Chemical Recycling: Comparative Study about the Depolymerization of PET Waste-Bottles to Obtain Terephthalic Acid †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Conventional Depolymerization
2.2. Microwave Assisted Reactions
3. Results and Discussion
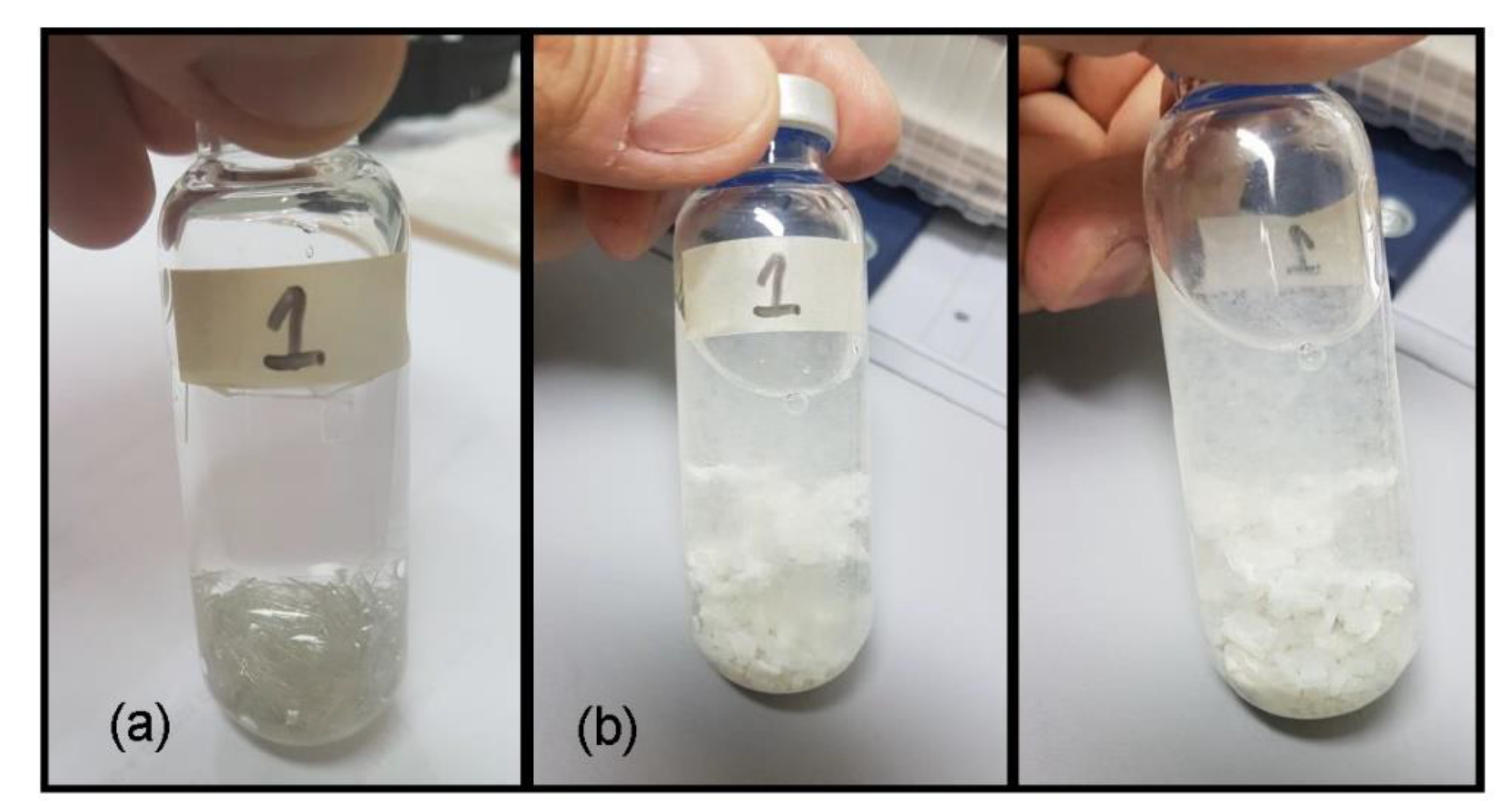
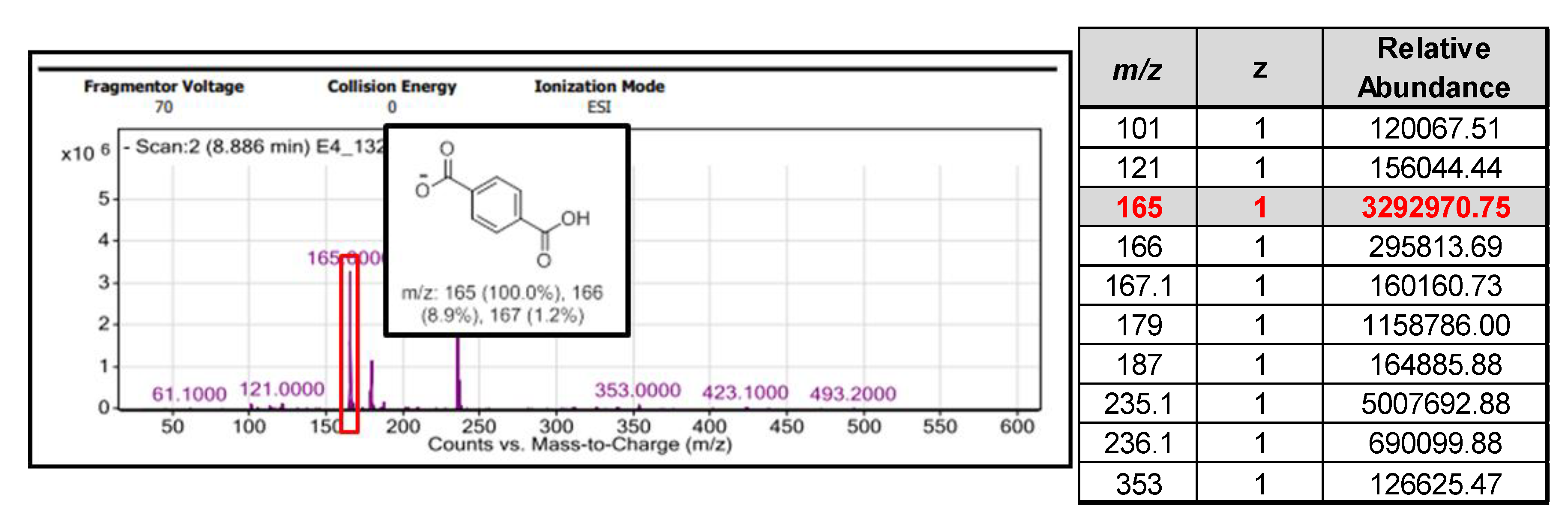
3.1. Conventional Reaction
3.2. Microwave Assisted Reactions
| Reaction | Zinc Source |
|---|---|
| 1 | Zinc Sulfate |
| 2 | Zinc Acetate |
| 3 | Zinc Oxide |
| 4 | Zinc Chloride |
| Reaction | Temperature | Time | Solvent |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11a | >200 °C | 5 min | Pentan-1-ol |
| 11b | 150 °C | 30 min | Pentan-1-ol |
| 12a | >200 °C | 5 min | Propan-1-ol |
| 12b | 150 °C | 30 min | Propan-1-ol |
| 13a | >200 °C | 5 min | Propan-2-ol |
| 13b | 150 °C | 30 min | Propan-2-ol |
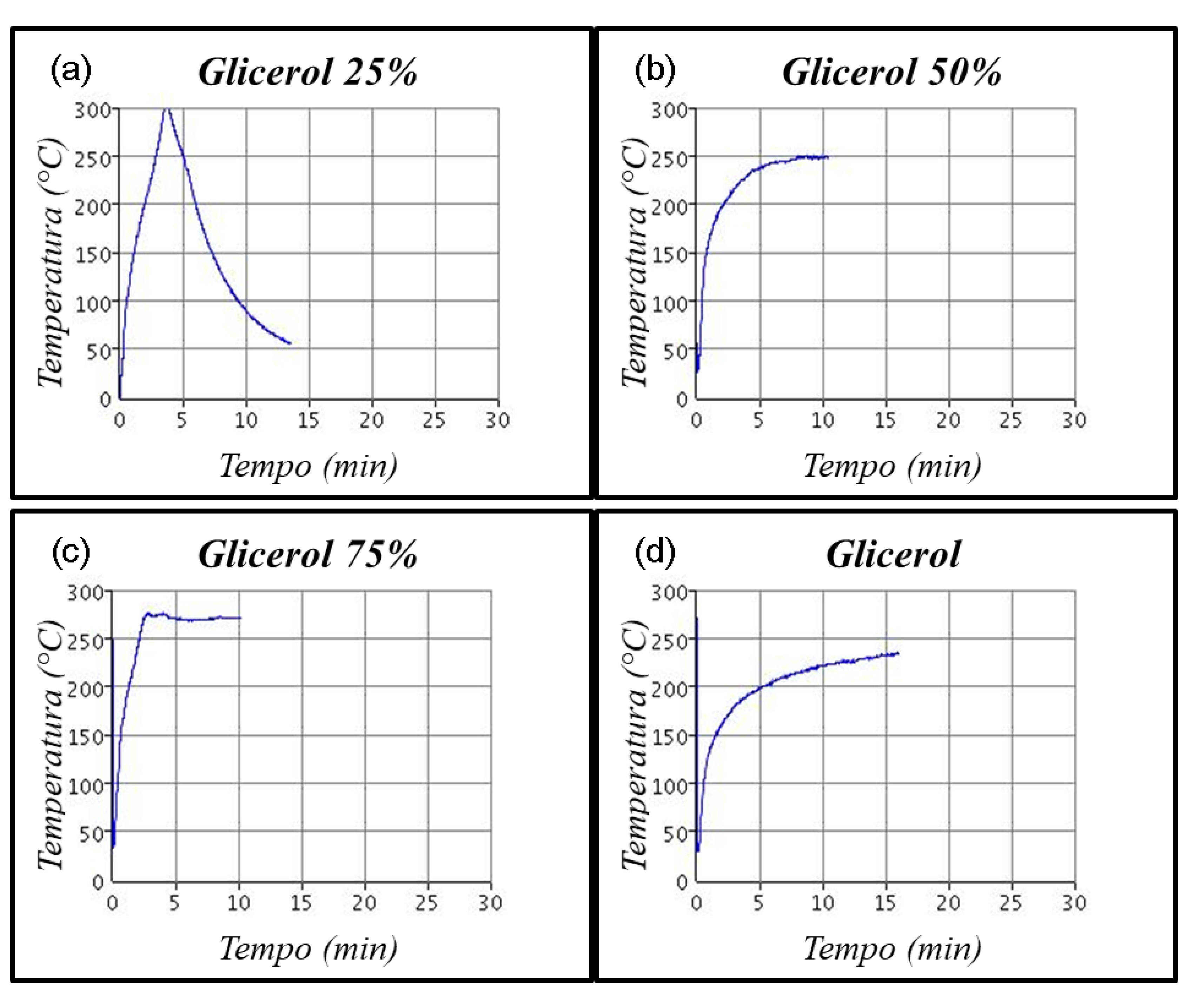
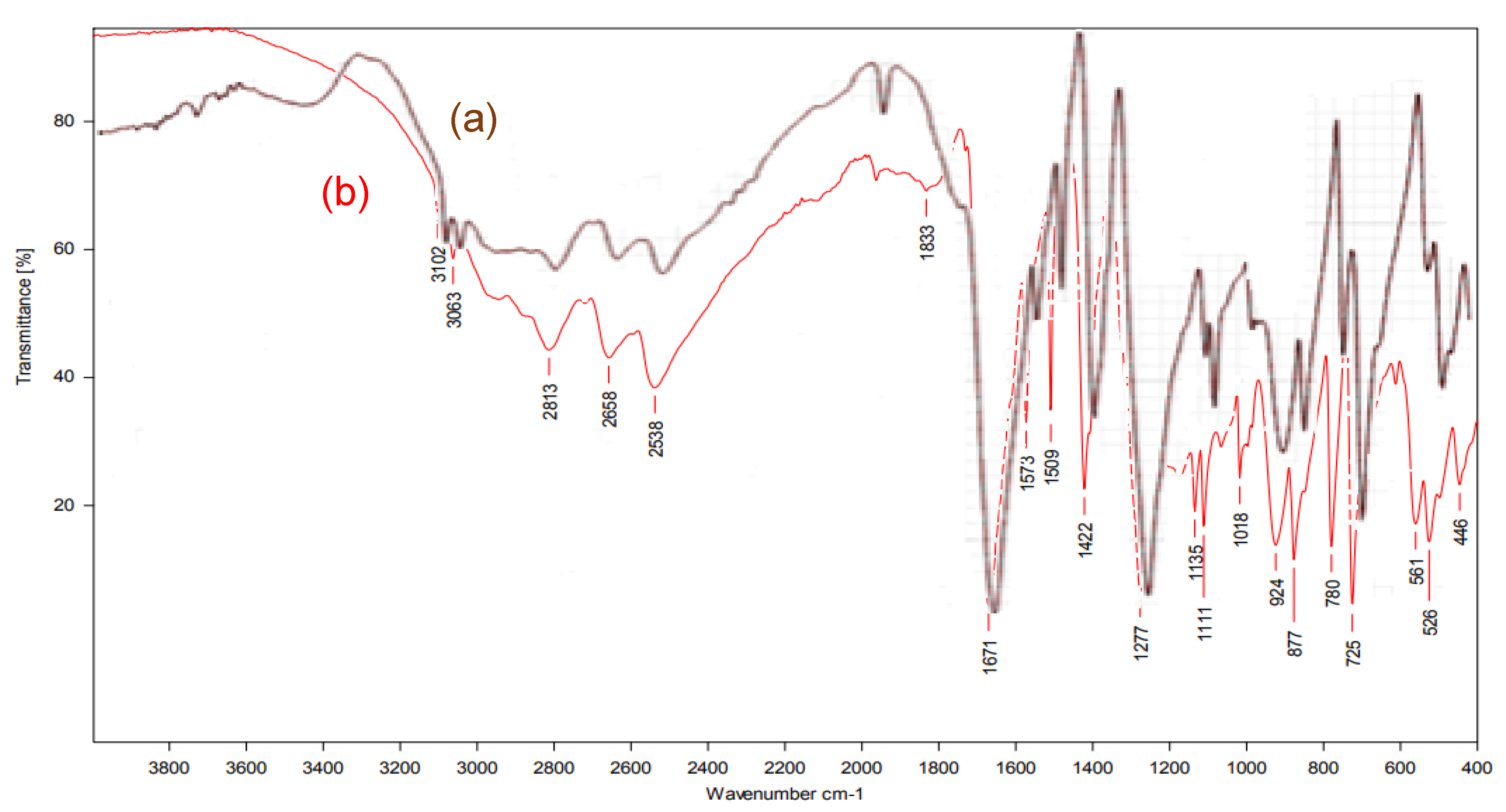
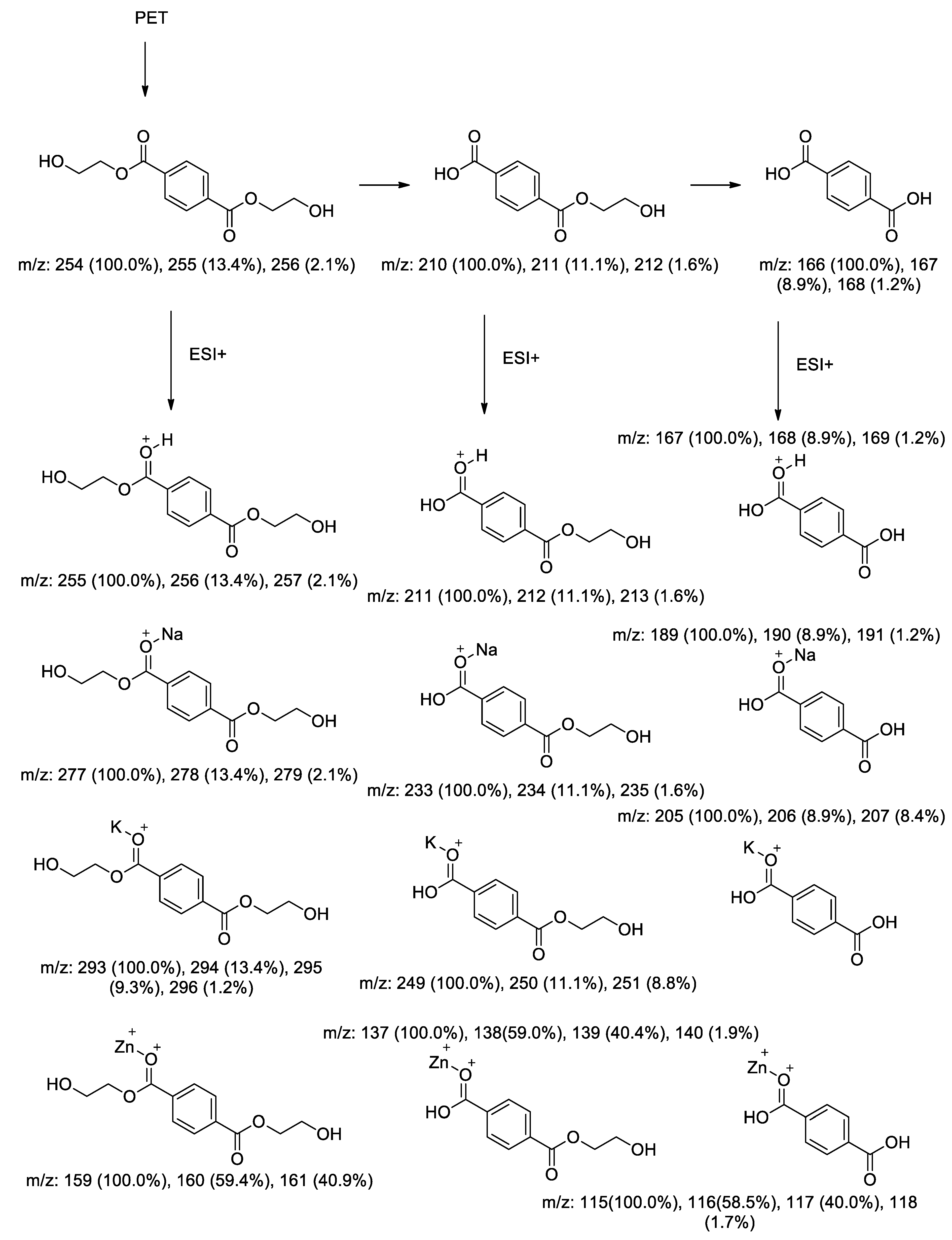
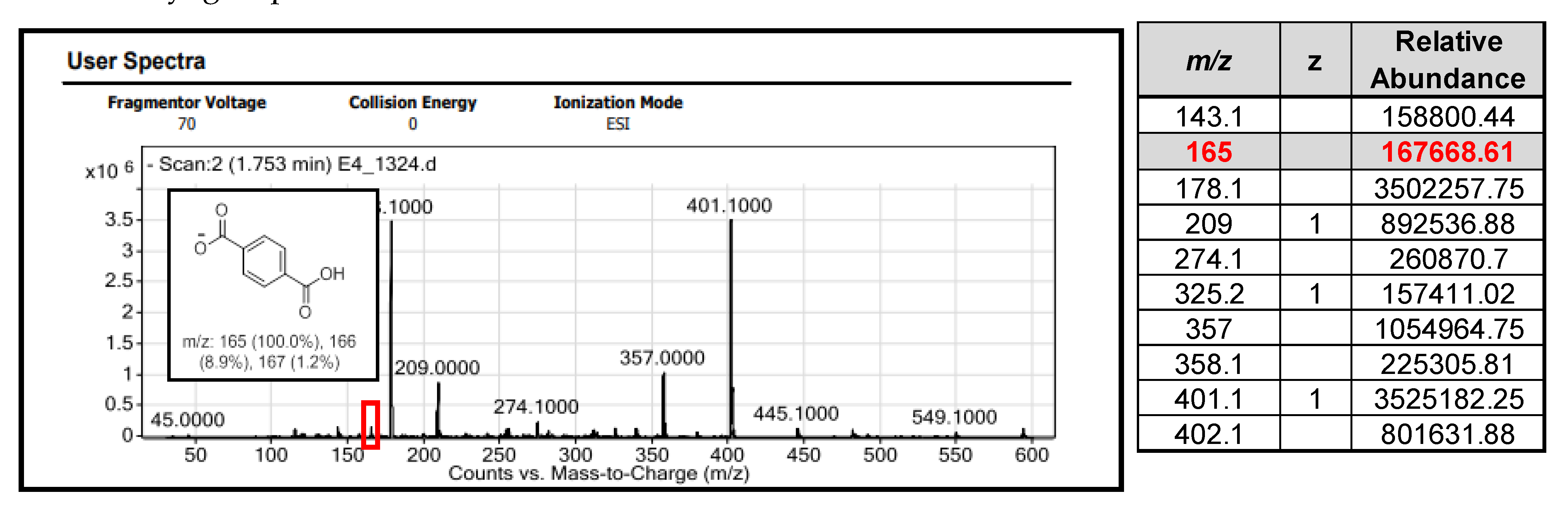
4. Conclusions
References
- Matar, S.; Hatch, L.F. Chemistry of Petroquemical Processes, 2nd ed.; Gulf Publishing Company: Houston, TX, USA, 2000; pp. 134–256. [Google Scholar]
- Grippi, S. Lixo, Reciclagem e sua História: Guia para as Prefeituras Brasileiras, 2nd ed.; Interciência: Varginha, Brazil, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lenardão, E.J.; Freitag, R.A.; Dabdoub, M.J.; Ferreira Batista, A.C.; da Cruz Silveira, C. “Green Chemistry”—Os 12 Princípios da Química Verde e sua Inserção nas Atividades de Ensino e Pesquisa. Quím. Nova 2003, 26, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.O.; Durão, F.V.; Pereira, G.D. MOF a partir de PET e glycerol. In Proceedings of the 16th Brazilian Science and Engineering Fair (Febrace 2018), São Paulo, Brazil, 13–15 March 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, D. Effects of temperature on catalytic hydrolysis of PET by Zinc Sulfate under microwave irradiation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 233, 1628–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikje, M.M.A.; Nazari, F. Microwave-Assisted Depolymerization of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) [PET] at Atmospheric Pressure; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 242–246. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavalcante, S.; Vieira, D.; Melo, I. Chemical Recycling: Comparative Study about the Depolymerization of PET Waste-Bottles to Obtain Terephthalic Acid. Proceedings 2019, 41, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06650
Cavalcante S, Vieira D, Melo I. Chemical Recycling: Comparative Study about the Depolymerization of PET Waste-Bottles to Obtain Terephthalic Acid. Proceedings. 2019; 41(1):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06650
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavalcante, Samir, Daniel Vieira, and Isis Melo. 2019. "Chemical Recycling: Comparative Study about the Depolymerization of PET Waste-Bottles to Obtain Terephthalic Acid" Proceedings 41, no. 1: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06650
APA StyleCavalcante, S., Vieira, D., & Melo, I. (2019). Chemical Recycling: Comparative Study about the Depolymerization of PET Waste-Bottles to Obtain Terephthalic Acid. Proceedings, 41(1), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06650




