Technologies to Aid Public Understanding in Running Performance †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
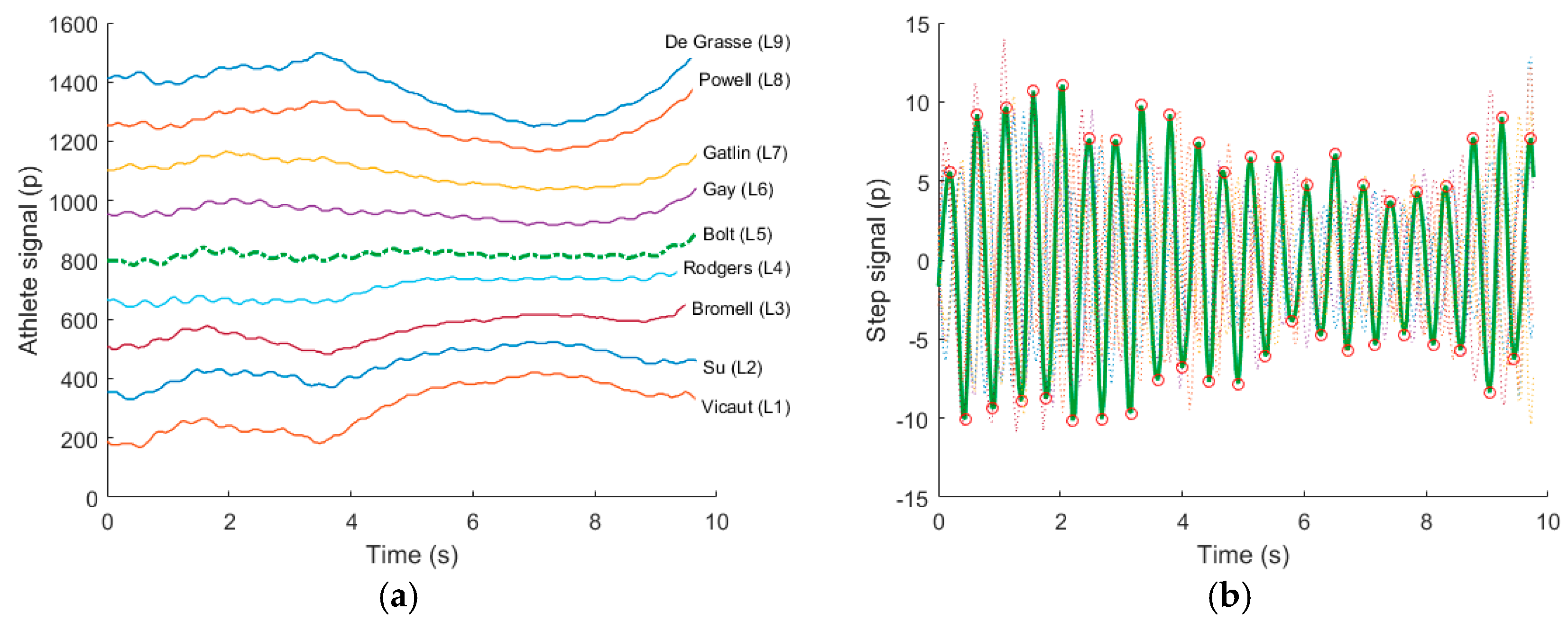
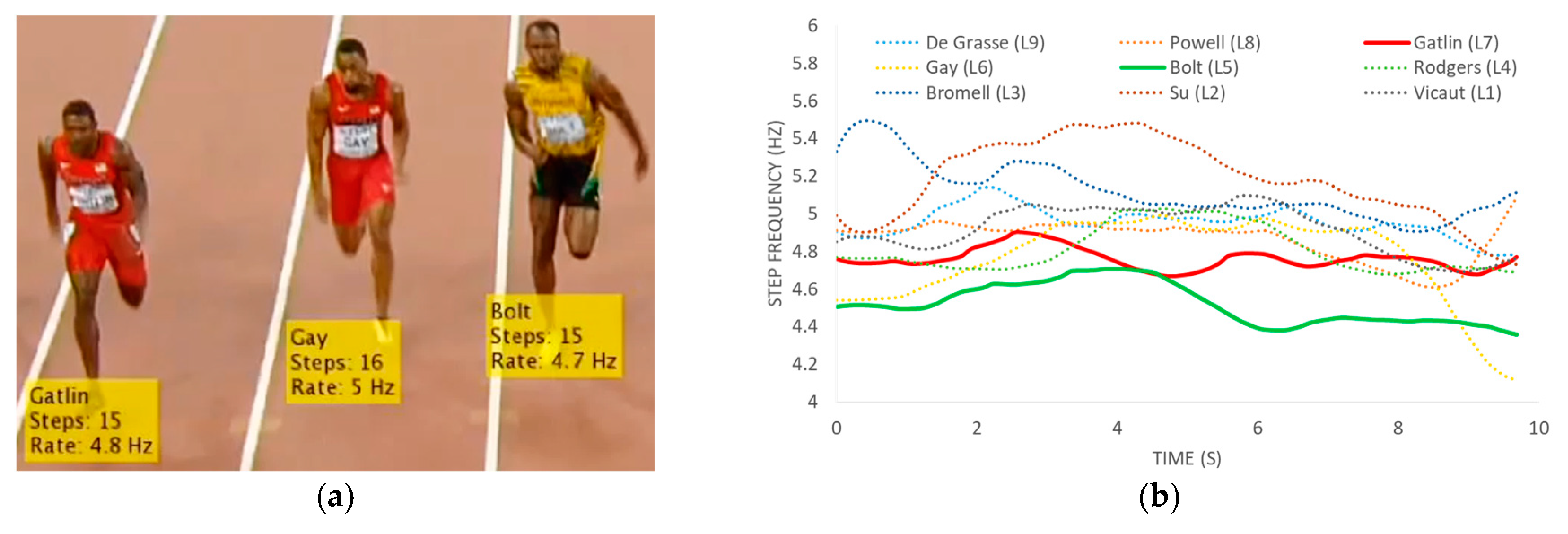
2.1. 100 m Sprint: Temporal Analysis
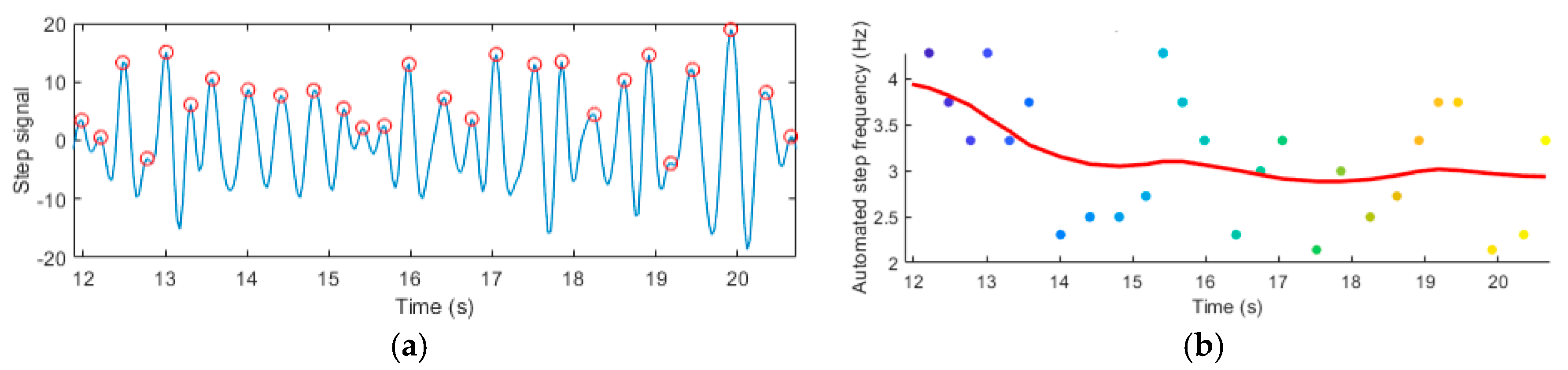
2.2. 1-Mile Endurance: Temporal Analysis
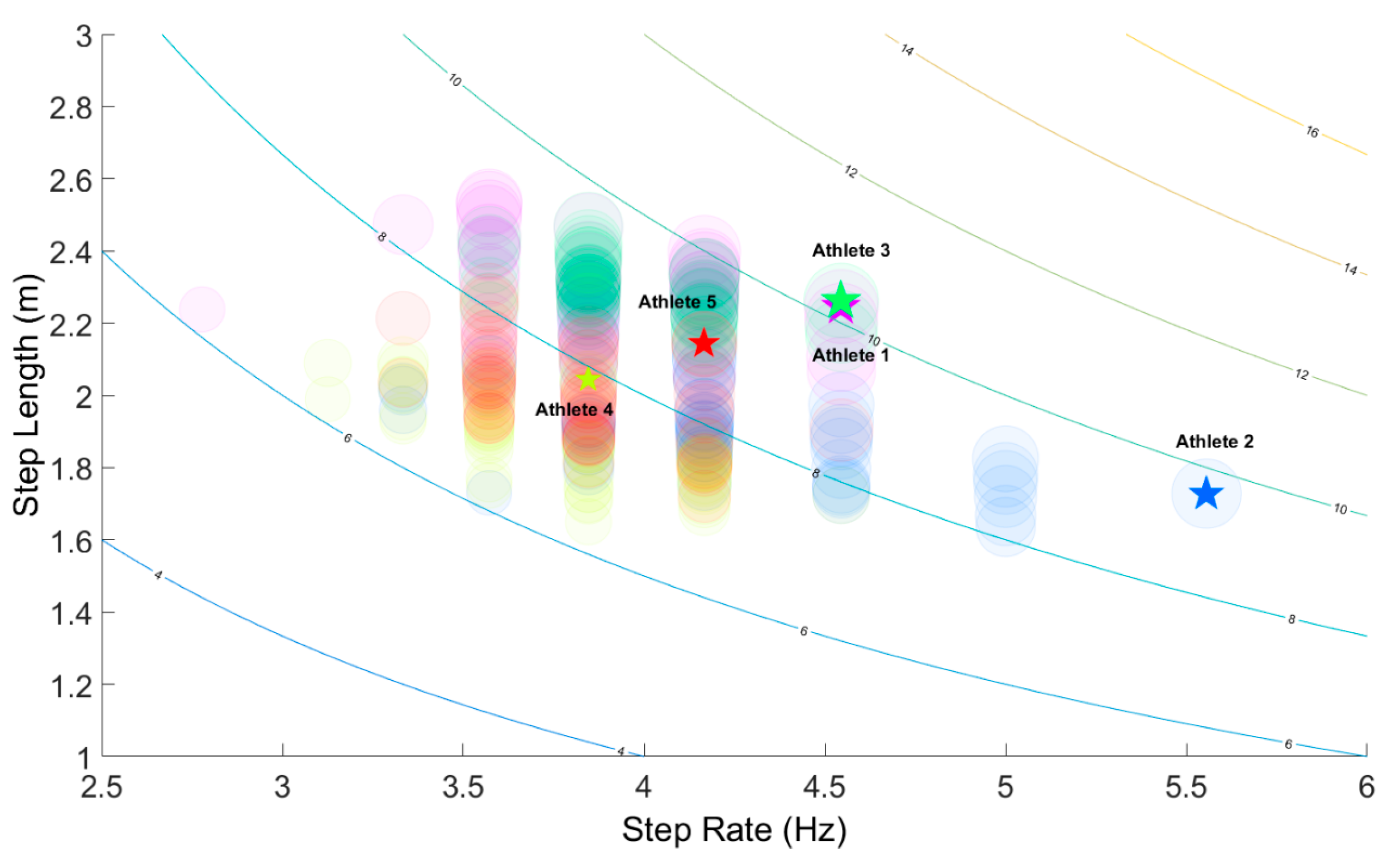
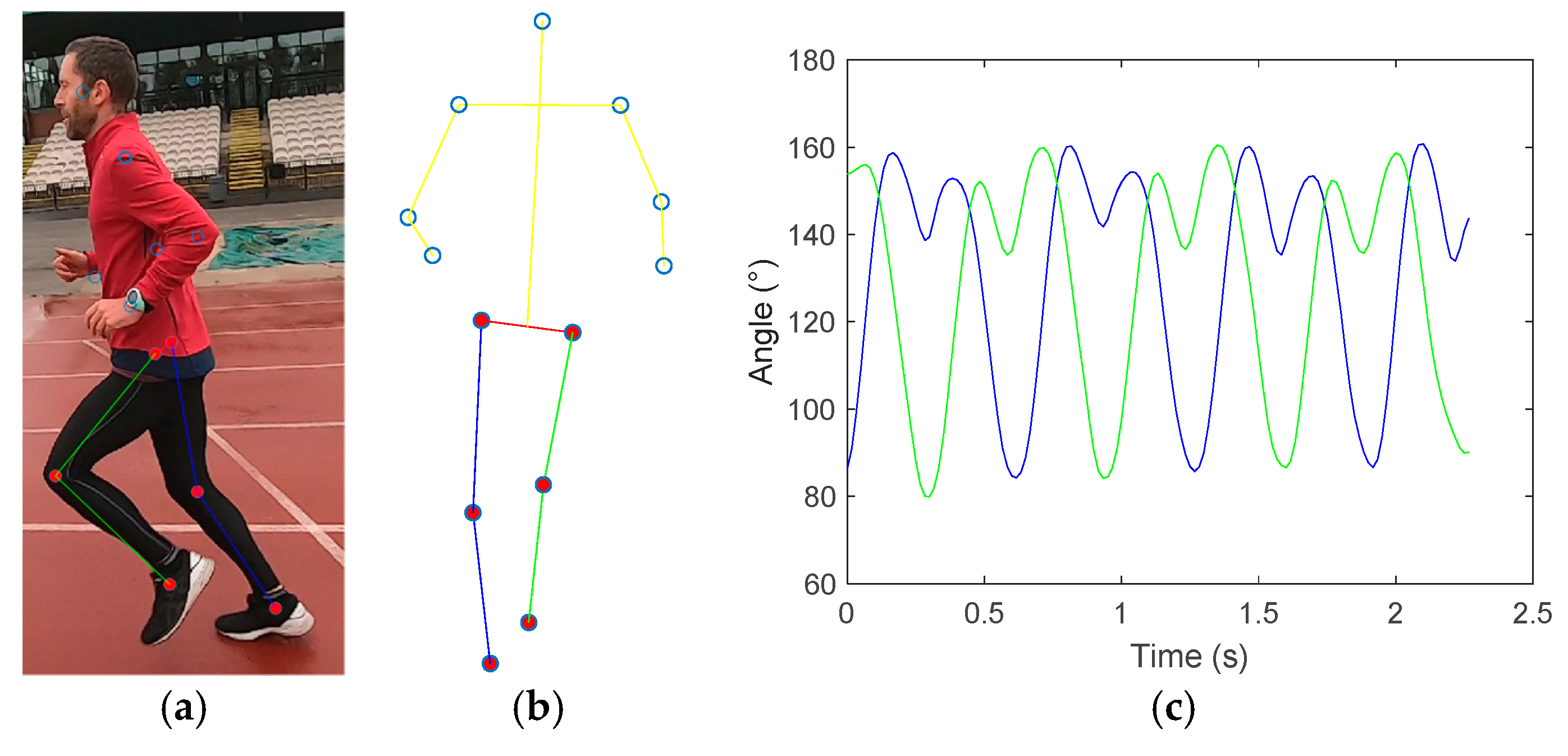
2.3. Training Setting: Spatial-Temporal Analysis
2.4. Data Assessment and Data Visualisation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunn, M.; Kelley, J. Non-invasive, spatio-temporal gait analysis for sprint running using a single camera. Procedia Eng. 2015, 112, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogez, G.; Weinzaepfel, P.; Schmid, C. LCR-Net++: Multi-person 2D and 3D pose detection in natural images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 42, 1146–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, J.; Caseiro, R.; Martins, P.; Batista, J. High-speed tracking with kernalized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D. Robust smoothing of gridded data in one and higher dimensions with missing values. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2010, 54, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Environment | Identified Steps | Absolute LOA | r2 | Ratio LOA | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step Frequency (Hz) | 100 m sprint | 400/400 (100%) | −0.12 ± 1.74 | 0.24 | 0.98 (×/÷1.43) | 0.12 |
| 1-mile endurance | 827/847 (97.6%) | 0.06 ± 0.32 | 0.12 | 1.02 (×/÷1.10) | 0.17 | |
| Training setting | 56/56 (100%) | 0.09 ± 0.59 | 0.47 | 1.03 (×/÷1.21) | 0.31 | |
| Step Length (m) | Training setting | 56/56 (100%) | 0.79 ± 0.59 | 0.91 | 1.81 (×/÷1.42) | 0.85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dunn, M.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Kelley, J.; Haake, S. Technologies to Aid Public Understanding in Running Performance. Proceedings 2020, 49, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020049026
Dunn M, Chiu C-Y, Kelley J, Haake S. Technologies to Aid Public Understanding in Running Performance. Proceedings. 2020; 49(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020049026
Chicago/Turabian StyleDunn, Marcus, Chuang-Yuan Chiu, John Kelley, and Steve Haake. 2020. "Technologies to Aid Public Understanding in Running Performance" Proceedings 49, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020049026
APA StyleDunn, M., Chiu, C.-Y., Kelley, J., & Haake, S. (2020). Technologies to Aid Public Understanding in Running Performance. Proceedings, 49(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020049026




