Abstract
The aim of this research work was to develop n-propyl gallate-encapsulated solid lipid nanoparticles (PG-SLNs) and load them into a hyaluronic acid (HA)-based hydrogel (HG) for intranasal delivery. Simple modified solvent injection technique was used for the preparation of the PG-SLNs via the quality-by design (QbD) approach. The optimized PG-SLNs, with an average hydrodynamic diameter of 103 ± 46.04 nm, polydispersity index (PDI) of 0.16 ± 0.001 and zeta potential of −36 ± 4.78 mV, were obtained. The percentage yield of PG-SLNs was found to be 80.78 ± 0.1%, with an encapsulation efficiency of 84 ± 0.5% and loading capacity of 60 ± 0.1%. In vitro drug release from the hydrogel-containing PG-SLNs showed sustained release profile with a lower burst effect (less than 20%) and controlled release to a greater extent within 720 min following diffusion-based release kinetics. The in vitro permeability studies showed the total permeation of PG from HG was 600 μg/cm2 within 60 min, showing significant permeation of PG. Findings of this work strongly emphasize that PG-SLNs-loaded hydrogel and permeation enhancer hold significant potential to be delivered through the intranasal route.
Published: 1 December 2020
1. Introduction
Over the past few years, intranasal (IN) administration has attracted considerable interest, since it provides a non-invasive route for circumvention of the blood–brain barrier. Drugs that are administrated to the nasal cavity can travel along the olfactory and trigeminal nerves to reach each part of the central nervous system. There are number of substances which are able to reach the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) part, the olfactory bulb, and other parts of the brain after IN administration, as mentioned in many in vivo studies conducted in mice [1]. A recent study has supported the evidence of IN delivery of peptides (melanocortin and insulin) to CSF in laboratory mice model [2,3].
Propyl gallate (PG), also known as propyl 3,4,5-tri-hydroxybenzoate, an ester form of gallic acid and propanol that functions as a synthetic antioxidant, has been shown in studies to potentially contribute to the mitochondrial impairment and inhibition of cellular respiration. PG has shown proven efficacy and has a vital anti-cancer effects on various normal/cancer cells that may lead to DNA genotoxicity, cytotoxicity, and fragmentation [4,5].
Hyaluronic acid (HA), a glycosaminoglycan, is a biological and structural component of extracellular matrix (ECM) that assists in morphogenesis, wound repair, and cellular signaling. Hydrogel (HG) made up of HA has been developed and evaluated for several biomedical applications. In this research, 14,000 Dalton HA was used for formulating HG.
The aim of this study was to develop and optimize PG-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (PG-SLNs) by applying QbD methodology and using response surface quadratic model. A further aim was to load PG-SLNs into chemically crosslinked HA-HG with permeation enhancer (Transcutol-P) and glutaraldehyde, which is suitable for nose-to-brain delivery [6].
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
PG, used as antioxidant compound, was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Budapest, Hungary). As excipients, HA (Mw = 1400 kDa) (Sigma-Aldrich, Budapest, Hungary), Tween 80 (Sigma-Aldrich, Budapest, Hungary), cholesterol (Molar Chemicals Ltd., Budapest, Hungary), Transcutol-P (diethyl glycol monoethyl ether) was supplied by Gattefossé (saint-Priest, France), ethanol 96% (Molar Chemicals Ltd., Budapest, Hungary), and sodium chloride physiological solution (Molar Chemicals Ltd., Budapest, Hungary) were used.
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Optimization of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles by Quality by Design Approach and Risk Assessment Strategy
The first step was the determination of the quality target product profile (QTPP) of the final product, which is the essential element to successfully complete the QbD-based initial risk assessment (RA). In the second step, the critical quality attributes (CQAs) of the final product and the critical process parameters (CPPs) of the selected production method were identified. Simultaneously, a primary knowledge space development was made as part of the QbD methodology, which included the collection, systematization, and visualization of all the products and process-relevant information. The LeanQbD® software (QbD Works LLC, Fremont, CA, USA, www.qbdworks.com) was used for the RA procedure. In this procedure, the first part was the interdependence rating among the QTPPs and CQAs, as well as among the CQAs and CPPs. A three-level scale was used to describe the relationship between the parameters: “high” (H), “medium” (M), or “low” (L). Then, a risk occurrence rating of the CPPs (or probability rating step) was made, applying the same three-grade scale (H/M/L) ranking structure. As the output of the initial RA evaluation, Pareto diagrams were generated by the software presenting the numerical data and the ranking of the CQAs and CPPs according to their potential impact.
2.2.2. Development of Optimized PG loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) by Modified Injection Method
PG-loaded SLNs were prepared through the modified injection method. The cholesterol was dissolved in 5 mL ethanol/acetone solvent mixture and injected slowly into 0.2% Tween 80 aqueous solution along with stirring at 700 rpm at 60 °C. After complete evaporation of organic phase, the formulation was centrifuged for 2 h at 13,500 rpm to collect the pellets free from other impurities. The collected pellets were freeze-dried. The lyophilization of nanoparticles was performed using 5% trehalose as cryoprotectant.
2.2.3. Preparation of Muco-Adhesive HA-Based HG Formulations with PG-loaded SLNs
HA-based HG was prepared with different concentrations (0.5%, 1%, 2%, 3% of HA) by soaking it in ultrapure water (HPLC grade) under constant stirring at 400 rpm for 30 min. After complete swelling of the polymer, the lyophilized SLNs were added. This was followed by the incorporation of SLNs into HA solution, whereafter constant stirring was performed with addition of 0.5% gluteraldehyde as crosslinker. Following the crosslinking step, 0.5% triethanolamine was added with stirring for 4 min until gel-like consistency appeared. Along with different concentrations of HA, hydrogel with and without permeation enhancer (1 mL of Transcutol-P) was developed.
2.2.4. Measurement of Particle Size, Surface Charge, and Polydispersity Index
A total of 6 mg of lyophilized SLNs was reconstituted in 6 mL of purified water, and in order to decrease the inter-particle aggregation, the solution was sonicated for 4 min. The mean particle size (Z-average), polydispersity index (PDI), and surface charge (zeta potential) of SLNs were evaluated in folded capillary cells using Malvern Zetasizer nano ZS (Malvern Instrument, Worcestershire, UK). The refractive index and temperature of the equipment were set at 25 °C and 1.445, respectively, and the total number of scans was 17.
2.2.5. Surface Morphology
The PG-SLNs were screened to analyze the surface properties via transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (FEI Tecnai G2 20 XTwin; FEI Corporate Headquarters, Hillsboro, OR, USA) run at 200 kV accelerating voltage. A few microliters of PG-SLNs liquid formulation was dispersed on a carbon-coated copper grid. A filter was used to clear extra drops of the sample dispersion and was put on the carbon-coated copper grid; extra drops were removed from the grid by using a filter paper in order to leave a thin liquid film spread over the holes. The sample was negatively charged with sodium silicotung state solution, which was instantly deposited within 1 min.
2.2.6. Viscosity, pH, Drug Contents, Spreadability, Swelling Index, In Vitro Mucoadhesion of HG
Viscosity measurements were performed at 3 °C temperature with a RheoStress 1 HAAKE instrument (Karlsruhe, Germany) conducted with cone–plate geometry (radius 49.9 mm, 1° angle and 0.052 mm gap). The apparent viscosity of the samples was measured over a shear rate sweep of 0.01–100 s−1.To measure the swelling index of HG at different concentrations, we used the gravimetric method. Lyophilized powder of HGs with and without cross linker were soaked in buffer solution of pH 7.4. The swollen HGs were removed from the medium and weighed at specific time durations of 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, and 4.5 h until the weight of the swelled HG became constant. The extra amount of water was removed from the surface of HG by slightly tapping of the surface with filter paper. The determination of pH, drug contents (quantified by using HPLC), spreadability, and in vitro mucoadhesion studies (in vitro displacement method) were also performed.
2.2.7. In Vitro Permeation Studies
In vitro permeation studies were performed on a modified horizontal side-bi-side type diffusion apparatus at 37 °C with 100 rpm continuous stirring (Thermo Haake C10-P5, Sigma-Aldrich Co., Budapest, Hungary). The two compartments were isolated by an isopropyl myristate-impregnated cellulose membrane (Pall Metericelcellulose membrane, 0.45 µm pore size) with a 0.69 cm2 diffusion surface. The acceptor phase was pH = 7.4 PBS, and the donor phase was pH = 5.6 simulated nasal electrolyte solution with a volume of 9 mL. PG solution, PG-SLNs, and PG-SLNs-loaded HG (1% HA) with and without permeation enhancer were placed on the donor phaseA total of 2 mL of the samples were withdrawn from the acceptor phase by pipette and were replaced with the same medium at predefined time intervals (5, 10, 15, and 60 min) during the study.
2.2.8. In Vitro Release Studies
The following study was performed under the nasal conditions at 30 °C by using dissolution apparatus. The medium was 50 mL phosphate-buffer saline of pH 5.60, in which free PG of around 10 mg was placed, along with lyophilized nanoparticle solution and HG contained almost the same quantity of drug. The medium was stirred with a magnetic stirrer at 50 rpm, and the sample was taken after time intervals of 5, 15, 30, 60, 180, 360, and 720 min. After this, each sample was filtered through a membrane filter and the drug concentration of the aliquots were analyzed by using HPLC at 272 nm. All the measurements were taken in triplicate manner. The in vitro drug release data of the all samples were evaluated kinetically while using various mathematical models such as Zero, First, Higuchi, and the Korsmeyer–Peppas model.
3. Results
3.1. Risk Assessment (RA) as a Part of QbD Approach
The results of RA study are represented in Figure 1. After the screening of the impact (L, M, H) of the QTPP and evaluating the CQAs and CPPs, RA was conducted using the Lean QbD software. The initial RA results presented the estimation of the interdependence between the QTPP and CQAs and between the CMAs/CPPs on a three-grade scale according to their impact on each other. The risk assessment of the level of the effect depended on the scientific knowledge present in different experiments and in the literature. The Lean QbD software also helped in measuring the severity score for each factor and ranking them according to their effect on the quality of the final drug-loaded SLNs (Figure 1(i,ii)).
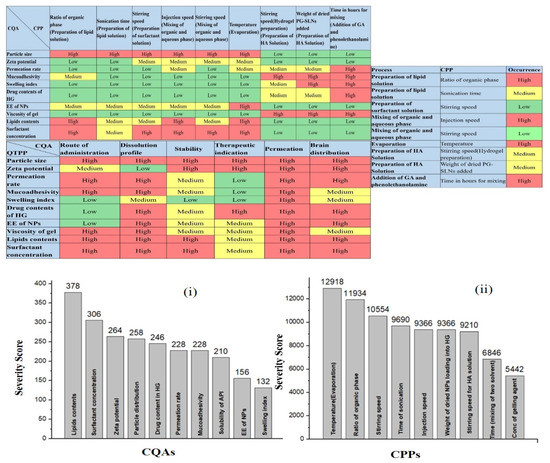
Figure 1.
Interdependence rating and estimation of the QTPP, CQAs and CQA-CPPs, and Pareto charts showing the severity/impact among selected (i) CQAs and (ii) CPPs.
3.2. Characterization of Nanoparticles and HG
3.2.1. Particle Size, Zeta Potential, PDI
Z-average, PDI, and zeta potential were measured for optimized PG-loaded SLNs. The Z-average of PG-SLNs was reported as 103 ± 46.04 nm, PDI of 0.16 ± 0.001, and zeta potential of −36 ± 4.78 mV. The results are within the nanorange, and the value of zeta potential indicated greater stability.
3.2.2. Morphological Study
The TEM images of PG loaded SLNs showed a spherical shape and uniform distribution without aggregation of SLNs, as shown in Figure 2. The TEM images also revealed that the particle size was ≈100 nm. The results of TEM images are comparable with the zeta results and are within the nano range; the acquired Z-average results are suitable for demonstrating the effects of synthesis parameters on particle size.
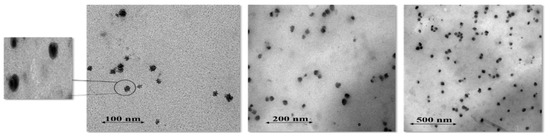
Figure 2.
TEM images of optimized PG-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles at various resolution scales (100, 200, 500 nm).
3.2.3. Swelling Index, pH, Percent Drug Contents, Spreadability, Viscosity, In Vitro Muco-Adhesivity Studies of HG
Swelling studies with and without cross linker were performed. The results showed that all the formulations without cross linker show greater swelling index as compared to chemically cross-linked HG as showed in Figure 3. The pH, viscosity, spreadability, in vitro mucoadhesion measurements were also performed as shown in Table 1. The viscosity measurement of all the formulations showed that there was an inverse proportion between shear rate and viscosity of HG; by increasing the shear rate, viscosity of HG decreased, as shown in Table 1.
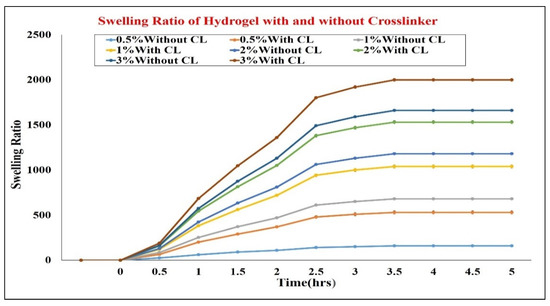
Figure 3.
Swelling ratio of hydrogel with and without crosslinker. CL = crosslinker.

Table 1.
Characterization of hydrogels in terms of different concentrations of polymer (hyaluronic acid).
3.2.4. In Vitro Release Study
In vitro release studies of PG-SLNs showed brust release of roughly 40% at the pH 5.6 within 1 h, as shown in Figure 4, while approximately >60% of drug was released within 8 h. However, initial burst released was less in the case of hydrogel (roughly 20%) with a controlled release to a greater extent as roughly 50% of the drug was released within 720 min, which was extraplotted up to 24 h at pH 5.6.
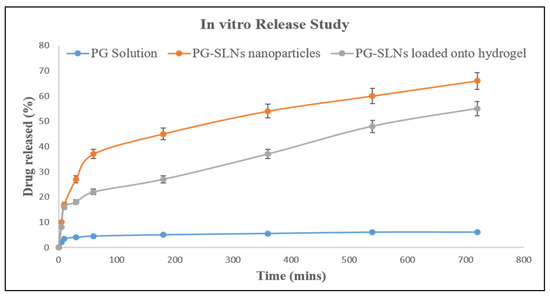
Figure 4.
In vitro release study of drug solution, PG-SLNs, and PG-SLNs-loaded hydrogel.
3.2.5. In Vitro Permeation
The side-bi-side type apparatus was used for determination of in vitro nasal permeation of PG solution, PG-SLNs, and PG-SLNs-loaded HG with and without permeation enhancer (Transcutol-P) (Figure 5). The maximum permeation of PG from PG-SLNs was ≈190 µg/cm2 after 60 min. The PG-SLNs-loaded HG without permeation enhancer showed less permeation round about 180 µg/cm2. In the case of PG solution, the permeation was less than <2 µg/cm2. However, when compared to HG with permeation enhancer (Transcutol-P), there was a significant difference of p < 0.05, and permeation value was about 600 µg/cm2.
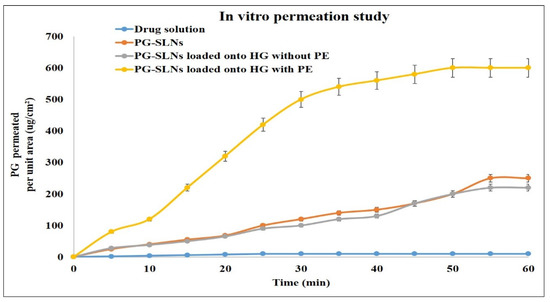
Figure 5.
In vitro permeation of drug solution, PG-SLNs, PG-SLN-loaded hydrogel without PE, and PG-SLN-loaded hydrogel with PE. PE = permeation enhancer.
4. Discussion
The objective of the present research work was to develop PG-SLNs followed by loading them into HA-HG for IN administration. The RA study was conducted from the early development stage to prioritize the CPPs that can affect the CQAs of the target product (formulation of PG-SLNs). The RA results evaluated the lipid contents, surfactant concentration, ratio of organic phase, and the temperature as the highest risk CMAs and CPPs, respectively, in terms of affecting the CQAs of PG-SLNs formulation. The CPPs of PG-SLNs were temperature and ratio of organic phase. The response surface quadratic model was implemented on the most critical factors to optimize them and develop the target PG-SLNs. Following the formulation of PG-SLNs, the nanosystem was loaded into HG, and in vitro investigations were performed. PG-SLNs showed a particle size of 103 ± 46.04 nm with a high negative surface charge that can assure high stability that is suitable for cellular binding and uptake of NPs in IN environment due to higher electrostatic interaction. Morphological studies further confirmed the nanosize and homogenous distribution of the spherically shaped SLNs, which is in accordance with the results of zeta measurements. The EE of PG reached 84 ± 0.477% in SLNs, which is in accordance with previous studies. In terms of all the measurements performed for HG at different concentrations, the HG with 1% concentration showed the best results in all performed studies, as shown in Table 1. The results of pH of optimum concentration of HG was 5.2 ± 0.3; drug contents were 82 ± 3.3; spreadability was 360 ± 0.33 mm2; mucoadhesion was good (showing potential adherence property); and the viscosity value was 1.88 Pa, which was not too high nor too low and could assure optimum flow property at the time of nasal administration. The in vitro release studies showed 60% drug release from HG, and samples were analyzed up to 720 min. The in vitro permeability studies showed the cumulative permeation of PG from HG was 600 μg/cm2 within 60 min.
5. Conclusions
PG-SLNs were successfully prepared in this study using the modified injection method. For the optimization of formulation and process parameters, we applied an initial risk assessment study as a part of the QbD approach. The PG-SLNs showed an average size of roughly 100 nm with a homogenous distribution, negative surface charge, drug release reaching roughly 60%, and high EE (>80%) (complying with the predefined QTPP). The viscosity and mucoadhesion results reflect enhanced adherence property of optimized HA-HG loaded with PG-SLNs. Compared to PG-SLNs, in vitro permeation studies showed the superiority of the PG-SLNs loaded into HA-HG and Transuctol-P system with a less initial burst effect and more sustained release. The optimized platform provides in vitro proof of the potential of combining the advantages of lipid-based NPs with HG as a promising intranasal delivery system.
Author Contributions
I.C. and G.K. conceived and designed the experiments; F.S. performed the experiments; F.S. and G.K. analyzed the data; I.C. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; F.S. wrote the paper; R.I. performed critical revision and revised the paper; I.C., G.K., and R.I. supervised. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to express their acknowledgement to the supporters. This study was supported by the Ministry of Human Capacities, Hungary (grant 20391-3/2018/FEKUSTRAT), and by the National Research, Development and Innovation Office, Hungary (GINOP 2.3.2-15-2016-00060) and (GINOP 2.3.4-15-2020-00006) projects.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| QbD | Quality by design |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| HG | Hydrogel |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| PG | Propyl gallate |
| SLNs | Solid lipid nanoparticles |
| QTPP | Quality target product profile |
| CPPs | Critical process parameters |
| CQAs | Critical quality attributes |
| EE | Encapsulation efficiency |
| CL | Cross-linker |
| PE | Penetration enhancer |
References
- Mistry, A.; Stolnik, S.; Illum, L. Nanoparticles for direct nose-to-brain delivery of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Pandey, R.S.; Patra, K.C.; Jain, S.K.; Soni, M.L.; Dangi, J.S.; Madan, J. Evaluation of neuropeptide loaded trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles for nose to brain delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 61, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, J.; Bicker, J.; Gouveia, F.; Liberal, J.; Oliveira, R.C.; Alves, G.; Falcão, A.; Falcão, A.C. Nose-to-brain delivery of levetiracetam after intranasal administration to mice. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 564, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskandani, M.; Barar, J.; Dolatabadi, J.E.N.; Hamishehkar, H.; Nazemiyeh, H. Formulation, characterization, and geno/cytotoxicity studies of galbanic acid-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1525–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Tikekar, R.V.; Nitin, N. Effect of antioxidant properties of lecithin emulsifier on oxidative stability of encapsulated bioactive compounds. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 450, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, R.; Pathak, K. Nanostructured lipid carrier versus solid lipid nanoparticles of simvastatin: Comparative analysis of characteristics, pharmacokinetics and tissue uptake. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).