A Method for Forest Canopy Height Inversion Based on UAVSAR and Fourier–Legendre Polynomial—Performance in Different Forest Types
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. RVoG Coherence Scattering Model
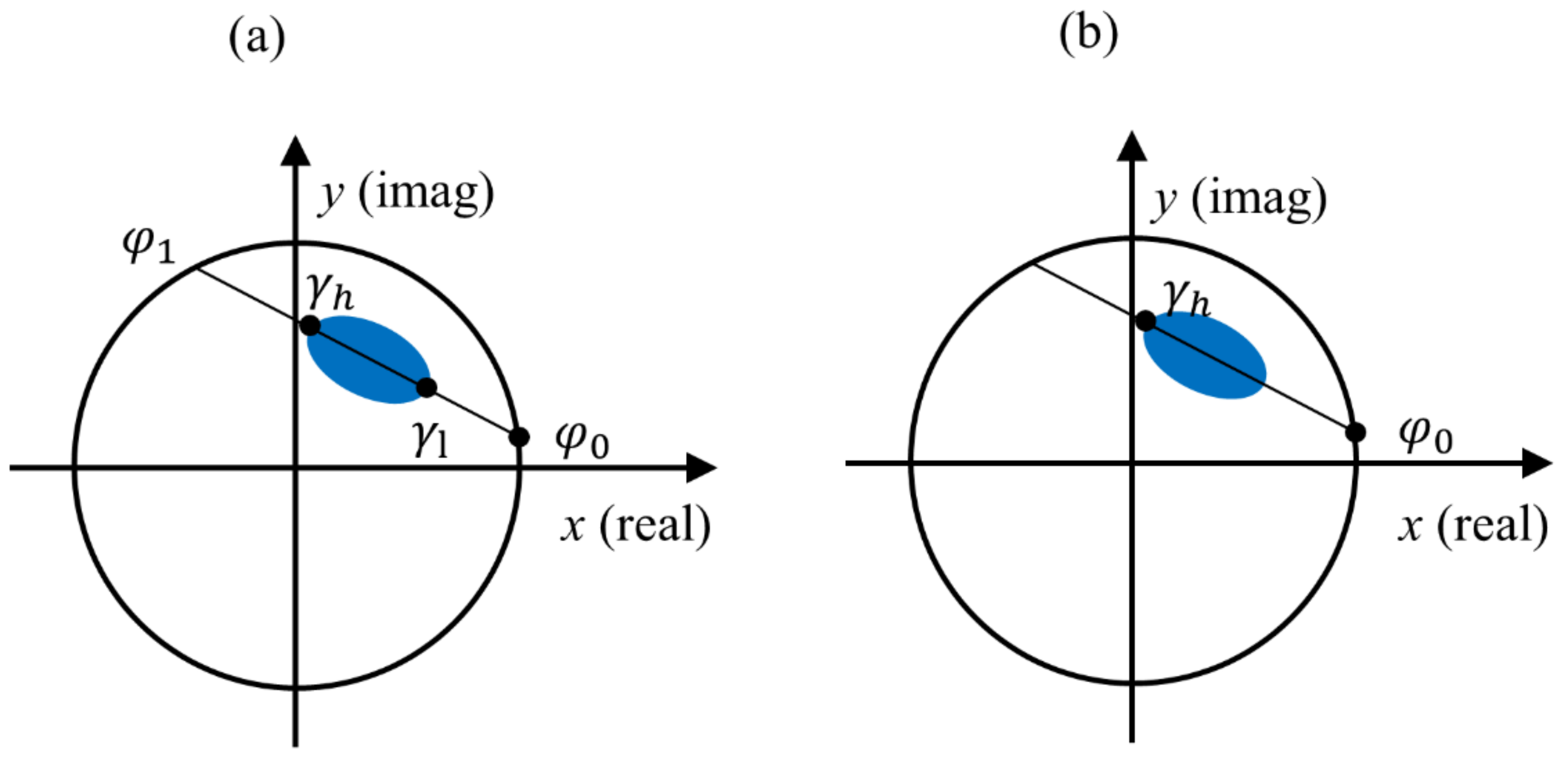
2.3. Baseline Selection Method
2.4. RVOG Three-Stage Method
2.5. FLPMethod
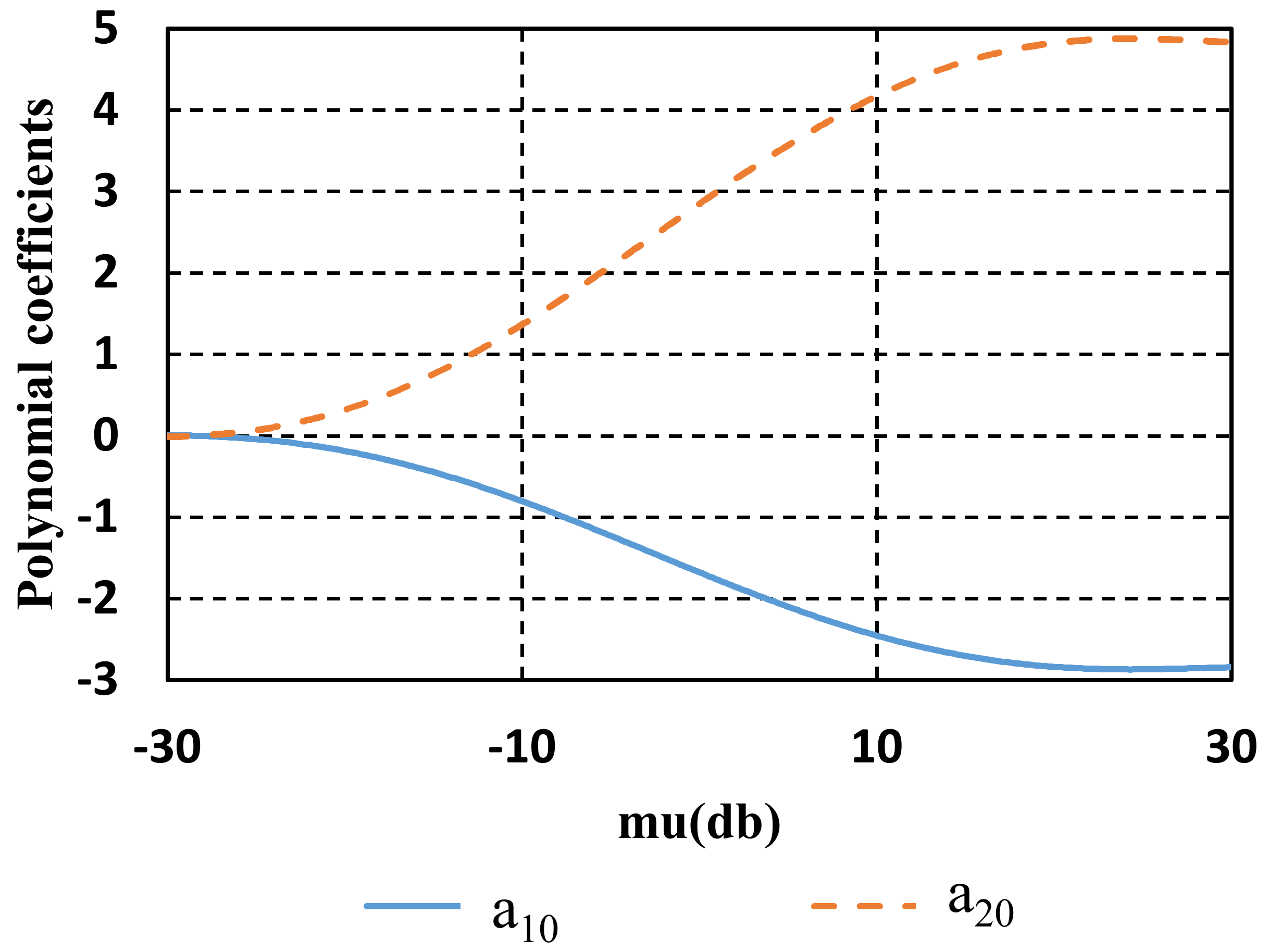
2.6. Fixed FLP Coefficients
2.7. A Novel Four-Stage Forest Canopy Height Inversion Method Based on FLP
3. Results
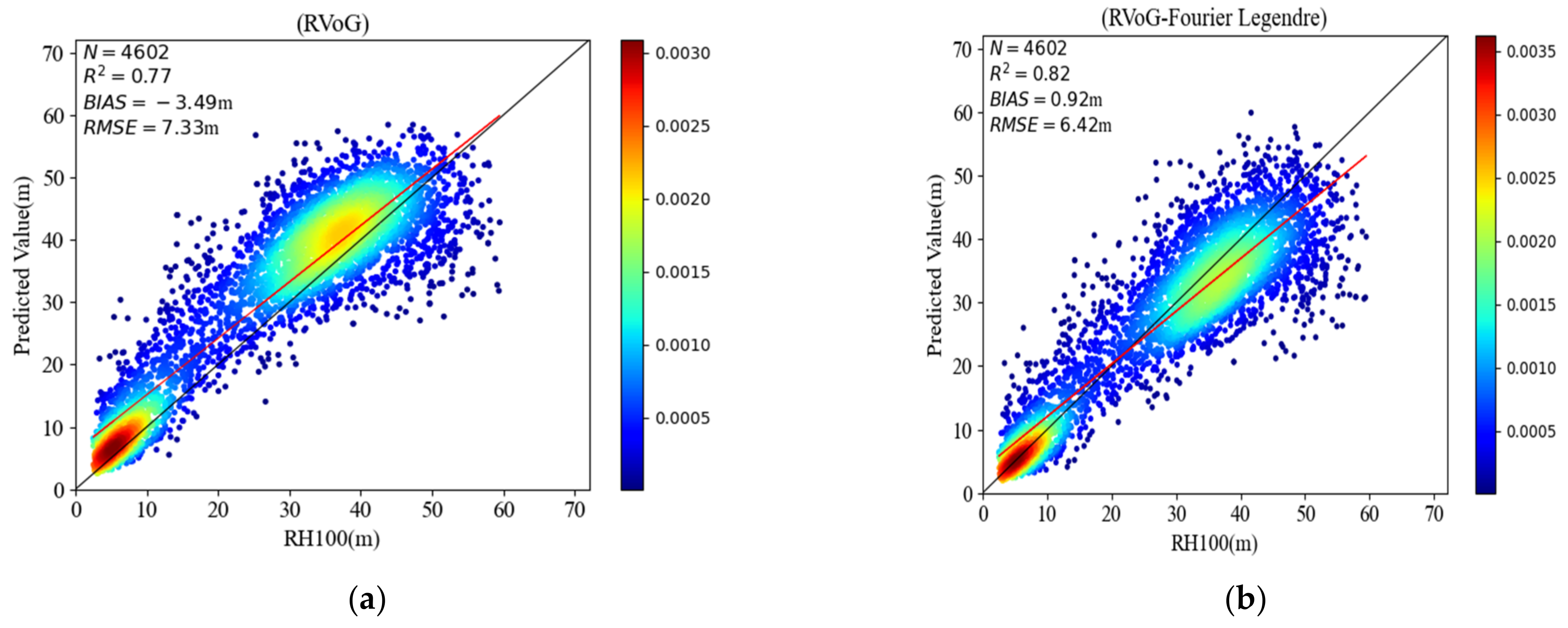
3.1. Estimation Results in Mangroves
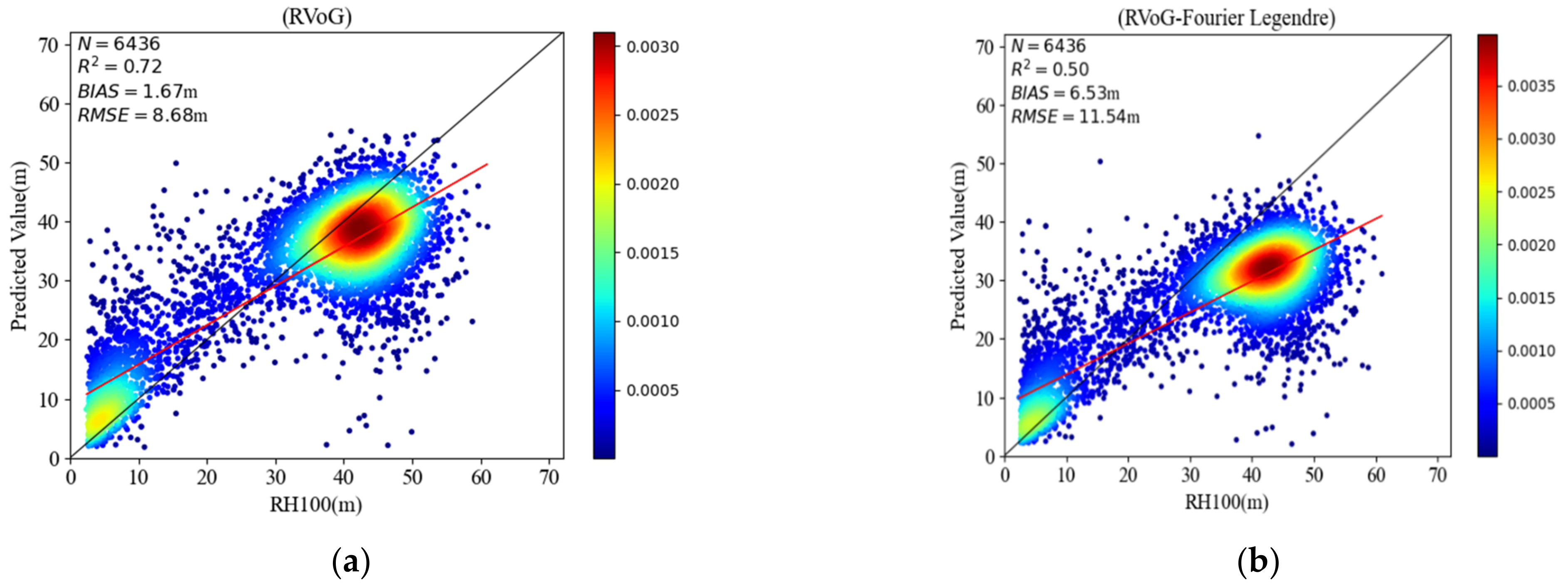
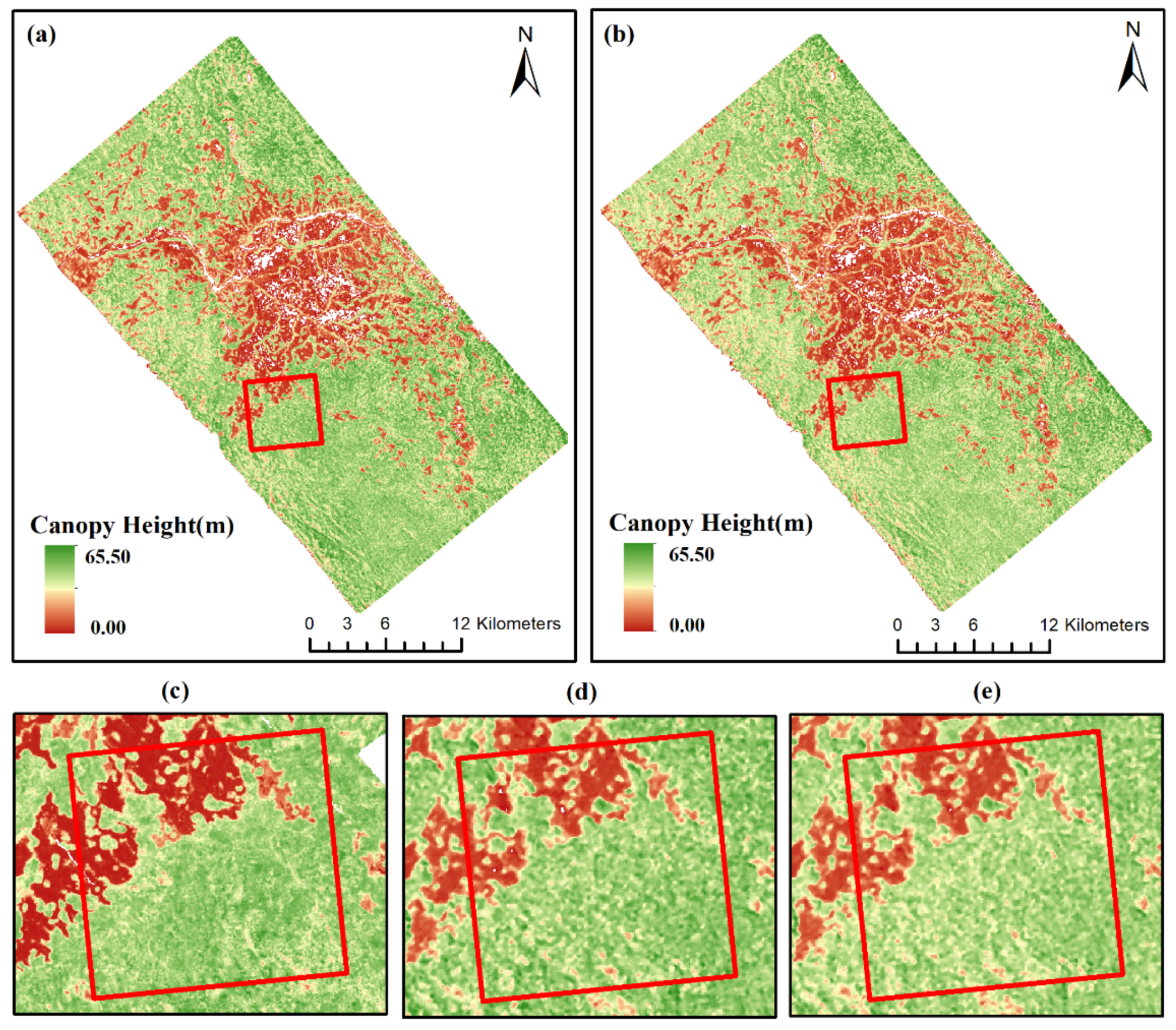
3.2. Estimation Results in Inland Forests
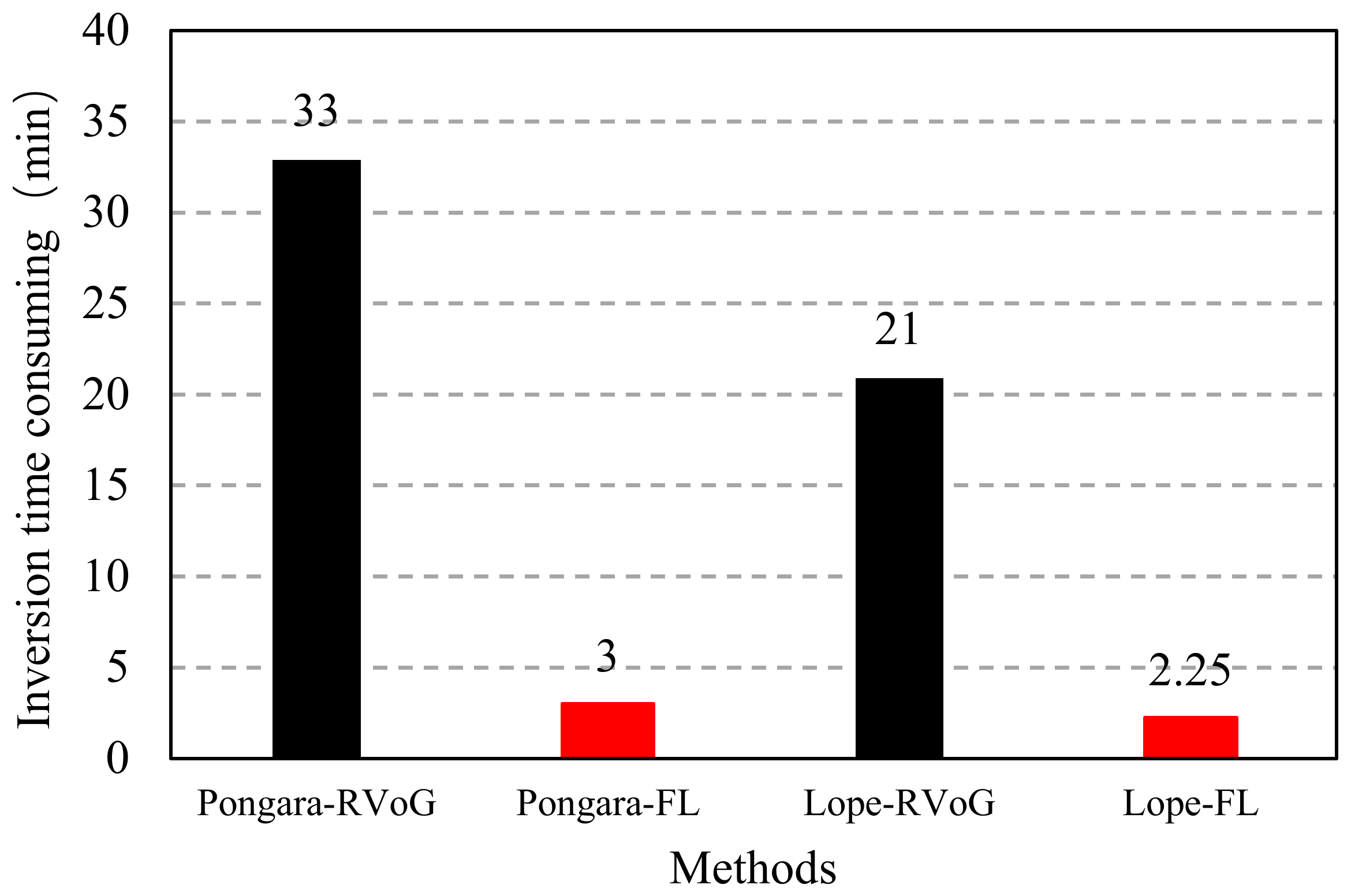
3.3. Model Efficiency Comparison
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences in Forest Types
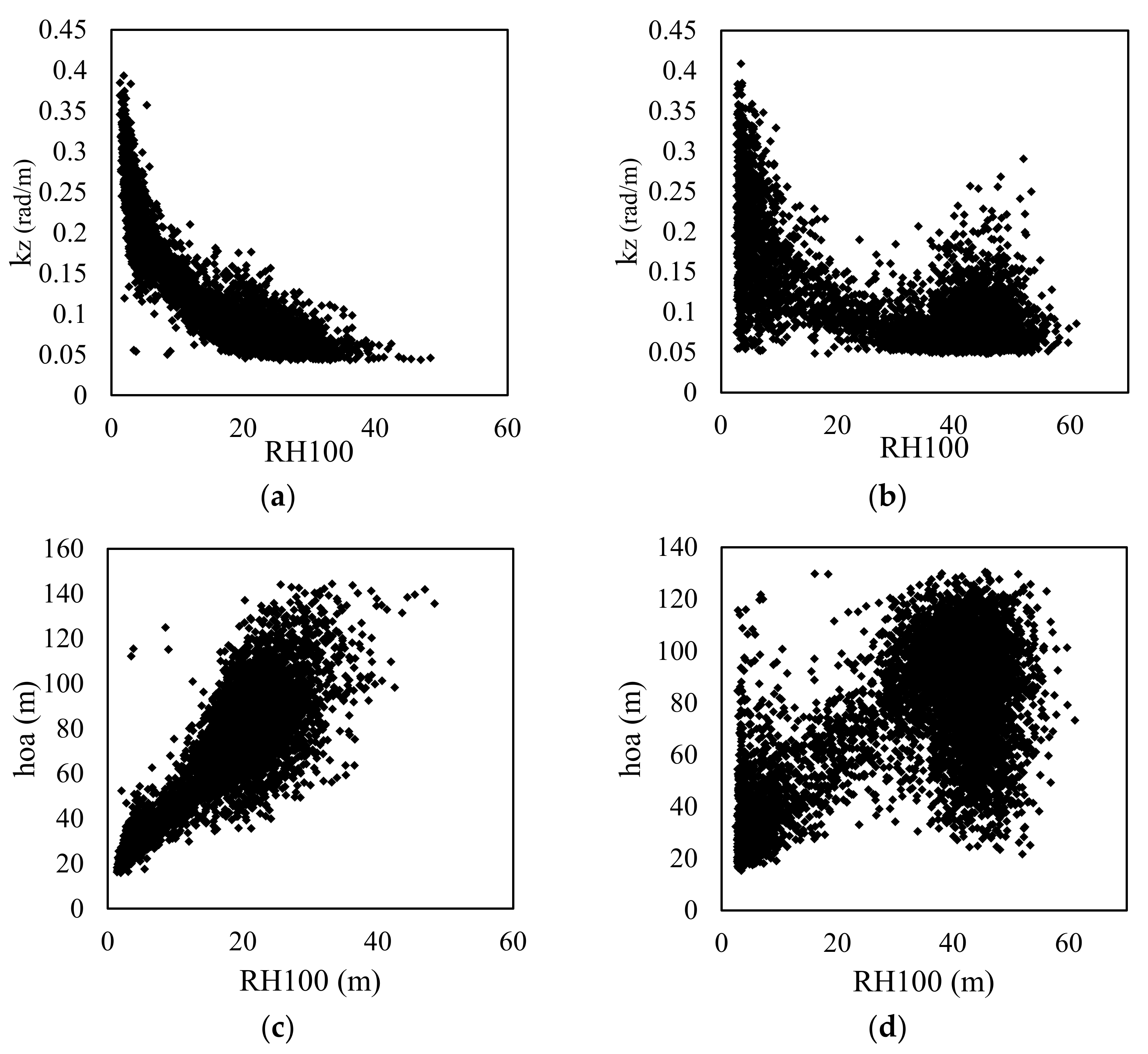
4.2. Impact of the Baseline Selection Method
4.3. The Impact of Temporal Decorrelation
4.4. The Impact of Microwave Penetration
4.5. Limitations of This Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonan, G.B. Forests and Climate Change: Forcings, Feedbacks, and the Climate Benefits of Forests. Science 2008, 320, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sexton, J.O.; Bax, T.; Siqueira, P.; Swenson, J.J.; Hensley, S. A comparison of lidar, radar, andfield measurements of canopy height in pine and hardwood forests of southeastern North America. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Lee, S.K.; Hancock, S.; Luthcke, S.; Tang, H.; Armston, J.; Dubayah, R. Improved forest height estimation by fusion of simulated GEDI Lidar data and TanDEM-X InSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Jeganathan, C.; Sharma, L.K.; Nathawat, M.S. A review of radar remote sensing for biomass estimation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 1779–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soja, M.J.; Quegan, S.; D’Alessandro, M.M.; Banda, F.; Scipal, K.; Tebaldini, S.; Ulander, L.M.H. Mapping above-ground biomass in tropical forests with ground-cancelled P-band SAR and limited reference data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, S.; Soosani, J.; Adeli, K.; Fadaei, H.; Naghavi, H.; Pham, T.D.; Bui, D.T. Improving accuracy estimation of forest aboveground biomass based on incorporation of ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-2A imagery and machine learning: A case study of the Hyrcanian Forest area (Iran). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Papathanssiou, K.P. Polarimetric optimization in radar interferometry. Electron. Lett. 1997, 33, 1176–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanassiou, K.; Cloude, S.R. Single-baseline polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zou, B.; Lin, M. Parameter inversion model base on PolInSAR images. In Proceedings of the Asian and Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR-2007), Huangshan, China, 5–9 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Neumanm, M.; Famil, L.F.; Reigber, A. Estimation of forest structure, ground and canopy layer characteristics from multi-baseline polarimetric interferometric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1086–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvia, P.; Lahivaara, T.; Maltamo, M.; Packalen, P.; Seppanen, A. Gaussian Process Regression for Forest Attribute Estimation from Airborne Laser Scanning Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3361–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieu, H.C.; Pham, M.N.; Le, V.N. Forest parameters inversion by mean coherence set from single-baseline polinsar data. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 2804–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebe, M.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Zoej, M.J.V. A Volume Optimization Method to Improve the Three-Stage Inversion Algorithm for Forest Height Estimation Using PolInSAR Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Cuong, T.H.; Nghia, P.M.; Minh, T.X.; Le, V.N.; Dang, C.H. An improved volume coherence optimization method for forest height estimation using PolInSAR images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Recent Advances in Signal Processing, Telecommunications & Computing (SigTelCom2019), Hanoi, Vietnam, 21–22 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Treuhaft, R.N.; Moghaddam, M.; van Zyl, J.J. Vegetation characteristics and underlying topography from interferometric radar. Radio Sci. 1996, 31, 1449–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Three-stage inversion process for polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEE Proc.-Radar Sonar Navig. 2003, 150, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Woodhouse, I.H.; Hope, J.; Minguez, S.; Osborne, P.; Wright, G. The Glen Affric Project: Forrest mapping using dual baseline polarimetric radar interferometry. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Retrieval of Bio- and Geophysical Parameters from SAR Data for Land Applications, Sheffield, UK, 11–14 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Garestier, F.; Le, T.T. Forest modeling for height inversion using single-baseline InSAR/Pol-InSAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1528–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Guo, H.; Song, P.; Tian, B.; Li, X.; Sun, Z. Combination of PolInSAR and LiDAR techniques for forest height estimation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, B. Estimation of pine forest height and underlying DEM using multi-baseline P-band PolInSAR data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannini, M.; Scheiber, R.; Moreira, A. Estimation of the minimum number of tracks for SAR tomography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R. Polarization coherence tomography. Radio Sci. 2006, 41, 1113–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R. Dual-baseline coherence tomography. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 41, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R. Polarisation Applications in Remote Sensing; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cloude, S.R.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Forest vertical structure estimation using coherence tomography. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Caicoya, A.T.; Kugler, F.; Papathanassiou, K.; Biber, P.; Pretzsch, H. Biomass estimation as a function of vertical forest structure and forest height—Potential and limitations for Radar Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Aachen, Germany, 7–10 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nafiseh, G.; Valentyn, T.; Alfred, S. A modified model for estimating tree height from polinsar with compensation for temporal decorrelation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; Peng, X.; Xie, Q.; Lin, D.; Liu, Z. A multibaseline polinsar forest height inversion model based on fourier–legendre polynomial. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fore, A.G.; Chapman, B.D.; Hawkins, B.P.; Hensley, S.; Jones, C.E.; Michel, T.R.; Muellerschoen, R.J. UAVSAR polarimetric calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3481–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.H.; Wang, C.C.; Zhu, J.J.; Fu, H.Q. Forest height inversion by combining S-RVOG model with terrain factor and PD coherence optimization. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sinica. 2015, 44, 686. [Google Scholar]
- Armston, J.; Tang, H.; Hancock, S.; Marselis, S.; Duncanson, L.; Kellner, J.; Hofton, M.; Blair, J.; Fatoyinbo, T.; Dubayah, R. Forest biomass estimation over three distinct forest types using TanDEM-X InSAR data and simulated GEDI lidar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111283. [Google Scholar]
- Kugler, F.; Schulze, D.; Hajnsek Pretzsch, H.; Papathanassiou, K.P. TanDEM-X Pol-InSAR performance for forest height estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6404–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Kugler, F.; Papathanassiou, K.; Hajnsek, I. Multibaseline polarimetric SAR interferometry forest height inversion approaches. In Proceedings of the ESA POLinSAR Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 24–28 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.B.; Zhu, B.D.; Yue, C.R.; Wang, N. Forest Canopy Height Inversion Based On Airborne Multi-Baseline PolInSAR. J. Geomat. 2022, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Denbina, M.; Simard, M.; Hawkins, B. Forest Height Estimation Using Multibaseline PolInSAR and Sparse Lidar Data Fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3415–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; He, B.; van Dijk, A.I.; Bai, X.; Quan, X. The impacts of spatial baseline on forest canopy height model and digital terrain model retrieval using P-band PolInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cloude, S.R.; Goodenough, D.G.; Hill, D.A.; Nesdoly, A. Radar forest height estimation in mountainous terrain using Tandem-X coherence data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3443–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Lin, H.; Wang, G.; Long, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Z. The Impact of Vertical Wavenumber on Forest Height Inversion by PolInSAR. In Proceedings of the 2018 Fifth International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Xi’an, China, 18–20 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.K.; Kugler, F.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K. The impact of temporal decorrelation over forest terrain in polarimetric SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Applications of Polarimetry and Polarimetric Interferometry (Pol-InSAR), ESA, Frascati, Italy, 26–30 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.K.; Kugler, F.; Papathanassiou, K.; Moreira, A. Forest height estimation by means of Pol-InSAR limitations posed by temporal decorrelation. In Proceedings of the 11th ALOS Kyoto & Carbon Initiative, Tsukuba, Japan, 28 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-K.; Kugler, F.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Hajnsek, I. Quantifying temporal decorrelation over boreal forest at L-and P-band. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on VDE, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2–5 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dall, J. InSAR elevation bias caused by penetration into uniform volumes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2319–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlund, M.; Baron, D.; Magdon, P.; Erasmi, S. Canopy penetration depth estimation with TanDEM-X and its compensation in temperate forests. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 147, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
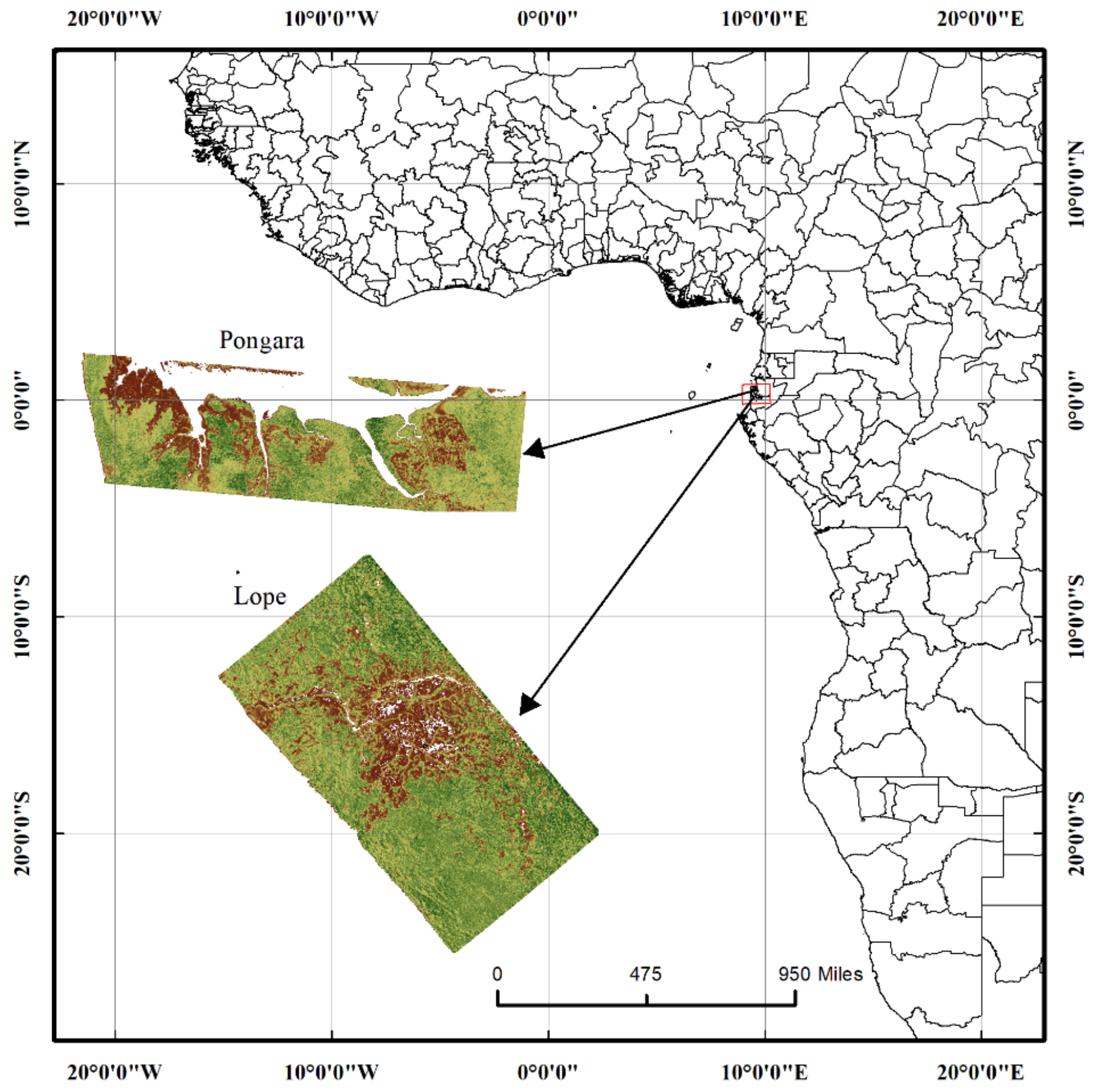


| Dataset | Description | Lope (Inland Tropical) | Pongara (Mangroves) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAR data acquisition | Acquisition Mode | PolSAR | |
| Steering Angle | 90 (deg) | ||
| Steering Angle | 40 (us) | ||
| Bandwidth | 80 (MHz) | ||
| Center Wavelength | 23.84 (cm) | ||
| Look Direction | Left | ||
| Range Resolution | 3.33 (m) | ||
| Azimuth Resolution | 4.80 (m) | ||
| Polarization Type | Full polarization | ||
| Average Along Track Velocity | 224.76 (m/s) | 224.97 (m/s) | |
| Look Angle | 21.48–65.43 (deg) | 21.87–65.34 (deg) | |
| Number of Tracks | 8 | 5 | |
| Vertical Baseline(m) | 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120 (m) | 0, 20, 45, 105 (m) | |
| Longitude | 11°25′53″ E~11°49′31″ E | 9°17′40″ E~10°0′29″ E | |
| Latitude | 0°3′58″ N~0°20′40″ S | 0°1′27″ N~0°14′15″ S | |
| RH100 (LiDAR) | Resolution | 25 m | |
| Height Range | 1.94–84.28 (m) | 1.80–65.11 (m) | |
| Test Area (Forest Type) | Inversion Model | R2 | RMSE | BIAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lope (Inland tropical forests) | RVoG | 0.72 | 8.68 | 1.67 |
| FL | 0.50 | 11.54 | 6.53 | |
| Pongara (Mangroves) | RVoG | 0.77 | 7.33 | −3.49 |
| FL | 0.82 | 6.42 | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, H.; Yue, C.; Yuan, H.; Wang, N.; Chen, S. A Method for Forest Canopy Height Inversion Based on UAVSAR and Fourier–Legendre Polynomial—Performance in Different Forest Types. Drones 2023, 7, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7030152
Luo H, Yue C, Yuan H, Wang N, Chen S. A Method for Forest Canopy Height Inversion Based on UAVSAR and Fourier–Legendre Polynomial—Performance in Different Forest Types. Drones. 2023; 7(3):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7030152
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Hongbin, Cairong Yue, Hua Yuan, Ning Wang, and Si Chen. 2023. "A Method for Forest Canopy Height Inversion Based on UAVSAR and Fourier–Legendre Polynomial—Performance in Different Forest Types" Drones 7, no. 3: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7030152
APA StyleLuo, H., Yue, C., Yuan, H., Wang, N., & Chen, S. (2023). A Method for Forest Canopy Height Inversion Based on UAVSAR and Fourier–Legendre Polynomial—Performance in Different Forest Types. Drones, 7(3), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7030152






