Abstract
Currently, various types of wheelchairs for badminton have been developed for weight saving and functional improvement. The purpose of this study was to evaluate each performance of two types of competitive wheelchairs for badminton made of two different metallic materials. One of the wheelchairs used in this study was made of magnesium composite material, which was 45 GPs of Young’s modulus, 1.738 g/cm3 of the specific weight, and 9.57 kg of weight. Another was made of scandium-aluminum composite material, which was 70 GPa of Young’s modulus, 2.70 g/cm3 of the specific weight, and 10.81 kg of weight. The frames and weights of the wheelchairs were similar. In this experiment, the subject’s electromyograms from six muscles in driving each wheelchair were measured and analyzed. Furthermore, the motion in driving was captured and analyzed using a three-dimensional motion capture system. This experiment led to the following result: no significant difference was found in wheelchair performance due to the different materials.
1. Introduction
In adapted sports, rules and tools have been devised to improve competition performance. Among these tools, various wheelchairs have been devised depending on the characteristics and rules of the competition. In addition, as competition increases, materials and designs have been devised to reduce weight [1,2,3]. In recent years, para-badminton competition has been attracting attention as an official event for the Tokyo 2020 Paralympic Games. However, since it was late to be adopted as an official event, it can be said that it is in an early development stage compared to other adapted sports.
Developments have begun against this background, and wheelchair frame materials are diversifying, even in badminton wheelchairs. However, in wheelchair badminton, there has been no engineering study of the effects of wheelchair materials on movement. In this study, we compared two types of aluminum wheelchairs, which are mainly used in badminton racing wheelchairs, and new wheelchairs developed using magnesium. For comparison, surface electromyograms and 3D motion analysis when using a wheelchair for competition were used.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Target
The subject was the world-ranking male wheelchair badminton player.
The wheelchair was the same as the one used by the subject during the actual competition (aluminum/scandium alloy (Al alloy), Young’s modulus 70 GPa, specific gravity 2.7 g/cm3, weight 10.81 kg), and the material was different. (Magnesium alloy (Mg alloy), Young’s modulus 45 GPa, specific gravity 1.738 g/cm3, weight 9.57 kg) were used. Although the two materials have significantly different Young’s modulus, it was not expected that the frame would flex during motion.
2.2. Measurement Operation
In each subject, two types of movements shown in Figure 1 were measured. The first movement is to dash back and forth a certain distance for 20 s (20 s Dash). The second movement involves stops with one stroke, and five sets are executed before and after (One Stroke).
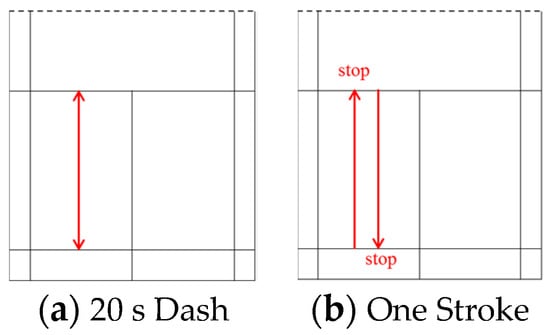
Figure 1.
Two types of movement: (a) To dash back and forth a certain distance for 20 s; (b) Stops with one stroke, and five sets are executed before and after. The distance of each movement is about 4 m.
2.3. EMG(Electromyogram) Analysis
A biosignal recording device, PolymatePro (Miyuki Giken Co., Ltd., Tokyo Japan, MP6000), was used for electromyogram measurement. The sampling frequency was 2000 Hz. Target muscles were biceps, triceps, deltoid, pectoral, rectus abdominis, and latissimus. Two active bioelectrodes were applied to each muscle. The distance between the centers of active bioelectrodes was 20 mm. Prior to exercise measurements, manual strength tests were performed using 100% MVC (Maximal Voluntary Contraction) as standard. The peak value was obtained after full-wave rectification of each muscle waveform obtained by manual strength test, and that value was adopted as the strength during isometric voluntary contraction. Signals obtained using the biological signal recording apparatus were analyzed using a general-purpose biological information analysis program BIMUTAS II (Kissei Comtech, Nagano, Japan). The time axis was synchronized based on signals recorded by the biosignal recorder and the 3D motion analysis system described below. After performing full-wave rectification on the data of each analysis interval extracted from the 3D motion analysis of each measurement motion, the average value was obtained and the mean amplitude was derived.
2.4. 3D Motion Analysis
The 3D motion analysis was performed with the 3D motion analysis system Mac3D (Motion Analysis) using 8 infrared cameras. The measurements were taken at the gymnasium wheelchair badminton court. In the coordinate system, the X axis is the front-rear direction (positive is front), the Y axis is left and right (positive is left), and the Z axis is vertical (positive is up). The measurement range was ±2000 mm on the X axis, ±1500 mm on the Y axis, and 150–1700 mm on the Z axis. There were 34 reflex markers on the subject’s body surface and 5 points. When the button is pressed, the lamp lights up, and at the same time, a synchronization signal is set using a device that generates electromotive force on the EMG side. The sampling frequency of the camera was 120 Hz. After interpolating the data, all data were extracted using a 5-point average.
2.5. Phase Division
Wheelchair movement is divided into contact period when the hand contacts with the hand rim and recovery period when the hand does not contact with the hand rim. This study focused on the contact time of each drive during each measurement movement. Each period was identified based on marker position information extracted from Mac3D.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The average amplitude obtained from the analysis was compared for each subject using a t-test. The significance level was less than 5%.
3. Results
3.1. 20 s Dash
3.1.1. Relationship between Electromyogram Mean Amplitude and Wheelchair Maximum Speed
In Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4, BB is biceps, TB is triceps, MD is deltoid, PM is great pectoral muscle, RA is rectus abdominis, and LD is latissimus.

Table 1.
Mean amplitude and standard deviation of mean amplitude for 20 s Dash (forward stroke).

Table 2.
P-value of mean amplitude for 20 s Dash (forward stroke).

Table 3.
Mean amplitude and standard deviation of mean amplitude for 20 s Dash (back stroke).

Table 4.
P-value of mean amplitude for 20 s Dash (back stroke).
First, we explain the results of a 20 s Dash forward stroke. Table 1 shows the mean amplitude and standard deviation obtained from the electromyogram. Table 2 shows the p-values obtained by t-test by comparing the average amplitude of each wheelchair with and without a racket. Figure 2a shows the maximum wheelchair speed obtained from a marker attached to the axle.
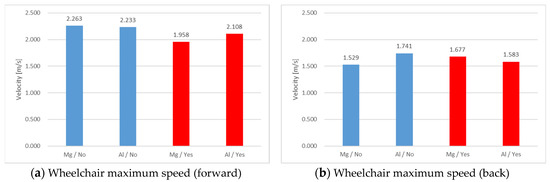
Figure 2.
Wheelchair maximum speed. From the left of each figure, Mg alloy no racket, Al alloy no racket, Mg alloy racket, Al alloy racket: (a) forward stroke; (b) back stroke. Each figure was created using three forward and four backward trials for 20 s.
From Table 1 and Table 2, the mean amplitude of Mg alloy wheelchairs was generally high, but overall, there was no significant difference. From Figure 2a, there was no significant difference in the maximum wheelchair speed with and without the racket.
Second, we explain the results of a 20 s Dash back stroke. Table 3 shows the mean amplitude and standard deviation obtained from the electromyogram. Table 4 shows the p-values obtained by t-test by comparing the average amplitude of each wheelchair with and without a racket. Figure 2b shows the maximum wheelchair speed obtained from a marker attached to the axle.
3.1.2. Ratio of Maximum Amplitude to Maximum Voluntary Contraction
From Figure 3, the ratio of maximum amplitude to maximum voluntary contraction did not change with the front and back strokes due to wheelchair material differences.
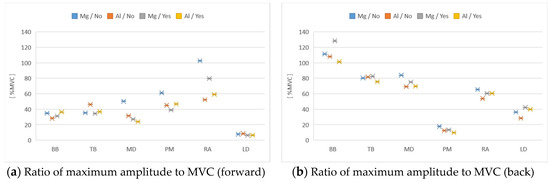
Figure 3.
Ratio of maximum amplitude to maximal voluntary contraction (MVC). From the left of each figure, BB, TB, MD, PM, RA, LD and, from the left of each muscle, Mg alloy no racket, Al alloy no racket, Mg alloy racket, Al alloy racket: (a) forward stroke; (b) back stroke.
3.2. One Stroke
3.2.1. Relationship between Electromyogram Mean Amplitude and Wheelchair Maximum Speed
First, we explain the results of a One Stroke forward stroke. Table 5 shows the mean amplitude and standard deviation obtained from the electromyogram. Table 6 shows the p-values obtained by t-test by comparing the average amplitude of each wheelchair with and without a racket. Figure 4a shows the maximum wheelchair speed obtained from a marker attached to the axle.

Table 5.
Mean amplitude and standard deviation of mean amplitude for One Stroke (forward stroke).

Table 6.
P-value of mean amplitude for One Stroke (forward stroke).
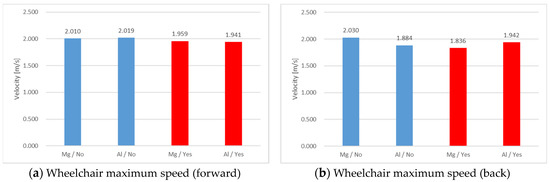
Figure 4.
Wheelchair maximum speed. From the left of each figure, Mg alloy no racket, Al alloy no racket, Mg alloy racket, Al alloy racket: (a) forward stroke; (b) back stroke.
From Table 5 and Table 6, the mean amplitude of Mg alloy wheelchairs was generally high, but overall, there was no significant difference. From Figure 4a, there was no significant difference in the maximum wheelchair speed with and without the racket.
Second, we explain the results of a One Stroke back stroke. Table 7 shows the mean amplitude and standard deviation obtained from the electromyogram. Table 8 shows the p-values obtained by t-test by comparing the average amplitude of each wheelchair with and without a racket. Figure 4b shows the maximum wheelchair speed obtained from a marker attached to the axle.

Table 7.
Mean amplitude and standard deviation of mean amplitude for One Stroke (back stroke).

Table 8.
P-value of mean amplitude for One Stroke (back stroke).
3.2.2. Ratio of Maximum Amplitude to Maximum Voluntary Contraction
From Figure 5, the ratio of maximum amplitude to maximum voluntary contraction did not change with the front and back strokes due to wheelchair material differences.
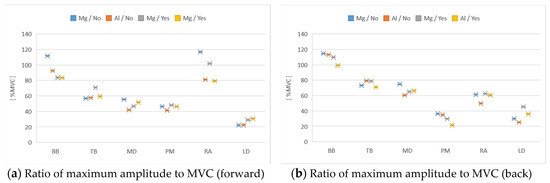
Figure 5.
Ratio of maximum amplitude to maximum voluntary contraction (MVC). From the left of each figure, BB, TB, MD, PM, RA, LD and, from the left of each muscle, Mg alloy no racket, Al alloy no racket, Mg alloy racket, Al alloy racket: (a) forward stroke; (b) back stroke.
4. Discussion
The mean amplitude of Mg alloy wheelchairs was generally high, but overall there was no significant difference. There was no significant difference in the maximum wheelchair speed with and without the racket.
Therefore, the amount of muscle activity required to move a wheelchair varies from material to material, but maximum wheelchair speed and the ratio of maximum amplitude to maximum voluntary contraction are not likely to be affected. In addition, regarding the items examined in this study, there was no significant difference in performance due to differences in wheelchair materials.
5. Conclusions
Using an electromyogram and a three-dimensional motion analysis system, two types of motions were measured using a wheelchair made of different materials for one wheelchair badminton player, and the performances of the wheelchairs were compared. The mean amplitude of Mg alloy wheelchairs was generally high, but overall, there was no significant difference. In addition, there was no significant difference in maximum wheelchair speed with and without rackets, so there was no relationship between mean amplitude and maximum wheelchair speed.
In conclusion, it was clarified that there were no significant differences in performance due to differences in wheelchair materials for the items examined in this study.
Funding
The research was funded by Tokyo Metropolitan Industrial Technology Research Institute.
Acknowledgments
This research was conducted in collaboration with OX ENGINEERING based on a research grant from the Tokyo Metropolitan Industrial Technology Research Center. Thanks to all involved.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Matsuo, K. Wheel chair for ball games. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Prosthet. Orthot. 2014, 30, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, D.; Iwata, A.; Kawasaki, J.; Shima, M.; Okuda, K. Biomechanics of Serve Motion in Wheelchair Tennis Players. Phys. Ther. Jpn. 2012, 39, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, K.; Kudo, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Mutsuzaki, H.; Wadano, Y. Factors affecting “tilting” success during wheelchair basketball: Angular velocity of the lower and upper trunk. Publ. Stud. Ibaraki Prefect. Univ. Health Sci. 2015, 20, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).