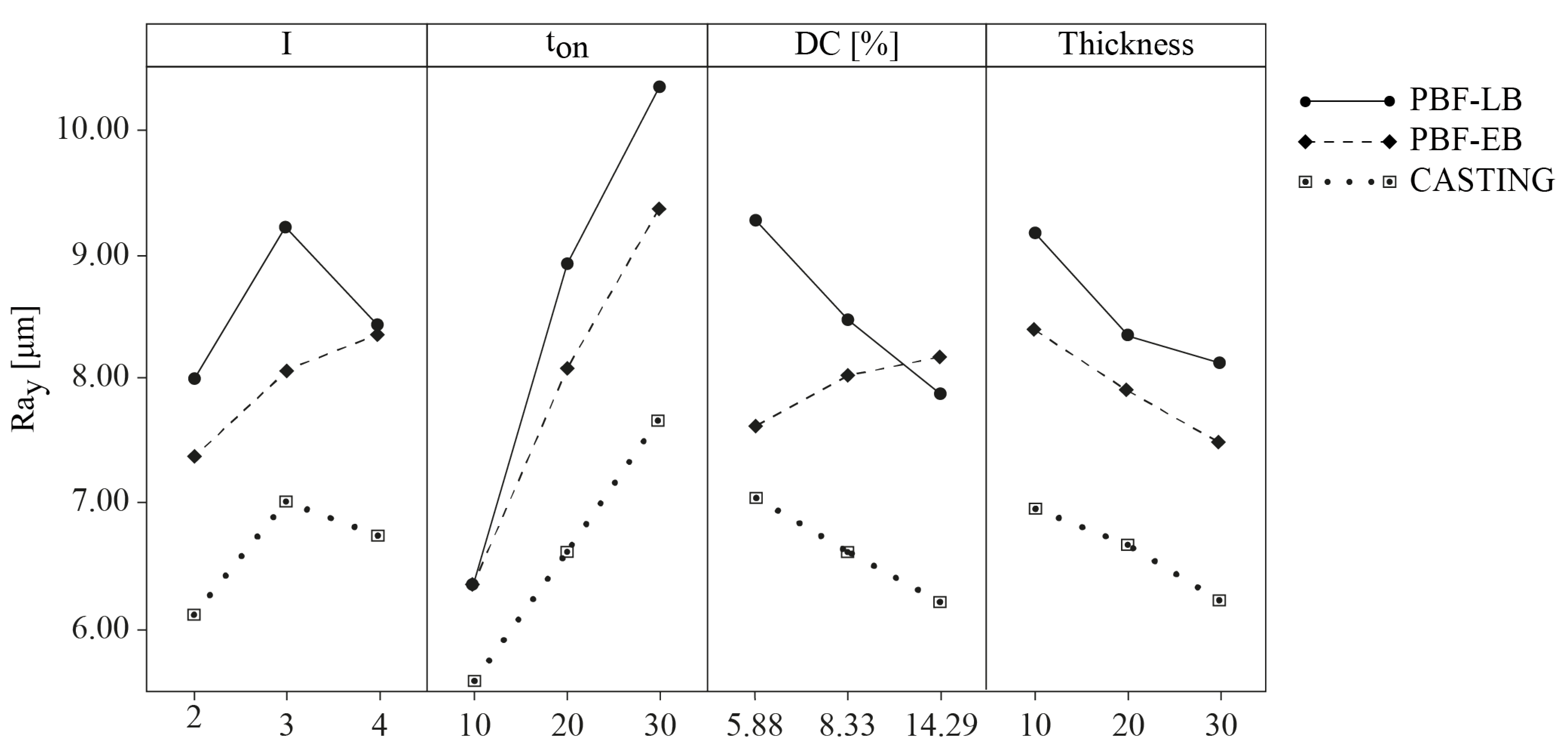
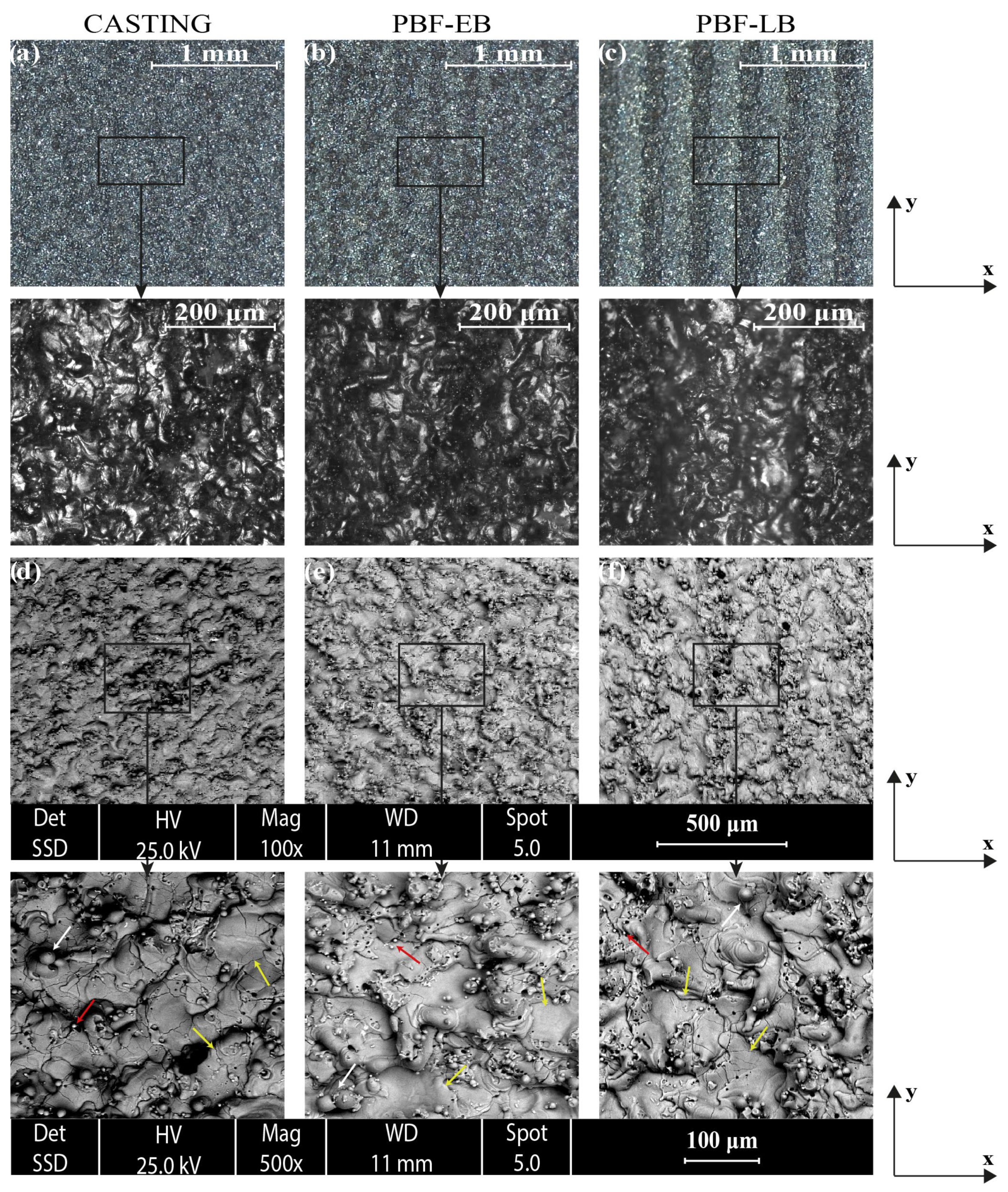
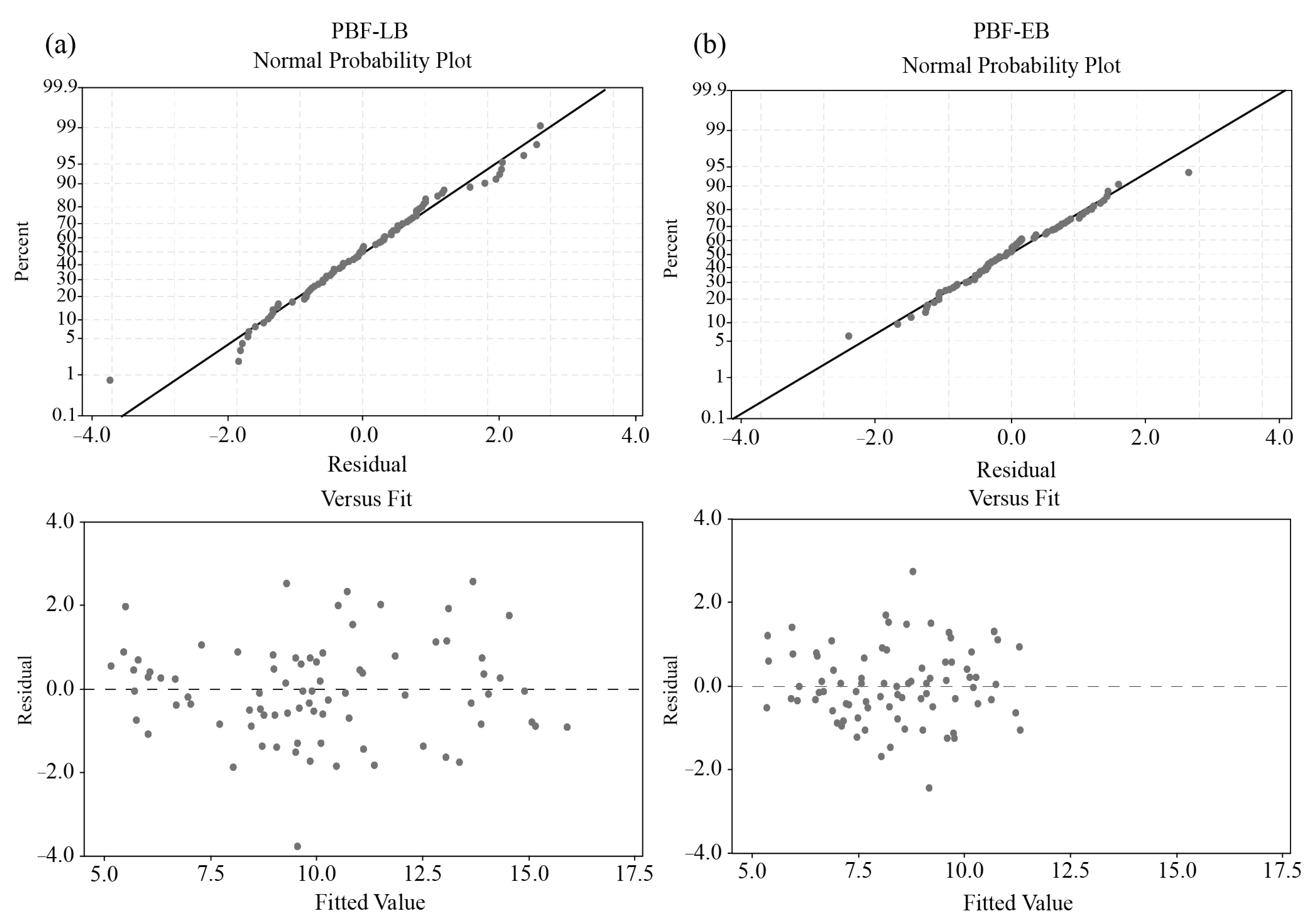
3. Results and Discussion
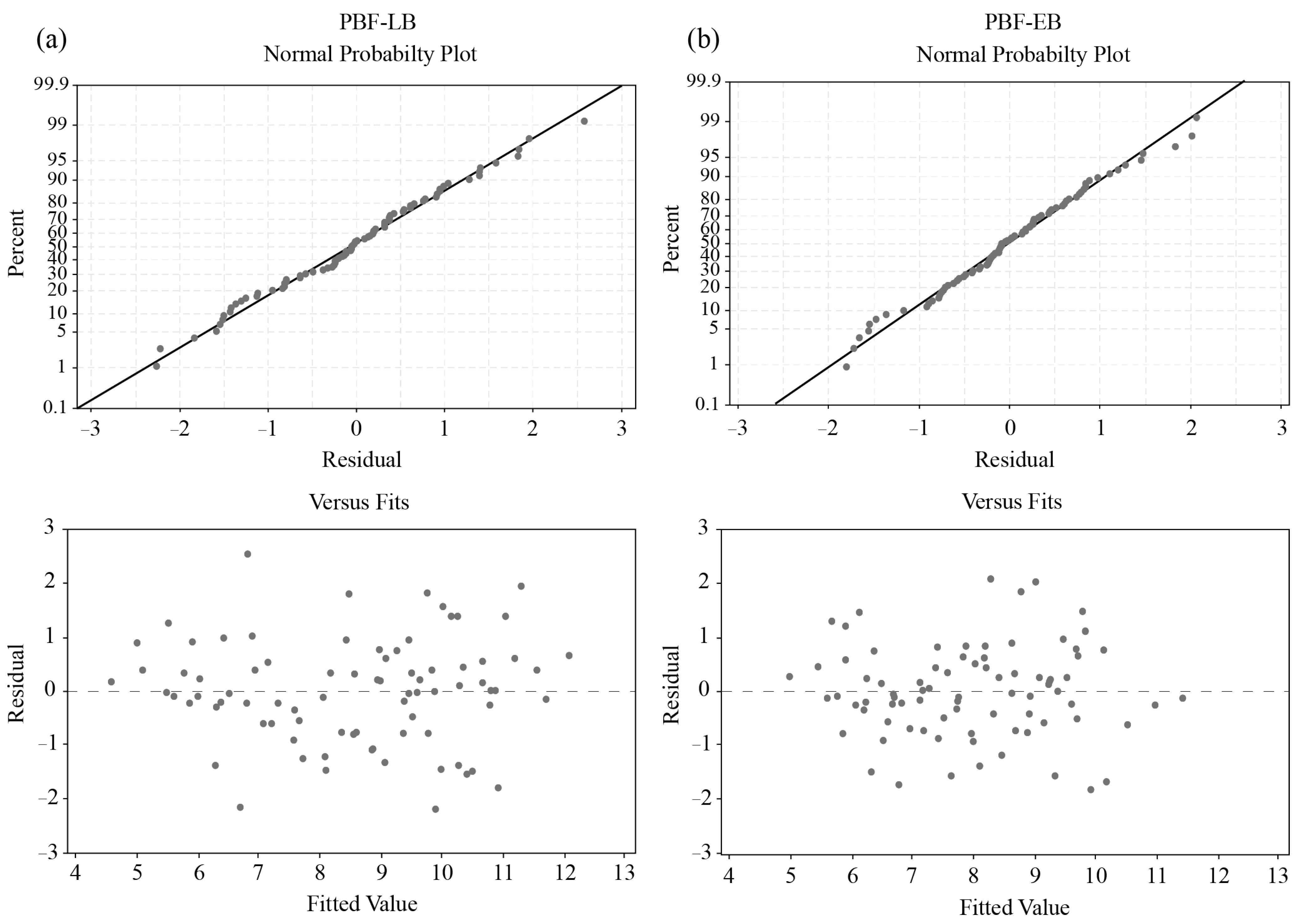
Regression Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variation Cause | DoF | Variance | F-Ratio | F-Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Examined Factor | 2 | 79.06 | 25.97 | 3.03 |
| Random Errors | 240 | 3.04 | ||
| Total | 242 |
| PBF-LB | PBF-EB | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | DF | Adj. SS | Adj. MS | p-Value | Source | DF | Adj. SS | Adj. MS | p-Value |
| Regression | 6 | 277.20 | 46.20 | 0.000 | Regression | 5 | 168.36 | 33.67 | 0.000 |
| I | 1 | 18.87 | 18.87 | 0.000 | I | 1 | 7.13 | 7.13 | 0.003 |
| ton | 1 | 20.36 | 20.36 | 0.000 | ton | 1 | 123.28 | 123.28 | 0.000 |
| DC | 1 | 23.45 | 23.45 | 0.000 | DC | 1 | 12.71 | 12.71 | 0.000 |
| Thickness | 1 | 14.41 | 14.42 | 0.000 | Thickness | 1 | 11.32 | 11.32 | 0.000 |
| I × I | 1 | 17.76 | 17.75 | 0.000 | I × DC | 1 | 17.52 | 17.52 | 0.000 |
| ton × ton | 1 | 6.01 | 6.01 | 0.017 | |||||
| Error | 74 | 74.79 | 1.01 | Error | 75 | 56.29 | 0.75 | ||
| Total | 80 | Total | 80 | ||||||
References
- Ho, K.H.; Newman, S.T.; Rahimifard, S.; Allen, R.D. State of the art in wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM). Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunieda, M.; Lauwers, B.; Rajurkar, K.P.; Schumacher, B.M. Advancing EDM through Fundamental Insight into the Process. CIRP Ann. 2005, 54, 64–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.K.; Singh, K.K.; Sachdeva, A.; Sharma, V.S.; Ojha, K.; Singh, S. Review of research work in sinking EDM and WEDM on metal matrix composite materials. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 50, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defanti, S.; Denti, L.; Vincenzi, N.; Gatto, A. Preliminary assessment of electro-chemical machining for aluminum parts produced by laser-based powder bed fusion. Smart Sustain. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 4, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhilash, P.M.; Chakradhar, D. Sustainability improvement of WEDM process by analysing and classifying wire rupture using kernel-based naive Bayes classifier. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Ramji, K.; Satyanarayana, B. Experimental Investigation and Optimization of Wire EDM Parameters for Surface Roughness, MRR and White Layer in Machining of Aluminium Alloy. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, J. Multi-response optimization of process parameters based on response surface methodology for pure titanium using WEDM process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 68, 2645–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsiyeh, D.; Lahiji, M.A.; Ghanbari, M.; Shirdar, M.R.; Golshan, A. Optimizing material removal rate (MRR) in WEDMing titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V) using the taguchi method. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 4, 3154–3161. [Google Scholar]
- Tosun, N.; Cogun, C.; Inan, A. The effect of cutting parameters on workpiece surface roughness in wire EDM. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2003, 7, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabade, U.A.; Karidkar, S.S. Analysis of Response Variables in WEDM of Inconel 718 Using Taguchi Technique. Procedia Cirp 2016, 41, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatarao, K.; Anup Kumar, T. An experimental parametric analysis on performance characteristics in wire electric discharge machining of Inconel 718. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2019, 14, 4836–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.; Raju, L.R.; Kumar, C.K. Modeling of kerf width and surface roughness in wire cut electric discharge machining of Ti-6Al-4V. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process. Mech. Eng. 2020, 234, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nain, S.S.; Garg, D.; Kumar, S. Evaluation and analysis of cutting speed, wire wear ratio, and dimensional deviation of wire electric discharge machining of super alloy Udimet-L605 using support vector machine and grey relational analysis. Adv. Manuf. 2018, 6, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarajaiah, D.; Muthumari, C. Evaluation of power consumption and MRR in WEDM of Ti–6Al–4V alloy and its simultaneous optimization for sustainable production. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Misra, J.P.; Singh, B. Experimental Investigation of Influence of Process Parameters on MRR during WEDM of Al6063 alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 2242–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Garg, R. Effects of process parameters on material removal rate in WEDM. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2009, 32, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.; Khanna, R.; Gupta, R. Multi Quality Characteristics of WEDM Process Parameters with RSM. Procedia Eng. 2013, 64, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalisgaonkar, R.; Kumar, J. Optimization of WEDM process of pure titanium with multiple performance characteristics using Taguchi’s DOE approach and utility concept. Front. Mech. Eng. 2013, 8, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poros, D.; Wisniewska, M.; Zaborski, S. Comparative analysis of wedm with different wire electrodes applied to cut titanium ti6al4v. J. Mach. Eng. 2020, 20, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyankara, K.P.M.; Perera, G.I.P. Experimental Investigation to Achieve Minimum Surface Roughness in Wire EDM Process. In ICSBE 2018: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Sustainable Built Environment; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 239–251. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Chakradhar, D.; Narendranath, S. Evaluation of WEDM performance characteristics of Inconel 706 for turbine disk application. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, J. Experimental investigation on material transfer mechanism in wedm of pure titanium (Grade-2). Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 847876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- kumar, S.; Khan, M.A.; Muralidharan, B. Processing of titanium-based human implant material using wire EDM. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2019, 34, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, R.; Choudhuri, B.; Barma, J.D.; Chakraborti, P. Study the impact of process parameters and electrode material on wire electric discharge machining performances. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 7552–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, R.; Daniel, M. Wire electrical discharge machining (EDM) setup parameters influence in functional surface roughness. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 41, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durairaj, M.; Sudharsun, D.; Swamynathan, N. Analysis of process parameters in wire EDM with stainless steel using single objective Taguchi method and multi objective grey relational grade. Procedia Eng. 2013, 64, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, N.; Cogun, C.; Tosun, G. A study on kerf and material removal rate in wire electrical discharge machining based on Taguchi method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 152, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.S.; Patnaik, A. Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process parameters using Taguchi method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 34, 911–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, N. The effect of the cutting parameters on performance of WEDM. KSME Int. J. 2003, 17, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, U.A.; Laxminarayana, P. Optimization of surface roughness and kerf width by wire cut-electrical discharge machining on inconel 625. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 27, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, J.R.; DeSilva, A.K.M.; Chantzis, D.; Antar, M. Sustainable machining: Process energy optimisation of wire electrodischarge machining of Inconel and titanium superalloys. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 164, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, J. Parametric Effect on Wire Breakage Frequency and Surface Topography in WEDM of Pure Titanium. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2013, 1, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, A.; Mufti, N.A.; Saleem, M.Q.; Khan, A.R. Parametric optimization for surface roughness, kerf and MRR in wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) using Taguchi design of experiment. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 2133–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyaa, P.; John, J.J.; Puviyarasan, M.; Prabhu, T.R.; Prasad, N.E. Wire EDM Parameter Optimization of AlSi10Mg Alloy. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 74, 2869–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franczyk, E.; Machno, M.; Zębala, W. Investigation and optimization of the slm and wedm processes’ parameters for the AlSi10Mg-sintered part. Materials 2021, 14, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calignano, F.; Manfredi, D.; Ambrosio, E.P.; Biamino, S.; Pavese, M.; Fino, P. Direct fabrication of joints based on direct metal laser sintering in aluminum and titanium alloys. Procedia CIRP 2014, 21, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, M.; Rizza, G.; Defanti, S.; Denti, L. Surface roughness prediction model for Electron Beam Melting (EBM) processing Ti6Al4V. Precis. Eng. 2021, 69, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, T.P.; Sethi, B.L. Surface modification by electrical discharge machining: A review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 3675–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4288; 1996-Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile Method—Rules and Procedures for the Assessment of Surface Texture. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- Calignano, F. Investigation of the accuracy and roughness in the laser powder bed fusion process. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2018, 13, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altug, M.; Erdem, M.; Ozay, C. Experimental investigation of kerf of Ti6Al4V exposed to different heat treatment processes in WEDM and optimization of parameters using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 78, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshkabilov, S.; Ara, I.; Sevostianov, I.; Azarmi, F.; Tangpong, X. Mechanical and thermal properties of stainless steel parts, manufactured by various technologies, in relation to their microstructure. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2021, 159, 103398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strumza, E.; Yeheskel, O.; Hayun, S. The effect of texture on the anisotropy of thermophysical properties of additively manufactured AlSi10Mg. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 29, 100762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Jiang, J.; Yu, D. Influence of machining parameters on surface roughness in finish cut of WEDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 34, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhuri, B.; Sen, R.; Ghosh, S.K.; Saha, S.C. Comparative machinability characterization of wire electrical discharge machining on different specialized AISI steels. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2020, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouralova, K.; Kovar, J.; Klakurkova, L.; Blazik, P.; Kalivoda, M.; Kousal, P. Analysis of surface and subsurface layers after WEDM for Ti-6Al-4V with heat treatment. Measurement 2018, 116, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouralova, K.; Kovar, J.; Klakurkova, L.; Prokes, T.; Horynova, M. Comparison of morphology and topography of surfaces of WEDM machined structural materials. Measurement 2017, 104, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Laser Power [W] | Scan Speed [mm/s] | Hatching Distance [mm] | Layer Thickness [µm] | Laser Spot Size [mm] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hatch (Core) | 170 | 1250 | 0.10 | 30 | 0.10 |
| Hatch (Skin) | 150 | 1000 | 0.10 | 30 | 0.10 |
| Contour | 120 | 1250 | - | - | 0.10 |
| Scan Speed [mm/s] | Focus Offset [mA] | Beam Current [mA] | Number of Contours | Hatch Contours [mm] | Line Offset [mm] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hatch | 45 | 25 | 20 | - | - | 0.2 |
| Contour | 850 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 0.290 | 0.200 |
| Level | Low | Medium | High |
|---|---|---|---|
| I [A] | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| ton [µs] | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| DC [%] | 5.88 | 8.33 | 14.29 |
| Thickness [mm] | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| Process | Rax (Std. Deviation) [μm] | Ray (Std. Deviation) [μm] | Vc (Std. Deviation) [μm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| CASTING | 6.88 (1.33) | 6.62 (1.39) | 1.30 (0.77) |
| PBF-EB | 8.63 (1.72) | 7.93 (1.68) | 1.32 (0.76) |
| PBF-LB | 9.99 (2.96) | 8.55 (2.10) | 1.35 (0.74) |
| Source of Variation | DoF | Variance | F-Ratio | F-Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASTING | Examined factor | 1 | 2.809 | 1.52 | 3.90 |
| Error | 160 | 1.849 | |||
| Total | 161 | ||||
| PBF-EB | Examined factor | 1 | 19.806 | 6.86 | 3.90 |
| Error | 160 | 2.889 | |||
| Total | 161 | ||||
| PBF-LB | Examined factor | 1 | 84.216 | 12.77 | 3.90 |
| Error | 160 | 6.594 | |||
| Total | 161 |
| Source of Variation | DoF | Variance | F-Ratio | F-Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vc | Examined factor | 2 | 3.80 × 10−2 | 0.07 | 3.03 |
| Random errors | 240 | 5.75 × 10−1 | |||
| Total | 242 | ||||
| Rax | Examined factor | 2 | 1.97 × 102 | 43.74 | 3.03 |
| Random errors | 240 | 4.51 | |||
| Total | 242 |
| PBF-LB | PBF-EB | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | DF | Adj. SS | Adj. MS | p-Value | Adj. SS | Adj. MS | p-Value |
| Regression | 10 | 43.63 | 4.36 | 0.000 | 41.51 | 4.15 | 0.000 |
| I | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.545 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.321 |
| ton | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.543 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.109 |
| DC | 1 | 1.58 | 1.58 | 0.000 | 1.38 | 1.38 | 0.000 |
| Thickness | 1 | 5 × 10−4 | 5 × 10−4 | 0.911 | 4.3 ×10−3 | 4.3 × 10−3 | 0.647 |
| I × ton | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.558 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.173 |
| I × DC | 1 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.003 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.000 |
| I × Thickness | 1 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.026 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.004 |
| ton × DC | 1 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.050 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.107 |
| ton × Thickness | 1 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.059 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.050 |
| DC × Thickness | 1 | 2.07 | 2.07 | 0.000 | 1.89 | 1.89 | 0.000 |
| Error | 70 | 2.97 | 0.04 | 2.41 | 0.03 | ||
| Total | 80 | ||||||
| PBF-LB | PBF-EB | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | DF | Adj. SS | Adj. MS | p-Value | Adj. SS | Adj. MS | p-Value |
| Regression | 14 | 607.05 | 43.36 | 0.000 | 179.61 | 12.83 | 0.000 |
| I | 1 | 274.36 | 274.36 | 0.000 | 4.36 | 4.36 | 0.029 |
| ton | 1 | 39.57 | 39.57 | 0.000 | 3.34 | 3.34 | 0.056 |
| DC | 1 | 2.92 | 2.92 | 0.162 | 3.95 | 3.95 | 0.038 |
| Thickness | 1 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.461 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.342 |
| I × I | 1 | 324.76 | 324.76 | 0.000 | 9.96 | 9.96 | 0.001 |
| ton × ton | 1 | 20.75 | 20.75 | 0.000 | 1.13 | 1.13 | 0.261 |
| DC × DC | 1 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.692 | 7.99 | 7.99 | 0.003 |
| Thickness × Thickness | 1 | 7.08 | 7.08 | 0.031 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.850 |
| I × ton | 1 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.580 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.301 |
| I × DC | 1 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.421 | 6.64 | 6.64 | 0.008 |
| I × Thickness | 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.984 | 1.06 | 1.06 | 0.276 |
| ton × DC | 1 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 0.330 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.647 |
| ton × Thickness | 1 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 0.245 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.998 |
| DC × Thickness | 1 | 16.37 | 16.37 | 0.001 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.659 |
| Error | 66 | 95.97 | 1.45 | 58.00 | 0.87 | ||
| Total | 80 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galati, M.; Antonioni, P.; Calignano, F.; Atzeni, E. Experimental Investigation on the Cutting of Additively Manufactured Ti6Al4V with Wire-EDM and the Analytical Modelling of Cutting Speed and Surface Roughness. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7020069
Galati M, Antonioni P, Calignano F, Atzeni E. Experimental Investigation on the Cutting of Additively Manufactured Ti6Al4V with Wire-EDM and the Analytical Modelling of Cutting Speed and Surface Roughness. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2023; 7(2):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7020069
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalati, Manuela, Paolo Antonioni, Flaviana Calignano, and Eleonora Atzeni. 2023. "Experimental Investigation on the Cutting of Additively Manufactured Ti6Al4V with Wire-EDM and the Analytical Modelling of Cutting Speed and Surface Roughness" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 7, no. 2: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7020069
APA StyleGalati, M., Antonioni, P., Calignano, F., & Atzeni, E. (2023). Experimental Investigation on the Cutting of Additively Manufactured Ti6Al4V with Wire-EDM and the Analytical Modelling of Cutting Speed and Surface Roughness. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 7(2), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7020069







