Preparation of Magnetic-Fluorescent Bifunctional Microrods as a Drug Delivery System via One-Step Electrospraying †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Fe3O4/NaYF4: Eu3+/PLGA Microrods
2.3. Drug Loading of Fe3O4/NaYF4: Eu3+/PLGA Microrods
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Cell Experiments
2.5.1. Cell Culture
2.5.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
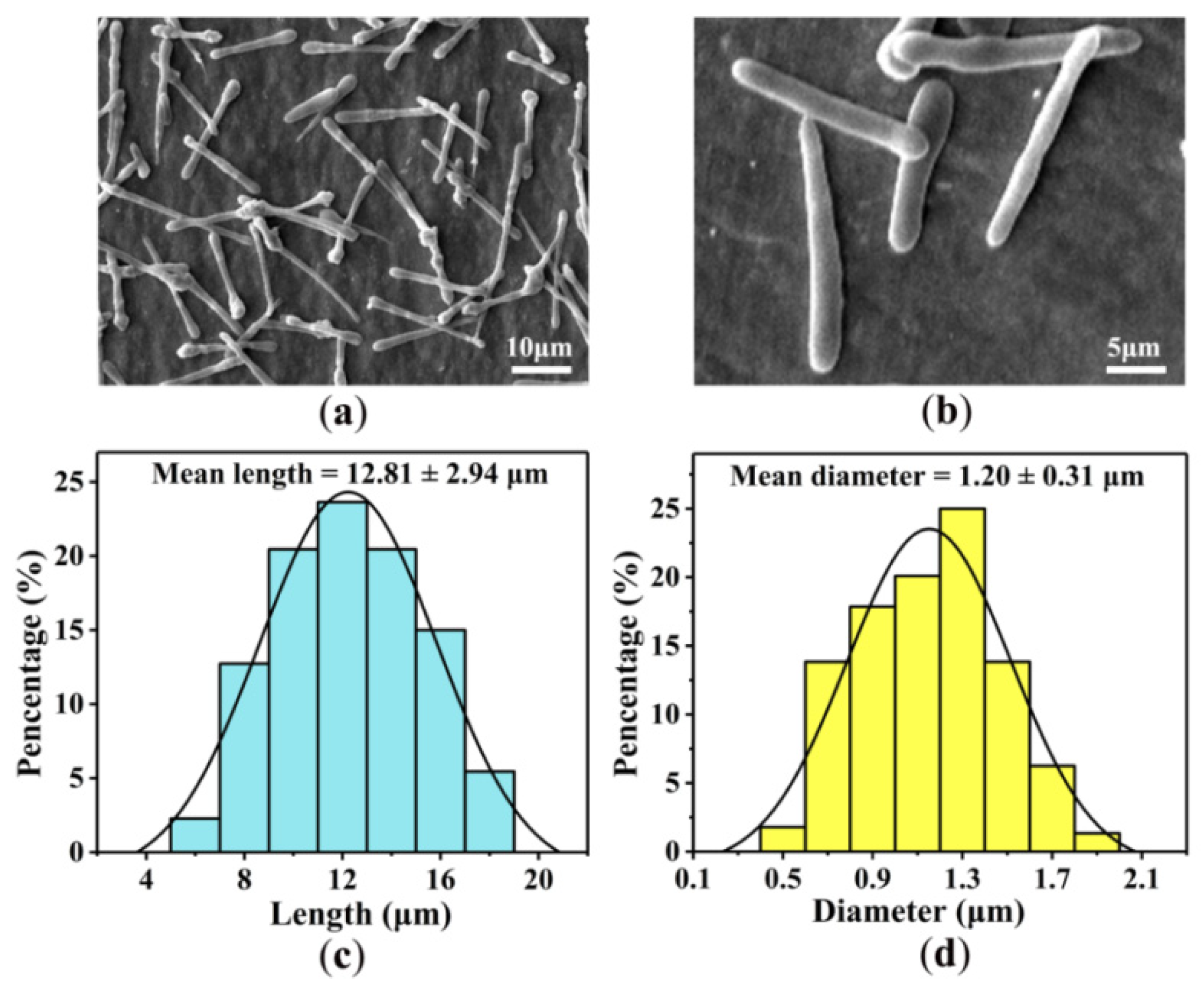
3.1. Morphology
3.2. Infrared Analysis and Thermal Stabilities
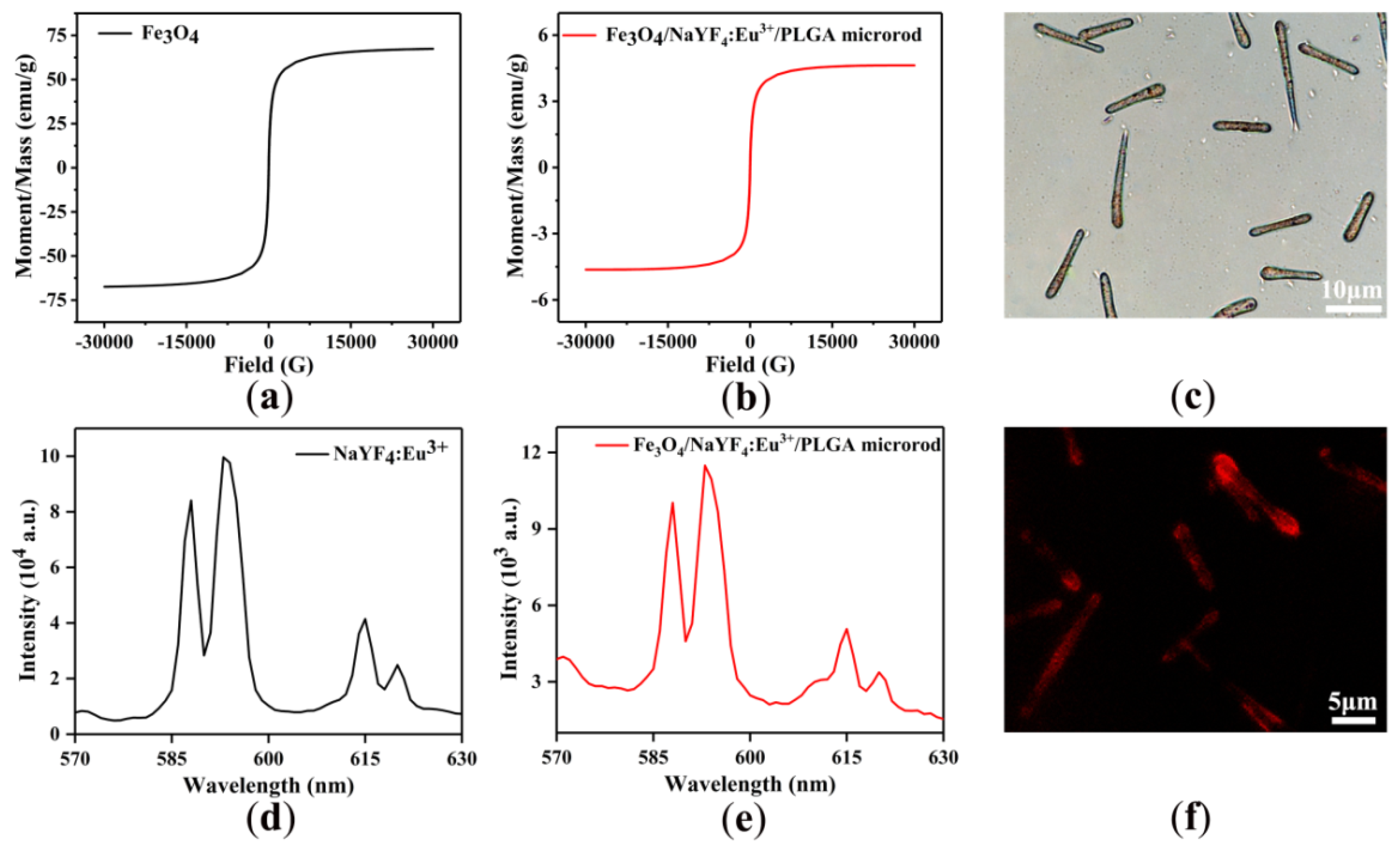
3.3. Magnetic and Fluorescent Properties
3.4. Hydrophobicity-Hydrophilicity
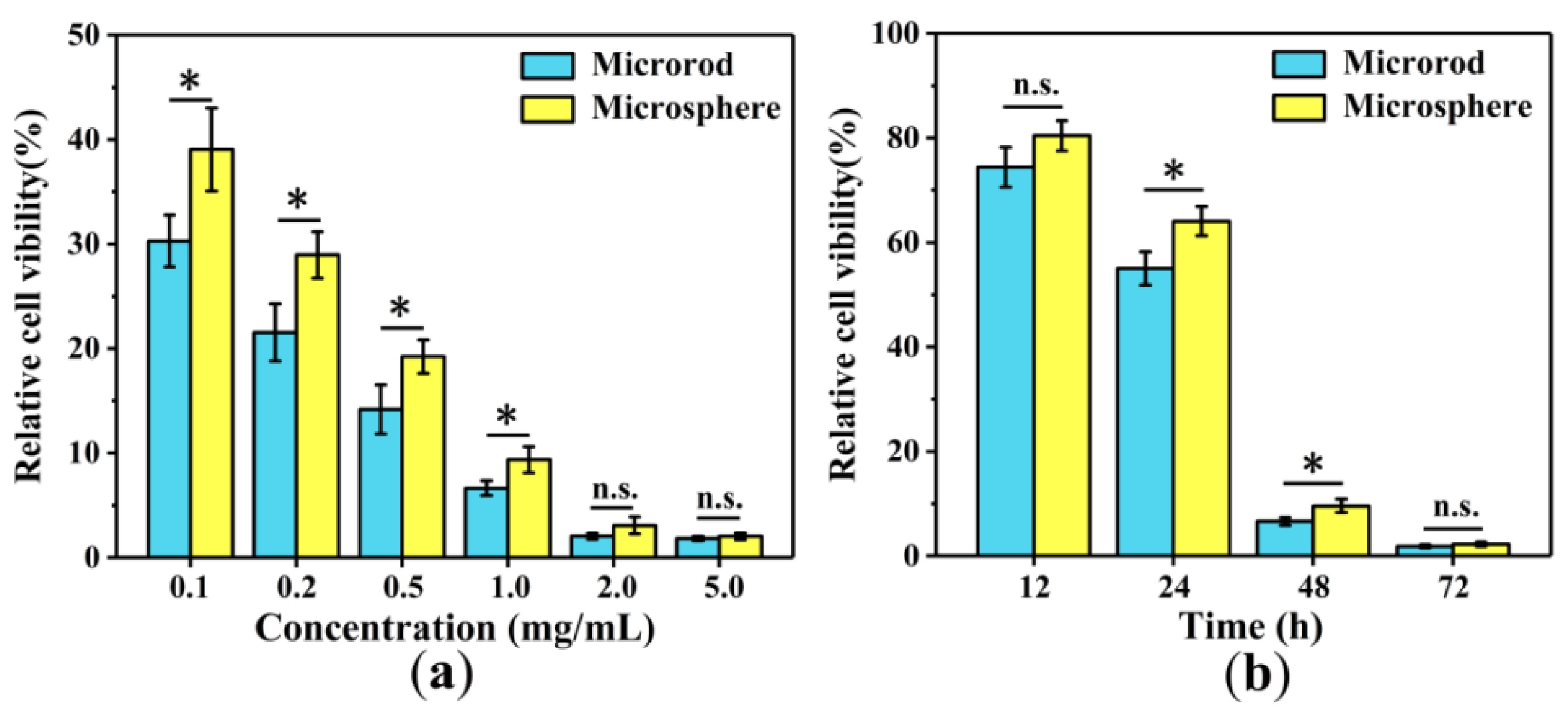
3.5. Cytotoxicity
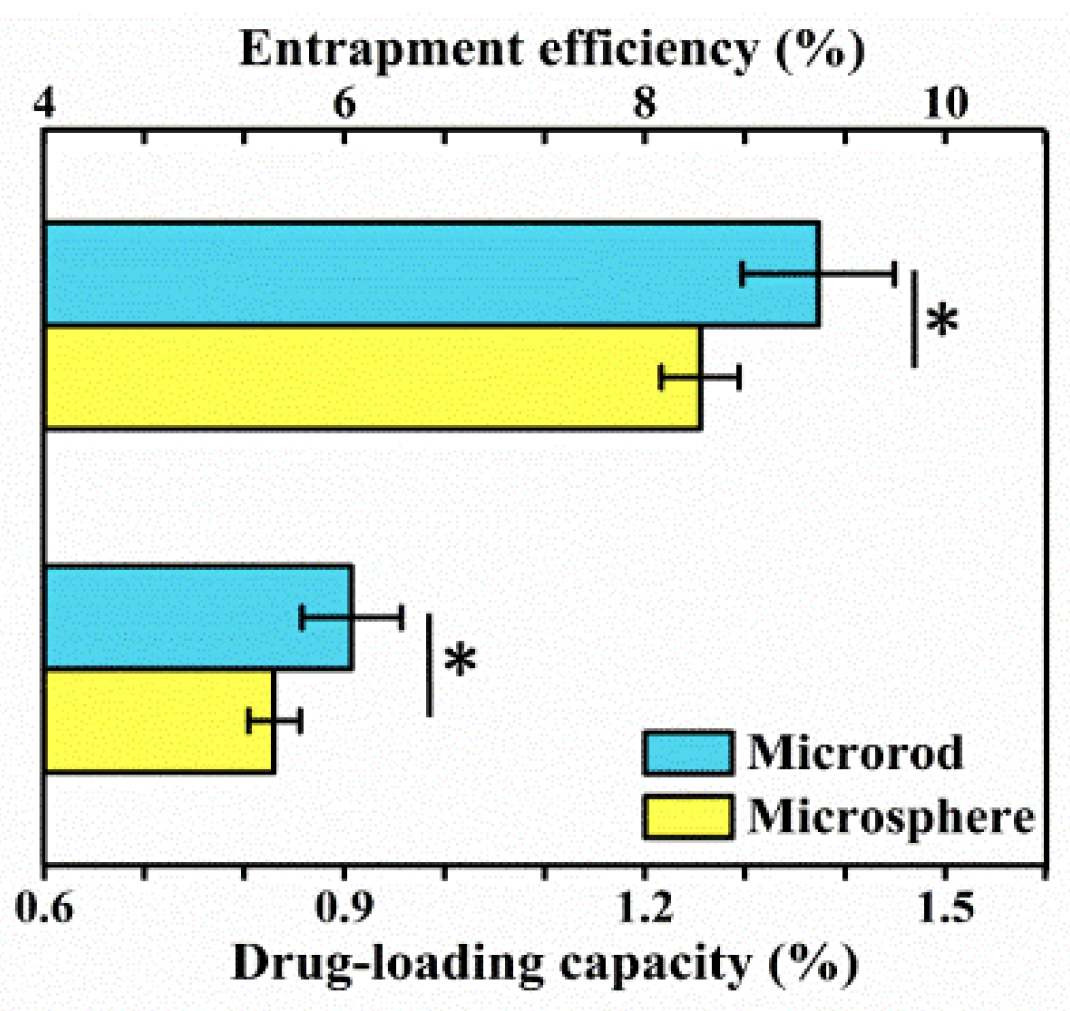
3.6. Entrapment Efficiency and Drug-Loading Capacity
3.7. Anti-Cancer Cell Efficiency
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PLGA | Poly (lactide-co-glycolide) |
| THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
| DEG | Diethylene glycol |
| HFIP | Hexafluoroisopropanol |
| DOX | doxorubicin |
| OD | optical density |
| PEI | polyethyleneimine |
| DDS | drug delivery system |
| MNP | magnetic nanoparticle |
| NP | nanoparticle |
| EE | entrapment efficiency |
| LC | drug-loading capacity |
| HUVEC | human umbilical vein endothelial cell |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| AO | Acridine Orange |
| PBS | phosphate buffer saline |
References
- Qian, C.M. Drug delivery systems (DDS): I. The definition, characteristic and classification of DDS. Northwest Pharm. J. 1995, 10, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Davoodi, P.; Lee, L.Y.; Xu, Q.; Sunil, V.; Sun, Y.; Soh, S.; Wang, C.-H. Drug delivery systems for programmed and on-demand release. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 132, 104–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grifantini, R.; Taranta, M.; Gherardini, L.; Naldi, I.; Parri, M.; Grandi, A.; Giannetti, A.; Tombelli, S.; Lucarini, G.; Ricotti, L.; et al. Magnetically driven drug delivery systems improving targeted immunotherapy for colon-rectal cancer. J. Control. Release 2018, 280, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Chen, D.; Shang, P.; Yin, D.C. A review of magnet systems for targeted drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2019, 302, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asfour, A.; Raoof, K.; Yonnet, J.P. Software Defined Radio (SDR) and Direct Digital Synthesizer (DDS) for NMR/MRI instruments at low-field. Sensors 2013, 13, 16245–16262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Ma, Q.; Dong, X. Direct electrospinning construction of nanocables with electrical conductive- magnetic core and insulative-photoluminescent sheath. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 95674–95681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, Q.; Hou, M.; Yan, C.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, R. Glucose functionalized carbon quantum dot containing organic radical for optical/MR dual-modality bioimaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 82, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Feng, F.; Yao, L.; Ma, G. One-step Preparation of Monodisperse Multifunctional Macroporous Particles through a Spontaneous Physical Process. Small 2018, 14, 1703570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelo, G.A.; Lodeiro, C.; Capelo, J.L.; Lorenzo, J.; Oliveira, E. Magnetic, fluorescent and hybrid nanoparticles: From synthesis to application in biosystems. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 106, 110104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, K.; Jana, D.; Ghorai, B.K.; Jana, N.R. AIEgen-Conjugated Magnetic Nanoparticles as Magnetic–Fluorescent Bioimaging Probes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3292–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Guan, X.; Zhong, S.; Chen, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, Z.; Xu, F.; Chen, P.; Wang, H. Multi-stimuli responsive smart chitosan-based microcapsules for targeted drug delivery and triggered drug release. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Qi, B.; Li, K.; Xu, J.; Song, Y.; Kang, D.; Fan, Y. Development of Magnetic-Fluorescent Bifunctional Drug Delivery System with Dual Drug Content and Enhanced Fluorescence. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 8094–8098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Xu, J.; Qi, B.; Li, K.; Gu, X.; Niu, X.; Fan, Y. One-Step Preparation of Poly(Lactide-Co-Glycolide) Fiber Rods Embedding with Luminescent Materials as a Drug Delivery System via Electrospray. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2018, 10, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Dorn, H.C.; Zhang, C. Assembly of Bio-Nanoparticles for Double Controlled Drug Release. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Cong, H.; Peng, Q.; Gu, C.; Tang, Q.; Xu, X.; Tian, C.; Zhai, F. Current status and future developments in preparation and application of nonspherical polymer particles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 256, 126–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Lu, W.; Qian, C.; Zeng, T.; Yin, L.; Wang, H.; Rao, L.; Liu, H.; Zeng, S. Urchin-like Ce/Tb co-doped GdPO4 hollow spheres for in vivo luminescence/X-ray bioimaging and drug delivery. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, S.E.; Ropp, P.A.; Pohlhaus, P.D.; Luft, J.C.; Madden, V.J.; Napier, M.E.; DeSimone, J.M. The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11613–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Luo, X.; Li, X. Shape effects of electrospun fiber rods on the tissue distribution and antitumor efficacy. J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinde, E.; Thammasiraphop, K.; Duong, H.T.; Yeow, J.; Karagoz, B.; Boyer, C.; Gooding, J.J.; Gaus, K. Pair correlation microscopy reveals the role of nanoparticle shape in intracellular transport and site of drug release. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, V.P.; Popovic, Z.; Chen, O.; Cui, J.; Fukumura, D.; Bawendi, M.G.; Jain, R.K. Fluorescent nanorods and nanospheres for real-time in vivo probing of nanoparticle shape-dependent tumor penetration. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 11417–11420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.M.; Endres, R.G. Target shape dependence in a simple model of receptor-mediated endocytosis and phagocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6113–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfi, S.; Bahari, A.; Mahjoub, S. In vitro biological evaluations of Fe3O4 compared with core–shell structures of chitosan-coated Fe3O4 and polyacrylic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 3497–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.K.; Huang, H.; Tao, X.Y. Enhanced luminescence properties of hexagonal-phase NaYF4: Eu3+microrods by annealing treatment. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 335–336, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Hu, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; Hu, X. A novel template-free and one-step method to fabricate hollow mesoporous structured upconversion luminescent NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2014, 129, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Fan, Y.; Sun, A.; Deng, X. Compositional or charge density modification of the endothelial glycocalyx accelerates flow-dependent concentration polarization of low-density lipoproteins. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 236, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, J.A.; Katare, Y.K.; Mitragotri, S. Making polymeric micro- and nanoparticles of complex shapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11901–11904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidinia-Anarkoli, A.; Boesveld, S.; Tuvshindorj, U.; Rose, J.C.; Haraszti, T.; De Laporte, L. An Injectable Hybrid Hydrogel with Oriented Short Fibers Induces Unidirectional Growth of Functional Nerve Cells. Small 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, K.; Niu, X.; Fan, Y. Electrospraying magnetic-fluorescent bifunctional Janus PLGA microspheres with dual rare earth ions fluorescent-labeling drugs. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 99034–99043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; He, Y.; Tian, X.; Wen, J.; Zhang, L. LSPR effects in a magnetic–luminescent heterostructure for efficient enhanced luminescence performance. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Qi, B.; Li, K.; Xu, J.; Liu, M.; Gu, X.; Niu, X.; Fan, Y. Study on the formation and properties of red blood cell-like Fe3O4/TbLa3(Bim)12/PLGA composite particles. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 12503–12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Milaji, K.N.; Zhao, H. Fabrication of superoleophobic surfaces by mask-assisted electrospray. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Kong, D. Functionalization of the surface of electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone) mats using zwitterionic poly(carboxybetaine methacrylate) and cell-specific peptide for endothelial progenitor cells capture. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 1646–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Li, P.; Fan, Y. Preparation of Magnetic-Fluorescent Bifunctional Microrods as a Drug Delivery System via One-Step Electrospraying. Proceedings 2021, 78, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08646
Xu J, Li P, Fan Y. Preparation of Magnetic-Fluorescent Bifunctional Microrods as a Drug Delivery System via One-Step Electrospraying. Proceedings. 2021; 78(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08646
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Junwei, Ping Li, and Yubo Fan. 2021. "Preparation of Magnetic-Fluorescent Bifunctional Microrods as a Drug Delivery System via One-Step Electrospraying" Proceedings 78, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08646
APA StyleXu, J., Li, P., & Fan, Y. (2021). Preparation of Magnetic-Fluorescent Bifunctional Microrods as a Drug Delivery System via One-Step Electrospraying. Proceedings, 78(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08646






