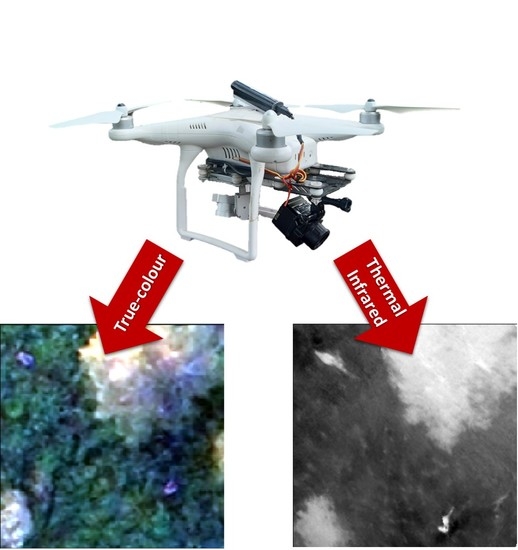
Evaluating the Efficacy and Optimal Deployment of Thermal Infrared and True-Colour Imaging When Using Drones for Monitoring Kangaroos
Abstract
Share and Cite
Brunton, E.A.; Leon, J.X.; Burnett, S.E. Evaluating the Efficacy and Optimal Deployment of Thermal Infrared and True-Colour Imaging When Using Drones for Monitoring Kangaroos. Drones 2020, 4, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones4020020
Brunton EA, Leon JX, Burnett SE. Evaluating the Efficacy and Optimal Deployment of Thermal Infrared and True-Colour Imaging When Using Drones for Monitoring Kangaroos. Drones. 2020; 4(2):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones4020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrunton, Elizabeth A., Javier X. Leon, and Scott E. Burnett. 2020. "Evaluating the Efficacy and Optimal Deployment of Thermal Infrared and True-Colour Imaging When Using Drones for Monitoring Kangaroos" Drones 4, no. 2: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones4020020
APA StyleBrunton, E. A., Leon, J. X., & Burnett, S. E. (2020). Evaluating the Efficacy and Optimal Deployment of Thermal Infrared and True-Colour Imaging When Using Drones for Monitoring Kangaroos. Drones, 4(2), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones4020020