Sustainability Assessment during Machining Ti-6Al-4V with Nano-Additives-Based Minimum Quantity Lubrication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
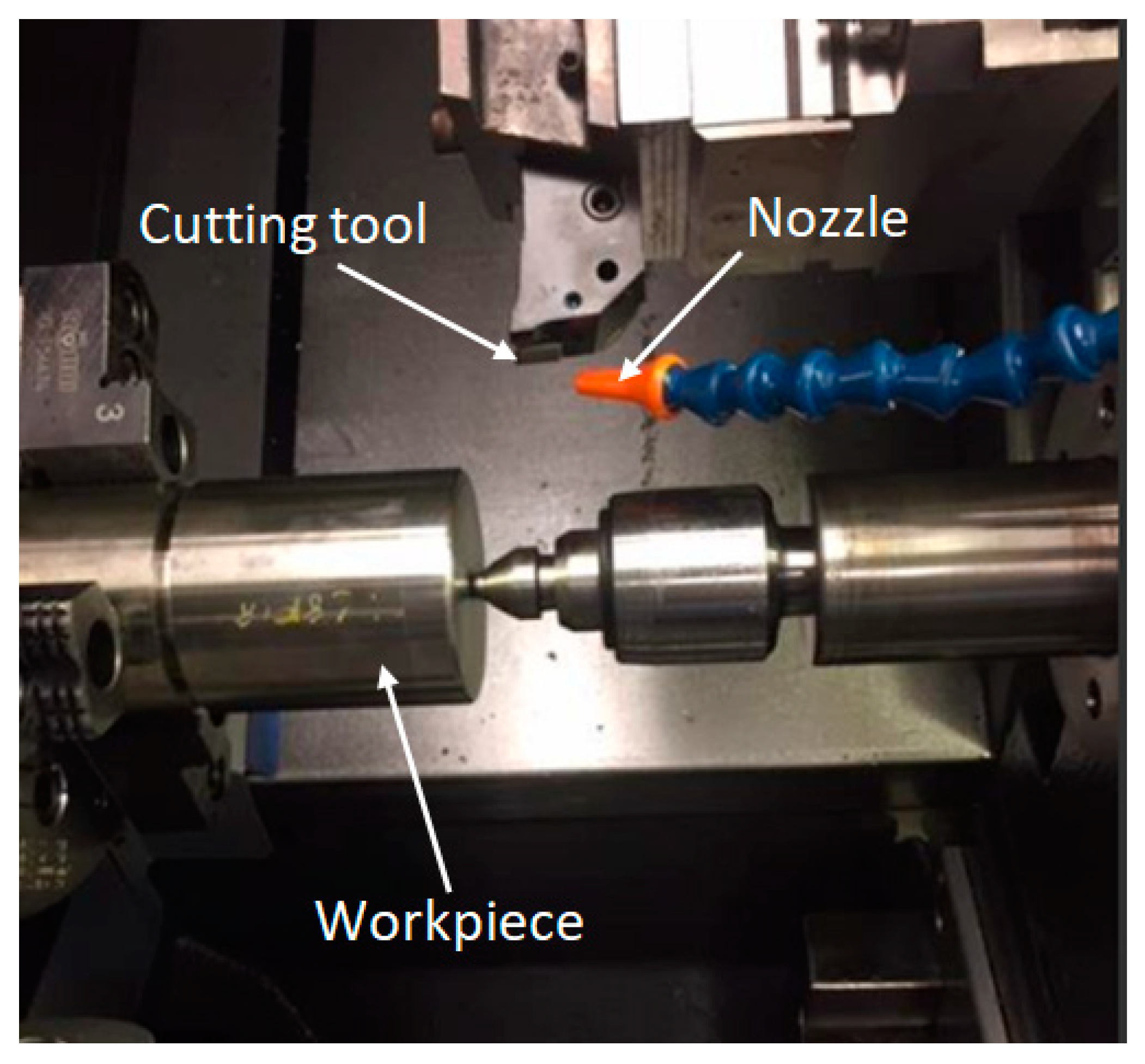
2. Experimentation and Methods
3. Experimental Results
4. Sustainability Assessment
- Selecting and defining the studied sustainable metrics and their corresponding indictors
- Normalizing/scaling the studied machining outputs, and sustainability metrics and indicators
- Weighting of normalized factors
- Calculating the overall sustainability assessment index (TWSI).
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garg, G.K.; Garg, S.; Sangwan, K. Development of an Empirical Model for Optimization of Machining Parameters to Minimize Power Consumption. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 346, 012078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Uhan, N.; Zhao, F.; Sutherland, J.W. A new approach to scheduling in manufacturing for power consumption and carbon footprint reduction. J. Manuf. Syst. 2011, 30, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, K.S. Development of a multi criteria decision model for justification of green manufacturing systems. Int. J. Green Econ. 2011, 5, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Kishawy, H.A. Cutting tool materials and tool wear. In Machining of Titanium Alloys; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kishawy, H.A.; Pang, L.; Balazinski, M. Modeling of tool wear during hard turning with self-propelled rotary tools. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2011, 53, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.A.; Gadallah, M.H.; Esawi, A.K. Modeling and optimization of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) using statistical design. Manuf. Rev. 2015, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishawy, H.A.; Hegab, H.; Umer, U.; Mohany, A. Application of acoustic emissions in machining processes: analysis and critical review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 1391–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishawy, H.A.; Haglund, A.; Balazinski, M. Modelling of material side flow in hard turning. CIRP Ann. 2006, 55, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishawy, H.A.; Elbestawi, M.A. Effect of process parameters on chip morphology when machining hardened steel. In Proceedings of the IMECE, ASME, New York, NY, USA, 16–21 November 1997; Volume 6, pp. 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- El-Mounayri, H.; Kishawy, H.; Tandon, V. Optimized CNC end-milling: A practical approach. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2002, 15, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, Z.; Hegab, H.; Kishawy, H.A. Analytical prediction of delamination during drilling composite laminates. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 26, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krolczyk, G.M.; Maruda, R.W.; Krolczyk, J.B.; Wojciechowski, S.; Mia, M.; Nieslony, P.; Budzik, G. Ecological trends in machining as a key factor in sustainable production—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, A.E.; de Oliveira, A.J. Optimizing the use of dry cutting in rough turning steel operations. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, A.E.; Micaroni, R. Cutting conditions for finish turning process aiming: the use of dry cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2002, 42, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.M.; Chou, S.Y. Experimental evaluation of minimum quantity lubrication in near micro-milling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, E.; Sasahara, H. A study of the effect of palm oil as MQL lubricant on high speed drilling of titanium alloys. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, N.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Ahmed, M. Effect of minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) on tool wear and surface roughness in turning AISI-4340 steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 172, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, D.U.; Diniz, A.E.; Miranda, G.W.A.; Coppini, N.L. Using a minimum quantity of lubricant (MQL) and a diamond coated tool in the drilling of aluminum–silicon alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 122, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obikawa, T.; Kamata, Y.; Shinozuka, J. High-speed grooving with applying MQL. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaggaz, A.; Hegab, H.; Deiab, I.; Kishawy, H.A. Hybrid nano-fluid-minimum quantity lubrication strategy for machining austempered ductile iron (ADI). Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 2018, 12, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Darras, B.; Kishawy, H. Sustainability assessment of machining with nano-cutting fluids. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 26, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Kishawy, H. Towards sustainable machining of Inconel 718 using nano-fluid minimum quantity lubrication. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2018, 2, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Khan, A.M.; Hegab, H.; Gong, L.; Mia, M.; Gupta, M.K.; He, N. Effects of hybrid Al2O3-CNT nanofluids and cryogenic cooling on machining of Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 3895–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Kishawy, H.A.; Umer, U.; Mohany, A. A model for machining with nano-additives based minimum quantity lubrication. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 2013–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatha, S.S.; Pal, A.; Singh, T. Performance evaluation of aluminum 6063 drilling under the influence of nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Jia, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X. Experimental evaluation of MoS2 nanoparticles in jet MQL grinding with different types of vegetable oil as base oil. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Kishawy, H.; Darras, B. Sustainable Cooling and Lubrication Strategies in Machining Processes: A Comparative Study. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 33, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P. Machining of Hard Materials; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Davim, J.P.; Sreejith, P.; Silva, J. Turning of brasses using minimum quantity of lubricant (MQL) and flooded lubricant conditions. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2007, 22, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrani, A.; Al-Samarrai, I.; Newman, S.T. Hybrid cryogenic MQL for improving tool life in machining of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 43, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrita, M.; Srikant, R.; Sitaramaraju, A. Performance evaluation of nanographite-based cutting fluid in machining process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandekar, S.; Sankar, M.R.; Agnihotri, V.; Ramkumar, J. Nano-cutting fluid for enhancement of metal cutting performance. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2012, 27, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.S.; Lee, P.H.; Lee, S.W. Experimental characterization of micro-drilling process using nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2011, 51, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.H.; Nam, J.S.; Li, C.; Lee, S.W. An experimental study on micro-grinding process with nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication (MQL). Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2012, 13, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, S.W. Experimental characterization on micro-end milling of titanium alloy using nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication with chilly gas. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 2741–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Darras, B.; Kishawy, H. Towards sustainability assessment of machining processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dureja, J.; Singh, R.; Singh, T.; Singh, P.; Dogra, M.; Bhatti, M.S. Performance evaluation of coated carbide tool in machining of stainless steel (AISI 202) under minimum quantity lubrication (MQL). Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2015, 2, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klocke, F.; Eisenblätter, G. Dry cutting. Cirp Ann. 1997, 46, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschätsch, H.; Reichelt, A. Cutting fluids (coolants and lubricants). In Applied Machining Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 349–352. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Long, Q.; Wen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L. Influence of pH on the stability characteristics of nanofluids. In Proceedings of the 2009 Symposium on Photonics and Optoelectronics, Wuhan, China, 14–16 August 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, Y.J.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, C.H.; Jung, Y.M.; Cheong, S.I.; Lee, C.G.; Ku, B.C.; Jang, S.P. Stability and thermal conductivity characteristics of nanofluids. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 455, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandsburger, L. Synthesis and Covalent Surface Modification of Carbon Nanotubes for Preparation of Stabilized Nanofluid Suspensions; McGill University: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Loos, M. Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: CNT Polymer Science and Technologyp; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hegab, H.; Umer, U.; Soliman, M.; Kishawy, H.A. Effects of nano-cutting fluids on tool performance and chip morphology during machining Inconel 718. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 3449–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Umer, U.; Soliman, M.; Kishawy, H. Performance evaluation of Ti-6Al-4V machining using nano-cutting fluids under minimum quantity lubrication. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 95, 4229–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaggaz, A.; Zawada, P.; Hegab, H.A.; Deiab, I. Coolant strategy influence on tool life and surface roughness when machining ADI. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 3875–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Kishawy, H.A.; Gadallah, M.H.; Umer, U.; Deiab, I. On machining of Ti-6Al-4V using multi-walled carbon nanotubes-based nano-fluid under minimum quantity lubrication. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishawy, H.; Hegab, H.; Saad, E. Design for sustainable manufacturing: Approach, implementation, and assessment. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaednia, H.; Jackson, R.L. The effect of nanoparticles on the real area of contact, friction, and wear. J. Tribol. 2013, 135, 041603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Experiment No. | A: Cutting Speed (m/min) | B: Feed Rate (mm/rev) | C: Nanoparticles Concentration (wt. %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 120 | 0.1 | 0 |
| 2 | 120 | 0.15 | 2 |
| 3 | 120 | 0.2 | 4 |
| 4 | 170 | 0.1 | 2 |
| 5 | 170 | 0.15 | 4 |
| 6 | 170 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 7 | 220 | 0.1 | 4 |
| 8 | 220 | 0.15 | 0 |
| 9 | 220 | 0.2 | 2 |
| Experiment No. | Surface Roughness (µm) | Max Flank Wear (mm) | Power Consumption (W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.891 | 0.236 | 2325 |
| 2 | 0.852 | 0.165 | 2041 |
| 3 | 1.692 | 0.162 | 1959 |
| 4 | 0.512 | 0.192 | 2079 |
| 5 | 1.421 | 0.153 | 2106 |
| 6 | 2.812 | 0.563 | 2454 |
| 7 | 0.563 | 0.180 | 2084 |
| 8 | 1.890 | 0.561 | 2634 |
| 9 | 0.951 | 0.242 | 2236 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kishawy, H.A.; Hegab, H.; Deiab, I.; Eltaggaz, A. Sustainability Assessment during Machining Ti-6Al-4V with Nano-Additives-Based Minimum Quantity Lubrication. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2019, 3, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3030061
Kishawy HA, Hegab H, Deiab I, Eltaggaz A. Sustainability Assessment during Machining Ti-6Al-4V with Nano-Additives-Based Minimum Quantity Lubrication. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2019; 3(3):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3030061
Chicago/Turabian StyleKishawy, Hossam A., Hussien Hegab, Ibrahim Deiab, and Abdelkrem Eltaggaz. 2019. "Sustainability Assessment during Machining Ti-6Al-4V with Nano-Additives-Based Minimum Quantity Lubrication" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 3, no. 3: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3030061
APA StyleKishawy, H. A., Hegab, H., Deiab, I., & Eltaggaz, A. (2019). Sustainability Assessment during Machining Ti-6Al-4V with Nano-Additives-Based Minimum Quantity Lubrication. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 3(3), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp3030061








