TI-Stan: Adaptively Annealed Thermodynamic Integration with HMC †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Background
- 1.
- Start at where , and draw C samples from this distribution (the prior).
- 2.
- Compute the Monte Carlo estimator for the expected energy at the current ,where is the current position of the t-th Markov chain.
- 3.
- Increment by , wherej is the index on the chains, is the weight associated with chain j, and
- 4.
- Re-sample the population of samples using importance sampling.
- 5.
- Use MCMC to refresh the current population of samples. This yields a more accurate sampling of the distribution at the current temperature. This step can be easily parallelized, as each sample’s position can be shifted independently of the others.
- 6.
- Return to step 2 and continue until reaches 1.
- 7.
2. Materials and Methods
| Algorithm 1 Thermodynamic integration with Stan |
|
2.1. Tests
2.1.1. Twin Gaussian Shells
2.1.2. Detection of Multiple Stationary Frequencies
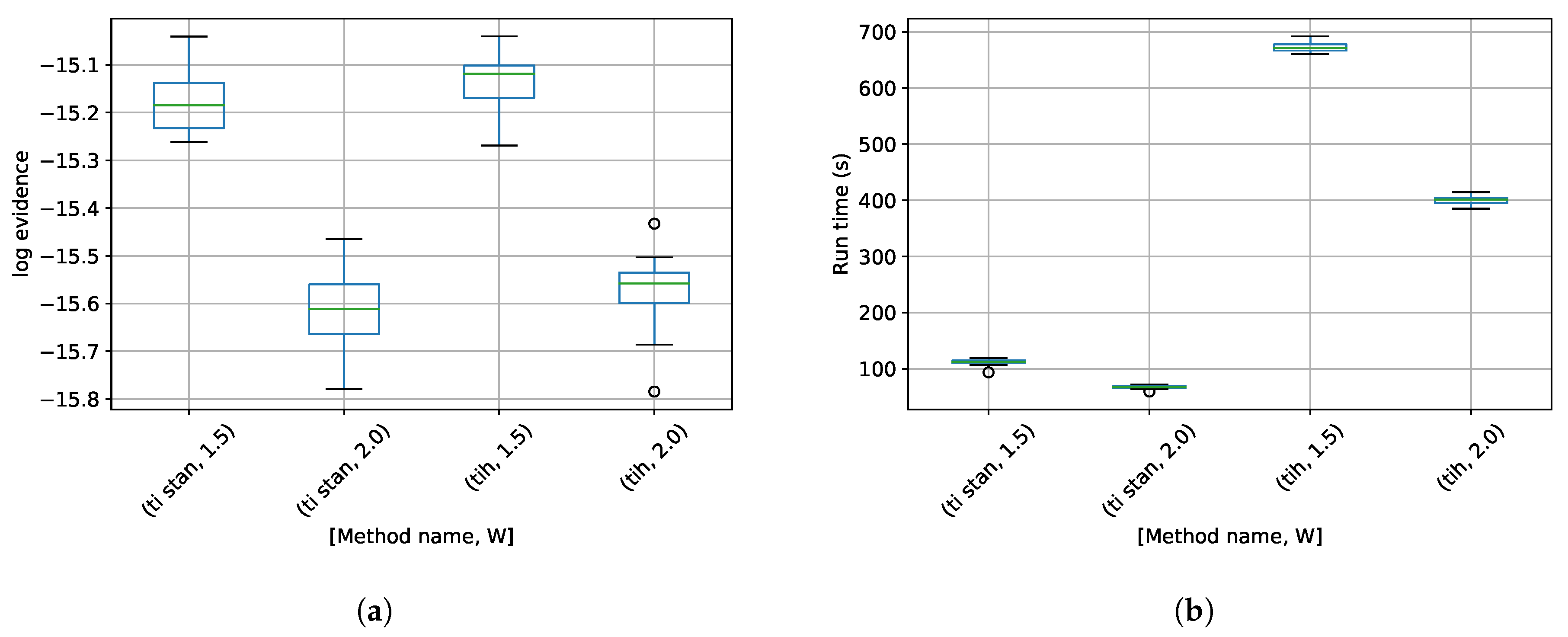
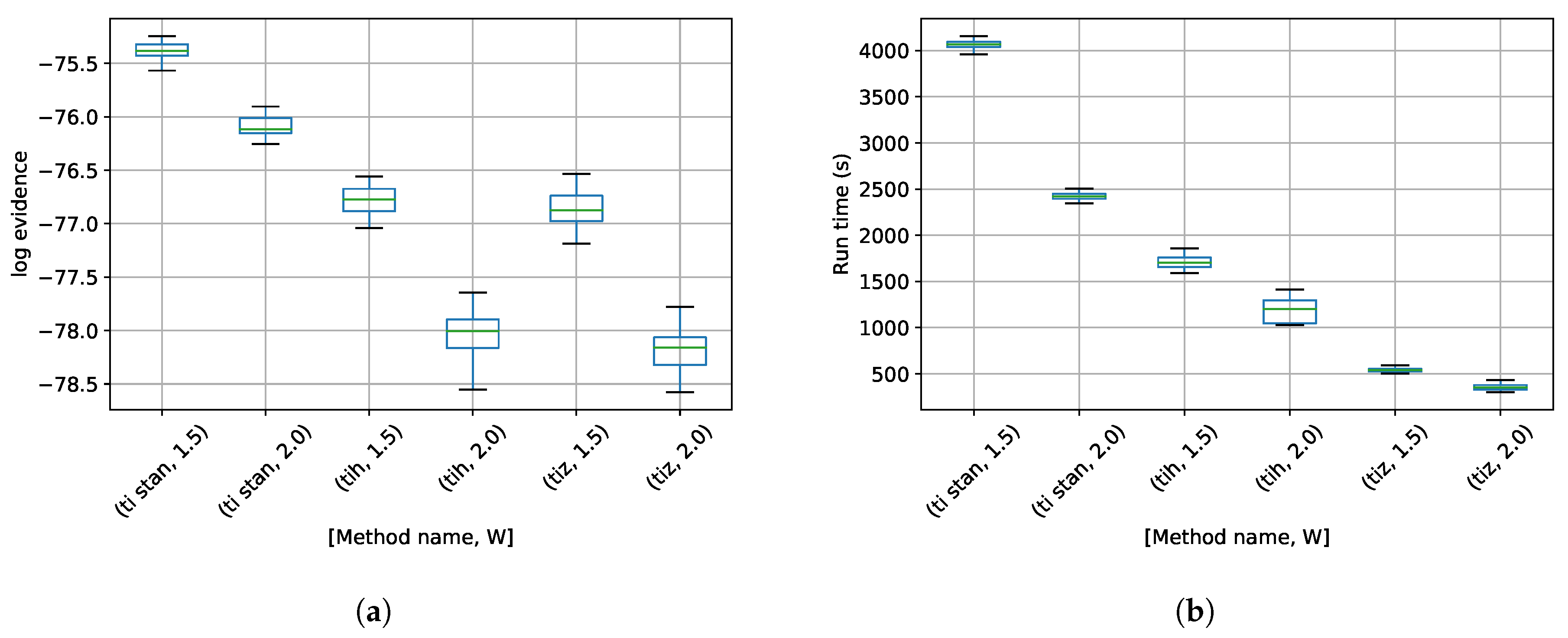
3. Results
4. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TI | Thermodynamic integration |
| BSS | Binary slice sampling |
| TI-Stan | Thermodynamic integration with Stan |
| TI-BSS | Thermodynamic integration with binary slice sampling |
| TI-BSS-H | Thermodynamic integration with binary slice sampling and the Hilbert curve |
| TI-BSS-Z | Thermodynamic integration with binary slice sampling and the Z-order curve |
| HMC | Hamiltonian Monte Carlo |
| NUTS | No U Turn Sampler |
| MCMC | Markov chain Monte Carlo |
References
- Henderson, R.W. Design and analysis of efficient parallel bayesian model comparison algorithms. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Mississippi, Oxford, MS, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood, J.G. Statistical Mechanics of Fluid Mixtures. J. Chem. Phys. 1935, 3, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goggans, P.M.; Chi, Y. Using thermodynamic integration to calculate the posterior probability in Bayesian model selection problems. AIP Conf. Proc. 2004, 707, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skilling, J. BayeSys and MassInf; Maximum Entropy Data Consultants Ltd.: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, B.; Gelman, A.; Hoffman, M.D.; Lee, D.; Goodrich, B.; Betancourt, M.; Brubaker, M.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Riddell, A. Stan : A Probabilistic Programming Language. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stan Development Team. PyStan: The Python Interface to Stan. 2018. Available online: http://mc-stan.org (accessed on 21 November 2019).
- Hoffman, M.D.; Gelman, A. The No-U-Turn Sampler: Adaptively Setting Path Lengths in Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1593–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, R.W. TI-Stan. 2019. original-date: 2019-07-04T09:56:19Z. Available online: https://github.com/rwhender/ti-stan. (accessed on 21 November 2019).
- Gelman, A.; Meng, X.L. Simulating normalizing constants: From importance sampling to bridge sampling to path sampling. Stat. Sci. 1998, 13, 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, C.J.; Papamarkou, T.; Girolami, M. The Controlled Thermodynamic Integral for Bayesian Model Evidence Evaluation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2016, 111, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, R.M. MCMC using Hamiltonian dynamics. In Handbook of Markov Chain Monte Carlo; Brooks, S., Gelman, A., Jones, G., Meng, X.L., Eds.; Chapman & Hall / CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Feroz, F.; Hobson, M.P.; Bridges, M. MultiNest: an efficient and robust Bayesian inference tool for cosmology and particle physics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 398, 1601–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, W.; Hobson, M.; Lasenby, A. PolyChord: Next-generation nested sampling. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, 4384–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretthorst, G.L. Bayesian Spectrum Analysis and Parameter Estimation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Bretthorst, G.L. Nonuniform sampling: Bandwidth and aliasing. AIP Conf. Proc. 2001, 567, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.W.; Goggans, P.M. Using the Z-order curve for Bayesian model comparison. In Bayesian Inference and Maximum Entropy Methods in Science and Engineering. MaxEnt 2017; Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics; Polpo, A., Stern, J., Louzada, F., Izbicki, R., Takada, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 239, pp. 295–304. [Google Scholar]


| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 0 Hz | Hz |
| j | (Hz) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||
| 2 |
| Parameter | Value | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| S | 200 | Number of binary slice sampling steps |
| M | 2 | Number of combined binary slice sampling and leapfrog steps |
| C | 256 | Number of chains |
| B | 32 | Number of bits per parameter in SFC |
| Parameter | Value | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| S | 200 | Number of steps allowed in Stan |
| C | 256 | Number of chains |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henderson, R.W.; Goggans, P.M. TI-Stan: Adaptively Annealed Thermodynamic Integration with HMC †. Proceedings 2019, 33, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019033009
Henderson RW, Goggans PM. TI-Stan: Adaptively Annealed Thermodynamic Integration with HMC †. Proceedings. 2019; 33(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019033009
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenderson, R. Wesley, and Paul M. Goggans. 2019. "TI-Stan: Adaptively Annealed Thermodynamic Integration with HMC †" Proceedings 33, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019033009
APA StyleHenderson, R. W., & Goggans, P. M. (2019). TI-Stan: Adaptively Annealed Thermodynamic Integration with HMC †. Proceedings, 33(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019033009






