Prediction Models for Distortions and Residual Stresses in Thermoset Polymer Laminates: An Overview
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Manufacturing Process of Thermoset Composites
3. Types and Sources of Distortion and Residual Stress during the Curing Processing of Thermosets
3.1. Anisotropy
- Polymerisation (reactions) and chemical shrinkage
- Thermal contraction (during cool-down)
3.2. Fibre Volume Fraction (Material Property) Gradient
3.3. Tool-Part Interaction (Stress Gradient)
4. Research on Cure-Cycle-Induced Residual Stresses
5. Predictive Models for Parameters during the Curing Process of Thermoset Polymers
5.1. Modelling of Cure Kinetics
5.2. Resin Shrinkage during Cure
5.3. Evolution of Resin Stiffness during Cure
6. Stress Models for Thermoset Polymers and Adhesives
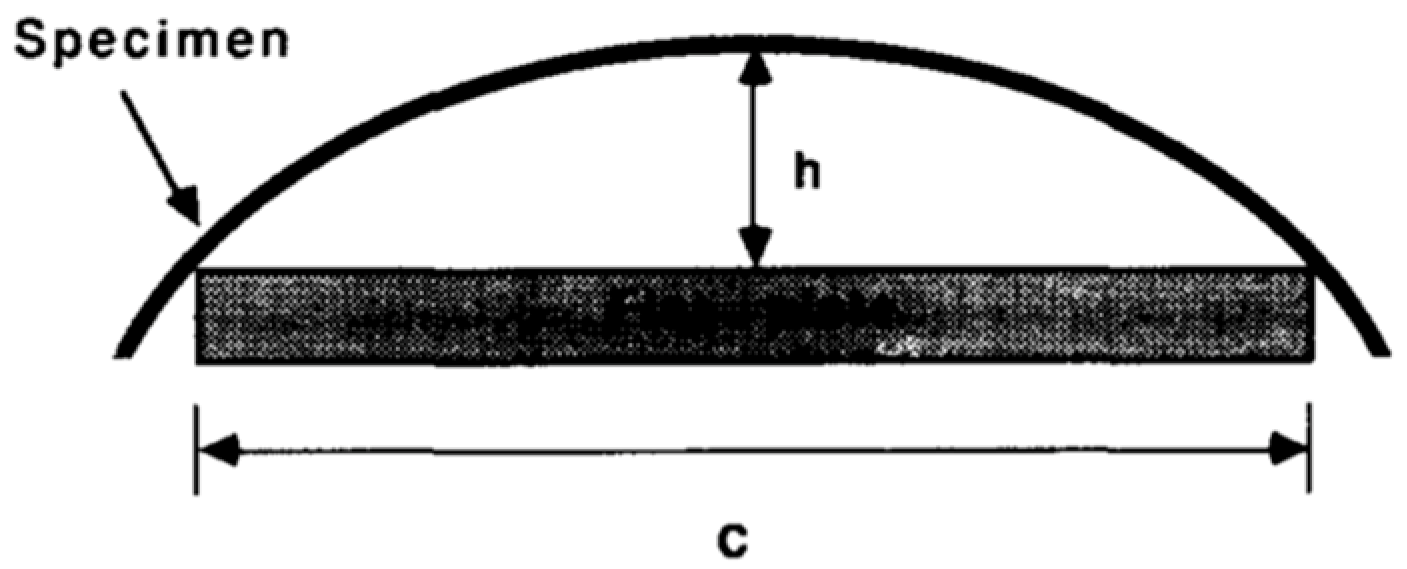
7. Predicting and Reducing the Distortions in Thermoset Composites
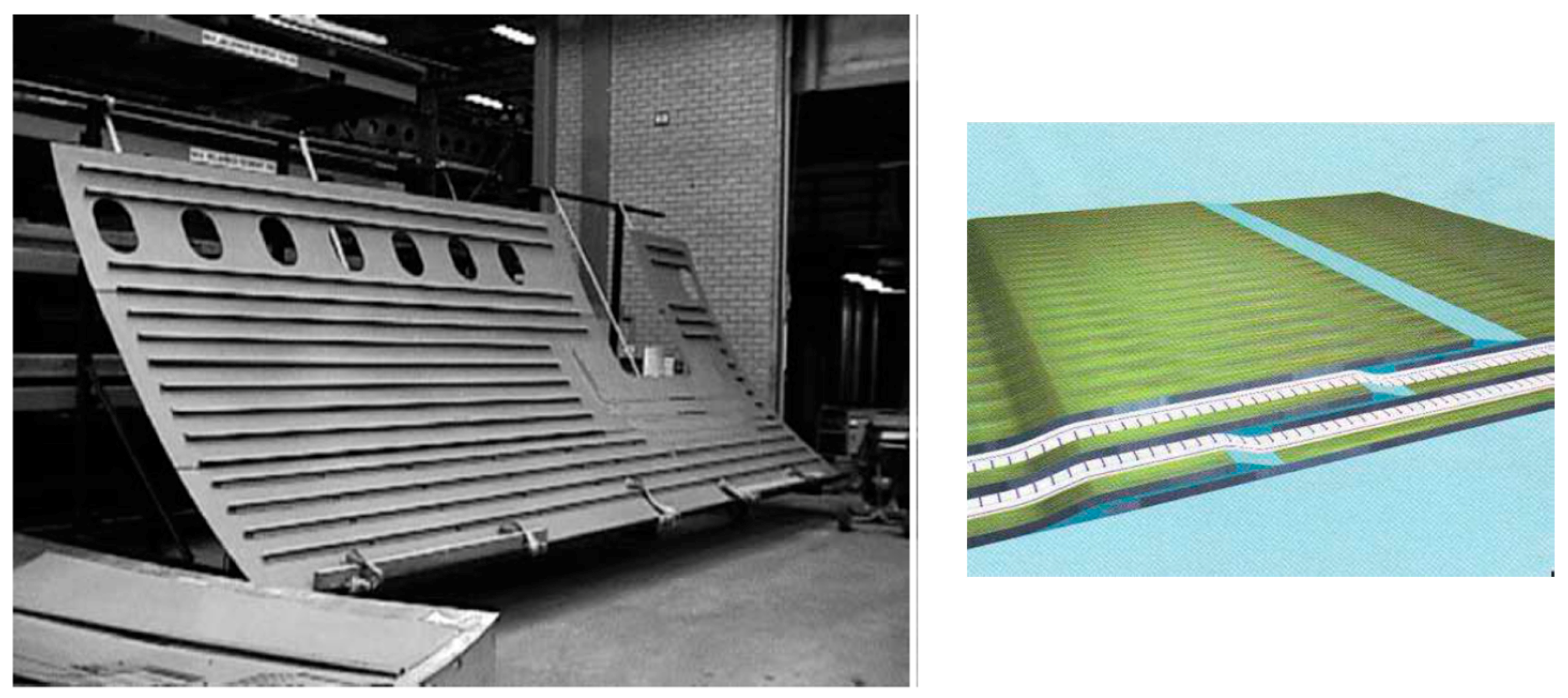
8. Manufacturing-Induced Residual Stresses and Distortions in Fibre Metal Laminates (FML)
8.1. Introduction
8.2. Effective Parameters in the Manufacturing of FML
- Stacking Sequence (laminate layup);
- o
- The difference in CTE of constituents in different directions;
- o
- Difference in shrinkage of the prepreg in different directions during cure;
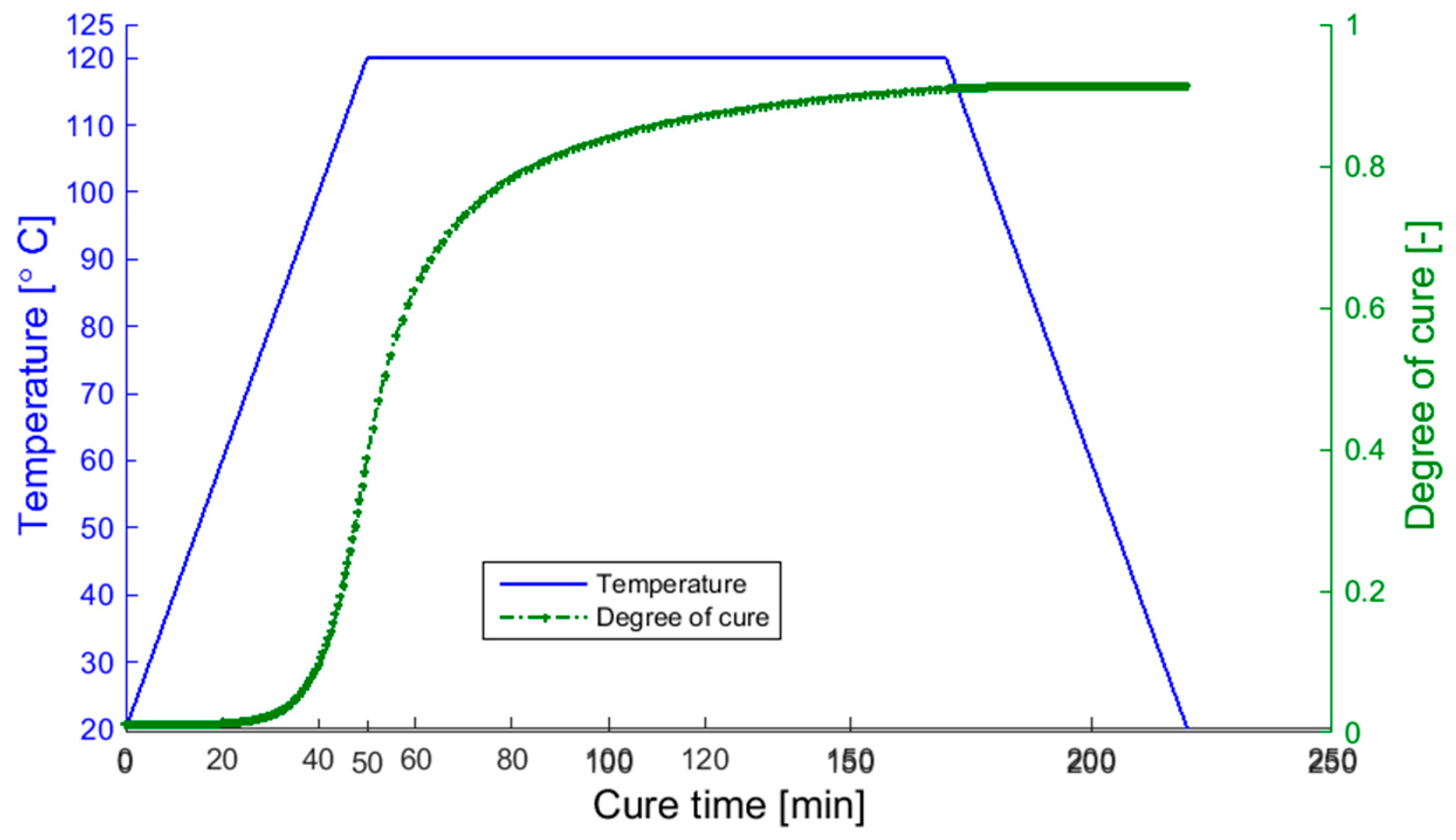
- Cure Cycle parameters like temperature, pressure, heating/cooling rates (see Figure 2);
- Material properties of the ingredients (resin type, fibre material, metal type);
- The thickness of layers in the laminate;
- Tool parameters like material properties and the friction between the tool and the laminate;
- Mould effect, which can be described as the boundary conditions that are imposed to the laminate while having deformations in different layers during the cure cycle;
- Trimming and drilling;
- Creating cut-outs for doors and windows of the fuselage panel;
- Attachment of reinforcement, i.e., large doublers and stringers in a second (bonding) cure cycle;
8.3. Research on the Prediction of Residual Stresses in FML
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hahn, H.T.; Pagano, N.J. Curing stresses in composite laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1975, 9, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, H.T. Residual stresses in polymer matrix composite laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.Y.; Hahn, H.T. Effect of curing stresses on the first ply-failure in composite laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1979, 13, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitsman, Y. Residual thermal stresses due to cool-down of epoxy-resin composites. J. Appl. Mech. 1979, 46, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyer, M.W. Calculations of the room-temperature shapes of unsymmetric laminatestwo. J. Compos. Mater. 1981, 15, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, O.; Kataoka, K. Residual stress measurement of laminated anisotropic plate by strain gauge method. Bull. JSME 1982, 25, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hyer, M.W. The room-temperature shapes of four-layer unsymmetric cross-ply laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1982, 16, 318–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.R.; Mulheron, M.; Bailey, J.E. Generation of thermal strains in GRP. J. Mater. Sci. 1983, 18, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairn, J.A.; Zoller, P. Matrix solidification and the resulting residual thermal stresses in composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1985, 20, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Dol, O.; SATO, M. Residual stress measurement of laminated anisotropic plate by strain gauge method in consideration of strain gauge stiffness and gauge base thickness. Bull. JSME 1986, 29, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, H.; Hyer, M.W. Non-linear temperature-curvature relationships for unsymmetric graphite-epoxy laminates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1987, 23, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.R.; Hahn, H.T. Process modeling of composite materials: Residual stress development during cure. Part II. Experimental validation. J. Compos. Mater. 1992, 26, 2423–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, D.W.; Rennick, T.S. Separating sources of manufacturing distortion in laminated composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2000, 19, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisnom, M.R.; Gigliotti, M.; Ersoy, N.; Campbell, M.; Potter, K.D. Mechanisms generating residual stresses and distortion during manufacture of polymer–matrix composite structures. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 522–529. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogetti, T.A.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr. Process-induced stress and deformation in thick-section thermoset composite laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1992, 26, 626–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, H.J.; Chou, H.L. Chemical shrinkage and diffusion-controlled reaction of an epoxy molding compound. Eur. Polym. J. 2000, 36, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawab, Y.; Jacquemin, F.; Casari, P.; Boyard, N.; Sobotka, V. Shape evolution of carbon epoxy laminated composite during curing. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 504, pp. 1145–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Msallem, Y.A.; Jacquemin, F.; Boyard, N.; Poitou, A.; Delaunay, D.; Chatel, S. Material characterization and residual stresses simulation during the manufacturing process of epoxy matrix composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, G.; Lyden, C.; Lawton, W.; Barrett, J.; Saboui, A.; Pape, H.; Peters, H.J. Importance of molding compound chemical shrinkage in the stress and warpage analysis of PQFPs. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. Part B Adv. Packag. 1996, 19, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrow, D.A., Jr.; Smith, L.V. Isolating components of processing induced warpage in laminated composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2002, 36, 2407–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisnom, M.R.; Potter, K.D.; Ersoy, N. Shear-lag analysis of the effect of thickness on spring-in of curved composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2007, 41, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, N.; Potter, K.; Wisnom, M.R.; Clegg, M.J. An experimental method to study the frictional processes during composites manufacturing. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappel, E.; Stefaniak, D.; Spröwitz, T.; Hühne, C. A semi-analytical simulation strategy and its application to warpage of autoclave-processed CFRP parts. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Kim, M.H.; Choi, H.S.; Chung, C.H.; Ahn, K.J.; Eom, Y.S. A study on the room-temperature curvature shapes of unsymmetric laminates including slippage effects. J. Compos. Mater. 1998, 32, 460–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernlund, G.; Rahman, N.; Courdji, R.; Bresslauer, M.; Poursartip, A.; Willden, K.; Nelson, K. Experimental and numerical study of the effect of cure cycle, tool surface, geometry, and lay-up on the dimensional fidelity of autoclave-processed composite parts. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2002, 33, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twigg, G.; Poursartip, A.; Fernlund, G. An experimental method for quantifying tool–part shear interaction during composites processing. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 13, 1985–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twigg, G.; Poursartip, A.; Fernlund, G. Tool–part interaction in composites processing. Part I: Experimental investigation and analytical model. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twigg, G.; Poursartip, A.; Fernlund, G. Tool–part interaction in composites processing. Part II: Numerical modelling. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, V.; Raghavan, J. Experimental study of tool–part interaction during autoclave processing of thermoset polymer composite structures. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Raghavan, J. Role of tool-part interaction in process-induced warpage of autoclave-manufactured composite structures. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, J.P. Residual thermal stresses in fibre reinforced composite materials—A review. J. Mech. Behav. Mater. 1988, 1, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.S.; Hahn, H.T. Residual stress development during processing of graphite/epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1989, 36, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crasto, A.S.; Kim, R.Y. On the determination of residual stresses in fiber-reinforced thermoset composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 1993, 12, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.R.; Hahn, H.T. Mechanical property and residual stress development during cure of a graphite/BMI composite. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1990, 30, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogetti, T.A.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr. Two-dimensional cure simulation of thick thermosetting composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1991, 25, 239–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; White, S.R. Viscoelastic analysis of processing-induced residual stresses in thick composite laminates. Mech. Compos. Mater. Struct. 1997, 4, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.R.; Kim, Y.K. Process-induced residual stress analysis of AS4/3501-6 composite material. Mech. Compos. Mater. Struct. 1998, 5, 153–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theriault, R.P.; Osswald, T.A.; Castro, J.M. Processing induced residual stress in asymmetric laminate panels. Polym. Compos. 1999, 20, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genidy, M.S.; Madhukar, M.S.; Russell, J.D. A new method to reduce cure-induced stresses in thermoset polymer composites, Part II: Closed loop feedback control system. J. Compos. Mater. 2000, 34, 1905–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhukar, M.S.; Genidy, M.S.; Russell, J.D. A new method to reduce cure-induced stresses in thermoset polymer composites, part I: Test method. J. Compos. Mater. 2000, 34, 1882–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.D.; Madhukar, M.S.; Genidy, M.S.; Lee, A.Y. A new method to reduce cure-induced stresses in thermoset polymer composites, part III: Correlating stress history to viscosity, degree of cure, and cure shrinkage. J. Compos. Mater. 2000, 34, 1926–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.R.; Hahn, H.T. Cure cycle optimization for the reduction of processing-induced residual stresses in composite materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1993, 27, 1352–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, P.; Cottu, J.P. Optimisation of the co-curing of two different composites with the aim of minimising residual curing stress levels. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1998, 58, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Lee, S.W. Cure simulation of thick composite structures using the finite element method. J. Compos. Mater. 2001, 35, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Geubelle, P.H.; Li, M.; Tucker, C.L., III. Dimensional accuracy of thermoset composites: Simulation of process-induced residual stresses. J. Compos. Mater. 2001, 35, 2171–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.; Vaziri, R.; Poursartip, A. A plane strain model for process-induced deformation of laminated composite structures. J. Compos. Mater. 2001, 35, 1435–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oota, K.; Saka, M. Cure shrinkage analysis of epoxy molding compound. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2001, 41, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanberg, J.M.; Holmberg, J.A. Prediction of shape distortions Part I. FE-implementation of a path dependent constitutive model. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanberg, J.M.; Holmberg, J.A. Prediction of shape distortions. Part II. Experimental validation and analysis of boundary conditions. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrieh, M.M.; Kamali, S.M. Theoretical and experimental studies on residual stresses in laminated polymer composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2005, 39, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlevliet, P.P.; Bersee, H.E.; Beukers, A. Residual stresses in thermoplastic composites—A study of the literature—Part I: Formation of residual stresses. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlevliet, P.P.; Bersee, H.E.; Beukers, A. Residual stresses in thermoplastic composites—A study of the literature—Part II: Experimental techniques. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlevliet, P.P.; Bersee, H.E.; Beukers, A. Residual stresses in thermoplastic composites—A study of the literature. Part III: Effects of thermal residual stresses. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 1581–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.S.; Du, S.; Zhang, B. Temperature field of thick thermoset composite laminates during cure process. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Msallem, Y.; Kassem, H.; Jacquemin, F.; Poitou, A. Experimental study of the induced residual stresses during the manufacturing process of an aeronautic composite material. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 2, 596–602. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, A.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zu, L. A three-dimensional thermo-viscoelastic analysis of process-induced residual stress in composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2015, 129, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zu, L. A comparison of process-induced residual stresses and distortions in composite structures with different constitutive laws. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2016, 35, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Su, H.; Jia, Y. Curing process-induced internal stress and deformation of fiber reinforced resin matrix composites: Numerical comparison between elastic and viscoelastic models. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2016, 24, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, X.; Dai, J.; Xi, S. A comparison of curing process-induced residual stresses and cure shrinkage in micro-scale composite structures with different constitutive laws. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2018, 25, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Xi, S.; Li, D. Numerical analysis of curing residual stress and deformation in thermosetting composite laminates with comparison between different constitutive models. Materials 2019, 12, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourour, S.; Kamal, M.R. Differential scanning calorimetry of epoxy cure: Isothermal cure kinetics. Thermochim. Acta 1976, 14, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamzeh, M.; Sinke, J.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Benedictus, R. Kinetic and thermo-viscoelastic characterisation of the epoxy adhesive in GLARE. Compos. Struct. 2015, 124, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capehart, T.W.; Hamid, G.K.; Taher, A. Cure Simulation of Thermoset Composite Panels. J. Compos. Mater. 2007, 41, 1339–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, N.; Tugutlu, M. Cure kinetics modeling and cure shrinkage behavior of a thermosetting composite. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 50, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.A.; Pagani, N.; Riccardi, C.C.; Borrajo, J.; Goyanes, S.N.; Mondragon, I. Cure kinetics and shrinkage model for epoxy-amine systems. Polymer 2005, 46, 3323–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamzeh, M.; Sinke, J.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Benedictus, R. Closed form expression for residual stresses and warpage during cure of composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2015, 133, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamzeh, M.; Sinke, J.; Benedictus, R. A large displacement orthotropic viscoelastic model for manufacturing-induced distortions in Fibre Metal Laminates. Compos. Struct. 2019, 209, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.D. Cure shrinkage of thermoset composites. Sampe Q. Soc. Adv. Mater. Process Eng. 1993, 24, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, K.M.B.; Hawryluk, M.; Gromala, P. Cure dependent characterisation of moulding compounds. In Proceedings of the 2011 12th International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems, Linz, Austria, 18–20 April 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nawab, Y.; Boyard, N.; Sobotka, V.; Casari, P.; Jacquemin, F. Measurement and modelling of chemical shrinkage of thermoset composites. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 504, pp. 1129–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghinia, M.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Ernst, L.J. Characterization and modeling the thermo-mechanical cure-dependent properties of epoxy molding compound. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2012, 32, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergheim, J.; Possart, G.; Steinmann, P. Modelling and computation of curing and damage of thermosets. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 53, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vreugd, J.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Ernst, L.J.; Pijnenburg, J.A.C.M. Modelling of viscoelastic properties of a curing adhesive. WIT Trans. Eng. Sci. 2007, 57, 241. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, L.J.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Saraswat, M.; Van ’T Hof, C.; Zhang, G.Q.; Yang, D.G.; Bressers, H.J.L. Fully cure-dependent modelling and characterization of EMC’s with application to package warpage simulation. In Proceedings of the 2006 7th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology, Shanghai, China, 26–29 August 2007; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, K.M.B.; De Vreugd, J.; Ernst, L.J. Analytical estimate for curing-induced stress and warpage in coating layers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminero, M.A.; Pavlopoulou, S.; Lopez-Pedrosa, M.; Nicolaisson, B.G.; Pinna, C.; Soutis, C. Analysis of adhesively bonded repairs in composites: Damage detection and prognosis. Compos. Struct. 2013, 95, 500–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.P.; Xiang, Z.G.; Hsu, S.L.; Schoch, A.B.; Carleen, S.A.; Matsumoto, D. Characterization of the crosslinking reaction in high performance adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 78, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.P.; Xiang, Z.G.; Hsu, S.L.; Schoch, A.B.; Carleen, S.A.; Matsumoto, D. Path to achieving molecular dispersion in a dense reactive mixture. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2015, 53, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.P.; Deshmukh, S.; Zhao, C.; Wamuo, O.; Hsu, S.L.; Schoch, A.B.; Carleen, S.A.; Matsumoto, D. An analysis of the role of nonreactive plasticizers in the crosslinking reactions of a rigid resin. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2017, 55, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vreugd, J.; Jansen, K.M.; Ernst, L.J.; Bohm, C. Prediction of cure induced warpage of micro-electronic products. Microelectron. Reliab. 2010, 50, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, D. Introduction to Percolation Theory; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Adolf, D.; Martin, J.E. Calculation of stresses in crosslinking polymers. J. Compos. Mater. 1996, 30, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, D.B.; Chambers, R.S. A thermodynamically consistent, nonlinear viscoelastic approach for modeling thermosets during cure. J. Rheol. 2007, 51, 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, L.; Deng, Y.; Gao, Z.; Xu, C.; Zhang, M. Study of gelation using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). J. Therm. Anal. 1997, 49, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menczel, J.D.; Prime, R.B. (Eds.) Thermal Analysis of Polymers: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hayaty, M.; Beheshty, M.H.; Esfandeh, M. A new approach for determination of gel time of a glass/epoxy prepreg. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 1438–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilyeu, B.; Brostow, W.; Menard, K.P. Separation of gelation from vitrification in curing of a fiber-reinforced epoxy composite. Polym. Compos. 2002, 23, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, J.; Andreasen, J.H.; Thomsen, O.T. A comparison of gel point for a glass/epoxy composite and a neat epoxy material during isothermal curing. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 48, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Li, M.; Su, Y. A new method to characterize the cure state of epoxy prepreg by dynamic mechanical analysis. Thermochim. Acta 2009, 487, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, W.; Jaunich, M.; McHugh, J. Carbon-fibre epoxy prepreg (CFC) curing in an autoclave analogue process controlled by Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA). Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, W. Investigation of the curing behaviour of carbon fibre epoxy prepreg by Dynamic Mechanical Analysis DMA. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamzeh, M.; Sinke, J.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Benedictus, R. A new procedure for thermo-viscoelastic modelling of composites with general orthotropy and geometry. Compos. Struct. 2015, 153, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamzeh, M.; Sinke, J.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Benedictus, R. Thermo-viscoelastic analysis of GLARE. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 99, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, K.M.B.; Wang, L.; Van’t Hof, C.; Ernst, L.J.; Bressers, H.J.L.; Zhang, G.Q. Cure, temperature and time dependent constitutive modeling of moulding compounds. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Thermal and Mechanical Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems, Brussels, Belgium, 10–12 May 2004; p. 581. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, K.M.B.; Wang, L.; Yang, D.G.; Van’t Hof, C.; Ernst, L.J.; Bressers, H.J.L.; Zhang, G.Q. Constitutive modeling of moulding compounds [electronic packaging applications]. In Proceedings of the 54th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4 June 2004; pp. 890–894. [Google Scholar]
- Van’t Hof, C.; Wisse, G.; Ernst, L.J.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Yang, D.G.; Zhang, G.Q.; Bressers, H.J.L. A novel tool for cure dependent viscoelastic characterization of packaging polymers. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Thermal and Mechanical Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems, Brussels, Belgium, 10–12 May 2004; pp. 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, D.J.; Mather, P.T.; White, S.R. Viscoelastic properties of an epoxy resin during cure. J. Compos. Mater. 2001, 35, 883–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; White, S.R. Stress relaxation behavior of 3501-6 epoxy resin during cure. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 2852–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Yang, Y.G.; Yu, H.H.; Sun, W.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhou, H.W. Assessment of residual stresses during cure and cooling of epoxy resins. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1995, 23, 1895–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J.; Toll, S.; Månson, J.A.E.; Hult, A. Residual stress build-up in thermoset films cured below their ultimate glass transition temperature. Polymer 1997, 38, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J.; Toll, S.; Månson, J.A.E.; Hult, A. Residual stress build-up in thermoset films cured above their ultimate glass transition temperature. Polymer 1995, 36, 3135–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Huang, P. Effect of cure cycle on temperature/degree of cure field and hardness for epoxy resin. E-Polymers 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.C.; Huang, P. Effect of cure cycle on curing process and hardness for epoxy resin. Express Polym. Lett. 2009, 3, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebl, C.; Johlitz, M.; Yagimli, B.; Lion, A. Three-dimensional chemo-thermomechanically coupled simulation of curing adhesives including viscoplasticity and chemical shrinkage. Comput. Mech. 2012, 49, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.G.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Ernst, L.J.; Zhang, G.Q.; Van Brief, W.D.; Bressers, H.J.L. Modeling of cure-induced warpage of plastic IC packages. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Thermal and Mechanical Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems, Brussels, Belgium, 10–12 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.G.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Ernst, L.J.; Zhang, G.Q.; Van Brief, W.D.; Bressers, H.J.L.; Fan, X.J. Prediction of process-induced warpage of IC packages encapsulated with thermosetting polymers. In Proceedings of the 54th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.G.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Wang, L.G.; Ernst, L.J.; Zhang, G.Q.; Bressers, H.J.L.; Fan, X. Micromechanical modeling of stress evolution induced during cure in a particle-filled electronic packaging polymer. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 2004, 27, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.G.; Jansen, K.M.; Ernst, L.J.; Zhang, G.Q.; Van Driel, W.D.; Bressers, H.J.L.; Janssen, J.H.J. Numerical modeling of warpage induced in QFN array molding process. Microelectron. Reliab. 2007, 47, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van’t Hof, C.; Jansen, K.M.; Wisse, G.; Ernst, L.J.; Yang, D.G.; Zhang, G.Q.; Bressers, H.J.L. Novel shear tools for viscoelastic characterization of packaging polymers. Microelectron. Reliab. 2007, 47, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghinia, M.; Jansen, K.M.; Ernst, L.J. Characterization of the viscoelastic properties of an epoxy molding compound during cure. Microelectron. Reliab. 2012, 52, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, K.M.B.; Qian, C.; Ernst, L.J.; Bohm, C.; Kessler, A.; Preu, H.; Stecher, M. Kinetic characterisation of molding compounds. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation Experiments in Microelectronics and Micro-Systems, London, UK, 16–18 April 2007; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- De Vreugd, J.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Ernst, L.J.; Bohm, C.; Kessler, A.; Preu, H. Effects of molding compound cure on warpage of electronic packages. In Proceedings of the 2008 10th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference, Singapore, 9–12 December 2008; pp. 675–682. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, K.M.B.; Qian, C.; Ernst, L.J.; Bohm, C.; Kessler, A.; Preu, H.; Stecher, M. Characterization and modeling of molding compound properties during cure. In Proceedings of the EuroSimE 2008-International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Micro-Systems, Breisgau, Germany, 20–23 April 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, K.M.; Öztürk, B. Warpage estimation of a multilayer package including cure shrinkage effects. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 3, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, Y. An improved analytical solution for process-induced residual stresses and deformations in flat composite laminates considering thermo-viscoelastic effects. Materials 2018, 10, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, L.J.B.; Powell, P.C.; Warnet, L. Thermally-induced shapes of unsymmetric laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1996, 30, 603–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, C.; Fernlund, G. Spring-in and warpage of angled composite laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 1895–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Pang, S.S.; Sterling, A.M.; Negulescu, I.I.; Stubblefield, M.A. Dynamic modeling of curing process of epoxy prepreg. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 1911–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapanapalli, S.K.; Smith, L.V. A linear finite element model to predict processing-induced distortion in FRP laminates. Compos. PART A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.K.; Kim, B.; Won, M.S.; Ahn, S.H. Fabrication of radar absorbing structure (RAS) using GFR-nano composite and spring-back compensation of hybrid composite RAS shells. Compos. Struct. 2006, 75, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capehart, T.W.; Muhammad, N.; Kia, H.G. Compensating thermoset composite panel deformation using corrective molding. J. Compos. Mater. 2007, 41, 1675–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.K.; Chu, W.S.; Ahn, S.H.; Won, M.S. Measurement and compensation of spring-back of a hybrid composite beam. J. Compos. Mater. 2007, 41, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, N.; Garstka, T.; Potter, K.; Wisnom, M.R.; Porter, D.; Stringer, G. Modelling of the spring-in phenomenon in curved parts made of a thermosetting composite. Compos. PART A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, N.; Potter, K.; Wisnom, M.R.; Clegg, M.J. Development of spring-in angle during cure of a thermosetting composite. Compos. PART A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 1700–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magniez, K.; Vijayan, A.; Finn, N. Apparent volumetric shrinkage study of RTM6 resin during the curing process and its effect on the residual stresses in a composite. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2012, 52, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelal, G.F.; Robotham, A.; Cantwell, W. Autoclave cure simulation of composite structures applying implicit and explicit FE techniques. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 2013, 9, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, B.; Roozbehjavan, P.; Ahmed, A.; Das, R.; Joven, R.; Koushyar, H.; Rodriguez, A.; Minaie, B. Prediction of residual stresses and distortion in carbon fiber-epoxy composite parts due to curing process using finite element analysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 28, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbeek, M. Characterisation of Fibre Metal Laminates under Thermo-mechanical Loadings. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Asundi, A.; Choi, A.Y. Fiber metal laminates: An advanced material for future aircraft. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1997, 63, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderliesten, R.C. Fatigue Crack Propagation and Delamination Growth in Glare. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Homan, J.J. Fatigue initiation in fibre metal laminates. Int. J. Fatigue 2006, 28, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinke, J. Development of fibre metal laminates: Concurrent multi-scale modeling and testing. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 6777–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderliesten, R.; Benedictus, R. Fiber/metal composite technology for future primary aircraft structures. J. Aircr. 2008, 45, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekıner, Z. An experimental study on the examination of springback of sheet metals with several thicknesses and properties in bending dies. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 145, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouati, O.; Joannic, D.; Gelin, J.C. Optimisation of process parameters for the control of springback in deep drawing. In Proceedings of the NUMIFORM 98: Sixth International Conference on Numerical Methods in Industrial Forming Processes, Enschede, The Netherlands, 22–25 June 1998; pp. 819–824. [Google Scholar]
- Lingbeek, R.; Huetink, J.; Ohnimus, S.; Petzoldt, M.; Weiher, J. The development of a finite elements based springback compensation tool for sheet metal products. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 169, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chung, K.; Li, X.X.; Park, T.; Zhou, G.F.; Yao, R. An automatic spring-back compensation method in die design based on a genetic algorithm. Met. Mater. Int. 2011, 17, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Hu, J.; Chung, K.; Zhou, G.F.; Yao, R. 8th International Conference and Workshop on Numerical Simulation of 3d Sheet Metal Forming Processes. In American Institute of Physics Conference Series; Web of Science Group: College Park, MD, USA, 2011; p. 1092. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, M.G.; Barlat, F. Finite element modeling using homogeneous anisotropic hardening and application to spring-back prediction. Int. J. Plast. 2012, 29, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Choi, W.J.; Park, S.Y. Spring-back characteristics of fiber metal laminate (GLARE) in brake forming process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 32, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krimbalis, P.P.; Poon, C.; Fawaz, Z.; Behdinan, K. On the prediction of induced residual stresses in fibre metal laminates. In Proceedings of the 7th Joint Canada-Japan Workshop on Composites, Fujisawa, Japan, 28–31 July 2008; pp. 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Hofslagare, P. Residual stress measurement on fibre-metal-laminates. J. Neutron Res. 2003, 11, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, I.; Alderliesten, R.C.; Benedictus, R. Design optimisation procedure for fibre metal laminates based on fatigue crack initiation. Compos. Struct. 2015, 120, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, I.; Alderliesten, R.C.; Benedictus, R. Lay-up optimisation of fibre metal laminates based on fatigue crack propagation and residual strength. Compos. Struct. 2015, 124, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamzeh, M.; Sinke, J.; Benedictus, R. On the prediction of cure-process shape deviations in fibre metal laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 1705–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamzeh, M.; Sinke, J.; Benedictus, R. Investigation of curing effects on distortion of fibre metal laminates. Compos. Struct. 2015, 122, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhamzeh, M.; Sinke, J.; Benedictus, R. On the investigation of residual stress and shape deviation development in manufacturing of GLARE. In Proceedings of the ECCM16-16th European Conference on Composite Materials, Seville, Spain, 22–26 June 2014. [Google Scholar]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abouhamzeh, M.; Sinke, J.; Benedictus, R. Prediction Models for Distortions and Residual Stresses in Thermoset Polymer Laminates: An Overview. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2019, 3, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3040087
Abouhamzeh M, Sinke J, Benedictus R. Prediction Models for Distortions and Residual Stresses in Thermoset Polymer Laminates: An Overview. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2019; 3(4):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3040087
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbouhamzeh, Morteza, Jos Sinke, and Rinze Benedictus. 2019. "Prediction Models for Distortions and Residual Stresses in Thermoset Polymer Laminates: An Overview" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 3, no. 4: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3040087
APA StyleAbouhamzeh, M., Sinke, J., & Benedictus, R. (2019). Prediction Models for Distortions and Residual Stresses in Thermoset Polymer Laminates: An Overview. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 3(4), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3040087





