Deterministic Propagation Modeling for Intelligent Vehicle Communication in Smart Cities †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simulation Urban Scenario
3. Results
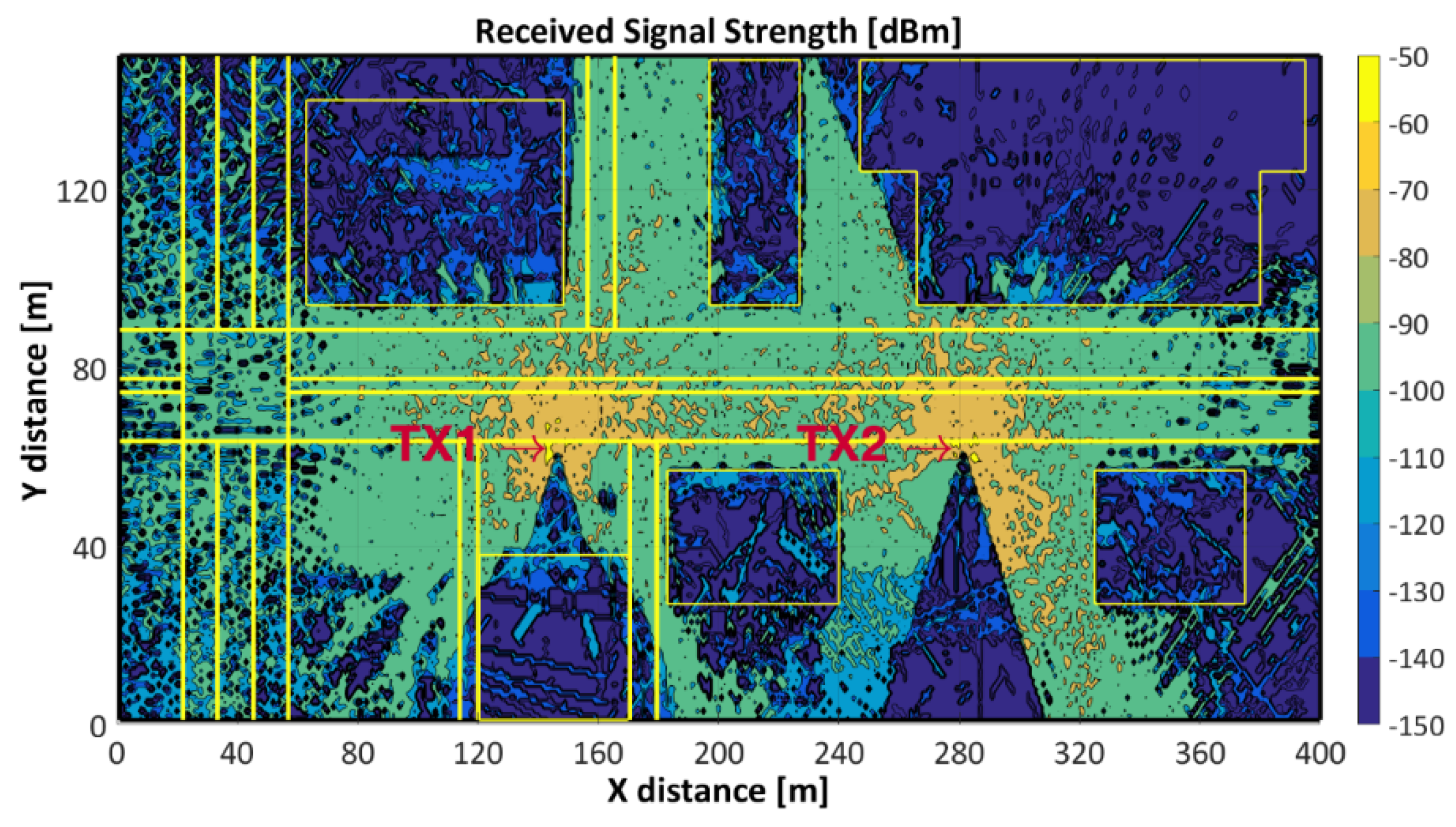
3.1. Received Signal Strength (RSS)
- -
- TX1 and TX2 in the same simulated placement to give coverage to AV1, AV2, ST1.
- -
- Two additional TX’s, one for coverage ST2 and another for ST3.
- -
- One TX, for coverage the roundabout, AV4, AV5 and AV6 areas.
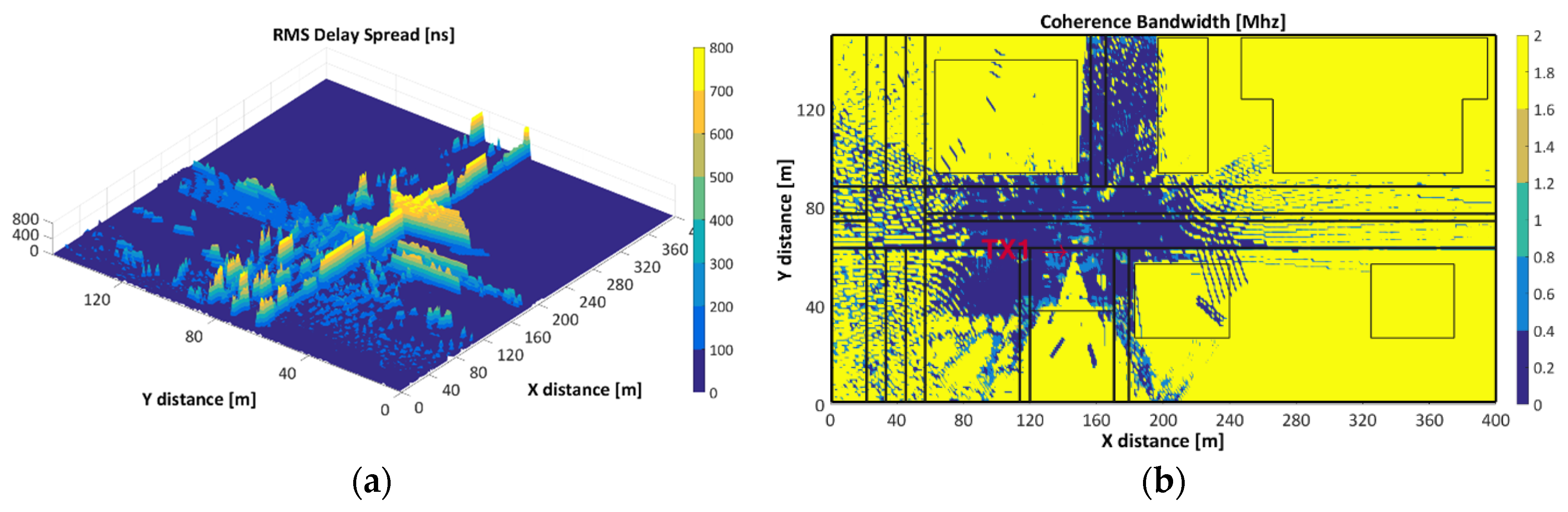
3.2. Time Dispersion Parameters
3.2.1. Root Mean Square Delay Spread (RMS Delay Spread) and Coherence Bandwidth (CB)
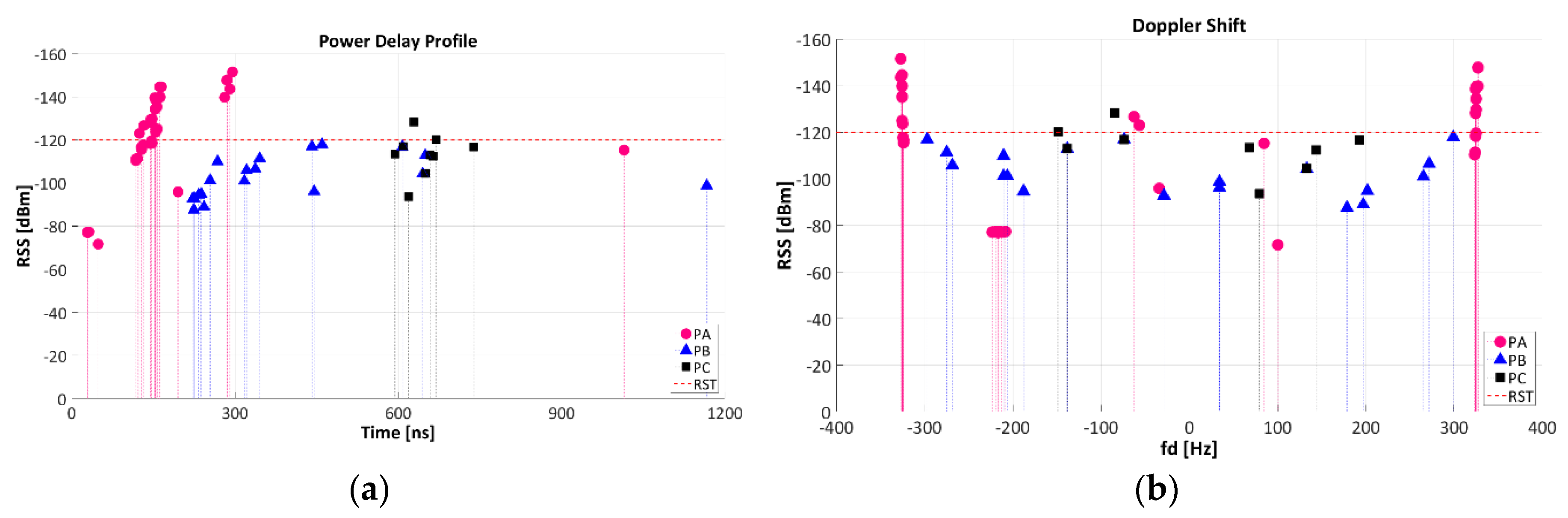
3.2.2. Power Delay Profile (PDP) and Doppler Shift (fd)
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United States Department of Transportation (USDOT). Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) Resources. Available online: https://www.its.dot.gov/v2i/index.htm (accessed on 16 October 2017).
- The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. IEEE Std 802.11 p-2010. Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications-Amendment 6: Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments; IEEE: w York, NY 10016-5997, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Aygun, B.; Boban, M.; Vilela, J.P.; Wyglinski, A.M. Geometry-based propagation modeling and simulation of vehicle-to-infrastructure links. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 83rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Nanjing, China, 15–18 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Viriyasitavat, W.; Boban, M.; Tsai, H.M.; Vasilakos, A. Vehicular communications: Survey and challenges of channel and propagation models. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2015, 10, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boban, M.; Barros, J.; Tonguz, O.K. Geometry-Based Vehicle-to-Vehicle Channel Modeling for Large-Scale Simulation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 4146–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matolak, D.W. Modeling the vehicle-to-vehicle propagation channel: A review. Radio Sci. 2014, 49, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozalvez, J.; Sepulcre, M.; Bauza, R. IEEE 802.11p Vehicle to Infrastructure Communications in Urban Environments. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azpilicueta, L.; Rawat, M.; Rawat, K.; Ghannouchi, F.; Falcone, F. Convergence analysis in deterministic 3D ray launching radio channel estimation in complex environments. Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J. 2014, 29, 256–271. [Google Scholar]
- Azpilicueta, L.; Vargas-Rosales, C.; Falcone, F. Deterministic Propagation Prediction in Transportation Systems. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2016, 11, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, T. Wireless Communications: Principles and Practice, 2nd ed.; Prenctice Hall, Ed.; Communications Engineering and Emerging Technologies Series; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
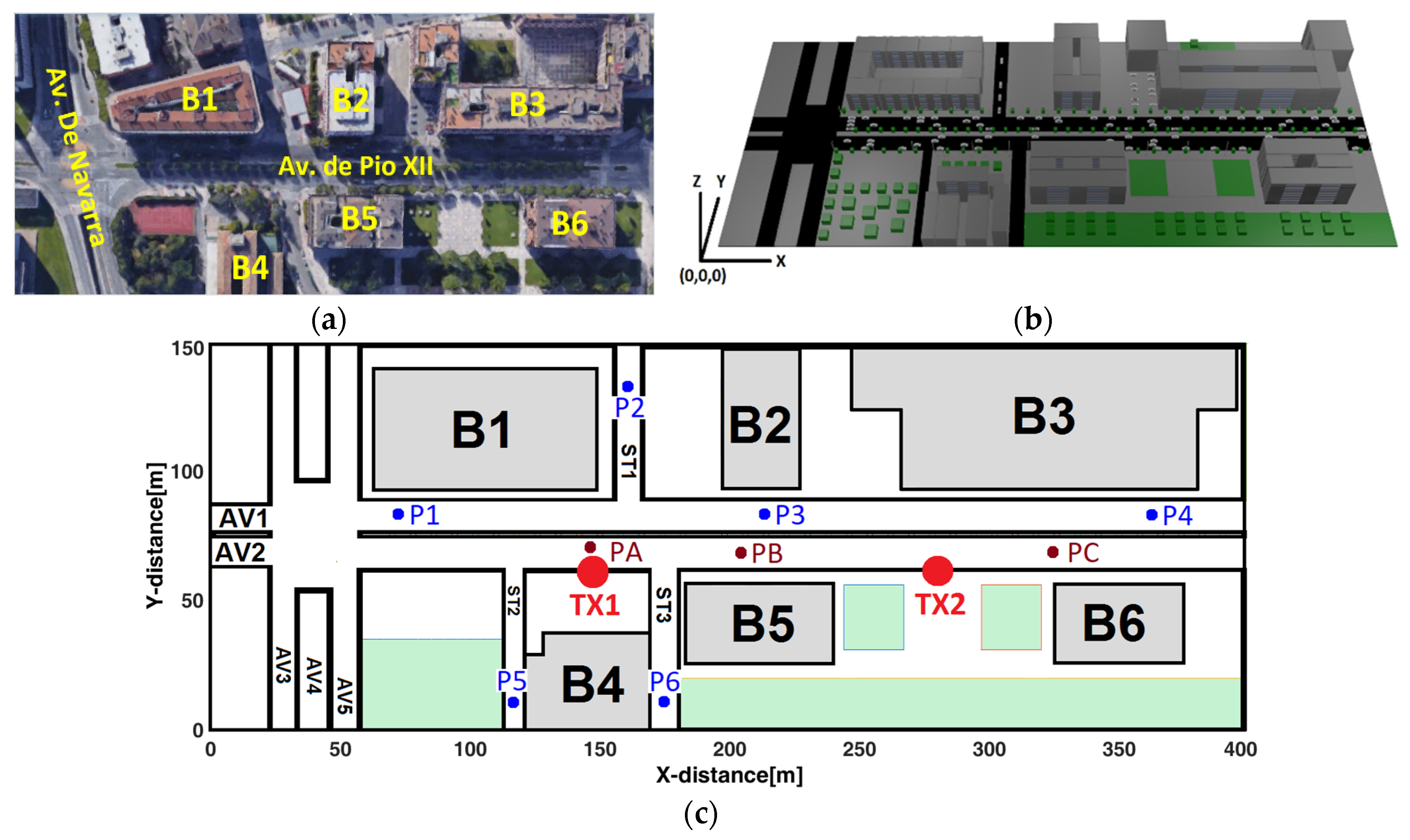
| Reference | Abbreviation | Coordinates (x, y, z) [m] |
|---|---|---|
| Main Avenues | AV1/AV2 | (x, 83, 0)/(x, 69, 0) |
| Streets | ST1/ST2/ST3 | (161, y, 0)/(117, y, 0)/(175, y, 0) |
| Transmitter antennas (TX) | TX1/TX2 | (146, 63, 3.5)/(281, 63, 3.5) |
| Passenger cars | P1/P2/P3 | (70, 83, 1.5)/(161, 40, 1.5)/(210, 83, 1.5). |
| P4/P5/P6 | (370, 83, 1.5)/(117, 10, 1.5)/(175, 10, 1.5). | |
| PA/PB/PC | (149, 70, 1.5)/(204, 70, 1.5)/(323, 10, 1.5). | |
| Buildings | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6 | Not applicable |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| TX: Pt/Gain/Frequency/Height. | 0 dBm/0 dB/5.9 GHz/3.5 m |
| RX: RST/Gain/Frequency/Height. | −120 dBm/0 dB/5.9 GHz/1.5 m |
| Antenna Polarization (RX, TX) | Omnidirectional |
| 3D Ray tracing: angular resolution/Reflections | 1 degree/7 |
| Scenario size/Unitary volume analysis | (400 × 150 × 22) m/1 m3 (1 × 1 × 1) m |
| TX | RX | RSS [dBm] |
|---|---|---|
| TX1 | P1/P2/P3/P4/P5/P6 | −94.66/−88.07/−81.44/−127.30/−122.81/−123.62 |
| TX2 | P1/P2/P3/P4/P5/P6 | −200.00/−200.00/−95.61/−85.55/−200.00/−194.65 |
| TX1+TX2 | P1/P2/P3/P4/P5/P6 | −94.66/−88.07/−81.28/−85.55/−122.81/−123.62 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Granda, F.; Azpilicueta, L.; Vargas-Rosales, C.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Aguirre, E.; Astrain, J.J.; Villandangos, J.; Falcone, F. Deterministic Propagation Modeling for Intelligent Vehicle Communication in Smart Cities. Proceedings 2018, 2, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-4-04898
Granda F, Azpilicueta L, Vargas-Rosales C, Lopez-Iturri P, Aguirre E, Astrain JJ, Villandangos J, Falcone F. Deterministic Propagation Modeling for Intelligent Vehicle Communication in Smart Cities. Proceedings. 2018; 2(3):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-4-04898
Chicago/Turabian StyleGranda, Fausto, Leyre Azpilicueta, Cesar Vargas-Rosales, Peio Lopez-Iturri, Erik Aguirre, Jose Javier Astrain, Jesus Villandangos, and Francisco Falcone. 2018. "Deterministic Propagation Modeling for Intelligent Vehicle Communication in Smart Cities" Proceedings 2, no. 3: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-4-04898
APA StyleGranda, F., Azpilicueta, L., Vargas-Rosales, C., Lopez-Iturri, P., Aguirre, E., Astrain, J. J., Villandangos, J., & Falcone, F. (2018). Deterministic Propagation Modeling for Intelligent Vehicle Communication in Smart Cities. Proceedings, 2(3), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-4-04898










