Halogenated 2,1,3-benzoxadiazoles as Potential Fluorescent Warheads for Covalent Protease Inhibitors †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
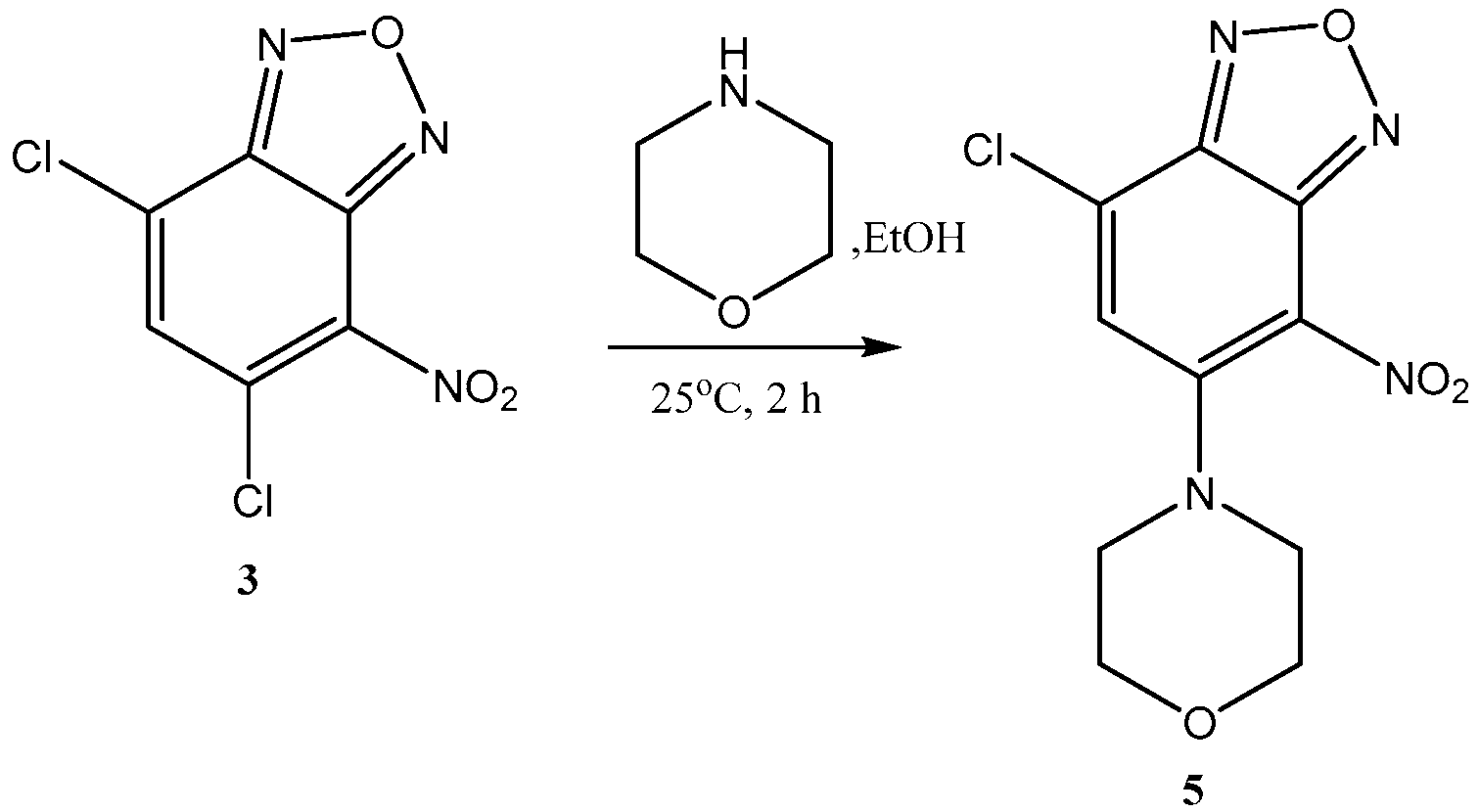
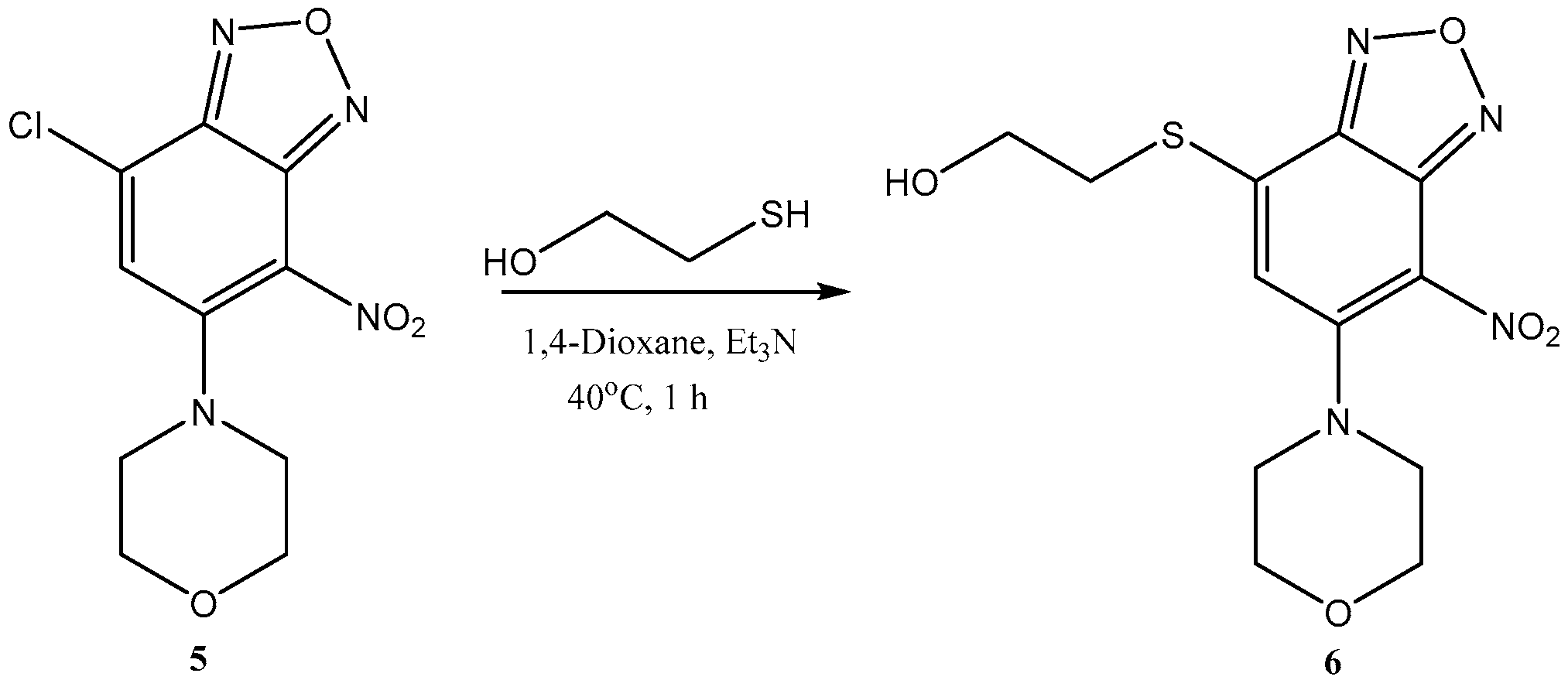
2. Results and Discussion
3. Methods
- Rf = 0.14 (DCM:MeOH, 10:1).
- mp: 213–215 °C.
- ESI-MS: m/z = 476.2 (100%, [M + H]+).
- UV spectrum (MeCN, 1 × 10−5 mol L-1), λmax, nm: 303 nm, 412 nm.
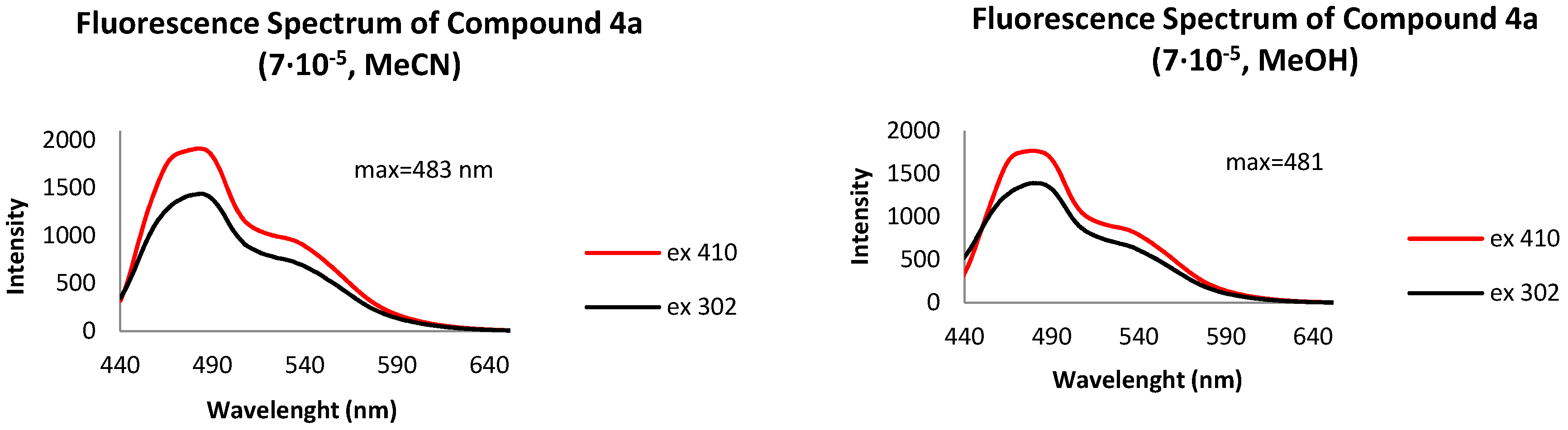
- Fluorescence spectrum, λmax, nm: 481 (MeOH), 483 (MeCN).
- Rf = 0.35 (EtOAc: Cyclohexane, 1:2).
- mp: 169–170 °C.
- ESI-MS: m/z = 566.2 (62%, [M + H]+), 588.2 (26%, [M + Na]+).
- UV-spectrum (MeCN, 1 × 10−5 mol L−1), λmax, nm: 302 nm, 411 nm.
- Fluorescence spectrum, λmax, nm: 478 (MeOH), 480 (MeCN).
- Rf = 0.48 (DCM:MeOH, 10:1).
- mp: 184–186 °C.
- UV-spectrum (MeCN, 1 × 10−5 mol L-1), λmax, nm: 312 nm, 440 nm.
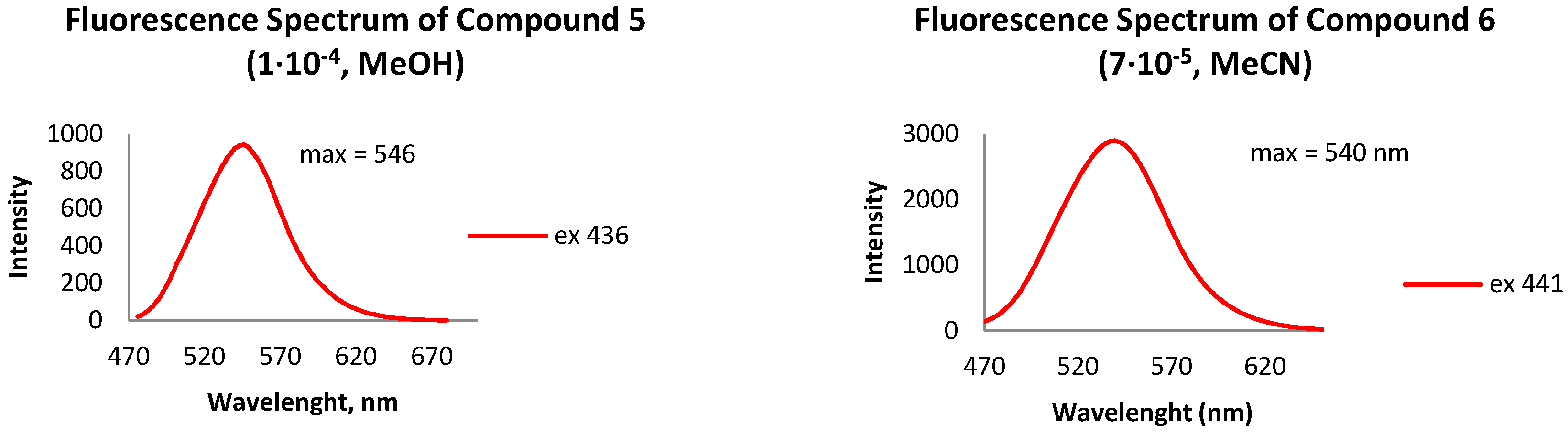
- Fluorescence spectrum, λmax, nm: 546 (MeOH).
- Rf = 0.29 (Toluene:EtOAc, 4:1).
- mp: 177–179 °C.
- UV spectrum (MeCN, 1 × 10−5 mol L−1), λmax, nm: 372 nm, 441 nm.
- Fluorescence spectrum, λmax, nm: 540 (MeCN).
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Schirmeister, T. Inhibition of cysteine proteases by peptides containing aziridine-2, 3-dicarboxylic acid building blocks. Biopolymers 1999, 51, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.C.; Asgian, J.L.; Ekici, Ö.D.; James, K.E. Irreversible inhibitors of serine, cysteine, and threonine proteases. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4639–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanon, D.A.; Banerjee, R.; Webster, E.R.; Bak, D.W.; Wang, C.; Weerapana, E. Investigating the Proteome Reactivity and Selectivity of Aryl Halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3330–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, P.; Johe, P.; Jung, S.; Kesselring, J.; Tenzer, S.; Distler, U.; Anh Le, T.; Engels, B.; Hellmich, U.A.; Opatz, T.; et al. Aromatic Warheads for Cysteine Protease Inhibitors, in preparation.
- Kupryushkin, M.S.; Konevet, D.A.; Vasilyeva, S.V.; Kuznetsova, A.S.; Stetsenko, D.A.; Pyshnyi, D.V. Oligonucleotide Functionalization by a Novel Alkyne-Modified Nonnucleosidic Reagent Obtained by Versatile Building Block Chemistry. Nucleos. Nucleot. Nucl. Acids 2013, 32, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilyeva, S.V. Novel Fluorescent Pyrimidine Nucleosides Containing 2, 1, 3-Benzoxadiazole and Naphtho-[1, 2, 3-CD] Indole-6 (2H)-One Fragments. Nucleos. Nucleot. Nucl. Acids 2014, 33, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Pirrung, M.C.; Liao, J. A fluorescent amino acid probe to monitor efficiency of peptide conjugation to glass surfaces for high density microarrays. Mol. BioSyst. 2012, 8, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenskowsky, L.; Schreuder, H.; Derdau, V.; Matter, H.; Volkmar, J.; Nazaré, M.; Opatz, T.; Petry, S. Identification and Characterization of a Single High-Affinity Fatty Acid Binding Site in Human Serum Albumin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Maisonneuve, S.; Xie, J. Synthesis of triazole-linked fluorescent saccharides and glycosyl amino esters. Synthesis 2012, 44, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Clausen, K.; Thorsen, M.; Lawesson, S.O.; Spatola, A.F. Synthesis of (R)-and (S)-(glu) thz and the corresponding bisthiazole dipeptide of dolastatin 3. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1984, 1, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, A.J.; Gray, A.C.G.; Katritzky, A.R. Heterocyclic rearrangements. Part VIII. Attempted intramolecular oxygen-transfer in chlorofurazanobenzofuroxans. J. Chem. Soc. B 1967, 9, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuznetsova, A.; Klein, P.; Opatz, T. Halogenated 2,1,3-benzoxadiazoles as Potential Fluorescent Warheads for Covalent Protease Inhibitors. Proceedings 2019, 9, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05670
Kuznetsova A, Klein P, Opatz T. Halogenated 2,1,3-benzoxadiazoles as Potential Fluorescent Warheads for Covalent Protease Inhibitors. Proceedings. 2019; 9(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05670
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuznetsova, Anastasiya, Philipp Klein, and Till Opatz. 2019. "Halogenated 2,1,3-benzoxadiazoles as Potential Fluorescent Warheads for Covalent Protease Inhibitors" Proceedings 9, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05670
APA StyleKuznetsova, A., Klein, P., & Opatz, T. (2019). Halogenated 2,1,3-benzoxadiazoles as Potential Fluorescent Warheads for Covalent Protease Inhibitors. Proceedings, 9(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05670




