Robust Dual-Loop MPC for Variable-Mass Feeding UAVs with Lyapunov Small-Gain Guarantees
Highlights
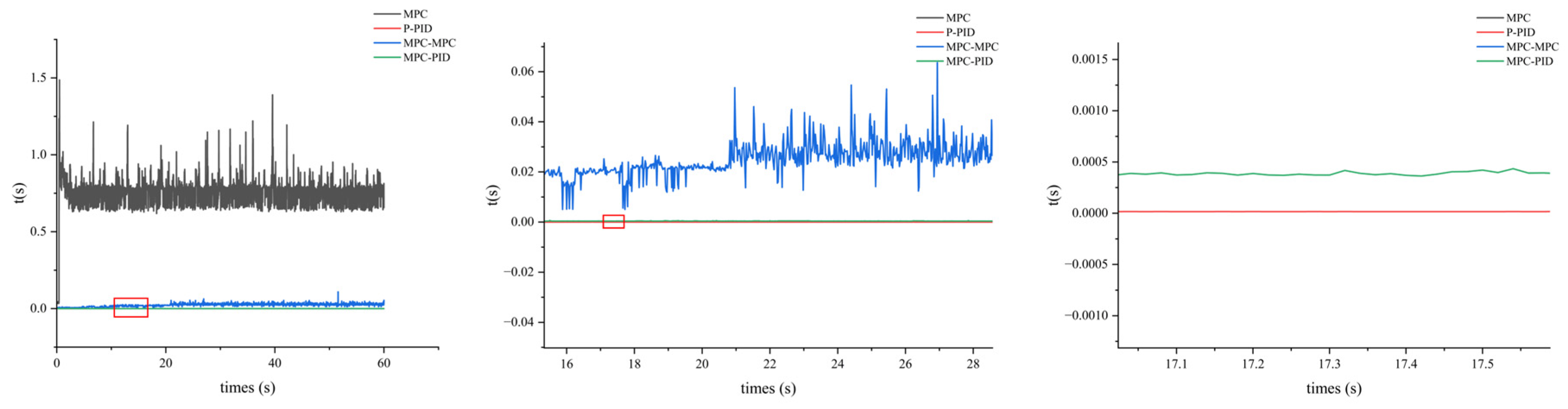
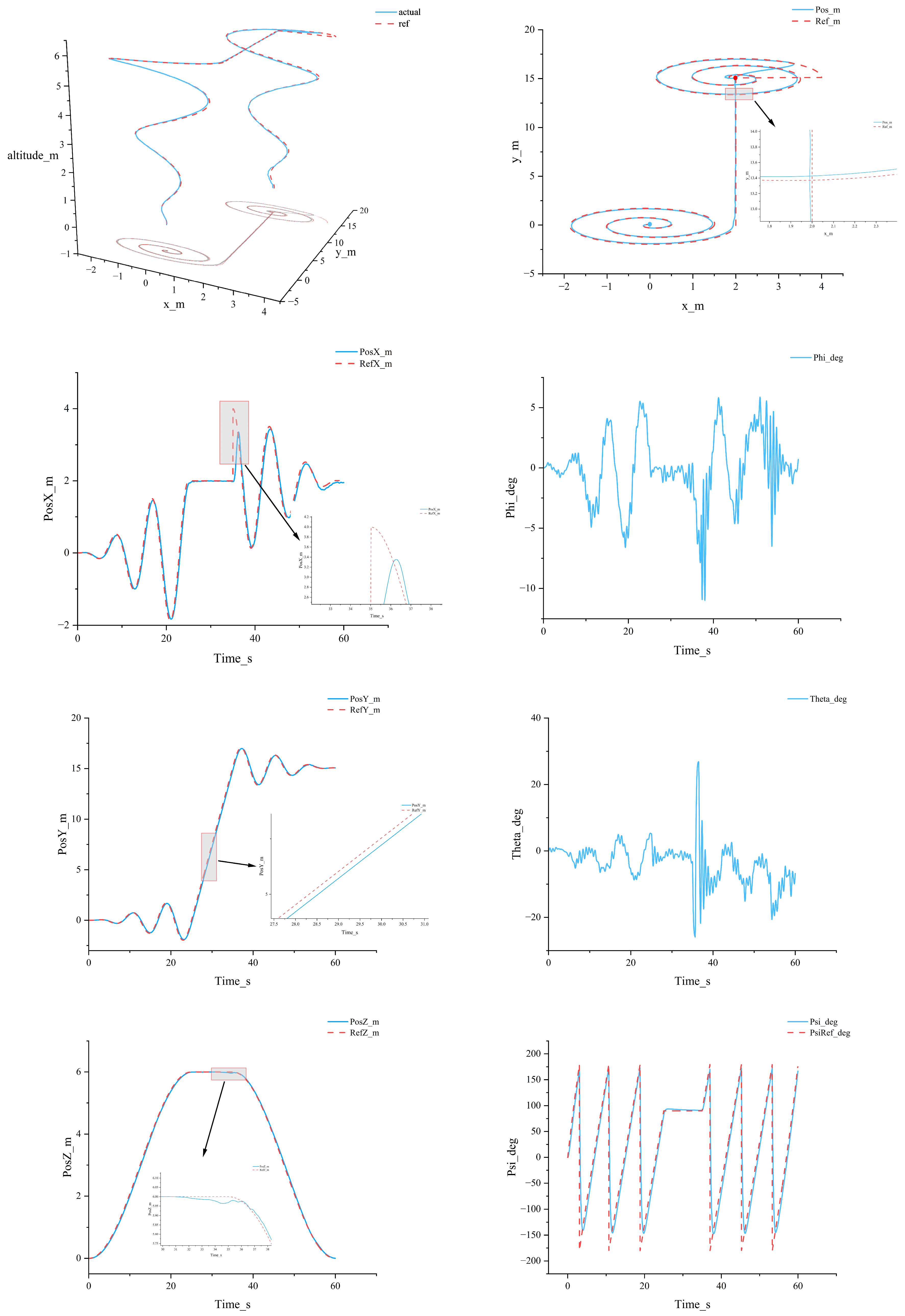
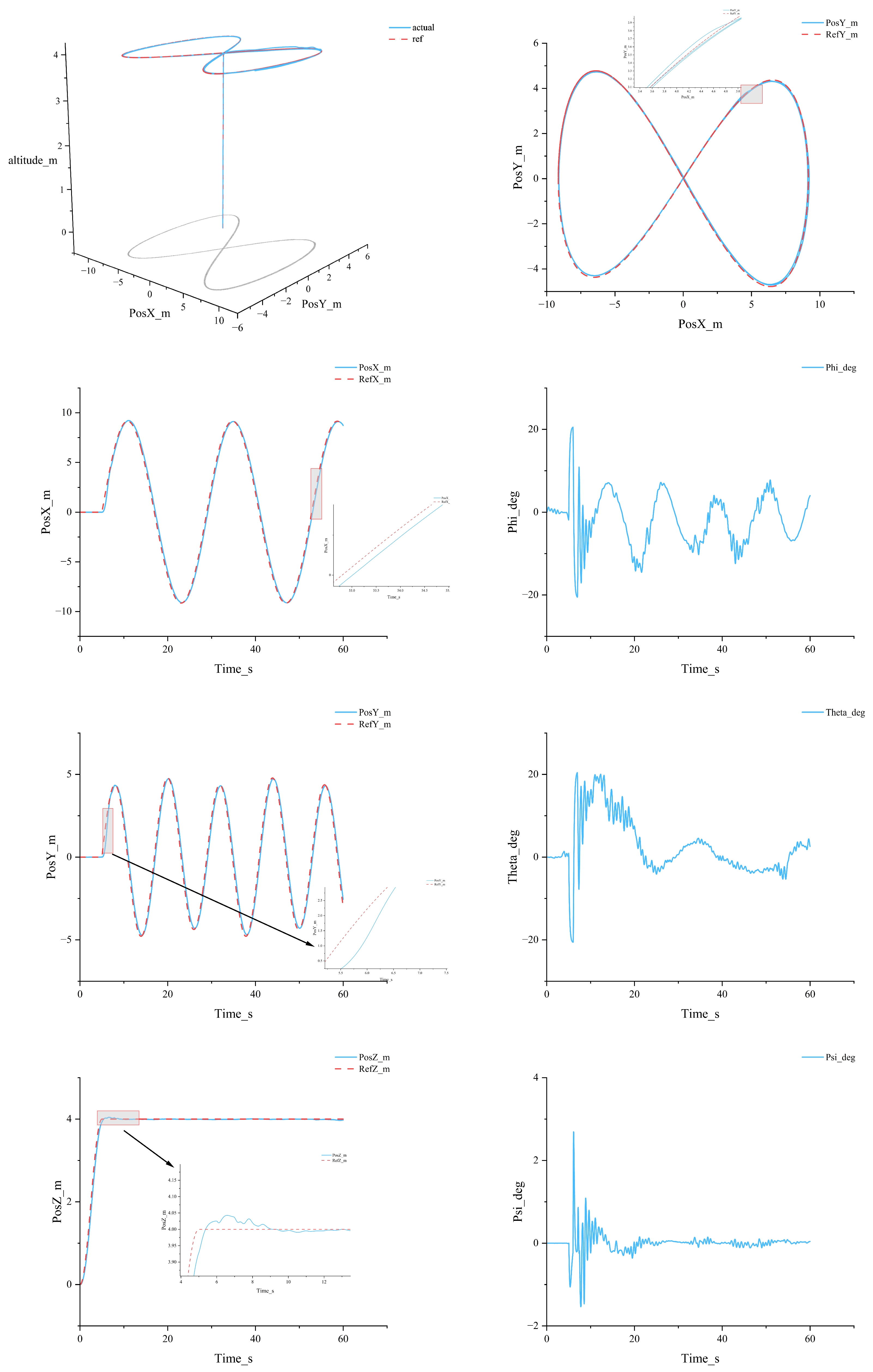
- A dual-loop MPC architecture (outer-loop position MPC + inner-loop attitude MPC), weight-tuned via an Adaptive Niche Radius Genetic Algorithm (ANRGA), markedly improves tracking accuracy and stability for feeding UAVs under variable mass, inertia and wind—achieving max x-axis error of 0.018 m, typical axis errors ≤ 0.5 m with minimal overshoot, and ~58% faster response than a conventional single-loop MPC.
- Among six metaheuristics tested for MPC weight optimization, ANRGA delivers the best overall control performance—lowest average fitness and superior ISE/IAE/ITSE/ITAE—while maintaining rapid yet non-premature convergence, indicating it is the most effective optimizer for the dual-loop MPC in this application.
- The controller’s ability to sustain stable, repeatable, and high-precision tracking under complex feeding trajectories and gust disturbances indicates practical feasibility for real aquaculture operations (e.g., spiral paths and figure-eight maneuvers). This implies reduced overfeeding and missed feeding, improved feed utilization, and enhanced operational safety. The implication is corroborated by the consistency between simulated trajectories and attitude responses and is further supported by the two-loop stability analysis (small-gain condition under varying mass/inertia).
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dynamic Modeling and Dual-Loop MPC Design
2.1. Controller Design
2.2. Extension to Large-Angle Operating Conditions
3. Adaptive Niche Radius Genetic Algorithm for MPC Optimization
3.1. Adaptive Adjustment of Weight Factors via Genetic Algorithms
3.2. Incorporation of Niching Technique
3.3. Stability Analysis of the System
- (1)
- ;
- (2)
- The terminal control gain is computed from , and the terminal weight is defined as the solution to the discrete algebraic Riccati equation (DARE):
- (3)
- The terminal invariant set is positively invariant under the closed-loop dynamics and satisfies the imposed constraints;
- (4)
- The small-gain or bandwidth separation condition of the dual-loop system holds.
4. Simulation Results and Analysis
4.1. Comparative Study with Different Controllers
4.2. Control Performance of the Dual-Loop MPC Under Different Optimization Algorithms
5. Conclusions
6. Discussion and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Algorithm A1. Optimization Process of MPC |
 |
References
- Subasinghe, R.; Soto, D.; Jia, J. Global Aquaculture and Its Role in Sustainable Development. Rev. Aquac. 2009, 1, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, C.; Arthur, R.; Norbury, H.; Allison, E.H.; Beveridge, M.; Bush, S.; Campling, L.; Leschen, W.; Little, D.; Squires, D. Contribution of Fisheries and Aquaculture to Food Security and Poverty Reduction: Assessing the Current Evidence. World Dev. 2016, 79, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genschick, S.; Kaminski, A.M.; Kefi, A.S.; Cole, S.M. Aquaculture in Zambia: An Overview and Evaluation of the Sector’s Responsiveness to the Needs of the Poor; CGIAR Research Program on Fish Agri-Food Systems: Lusaka, Zambia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kassam, L. Assessing the Contribution of Aquaculture to Poverty Reduction in Ghana. Ph.D. Thesis, SOAS University of London, London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Leung, P.; Hishamunda, N. Commercial Aquaculture and Economic Growth, Poverty Alleviation and Food Security. Assessment Framework; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsuzzaman, M.M.; Mozumder, M.M.H.; Mitu, S.J.; Ahamad, A.F.; Bhyuian, M.S. The Economic Contribution of Fish and Fish Trade in Bangladesh. Aquac. Fish. 2020, 5, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sribhibhadh, A. Role of Aquaculture in Economic Development Within Southeast Asia. J. Fish. Board Can. 1976, 33, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Sun, X.; Hong, Q.; Duan, Q. Intelligent Fish Feeding Based on Machine Vision: A Review. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 231, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Li, D.; Qiao, X.; Rauschenbach, T. Integrated Navigation for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles in Aquaculture: A Review. Inf. Process. Agric. 2020, 7, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wei, Q.; An, D. Intelligent Monitoring and Control Technologies of Open Sea Cage Culture: A Review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 169, 105119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Wei, Y.; An, D.; Liu, J. Application of Intelligent and Unmanned Equipment in Aquaculture: A Review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 199, 107201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.; Feng, J.; Wu, X. Development Status and Prospect of Aviation Plant Protection in China. Agrochemicals 2022, 61, 469–477. [Google Scholar]
- De Lima, R.L.P.; Paxinou, K.; Boogaard, F.C.; Akkerman, O.; Lin, F.-Y. In-Situ Water Quality Observations under a Large-Scale Floating Solar Farm Using Sensors and Underwater Drones. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhang, R.; Yang, J.; Chen, L. Development Status and Key Technologies of Plant Protection UAVs in China: A Review. Drones 2022, 6, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Xiang, Y.; Geng, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, N.; Du, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, L. Improving UAV Hyperspectral Monitoring Accuracy of Summer Maize Soil Moisture Content with an Ensemble Learning Model Fusing Crop Physiological Spectral Responses. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 160, 127299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, F.; Tian, X.; Ge, S.; Man, C.; Xiao, M. Research on Precise Feeding Strategies for Large-Scale Marine Aquafarms. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lan, Y.; Fritz, B.K.; Clint Hoffmann, W.; Liu, S. Review of Agricultural Spraying Technologies for Plant Protection Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV). Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, S.; Shi, Y.; Khan, Y.A.; Khodaverdian, M.; Javaid, U. Robust Adaptive Control Law Design for Enhanced Stability of Agriculture UAV Used for Pesticide Spraying. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 155, 109676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, K.; Asadi, D.; Nabavi-Chashmi, S.-Y.; Tutsoy, O. Modified Adaptive Discrete-Time Incremental Nonlinear Dynamic Inversion Control for Quad-Rotors in the Presence of Motor Faults. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 188, 109989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Ahn, C.K.; Liu, D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C. Near-Asteroid Spacecraft Formation Control with Prescribed-Performance: A Dynamic Event-Triggered Reinforcement Learning Control Approach. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2025, 161, 110138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Ozguner, U. Sliding Mode Control of a Quadrotor Helicopter. In Proceedings of the 45th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, San Diego, CA, USA, 13–15 December 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 4957–4962. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, D.; Ha, C. Control of a Quadrotor Using a Smart Self-Tuning Fuzzy PID Controller. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pounds, P.E.I.; Bersak, D.R.; Dollar, A.M. Stability of Small-Scale UAV Helicopters and Quadrotors with Added Payload Mass under PID Control. Auton. Robot. 2012, 33, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapnopoulos, A.; Alexandridis, A. A Cooperative Particle Swarm Optimization Approach for Tuning an MPC-Based Quadrotor Trajectory Tracking Scheme. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 127, 107725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Abdi, S.; Debilou, A.; Guettal, L.; Guergazi, A. Robust Trajectory Tracking Control of a Quadrotor under External Disturbances and Dynamic Parameter Uncertainties Using a Hybrid P-PID Controller Tuned with Ant Colony Optimization. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2025, 160, 110053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Yao, P.; Huang, Y.; Su, Z.; Yu, Y. Distributed Trajectory Optimization for Multiple Solar-Powered UAVs Target Tracking in Urban Environment by Adaptive Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trad, T.Y.; Choutri, K.; Lagha, M.; Meshoul, S.; Khenfri, F.; Fareh, R.; Shaiba, H. Real-Time Implementation of Quadrotor UAV Control System Based on a Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 81, 4757–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffyn Yuste, P.; Iglesias Martínez, J.A.; Sanchis De Miguel, M.A. Simulation-Based Evaluation of Model-Free Reinforcement Learning Algorithms for Quadcopter Attitude Control and Trajectory Tracking. Neurocomputing 2024, 608, 128362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gün, A. Attitude Control of a Quadrotor Using PID Controller Based on Differential Evolution Algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 229, 120518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Li, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wu, G.; Wang, Y. Quadrotor Navigation Considering Attitude: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Method Using Tangent Path Rewards. Expert Syst. Appl. 2026, 298, 129762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, S.; Wang, H. Parameter Optimization Design of MPC Controller in AUV Motion Control Based on Improved Black-Winged Kite Algorithm. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Xue, W.; Ding, Y.; Li, D. Disturbance-Rejection Guaranteed Mpc Design for Mimo Systems with Application to a 2-Dof Helicopter. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2025, 168, 110757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Tang, J.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Cao, D. A Data-Driven Neural Model Predictive Controller for Multi-Layer Nonlinear Vibration Isolation System. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2025, 166, 110583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberge, V.; Tarbouchi, M.; Labonte, G. Fast Genetic Algorithm Path Planner for Fixed-Wing Military UAV Using GPU. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; He, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X. Efficient Trajectory Planning for UAVs Using Hierarchical Optimization. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 60668–60681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Ren, J.; Hua, Y.; Li, Q. Online Nonparametric Identification Modeling of Ship Maneuvering Motion Based on PSO-Optimized Incremental Gaussian Mixture Model. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 160, 111962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zeng, H.; Yin, L. Dynamic Distributed Multi-Objective Mantis Search Algorithm Based on Transformer Hybrid Strategy for Novel Power System Dispatch. Energy 2025, 332, 136075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffo, G.V.; Ortega, M.G.; Rubio, F.R. An Integral Predictive/Nonlinear H∞ Control Structure for a Quadrotor Helicopter. Automatica 2010, 46, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, E.-H.; Xiong, J.-J.; Luo, J.-L. Second Order Sliding Mode Control for a Quadrotor UAV. ISA Trans. 2014, 53, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

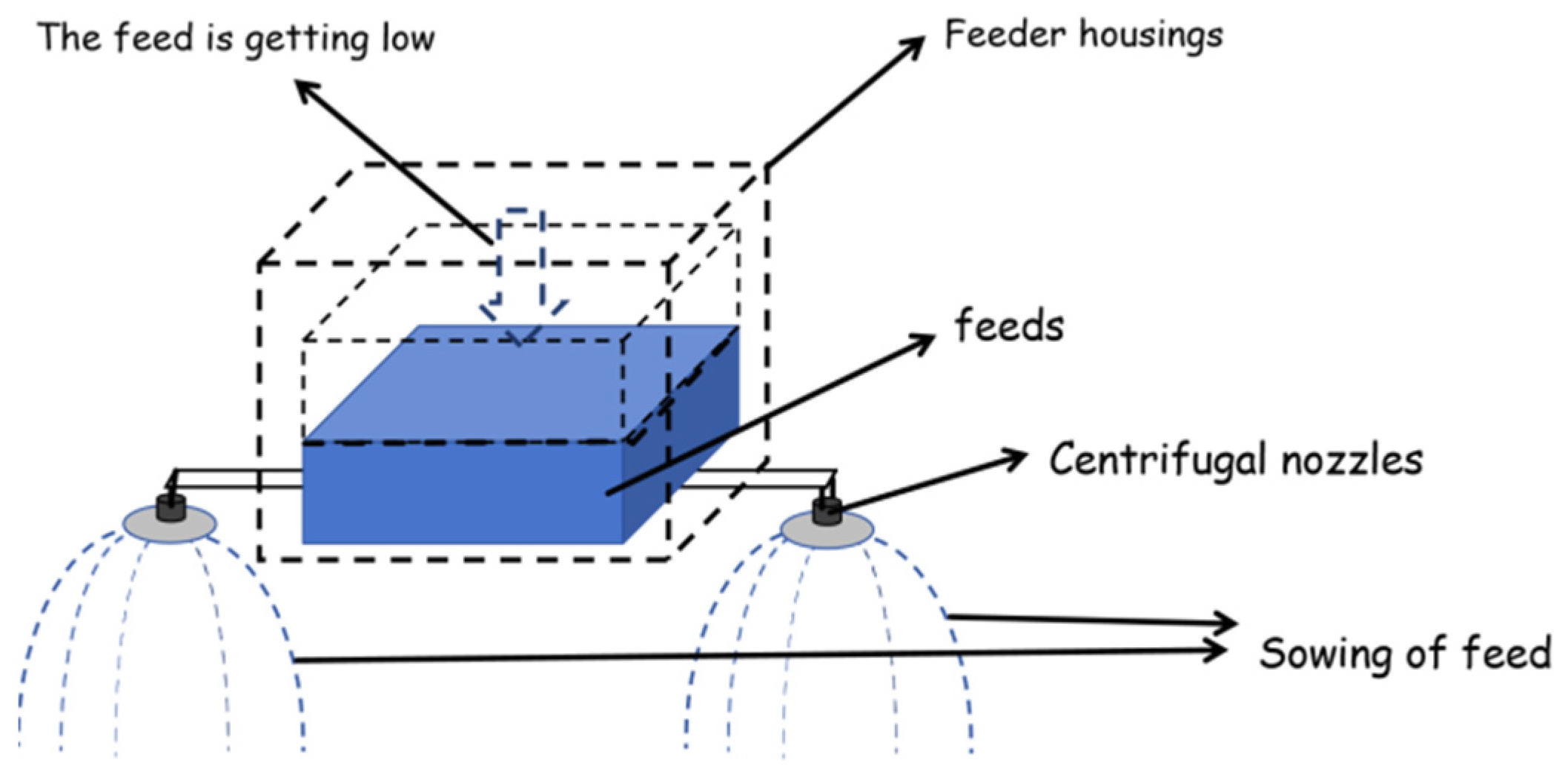
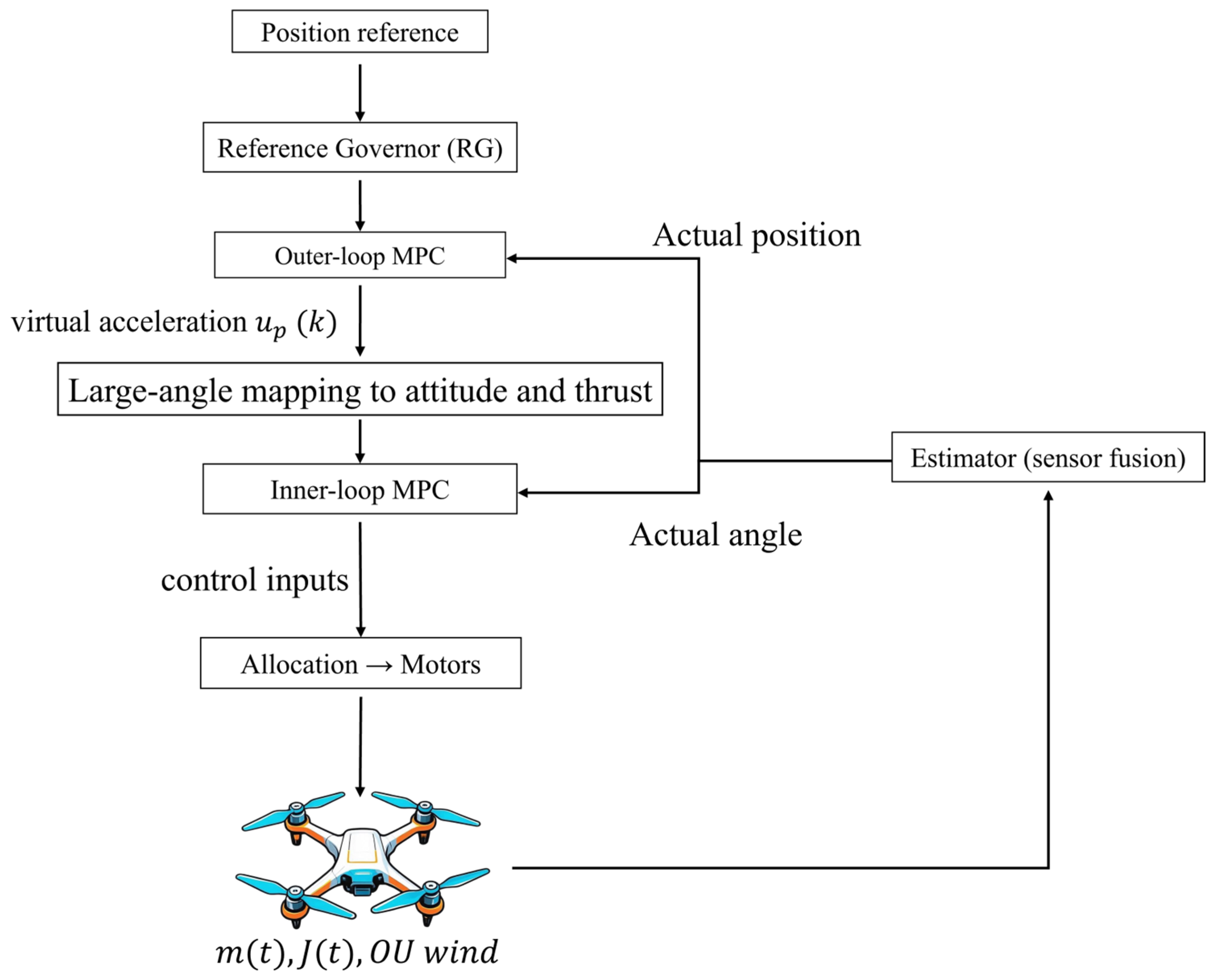
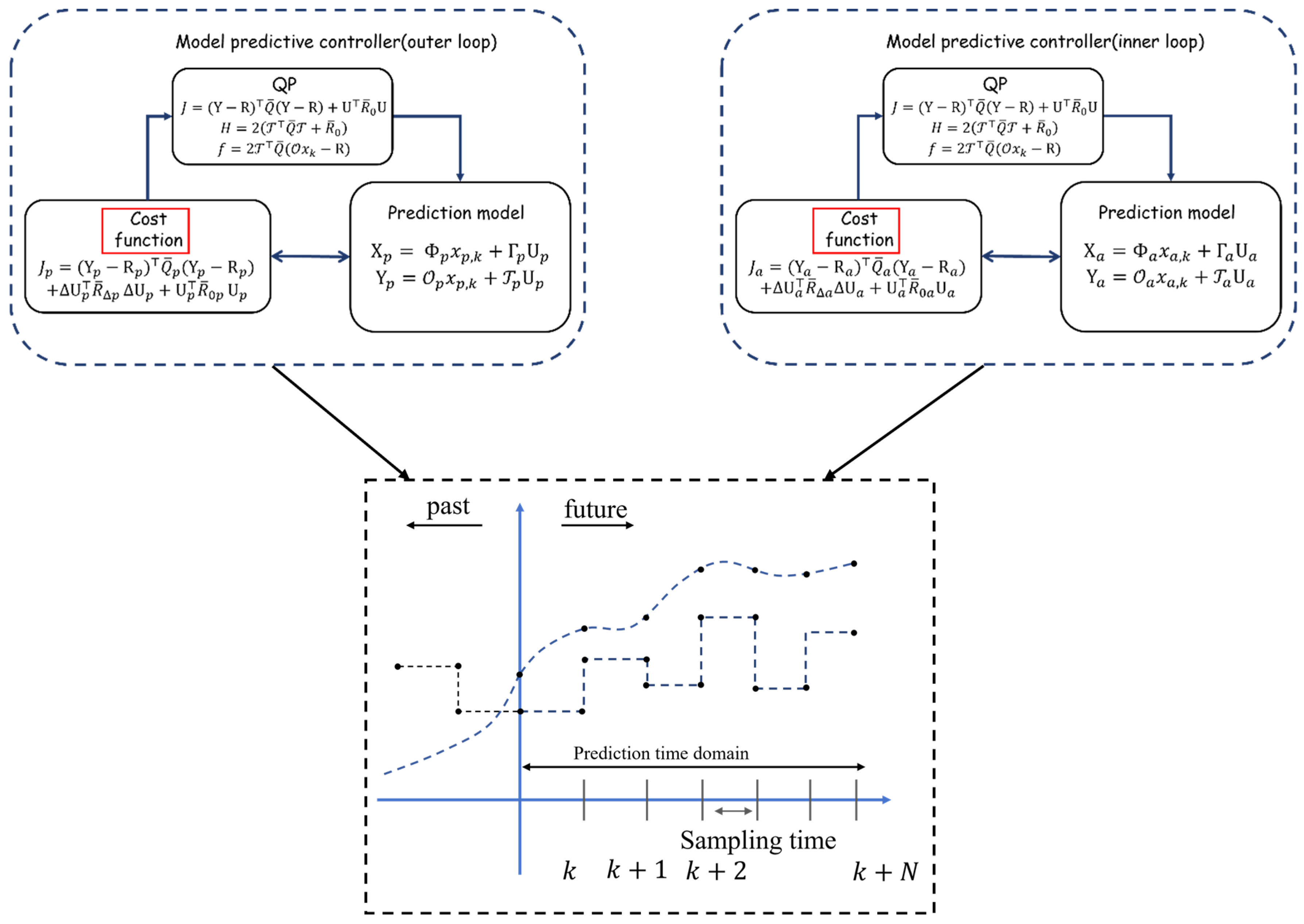

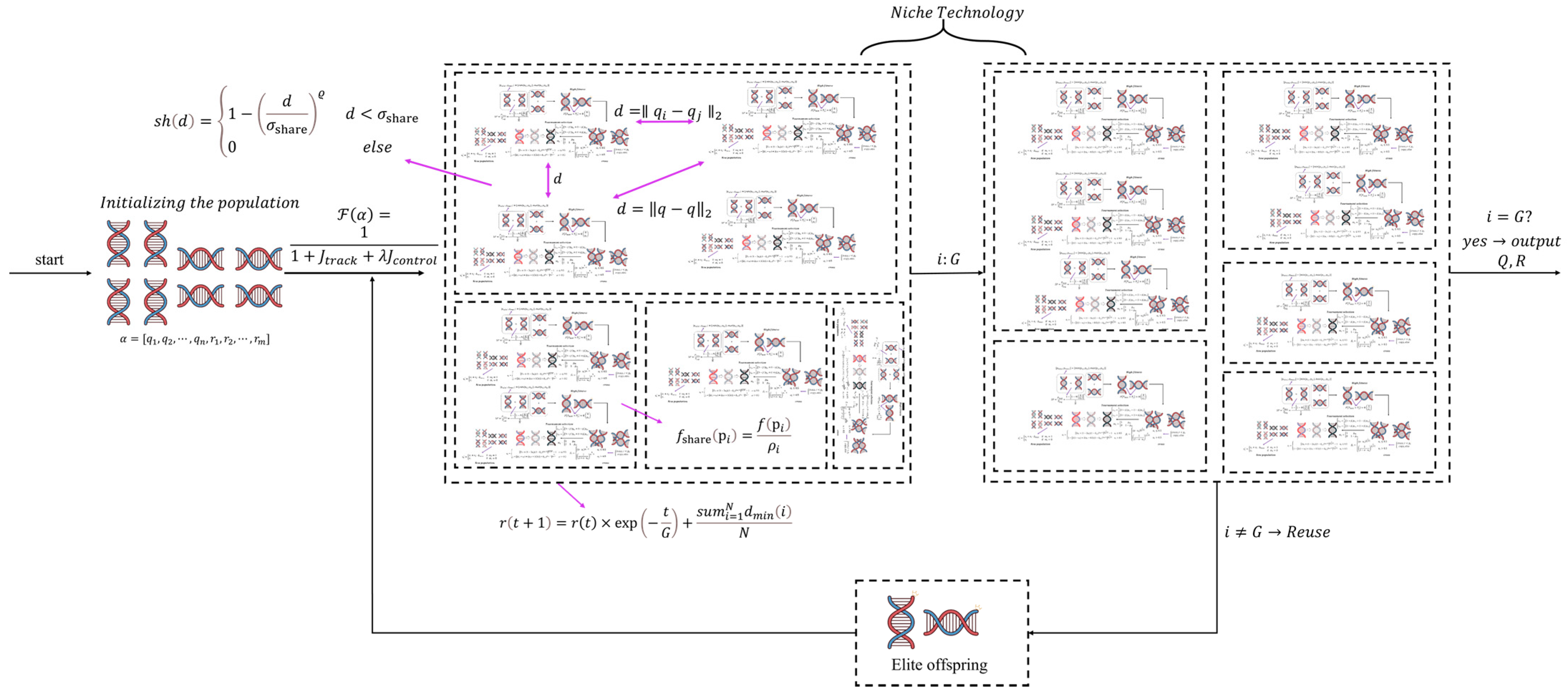




| Variables | Explanation | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Average wind speed | ||
| Time constant | ||
| Large-scale perturbation intensity | ||
| Intensity of small-scale turbulence | ||
| Aerodynamic parameters |
| Algorithms | Average Fitness | Position | ISE | IAE | ITSE | ITAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA | 10.3654 | x | 0.000215173 | 0.038871587 | 0.001866838 | 0.305870191 |
| y | 0.00014437 | 0.03098914 | 0.001201626 | 0.255337156 | ||
| z | 10.12536554 | 3.332748304 | 4.011823729 | 1.774057728 | ||
| PSO | 10.3656 | x | 0.000209744 | 0.037749126 | 0.001826505 | 0.287396506 |
| y | 0.000116342 | 0.027695836 | 0.000930779 | 0.219257914 | ||
| z | 10.12476443 | 3.334065471 | 4.012470412 | 1.758141291 | ||
| GOA | 10.3652 | x | 0.000610794 | 0.062688509 | 0.005760842 | 0.516707276 |
| y | 0.000108194 | 0.023615554 | 0.00087144 | 0.19827557 | ||
| z | 10.12476715 | 3.344654568 | 4.012388443 | 1.843790076 | ||
| POA | 10.3654 | x | 0.000191671 | 0.03938835 | 0.001201294 | 0.237062265 |
| y | 0.000113357 | 0.027202972 | 0.000914783 | 0.217212464 | ||
| z | 10.1254051 | 3.33610989 | 4.01277184 | 1.76787313 | ||
| ACOR | 10.3660 | x | 0.000520045 | 0.054400741 | 0.00498513 | 0.454516737 |
| y | 0.000132314 | 0.017003337 | 0.00040151 | 0.135319912 | ||
| z | 10.1257645 | 3.349032802 | 4.016482238 | 1.813609035 | ||
| ANRGA | 10.3648 | x | 0.000177635 | 0.037597793 | 0.001807915 | 0.292830781 |
| y | 0.000106948 | 0.018234861 | 0.000467757 | 0.228636622 | ||
| z | 10.1247436 | 3.33351663 | 4.01196195 | 1.76519455 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, H.; Li, X.; Xu, W.; Yi, Y.; Luo, X.; Mao, X. Robust Dual-Loop MPC for Variable-Mass Feeding UAVs with Lyapunov Small-Gain Guarantees. Drones 2025, 9, 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9120851
Qi H, Li X, Xu W, Yi Y, Luo X, Mao X. Robust Dual-Loop MPC for Variable-Mass Feeding UAVs with Lyapunov Small-Gain Guarantees. Drones. 2025; 9(12):851. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9120851
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Haixia, Xiaohao Li, Wei Xu, Youheng Yi, Xiwen Luo, and Xing Mao. 2025. "Robust Dual-Loop MPC for Variable-Mass Feeding UAVs with Lyapunov Small-Gain Guarantees" Drones 9, no. 12: 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9120851
APA StyleQi, H., Li, X., Xu, W., Yi, Y., Luo, X., & Mao, X. (2025). Robust Dual-Loop MPC for Variable-Mass Feeding UAVs with Lyapunov Small-Gain Guarantees. Drones, 9(12), 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9120851






