Analysis of Cognitive Load Using EEG when Interacting with Mobile Devices †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals and Background
2.1. Cognitive Load
2.1.1. Cognitive Load Fundamentals
2.1.2. EEG-Based Cognitive Load Analysis
2.2. Mobile-Device Interaction Background
3. Proposed Taxonomy: HuSBIT-10
- (A) Automated. This represents the tasks with or without a minimal cognitive effort that we typically perform automatically or unconsciously.
- (M) psychoMotor. This kind of task requires a quick or direct interaction with the smartphone, where the main difficulty is to perform a touching interaction carefully or with proper accuracy.
- (P) Production. It includes tasks which require basic content creation, requiring creative skills to produce new content.
- (E) Exploration. This kind of tasks requires the analysis of a set of data to obtain specific information.
- (C) Consumption. It defines the tasks that require content consumption.
4. Experiment: Cognitive Load in Smartphone Interactions
4.1. Experiment Protocol and Method
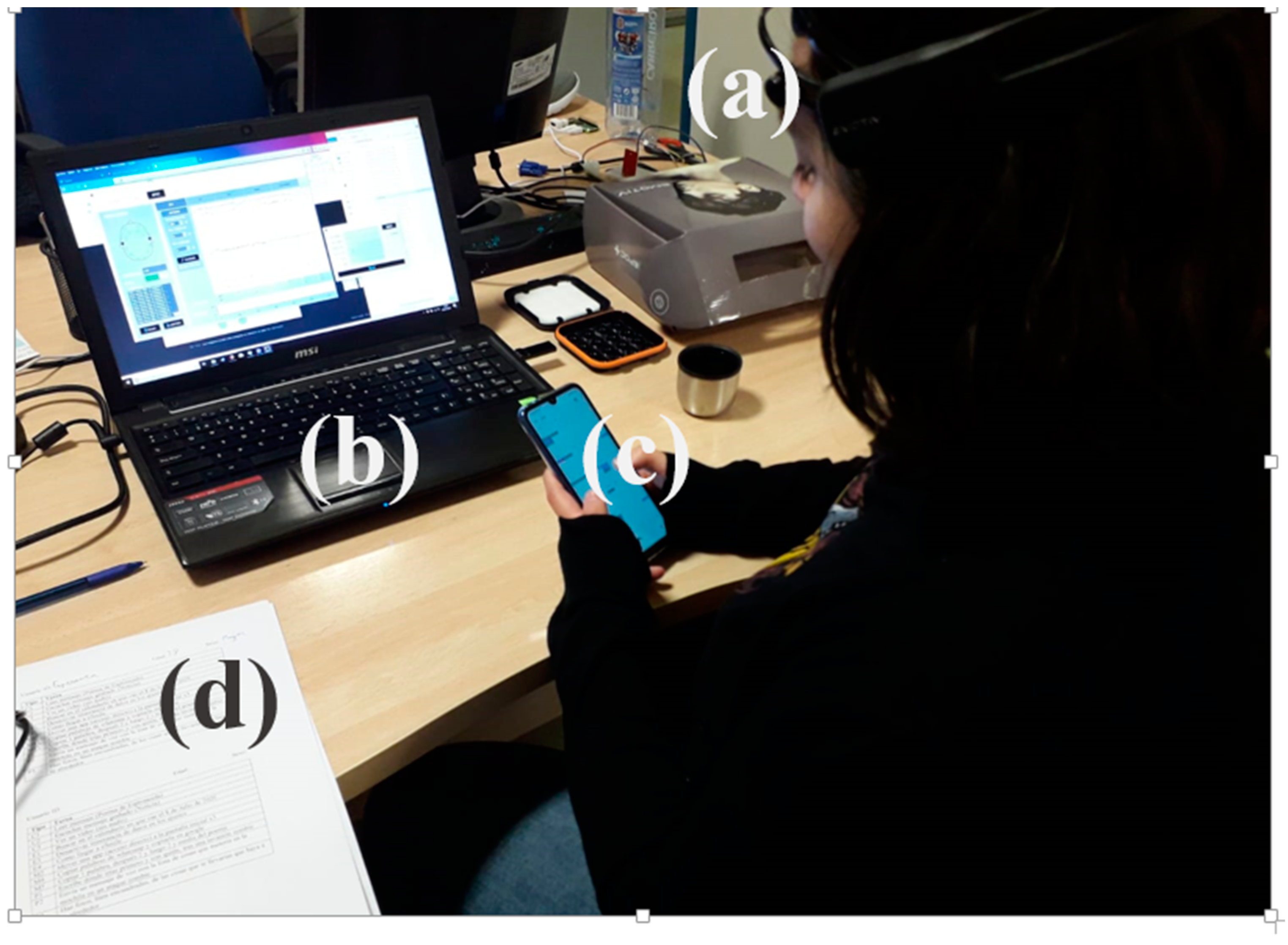
4.2. Material
4.3. EEG Data Processing
4.4. Result
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harari, G.M.; Lane, N.D.; Wang, R.; Crosier, B.S.; Campbell, A.T.; Gosling, S.D. Using Smartphones to collect behavioral data in psychological science: Opportunities, practical considerations, and challenges. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2000, 11, 838–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Leach, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chow, P.; Fua, K.; Teachman, B.A.; Barnes, L.E. Assessing Social Anxiety using GPS Trajectories and Point-of-Interest Data. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Heidelberg, Germany, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 898–903. [Google Scholar]
- Lupton, D.; Jutel, A. ‘It’s like having a physician in your pocket!’ A critical analysis of self-diagnosis smartphone apps. Soc. Sci. Med. 2015, 133, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimova, B. Mobile Phone Apps in the Management and Assessment of Mild Cognitive Impairment and/or Mild-to-Moderate Dementia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotero, L.A.A. Teoría de la carga cognitiva, diseño multimedia y aprendizaje: Un estado del arte. Magis Rev. Int. Investig. Educ. 2012, 5, 75–92. [Google Scholar]
- Sweller, J. Cognitive Load Theory, Learning Difficulty, and Instructional Design. Learn. Instr. 1994, 4, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.E. The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, T.S. Recent Advances in Cognitive Load Theory Research: Implications for Instructional Designers. Malays. Online J. Instr. Technol. 2005, 2, 106–117. [Google Scholar]
- Paas, F.; Tuovinen, J.E.; Tabbers, H.; van Gerven, P.W.M. Cognitive Load Measurement as a Means to Advance Cognitive Load Theory. Educ. Psychol. 2003, 38, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweller, J. Discussion of ‘Emerging Topics in Cognitive Load Research: Using Learner and Information Characteristics in the Design of Powerful Learning Environments’. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2006, 20, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.C.; Mayer, R.E. E-Learning and the Science of Instruction: Proven Guidelines for Consumers and Designers of Multimedia Learning; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, J. Measurement of Cognitive Load in HCI Systems Using EEG Power Spectrum: An Experimental Study. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 84, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achermann, P.; Borbély, A.A. Low-frequency (<1 Hz) oscillations in the human sleep electroencephalogram. Neuroscience 1997, 81, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Klimesch, W. EEG Alpha and Theta Oscillations Reflect Cognitive and Memory Performance: A Review and Analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonenko, P.; Paas, F.; Grabner, R.; van Gog, T. Using Electroencephalography to Measure Cognitive Load. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2010, 22, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, A.; Lukander, K.; Korpela, J.; Sallinen, M.; Müller, K. Estimating Brain Load from the EEG. Sci. World J. 2009, 9, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, A.; Reiner, M. Real Time EEG Based Measurements of Cognitive Load Indicates Mental States during Learning. J. Educ. Data Min. 2017, 9, 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- Trammell, J.P.; MacRae, P.G.; Davis, G.; Bergstedt, D.; Anderson, A.E. The Relationship of Cognitive Performance and the Theta-Alpha Power Ratio Is Age-Dependent: An EEG Study of Short-Term Memory and Reasoning during Task and Resting-State in Healthy Young and Old Adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.; Tan, D.S.; Hudson, S.E.; Shenoy, P.; Rao, R.P.N. Feasibility and Pragmatics of Classifying Working Memory Load with an Electroencephalograph. In Proceedings of the 2008 Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Florence, Italy, 5–10 April 2008; pp. 835–844. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, H. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Mental Load Classification Based on EEG Data. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 76, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoober, S. How Do Users Really Hold Mobile Devices? 2013. Mobile Matters. Available online: https://www.uxmatters.com/mt/archives/2013/02/how-do-users-really-hold-mobile-devices.php? (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Karam, M.; Schraefel, M.C. A Taxonomy of Gestures in Human Computer Interactions s.n. 2005. Project Report. Available online: https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/261149/ (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Wroblewski, L. Touch Gesture Reference Guide. Available online: https://www.lukew.com/ff/entry.asp?1071 (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Lee, H.E.; Lee, Y.J. A Study on Content and Interaction Types on Smartphone. Adv. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2015, 120, 208–210. [Google Scholar]
- Love, S. Understanding Mobile Human-Computer Interaction; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cabañero, L.; Hervás, R.; Bravo, J.; Rodríguez-Benitez, L. eeglib: Computational analysis of cognitive performance during the use of video games. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2019. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Cabañero, L.; Hervás, R.; Bravo, J.; Rodríguez-Benitez, L. Computational EEG Analysis Techniques When Playing Video Games: A Systematic Review. Proceedings 2018, 2, 483. [Google Scholar]
- Luna, J.M.; Hervás, R.; Fontecha, J.; Bravo, J. A Friendly Navigation-System Based on Points of Interest, Augmented Reality and Context-Awareness. In Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Ubiquitous Computing and Ambient Intelligence (UCAmI 2012), Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain, 3–5 December 2012; Volume 7656, ISBN 978-3-642-35377-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hervás, R.; Bravo, J.; Fontecha, J.; Villarreal, V. Achieving Adaptive Augmented Reality through Ontological Context-Awareness applied to AAL Scenarios. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2013, 19, 1334–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, J.; Villarreal, V.; Hervás, R.; Urzaiz, G. Using a communication model to collect measurement data through mobile devices. Sensors 2012, 12, 9253–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.; Hervás, R.; de la Franca, C.G.L.; Mondéjar, T.; Ochoa, S.F.; Favela, J. Assessing empathy and managing emotions through interactions with an affective avatar. Health Inform. J. 2018, 24, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Task Category | Id | Task Type | Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automated | A1 | Query an item | (α) (τ, ι) | Check time/Check if there are notifications/Check if I have WiFi |
| A2 | Action on any physical button | (α) (τ) | Turn on-off device/Turn up-down Volume | |
| psychoMotor | M1 | Pattern | (α) (τ, ι) | Device unlock (with unlock pattern) |
| M2 | Move | (α) (τ, ι) | Add and move a shortcut | |
| M3 | Dismiss | (α) (τ, ι) | Close opened apps, Close notification preview | |
| M4 | Copy & Paste | (α) (τ, ι) | Share information among applications | |
| M5 | Select | (α) (τ, ι) | Select a part of a text | |
| Production | P1 | Text Production | (α) (τ, ι) | Add a new contact/Set an alarm/Write a message/Reminder |
| P2 | Voice Production | (α) (τ, ς) | Make a call/Make a voice command/Create voice message | |
| P3 | Visual Production | (α) (τ, ι) | Take a photo | |
| Exploration | E1 | Search on a textual set | (α) (τ, ι) | Search for a contact/Search for a song/Search for date in the calendar/Last call made to someone |
| E2 | Search on a visual set | (α) (τ, ι) | Search for a specific application/Browse images/Change direct-access settings (e.g., airplane mode) | |
| E3 | Analysis of textual contents | (α) (τ, ι) | Change settings details (e.g., data roaming)/Do a search in an Internet Browser | |
| E4 | Analysis of visual contents | (α) (τ, ι) | Search for a route/site on a map | |
| Consumption | C1 | Text Consumption | (ρ) (ι) | View/Read notifications, Read a text message |
| C2 | Audio Consumption | (ρ) (η) | Listen to an audio message/Listen to a podcast | |
| C3 | Media Consumption | (ρ) (ι, η) | Watch a video |
| Task Category | Task Type | Specific Task in the Experiment |
|---|---|---|
| Consumption | C1 | Read a message that contains a poem by Espronceda |
| C2 | Listen to a podcast from the daily news | |
| C3 | Watch a video | |
| Exploration | E1 | Search for a given date in the calendar |
| E3 | Switch off the data roaming in the device settings | |
| E4 | Search how to reach a given place (about 500 m away) in the map from the current location | |
| psychoMotor | M2 | Add and move an app shortcut (2 times) |
| M4 | Copy a message into the browser search box (Google widget) | |
| M5 | Select one word, then two and, finally, two and a half words in a Wikipedia article | |
| Production | P1 | Write down the places where you would go in a zombie apocalypse |
| P2 | Create a voice message with the list of objects you would collect in a zombie apocalypse | |
| P3 | Take an artistic photo of one object around you |
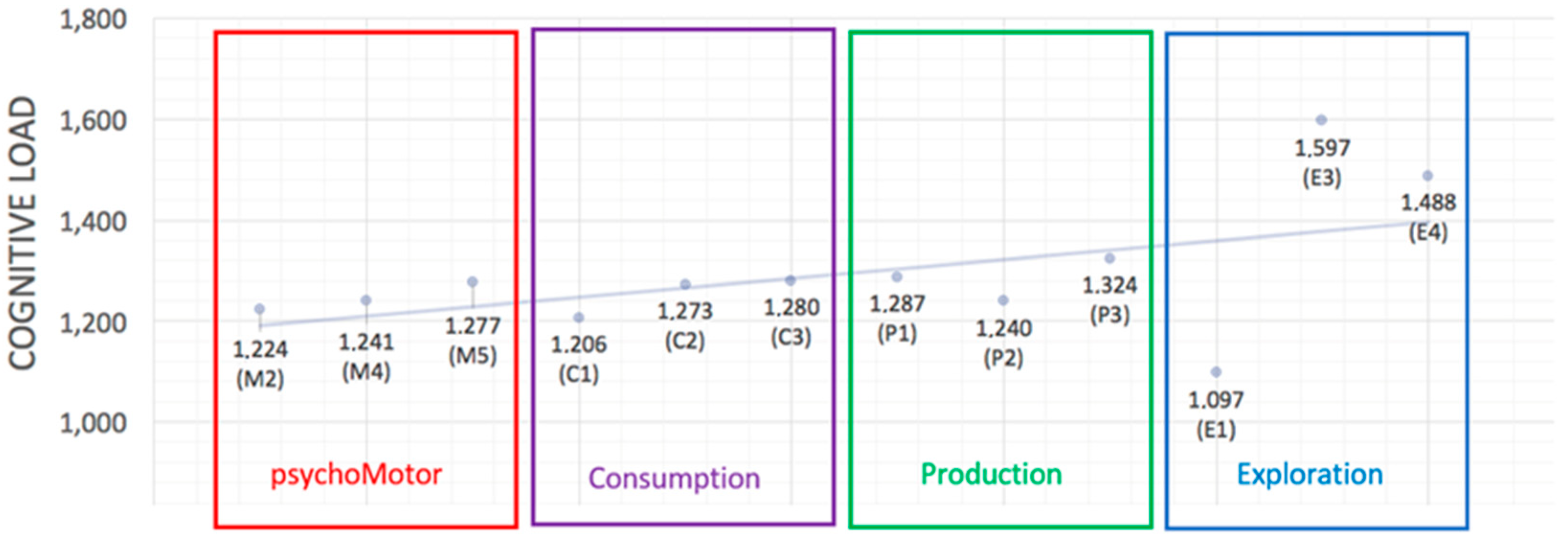
| Task Category | Averaged Cog. Load | Standard Deviation | Task Types | Averaged Cog. Load |
| Consumption | C1 | 1.206 | ||
| 1.253 | 0.251 | C2 | 1.273 | |
| C3 | 1.280 | |||
| Exploration | E1 | 1.097 | ||
| 1.394 | 0.247 | E3 | 1.597 | |
| E4 | 1.488 | |||
| psychoMotor | M2 | 1.224 | ||
| 1.247 | 0.297 | M4 | 1.241 | |
| M5 | 1.277 | |||
| Production | P1 | 1.287 | ||
| 1.284 | 0.255 | P2 | 1.240 | |
| P3 | 1.324 |
© 2019 by the authors. Submitted for possible open access publication under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabañero, L.; Hervás, R.; González, I.; Fontecha, J.; Mondéjar, T.; Bravo, J. Analysis of Cognitive Load Using EEG when Interacting with Mobile Devices. Proceedings 2019, 31, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031070
Cabañero L, Hervás R, González I, Fontecha J, Mondéjar T, Bravo J. Analysis of Cognitive Load Using EEG when Interacting with Mobile Devices. Proceedings. 2019; 31(1):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031070
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabañero, Luis, Ramón Hervás, Iván González, Jesús Fontecha, Tania Mondéjar, and José Bravo. 2019. "Analysis of Cognitive Load Using EEG when Interacting with Mobile Devices" Proceedings 31, no. 1: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031070
APA StyleCabañero, L., Hervás, R., González, I., Fontecha, J., Mondéjar, T., & Bravo, J. (2019). Analysis of Cognitive Load Using EEG when Interacting with Mobile Devices. Proceedings, 31(1), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031070







