Yield Estimation of Longline Aquaculture by the Shadows of Buoys Based on UAV Orthophoto Image
Highlights
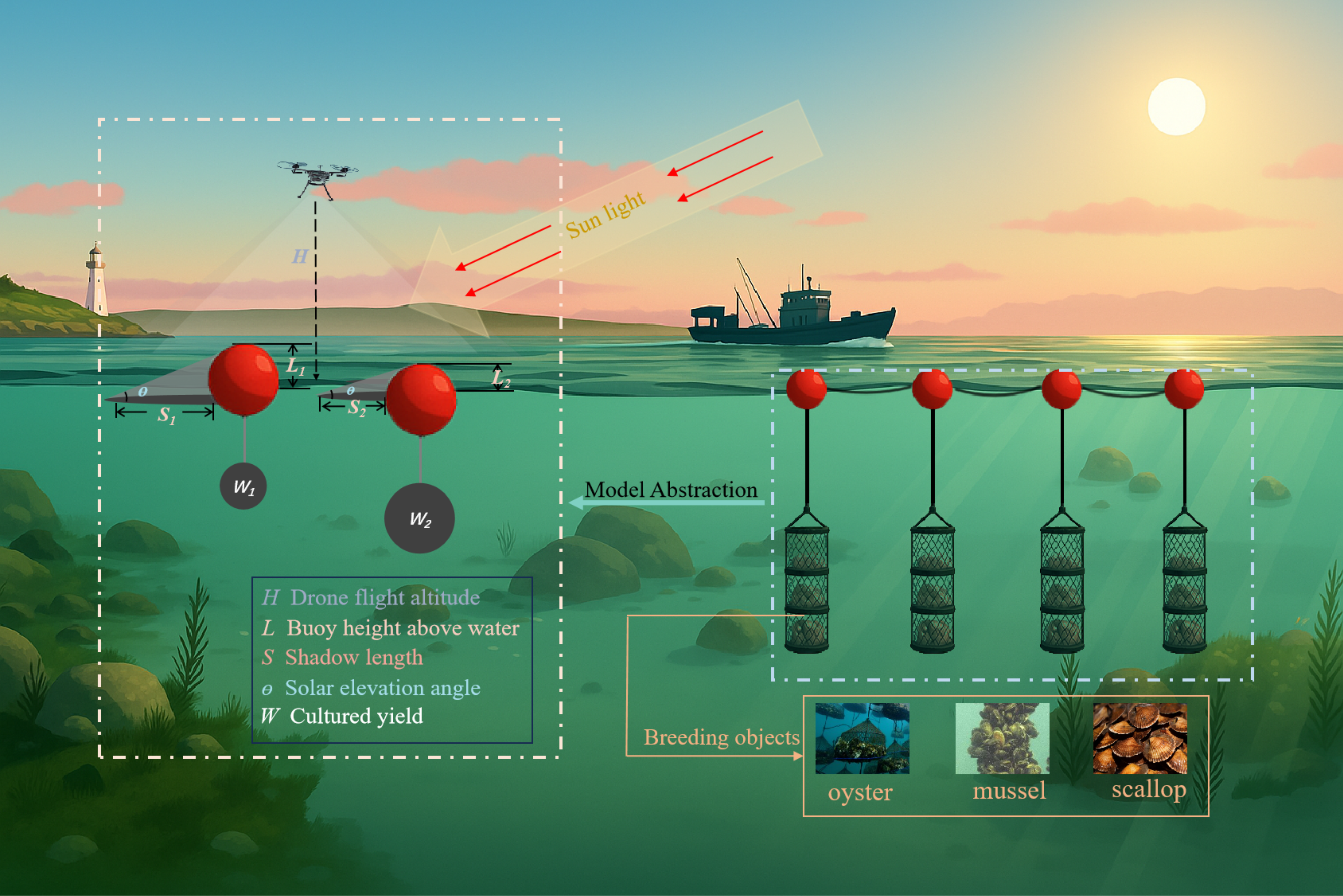
- Developed a physically interpretable Shadow Geometry Inversion for Aquaculture (SGIA) model that estimates yield in longline aquaculture through the geometric relationship between buoy shadows and solar altitude using UAV imagery.
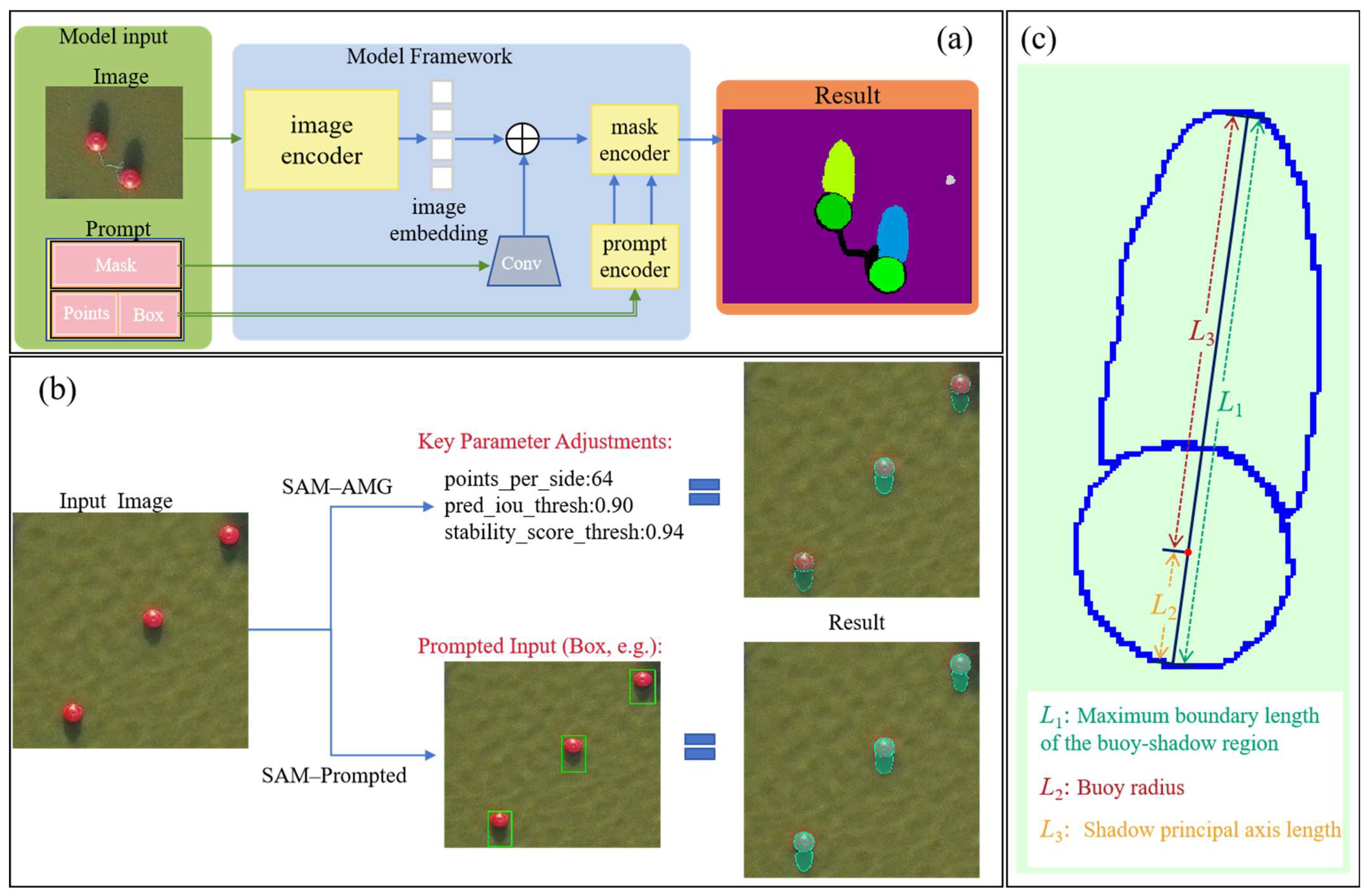
- Applied the Segment Anything Model (SAM) for automatic buoy and shadow boundary extraction, achieving precise segmentation across variable lighting and water-surface conditions without retraining or manual labeling.
- Provides a physically interpretable and non-contact method for high-precision yield estimation in suspended longline aquaculture, offering a scalable alternative to labor-intensive field measurements.
- Explores the potential of foundation models such as SAM for extracting water-surface shadows and fine geometric features from UAV imagery, paving the way for broader remote-sensing applications in aquatic environments.
Abstract
1. Introduction
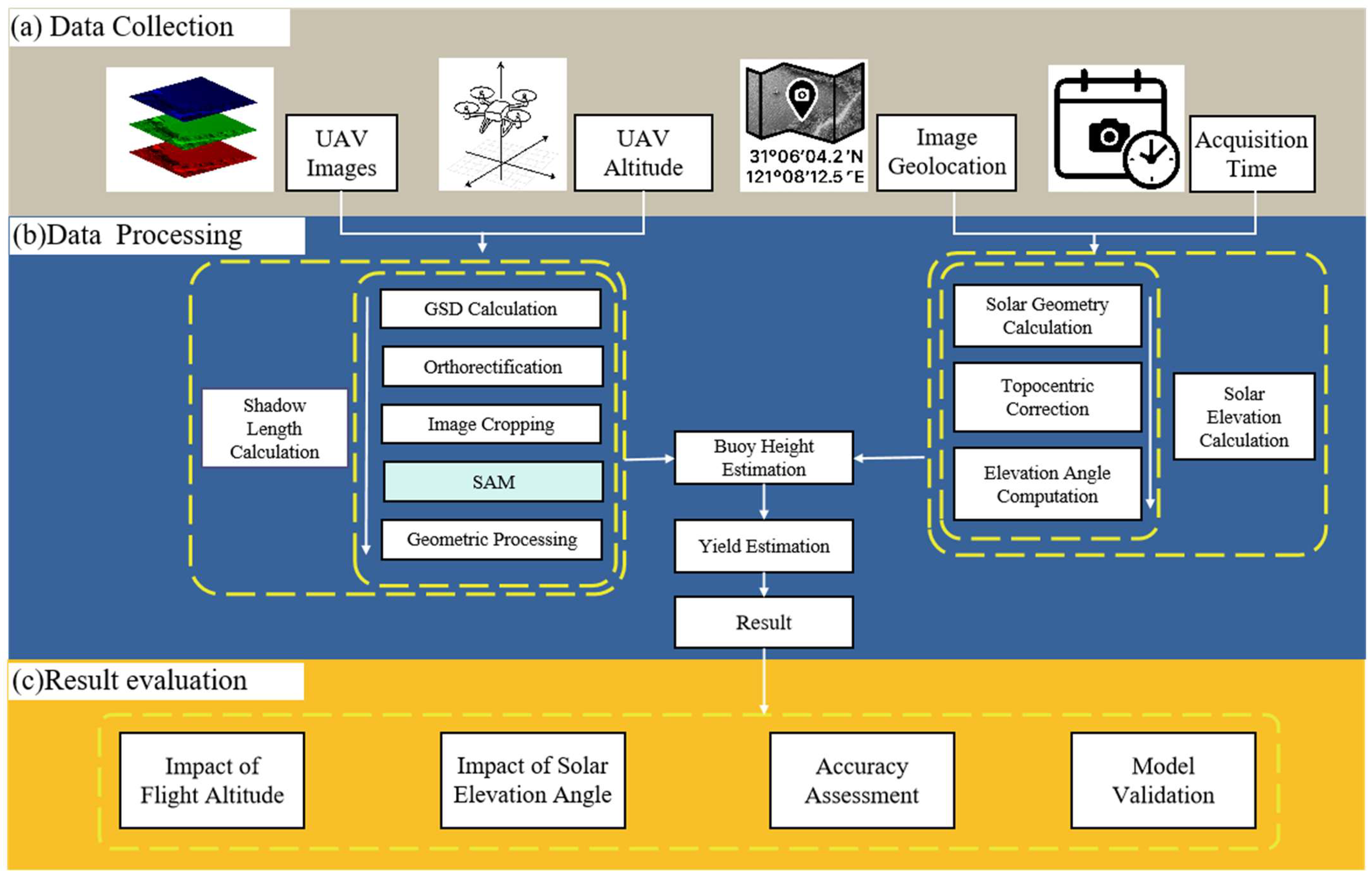
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yield Estimation Model
2.2. SAM-Based Automatic Segmentation of Buoy Shadows
3. Experiments
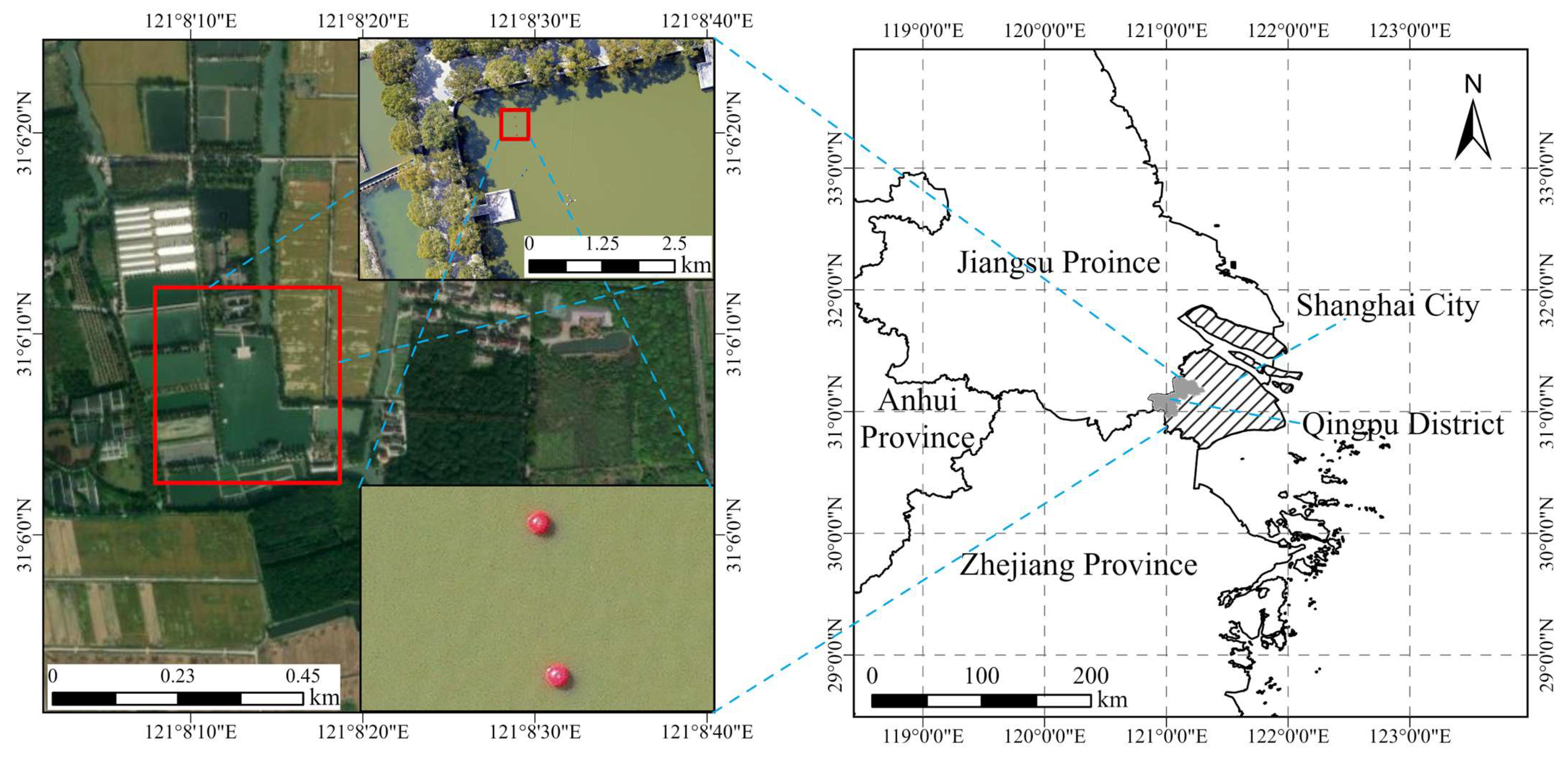
3.1. Experimental Design
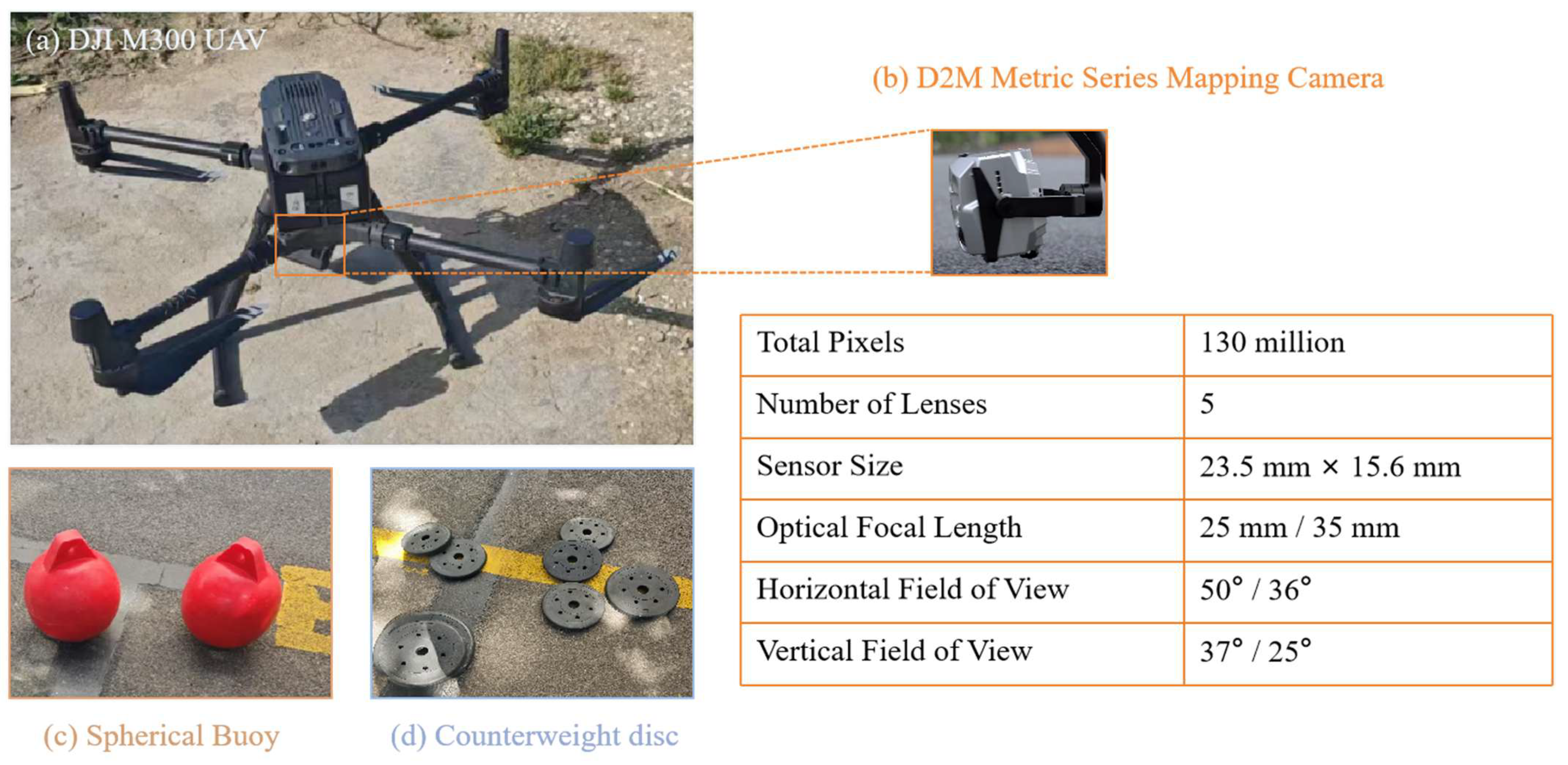
3.2. Experimental Equipment
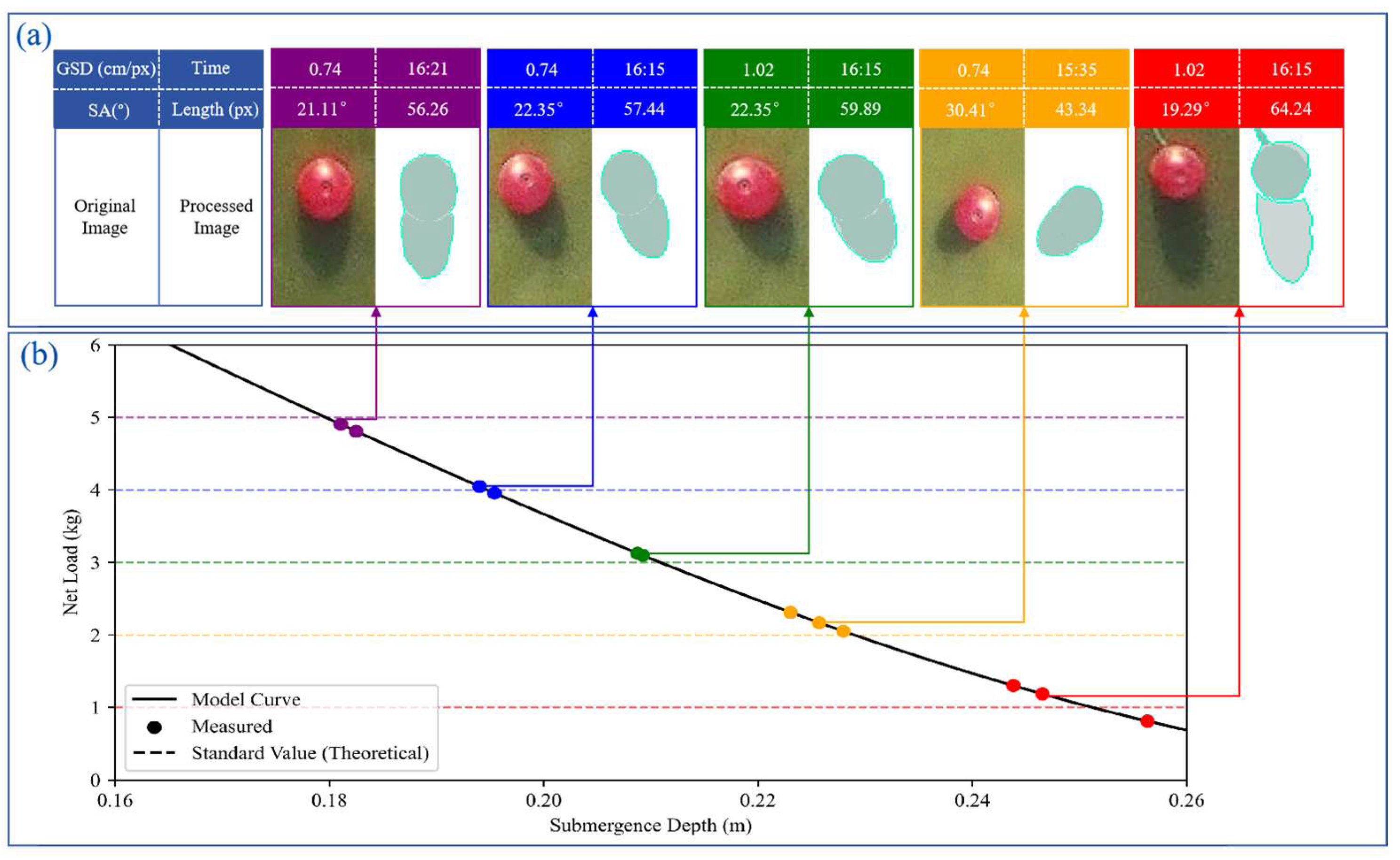
3.3. Experimental Validation
4. Result
4.1. Experimental Results
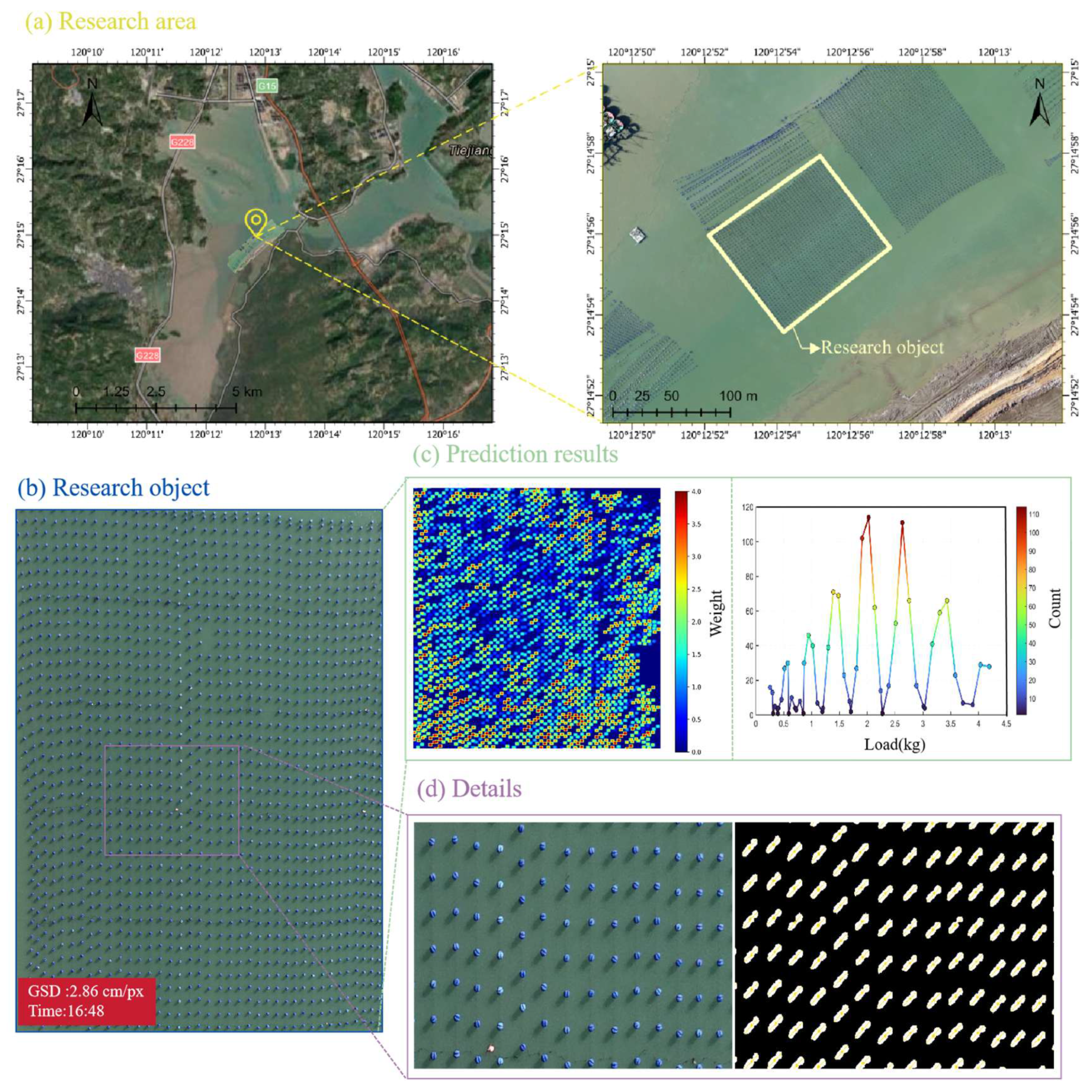
4.2. Field Application
5. Discussion
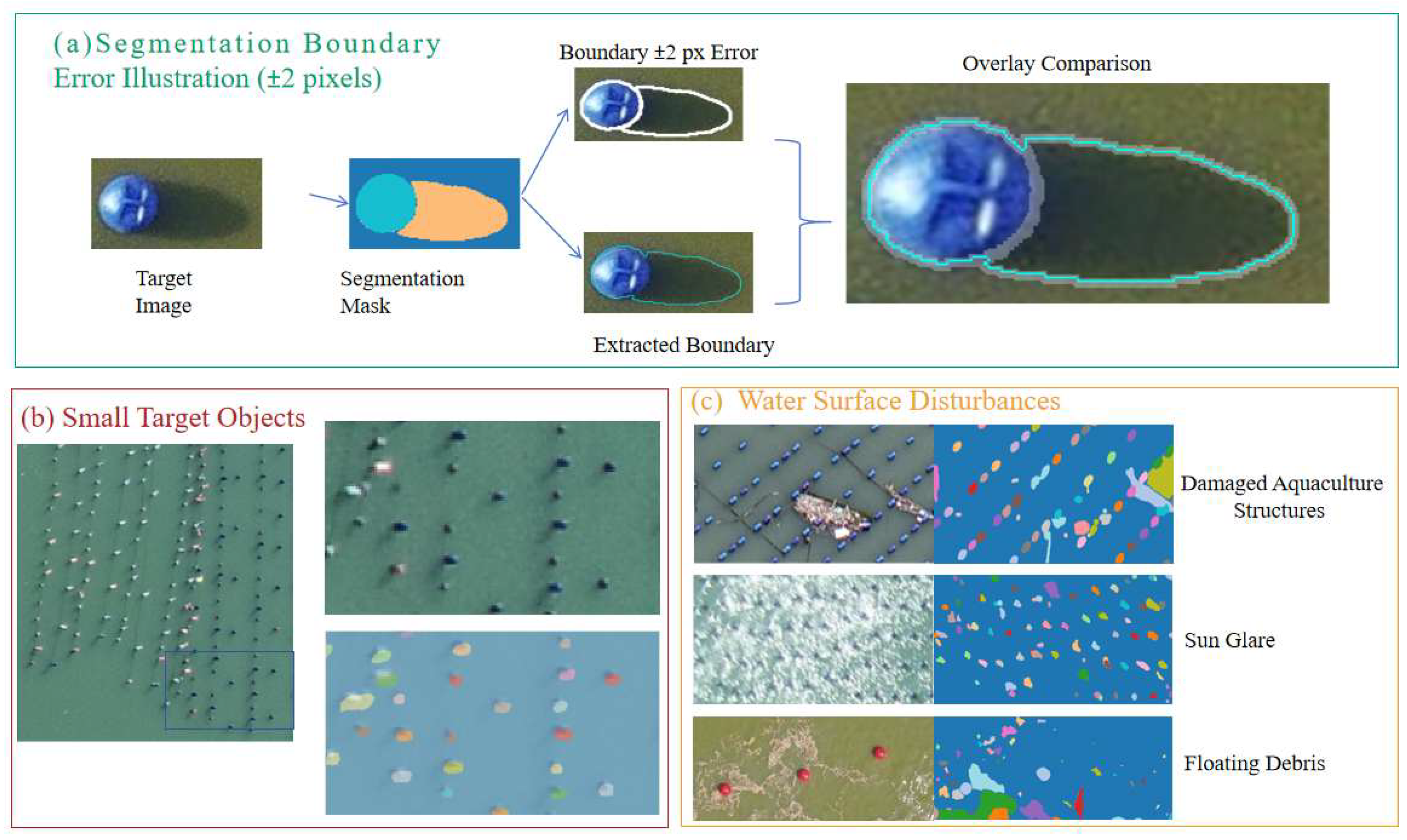
5.1. Performance Evaluation of SAM for Buoy Shadow Segmentation
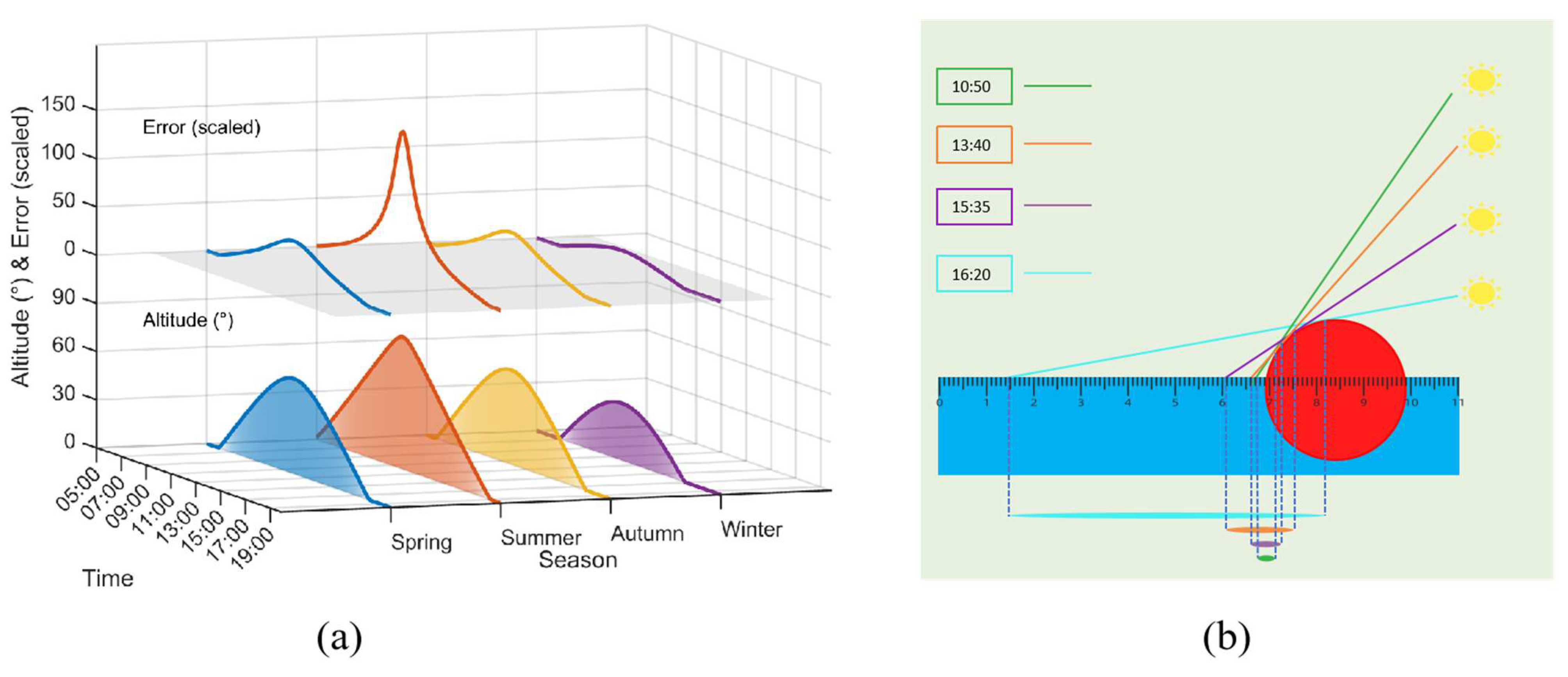
5.2. Influence of Solar Altitude Angle on Model Accuracy
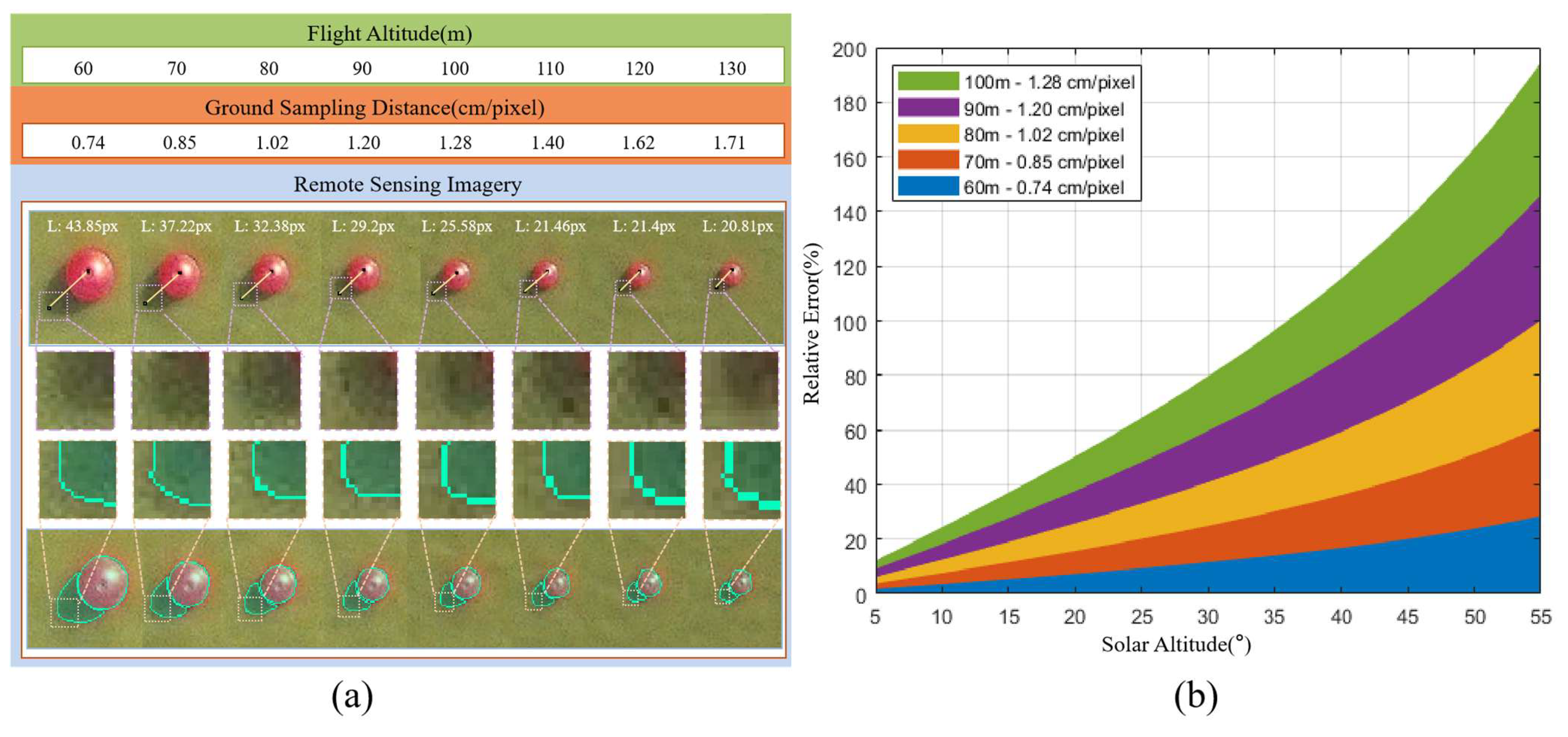
5.3. Impact of Different Flight Altitudes on Experimental Accuracy
5.4. Impact of Environmental Factors on Model Accuracy
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fong, C.R.; Gonzales, C.M.; Rennick, M.; Gardner, L.D.; Halpern, B.S.; Froehlich, H.E. Global Yield from Aquaculture Systems. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.; Saurel, C.; Nielsen, P.; Petersen, J.K. Production Characteristics and Optimization of Mitigation Mussel Culture. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascorda Cabre, L.; Hosegood, P.; Attrill, M.J.; Bridger, D.; Sheehan, E.V. Offshore Longline Mussel Farms: A Review of Oceanographic and Ecological Interactions to Inform Future Research Needs, Policy and Management. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1864–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, Ş.; Erdem, Ö.A.; Sabanci, F.; Gökvardar, A.; Serdar, S.; Ertan, A. Effects of Different Culture Methods on Growth, Meat Yield, and Nutritional Composition of Mediterranean Mussels (Mytilus Galloprovincialis), South Side of Marmara Sea, Türkiye. Eur. Zool. J. 2024, 91, 869–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, B.H.; Ebeling, M.W.; Michler-Cieluch, T. Mussel Cultivation as a Co-Use in Offshore Wind Farms: Potential and Economic Feasibility. Aquac. Econ. Manag. 2010, 14, 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, G.; You, X. Experimental Investigation of the Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Longline Aquaculture Facilities under Current and Wave Conditions. Fishes 2023, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heasman, K.G.; Scott, N.; Sclodnick, T.; Chambers, M.; Costa-Pierce, B.; Dewhurst, T.; Isbert, W.; Buck, B.H. Variations of Aquaculture Structures, Operations, and Maintenance with Increasing Ocean Energy. Front. Aquac. 2024, 3, 1444186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriss, B.E.; Conway-Cranos, L.L.; Sanderson, B.L.; Hoberecht, L. Bivalve Aquaculture and Eelgrass: A Global Meta-Analysis. Aquaculture 2019, 498, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamp, T.; Pittman, S.J.; Holmes, L.A.; Rees, A.; Ciotti, B.J.; Thatcher, H.; Davies, P.; Hall, A.; Wells, G.; Olczak, A.; et al. Restorative Function of Offshore Longline Mussel Farms with Ecological Benefits for Commercial Crustacean Species. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 174987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, P.B.; Glud, R.N.; Dalsgaard, T.; Gillespie, P. Impacts of Longline Mussel Farming on Oxygen and Nitrogen Dynamics and Biological Communities of Coastal Sediments. Aquaculture 2003, 218, 567–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoste, E.; Drouin, A.; Weise, A.M.; Archambault, P.; McKindsey, C.W. Low Benthic Impact of an Offshore Mussel Farm in Îles-de-La-Madeleine, Eastern Canada. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2018, 10, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troell, M.; Joyce, A.; Chopin, T.; Neori, A.; Buschmann, A.H.; Fang, J.G. Ecological Engineering in Aquaculture—Potential for Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA) in Marine Offshore Systems. Aquaculture 2009, 297, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, R.; Lima, A.R.; Fox, J.M. Short-Term Effects of a Research-Scale Oyster Cage Aquaculture System on Sediment Transport, Water Quality, and Seagrass Meadow Health in Copano Bay, TX, USA. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1382153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.; Houle, K.; Suhrbier, A.; Hudson, B.; Ruesink, J. Estuarine Community Response to Longline Spacing in Intertidal Oyster Culture. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2025, 17, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeki, S.; Debrot, A.O.; Den Brink, A.M.; Ariyati, R.W.; Lakshmi Widowati, L. Increased Production of Green Mussels (Perna viridis) Using Longline Culture and an Economic Comparison with Stake Culture on the North Coast of Java, Indonesia. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, A.; Prasyad, H.; Oiry, S.; Davies, B.F.R.; Brunier, G.; Barillé, L. Mapping Intertidal Oyster Farms Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) High-Resolution Multispectral Data. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 291, 108432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, A.; Tovar-Sánchez, A.; Olivé, I.; Navarro, G. Using a UAV-Mounted Multispectral Camera for the Monitoring of Marine Macrophytes. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 722698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lu, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, F. An Efficient Downwelling Light Sensor Data Correction Model for UAV Multi-Spectral Image DOM Generation. Drones 2025, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Nie, K.; Lu, X.; Fan, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, F. A Solar Trajectory Model for Multi-Spectral Image Correction of DOM from Long-Endurance UAV in Clear Sky. Drones 2025, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, P.A.; Khatei, A.; Posti, R.; Sidiq, M.J.; Pandey, P.K. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Fisheries and Aquaculture: A Comprehensive Overview. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Gu, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Tang, R.; He, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, B. Monitoring Water Quality Parameters of Freshwater Aquaculture Ponds Using UAV-Based Multispectral Images. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodofili, E.N.; Lecours, V.; LaRue, M. Remote Sensing Techniques for Automated Marine Mammals Detection: A Review of Methods and Current Challenges. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsolmoali, P.; Zareapoor, M.; Wang, R.; Zhou, H.; Yang, J. A Novel Deep Structure U-Net for Sea-Land Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3219–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machefer, M.; Lemarchand, F.; Bonnefond, V.; Hitchins, A.; Sidiropoulos, P. Mask R-CNN Refitting Strategy for Plant Counting and Sizing in UAV Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, J.; Wang, J. MDOAU-Net: A Lightweight and Robust Deep Learning Model for SAR Image Segmentation in Aquaculture Raft Monitoring. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4504505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, B.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, X.; Liu, C. A Modeling Method for Automatic Extraction of Offshore Aquaculture Zones Based on Semantic Segmentation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Cheng, S.-C.; Chang, C.-C. Semantic Scene Modeling for Aquaculture Management Using an Autonomous Drone. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Advanced Imaging Technology (IWAIT), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 5–7 January 2020; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11515, pp. 374–378. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Xie, X.; Han, J.; Guo, L.; Xia, G.-S. Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification Meets Deep Learning: Challenges, Methods, Benchmarks, and Opportunities. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 3735–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuia, D.; Persello, C.; Bruzzone, L. Domain Adaptation for the Classification of Remote Sensing Data: An Overview of Recent Advances. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.-Y.; et al. Segment Anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 4–6 October 2023; pp. 4015–4026. [Google Scholar]
- Osco, L.P.; Wu, Q.; De Lemos, E.L.; Gonçalves, W.N.; Ramos, A.P.; Li, J.; Junior, J.M. The Segment Anything Model (SAM) for Remote Sensing Applications: From Zero to One Shot. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 124, 103540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Meng, D.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, G. Segment Anything Model (SAM) Assisted Remote Sensing Supervision for Mariculture—Using Liaoning Province, China as an Example. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Nie, K.; Yuan, S.; Fan, W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, F. Mapping for Larimichthys crocea Aquaculture Information with Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data Based on Segment Anything Model. Fishes 2025, 10, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chary, K.; Brigolin, D.; Callier, M.D. Farm-Scale Models in Fish Aquaculture—An Overview of Methods and Applications. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 2122–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, H.; Pierce, M.; Benter, A. Real-Time Environmental Monitoring for Aquaculture Using a LoRaWAN-Based IoT Sensor Network. Sensors 2021, 21, 7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurdin, N.; Aris, A.; AS, M.A. Seasionality of Kappaphycus Alvarezii Production Trends in South Sulawesi Using UAV Monitoring. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2025, 39, 101659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overrein, M.M.; Tinn, P.; Aldridge, D.; Johnsen, G.; Fragoso, G.M. Biomass Estimations of Cultivated Kelp Using Underwater RGB Images from a Mini-ROV and Computer Vision Approaches. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1324075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
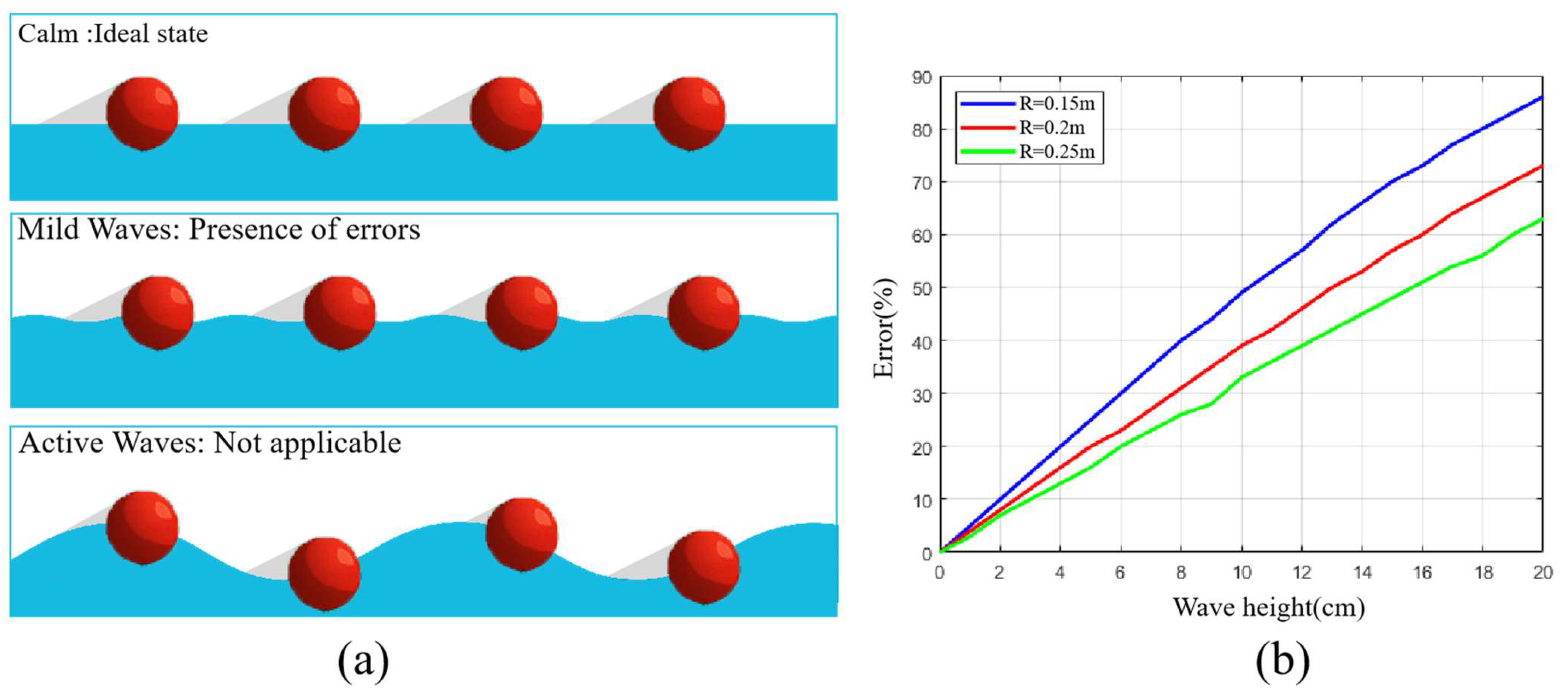
| Category | Wind Force Level | Wind Force Name | Wind Speed (knots) | Wind Force Impact on Water Surface | Wave Height (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calm | 0 | Calm | 0 | Like a mirror | 0 |
| Mild Waves | 1 | Light air | 1–3 | Light ripples | 0.1 |
| Active Waves | 2 | Light breeze | 4–6 | Small waves | 0.2–0.3 |
| 3 | Gentle breeze | 7–10 | Waves with breaking crests | 0.6–1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, D.; Zhang, S.; Xu, X.; Wu, Q.; Fan, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Wang, F. Yield Estimation of Longline Aquaculture by the Shadows of Buoys Based on UAV Orthophoto Image. Drones 2025, 9, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9110786
Yang D, Zhang S, Xu X, Wu Q, Fan W, Zhang L, Wu S, Wang F. Yield Estimation of Longline Aquaculture by the Shadows of Buoys Based on UAV Orthophoto Image. Drones. 2025; 9(11):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9110786
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Dongxu, Shengmao Zhang, Xirui Xu, Qi Wu, Wei Fan, Leilei Zhang, Siyao Wu, and Fei Wang. 2025. "Yield Estimation of Longline Aquaculture by the Shadows of Buoys Based on UAV Orthophoto Image" Drones 9, no. 11: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9110786
APA StyleYang, D., Zhang, S., Xu, X., Wu, Q., Fan, W., Zhang, L., Wu, S., & Wang, F. (2025). Yield Estimation of Longline Aquaculture by the Shadows of Buoys Based on UAV Orthophoto Image. Drones, 9(11), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9110786







