High-Precision Adjustment of Welding Depth during Laser Micro Welding of Copper Using Superpositioned Spatial and Temporal Power Modulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
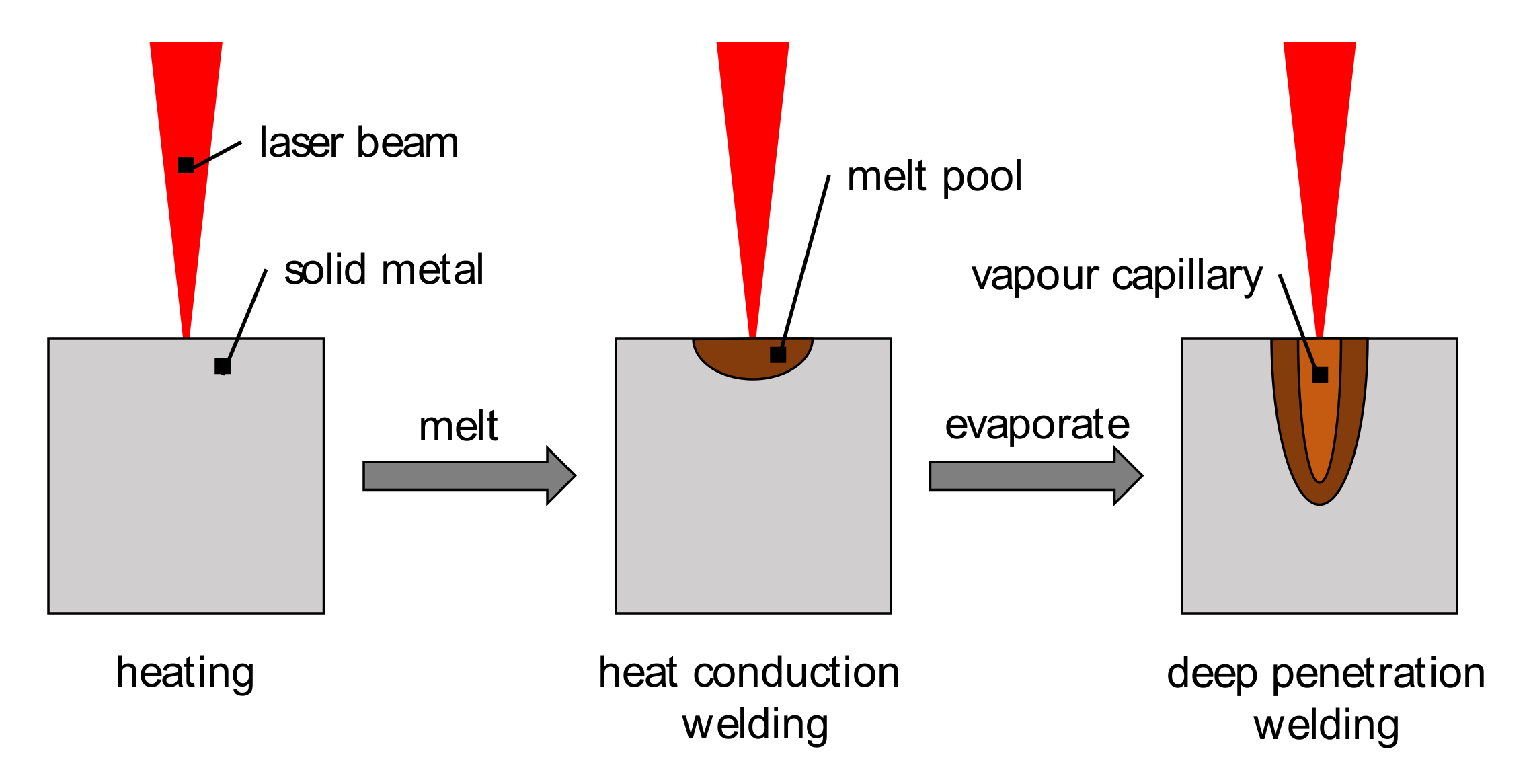
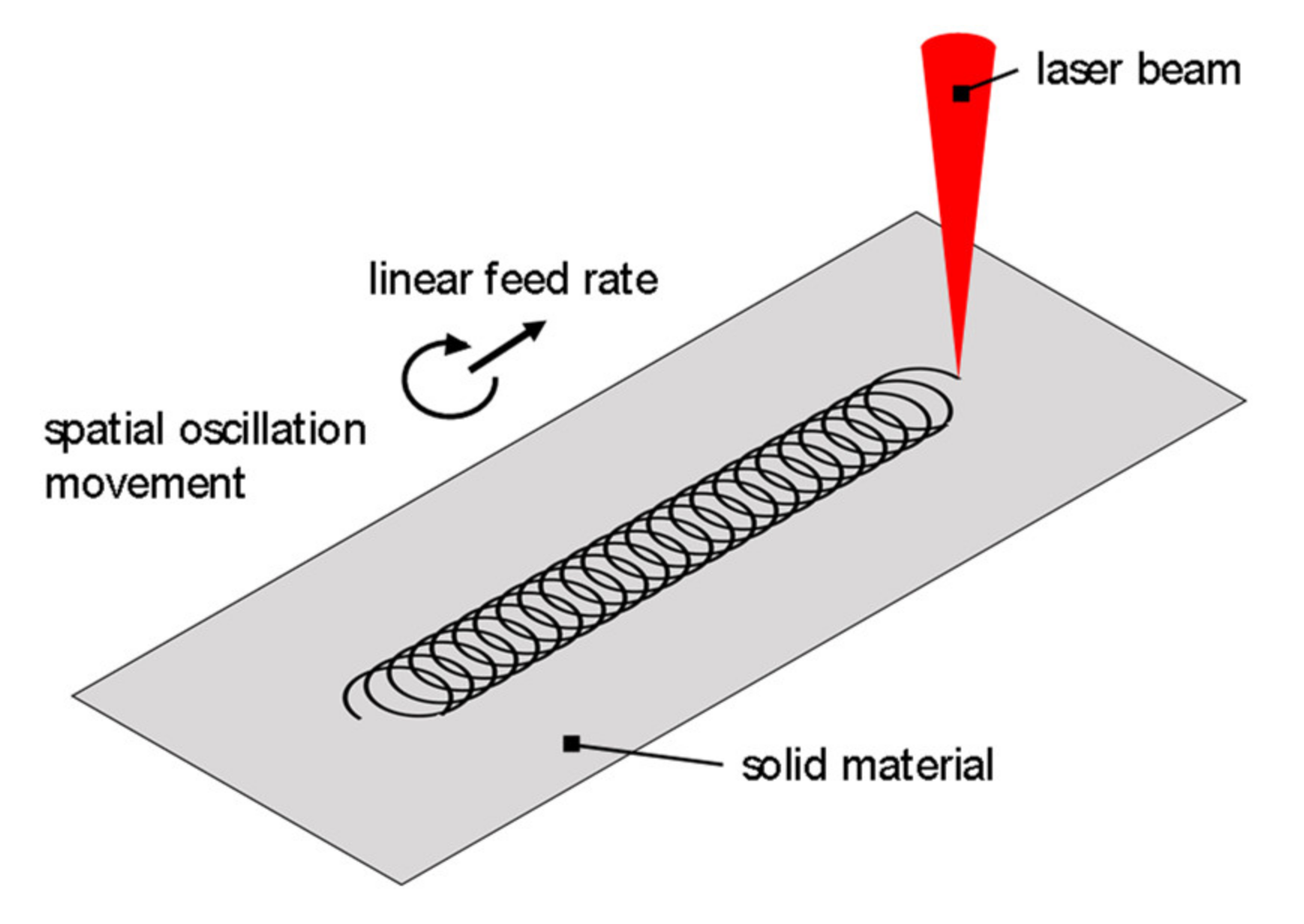
2.1. Theoretical Principles
2.2. Experimental Plan and Setup
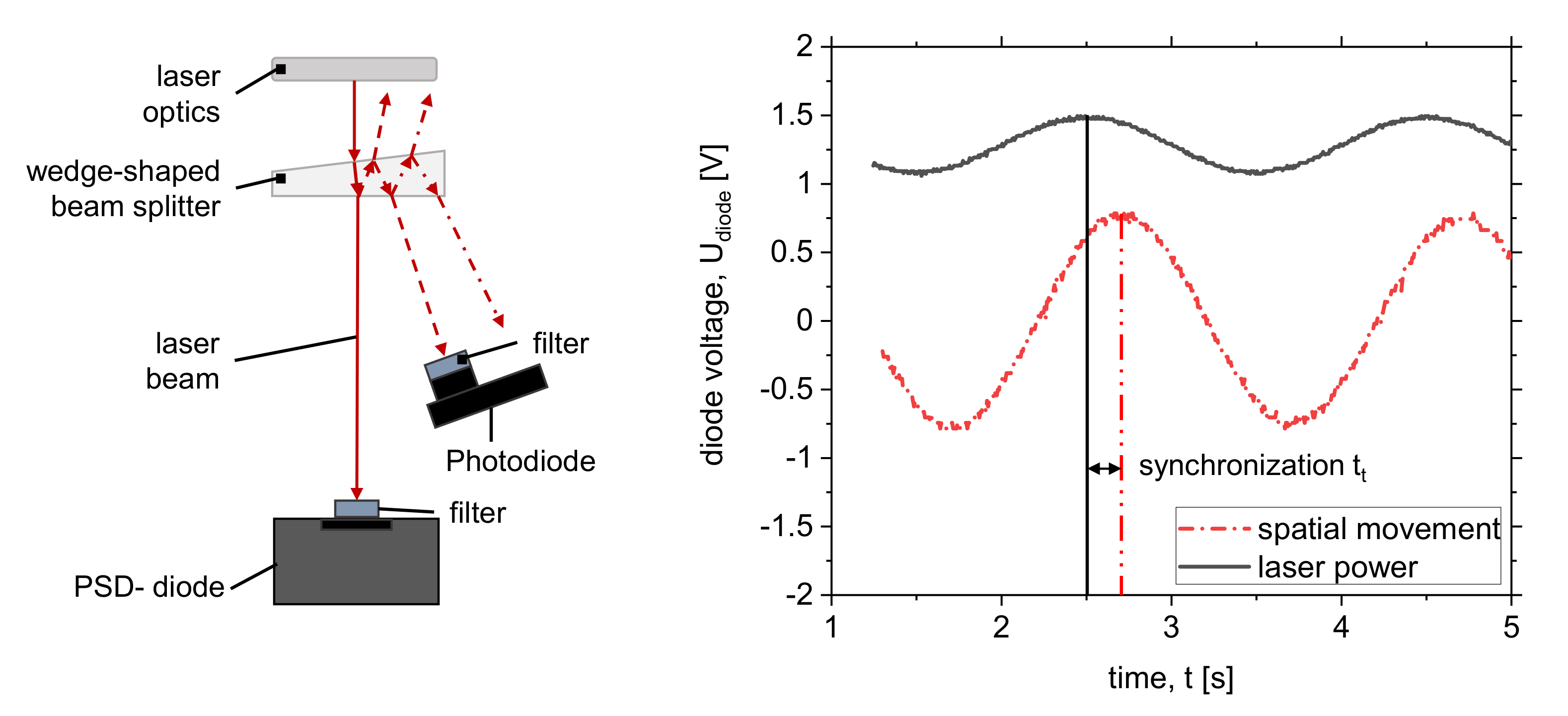
2.3. Experimental Setup for Synchronizing Temporal and Spatial Power Modulation
2.4. Experimental Setup for Measuring of Laser Energy Coupling
3. Results
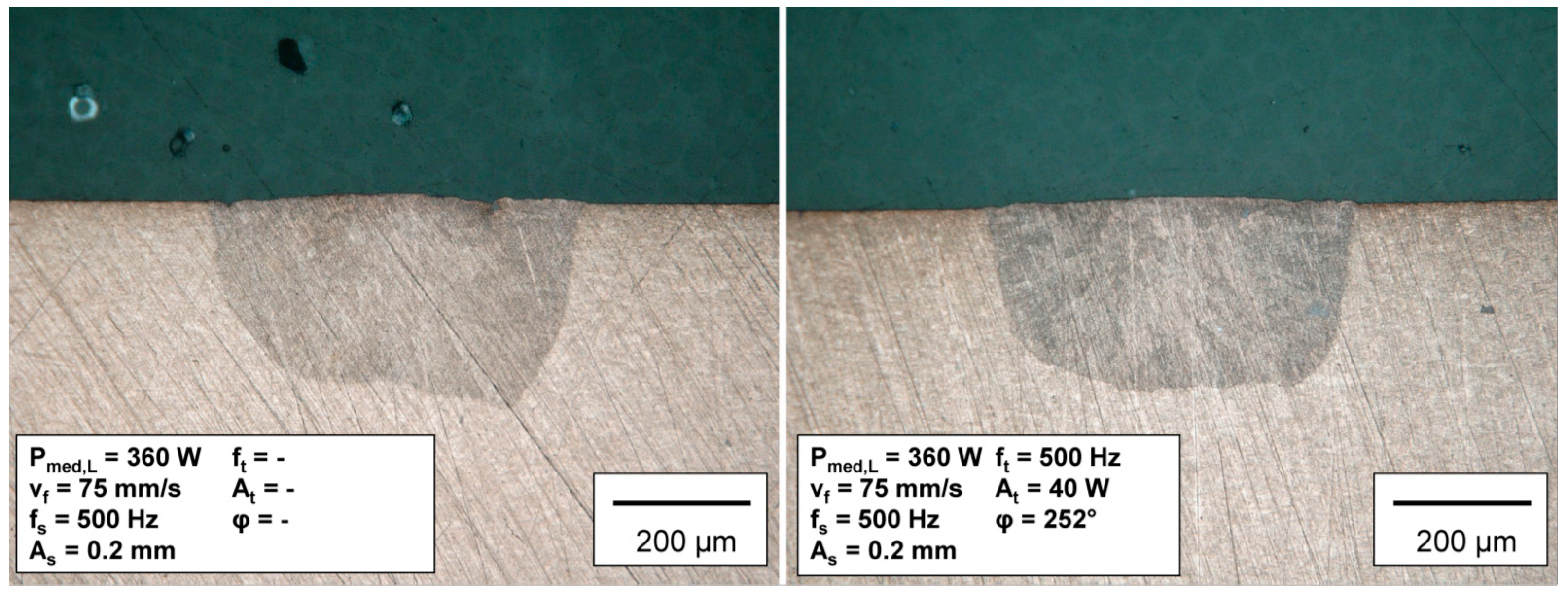
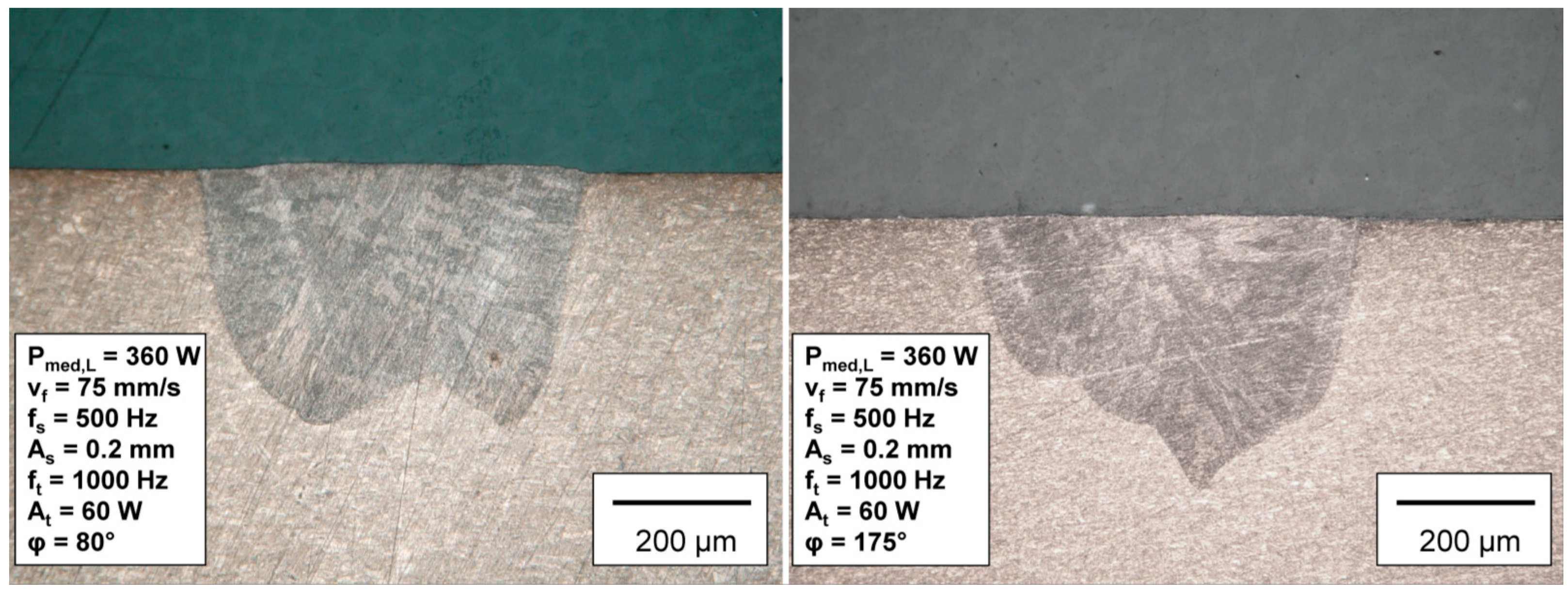
3.1. Bed on Plate Weld on Copper CuSn6
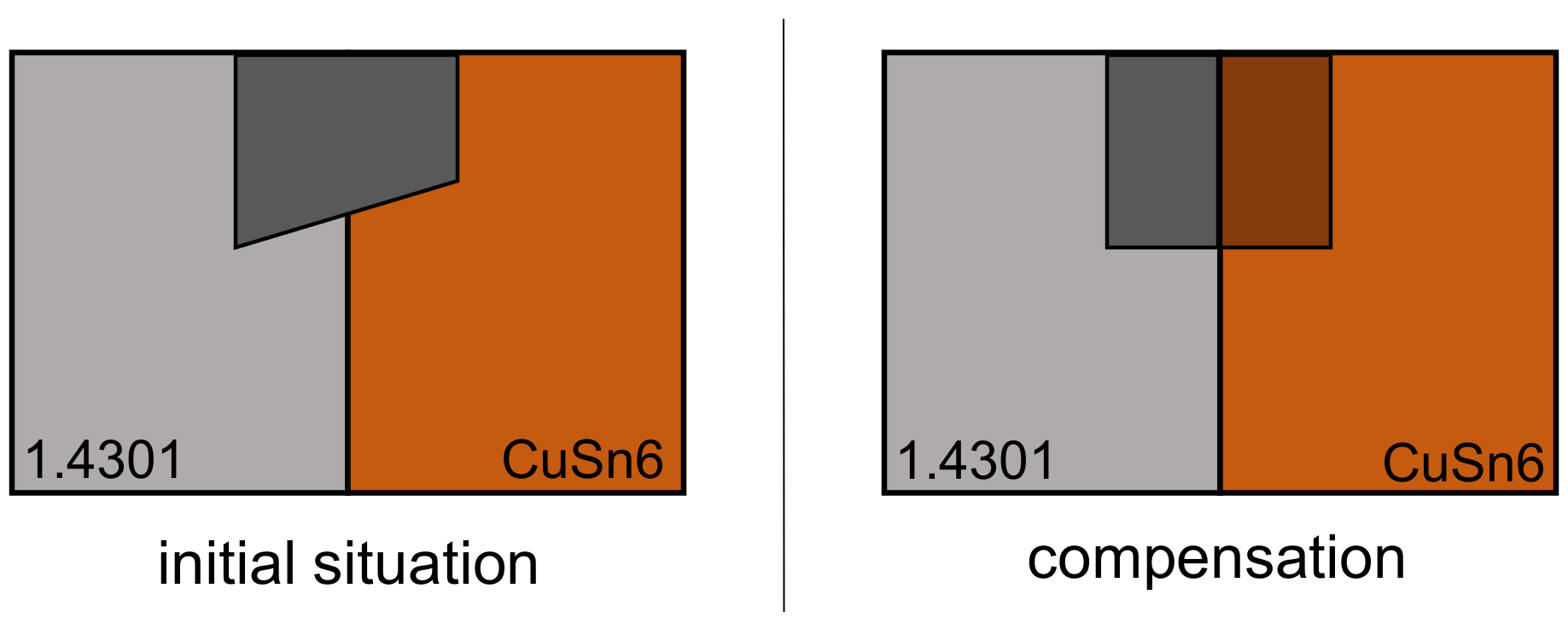
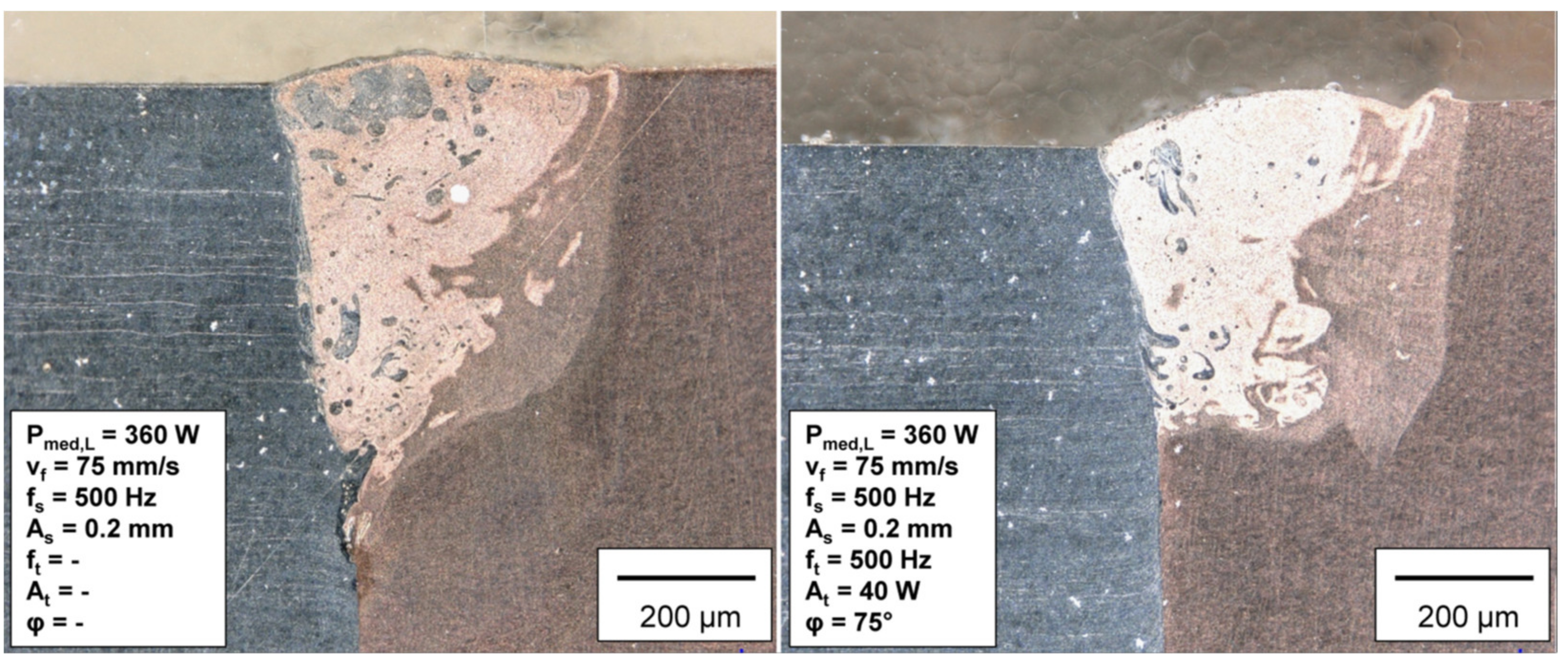
3.2. Dissimilar Welds of CuSn6 Copper and 1.4301 Stainless Steel in Butt Joint Configuration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
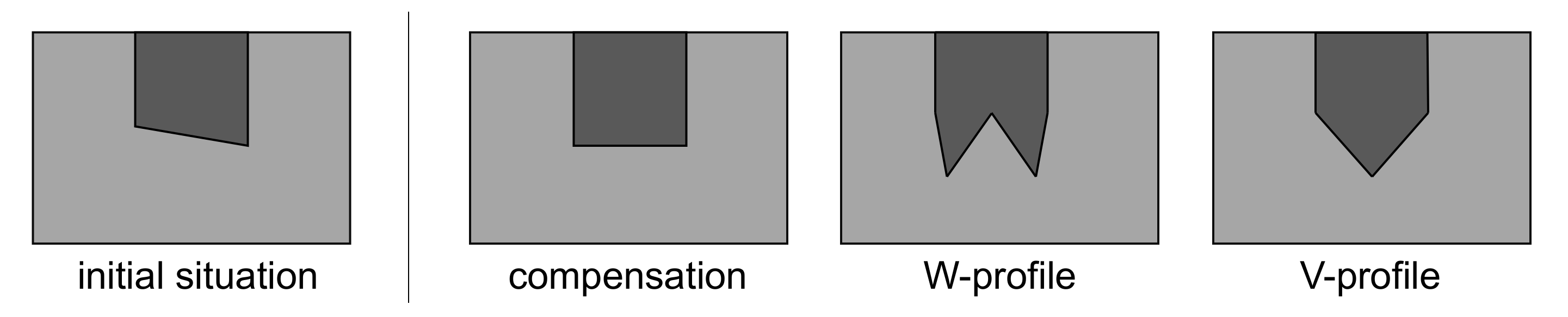
- Based on the standard weld seam, it has been shown that in addition to compensating for seam tilt, it is also possible to create other cross-section profiles such as W and V shapes.
- The feasibility to control the laser energy deposition during laser micro welding by means of synchronized temporal and spatial power modulation is shown.
- The difference in the welding depth could be reduced in the parameter space examined in this work by 8.5%-points for bed on plate welds on CuSn6 and by 39% points for dissimilar material systems in the butt joint configuration between 1.4301 and CuSn6.
- A variation of the position of maximum and minimum laser power on the weld seam is crucial for successful adjustment of the weld seam geometry.
- Measurement of energy coupling during the welding process can be used to analyze changes in the energy coupling due to modified power modulation in detail.
- The uneven welding depth in butt joints of dissimilar materials can be compensated by exposing higher laser power on the material with increased thermal conductivity and reflectivity and vice versa.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heinen, P.; Haeusler, A.; Mehlmann, B.; Olowinsky, A. Laser Beam Micro welding of Lithium-ion Battery Cells with Copper Connectors for Electrical Connections in Energy Storage Devices. Laser Eng. 2017, 36, 147–167. [Google Scholar]
- Mehlmann, B.; Gehlen, E.; Olowinsky, A.; Gillner, A. Laser Micro Welding for Ribbon Bonding. Physics Procedia 2014, 56, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bono, P.; Blackburn, J. Laser welding of copper and aluminium battery interconnections. In Proceedings of the Industrial Laser Applications Symposium 2015, Kenilworth, UK, 17 March 2015; p. 96570M. [Google Scholar]
- Gedicke, J.; Mehlmann, B.; Olowinsky, A.; Gillner, A. Laser beam welding of electrical interconnections for lithium-ion batteries. In Proceedings of the 29th International Congress on Applications of Lasers & Electro-Optics (ICALEO 2010), Anaheim, CA, USA, 26–30 September 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heider, A.; Stritt, P.; Hess, A.; Weber, R.; Graf, T. Process Stabilization at welding Copper by Laser Power Modulation. Physics Procedia 2011, 12, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, M.; Han, H.N.; Kim, C. Microstructure and Solidification Crack Susceptibility of Al 6014 Molten Alloy Subjected to a Spatially Oscillated Laser Beam. Materials 2018, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Punzel, E.; Hugger, F.; Dörringer, R.; Dinkelbach, T.L.; Bürger, A. Comparison of different system technologies for continuous-wave laser beam welding of copper. Procedia CIRP 2020, 94, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F.; Mehlmann, B.; Gedicke, J.; Olowinsky, A.; Gillner, A.; Poprawe, R. Laser Beam Micro Welding with High Brilliant Fiber Lasers. J. Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 2010, 5, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F. Laserstrahl-Mikroschweißen mit Strahlquellen hoher Brillanz und örtlicher Leistungsmodulation; Shaker: Aachen, Germany, 2012; ISBN 3844010416. [Google Scholar]
- Jarwitz, M.; Fetzer, F.; Weber, R.; Graf, T. Weld Seam Geometry and Electrical Resistance of Laser-Welded, Aluminum-Copper Dissimilar Joints Produced with Spatial Beam Oscillation. Metals 2018, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aden, M.; Heinen, P.; Olowinsky, A. Seam Formation in Laser Beam Micro-Welding with Spatial Power Modulation. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 8, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrna, L.; Horník, P.; Jedlicka, P.; Pavelka, J. Study of laser wobbling welding process through the radiation of plasma plume. In Proceedings of the Laser in Manufacturing Conference, Munich, Germany, 26–29 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Häusler, A.; Mehlmann, B.; Olowinsky, A.; Gillner, A.; Poprawe, R. Efficient Copper Micro welding with Fibre Lasers using Spatial Power Modulation. Laser Eng. 2017, 36, 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- Häusler, A. Präzisionserhöhung beim Laserstrahl-Mikroschweißen Durch Angepasstes Energiemanagement, 1st ed.; Aprimus Verlag: Aachen, Germany, 2021; ISBN 978-3-86359-933-1. [Google Scholar]
- Conzen, J.H.; Haeusler, A.; Stollenwerk, J.; Gillner, A.; Poprawe, R.; Loosen, P. Laserstrahl-Mikroschweißen von Mikroelektronische Baugruppen unter Anwendung von Örtlicher und Zeitlicher Energiedeposition; Elektronische Baugruppen und Leiterplatten EBL: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Stritt, P.; Weber, R.; Graf, T.; Müller, S.; Ebert, C. Utilizing Laser Power Modulation to Investigate the Transition from Heat-Conduction to Deep-Penetration Welding. Physics Procedia 2011, 12, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraetzsch, M.; Standfuss, J.; Klotzbach, A.; Kaspar, J.; Brenner, B.; Beyer, E. Laser beam welding with high-frequency beam oscillation: Welding of dissimilar materials with brilliant fiber lasers. Physics Procedia 2011, 12, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Chen, Y.; Lei, Z.; Zhao, S.; Lin, S. Laser welding-brazing under temporal and spatial power modulation for dissimilar materials AA6061 to Ti6Al4V joints. Manuf. Lett. 2021, 29, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hügel, H.; Graf, T. Laser in der Fertigung: Grundlagen der Strahlquellen, Systeme, Fertigungsverfahren, 2nd ed.; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-8348-9570-7. [Google Scholar]
- Engler, S.; Ramsayer, R.; Poprawe, R. Process Studies on Laser Welding of Copper with Brilliant Green and Infrared Lasers. Physics Procedia 2011, 12, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M. Modellierung des Lasertiefschweißens; Teubner: Stuttgart, Germany, 1996; ISBN 978-3519062189. [Google Scholar]
- Mehlmann, B. Spatially Modulated Laser Beam Micro Welding of CuSn6 and Nickel-plated DC04 Steel for Battery Applications. JLMN 2014, 9, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweier, M.; Heins, J.F.; Haubold, M.W.; Zaeh, M.F. Spatter Formation in Laser Welding with Beam Oscillation. Physics Procedia 2013, 41, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco, D.F. Wobbling Laser Beam Welding of Copper. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nova de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal, September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Häusler, A.; Schürmann, A.; Schöler, C.; Olowinsky, A.; Gillner, A.; Poprawe, R. Quality improvement of copper welds by laser microwelding with the usage of spatial power modulation. J. Laser Appl. 2017, 29, 22422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, M.; Häusler, A.; Olowinsky, A.; Gillner, A.; Poprawe, R. Comparing 1070 nm and 515 nm Wavelength Laser Beam Sources in Terms of Efficiency for Laser Micowelding Copper. Lasers Eng. 2020, 46, 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Warlimont, H.; Martienssen, W. Springer Handbook of Materials Data; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-69741-3. [Google Scholar]
- Hummel, M.; Schöler, C.; Häusler, A.; Gillner, A.; Poprawe, R. New approaches on laser micro welding of copper by using a laser beam source with a wavelength of 450 nm. J. Adv. Join. Process. 2020, 1, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material Property | CuSn6 | 1.4301 |
|---|---|---|
| Absorptivity (λ = 1064 nm) | 7.9% | 37.2% |
| Heat conductivity | 75 W/mK | 15 W/mK |
| Heat capacity | 377 J/kgK | 500 J/kgK |
| Liquidus temperature | 1323 K | 1673 K |
| Profile/Weld | Feed Rate | Average Laser Power | Frequency Temporal | Amplitude Temporal | Frequency Spatial | Amplitude Spatial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 75 mm/s | 360 W | 500 Hz | 40 W | 500 Hz | 0.2 mm |
| Compensation | 75 mm/s | 360 W | 500 Hz | 40 W | 500 Hz | 0.2 mm |
| W-profile | 75 mm/s | 360 W | 1000 Hz | 60 W | 500 Hz | 0.2 mm |
| V-profile | 75 mm/s | 360 W | 1000 Hz | 60 W | 500 Hz | 0.2 mm |
| Dissimilar material | 75 mm/s | 360 W | 500 Hz | 40 W | 500 Hz | 0.2/0.3 mm |
| Profile | Maximum Laser Power | Minimum Laser Power |
|---|---|---|
| Compensation | φ = 255–285° | φ = 75–105° |
| W-profile | φ = 75–105°/255–285° | φ = 165–195°/345–375° |
| V-profile | φ = 165–195°/345–375° | φ = 75–105°/255–285° |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hummel, M.; Häusler, A.; Gillner, A. High-Precision Adjustment of Welding Depth during Laser Micro Welding of Copper Using Superpositioned Spatial and Temporal Power Modulation. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5040127
Hummel M, Häusler A, Gillner A. High-Precision Adjustment of Welding Depth during Laser Micro Welding of Copper Using Superpositioned Spatial and Temporal Power Modulation. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2021; 5(4):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5040127
Chicago/Turabian StyleHummel, Marc, André Häusler, and Arnold Gillner. 2021. "High-Precision Adjustment of Welding Depth during Laser Micro Welding of Copper Using Superpositioned Spatial and Temporal Power Modulation" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 5, no. 4: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5040127
APA StyleHummel, M., Häusler, A., & Gillner, A. (2021). High-Precision Adjustment of Welding Depth during Laser Micro Welding of Copper Using Superpositioned Spatial and Temporal Power Modulation. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 5(4), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5040127






