Impact of Multiple Parameters on Energy Performance of PV-DSF Buildings †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Building Description
2.3. Considered Parameters
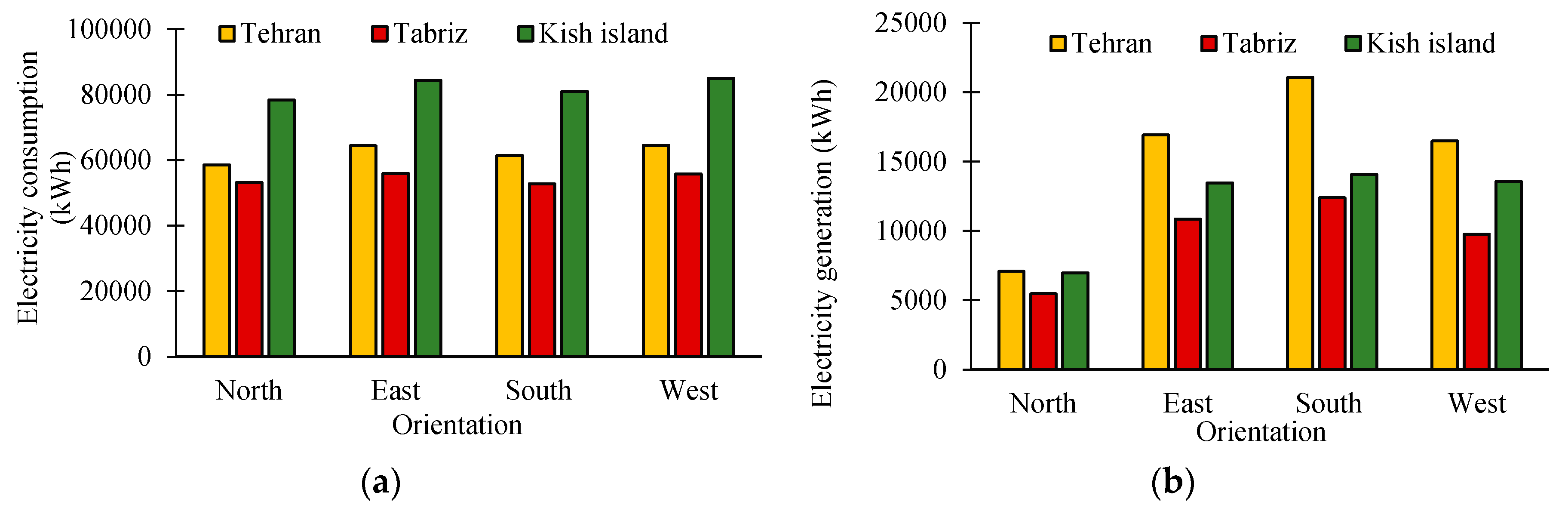
- Building orientation: To find the optimal orientation, the energy performance is assessed for north, south, east and west oriented PV-DSF.
- Cavity width: The distance between inner and outer skins is one the influential parameters on energy performance. For this reason, the electricity consumption and generation are calculated for three different widths of 0.4, 0.8 and 1.2 m.
- Optical properties of PV: The optical properties such as solar transmittance can significantly affect the energy performance and thus, four scenarios as shown in Table 2, are considered for the PV.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Building Orientation
3.2. Cavity Width
3.3. PV Module Transparency
4. Conclusions
- The south-oriented PV-DSF has the maximum generation for all the cities. Considering the net electricity use, the south facing PV-DSF building has the superior performance.
- With increase in cavity width from 0.4 to 1.2 m, the building energy use is declined by 5.88, 5.19 and 7.49 MWh for Tehran, Tabriz and Kish Island, respectively. However, the cavity width has negligible impact on electricity generation for all the considered cities.
- With decrease in SHGC of the outer skin, the annual electricity consumption is declined by 4.04, 1.73 and 5.67 MWh for Tehran, Tabriz and Kish Island, respectively. The annual generation differs from 6.97 MWh to 7.08 MWh for Tehran, from 5.40 MWh to 5.47 MWh for Tabriz and from 6.87 MWh to 6.98 MWH for Kish Island considering different optical properties.
References
- Wang, N.; Phelan, P.E.; Harris, C.; Langevin, J.; Nelson, B.; Sawyer, K. Past visions, current trends, and future context: A review of building energy, carbon, and sustainability. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 8, 976–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Xie, L.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, X. A comparative study on thermal performance evaluation of a new double skin façade system integrated with photovoltaic blinds. Appl. Energy 2017, 199, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Curcija, D.C.; Lu, L.; Selkowitz, S.E.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W. Numerical investigation of the energy saving potential of a semi-transparent photovoltaic double-skin facade in a cool-summer Mediterranean climate. Appl. Energy 2016, 165, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Lu, L.; Yang, H. An experimental study of the thermal performance of a novel photovoltaic double-skin facade in Hong Kong. Sol. Energy 2013, 97, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Short circuit current (A) | 6.20 |
| Module current at maximum power (A) | 5.6 |
| Open circuit voltage (V) | 60 |
| Module voltage at maximum power (V) | 50.5 |
| Rated electric power output (W) | 48,000 |
| Parameter | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar transmittance | 0.837 | 0.409 | 0.298 | 0.114 |
| Solar reflectance (front) | 0.075 | 0.431 | 0.369 | 0.08 |
| Solar reflectance (rear) | 0.075 | 0.53 | 0.201 | 0.04 |
| Visible transmittance | 0.898 | 0.301 | 0.14 | 0.06 |
| Visible reflectance (front) | 0.081 | 0.501 | 0.414 | 0.12 |
| Visible reflectance (rear) | 0.081 | 0.275 | 0.174 | 0.03 |
| Emissivity (front) | 0.84 | 0.447 | 0.637 | 0.83 |
| Emissivity (rear) | 0.84 | 0.703 | 0.779 | 0.9 |
| City | Type | Heating (MWh) | Cooling (MWh) | Total Electricity Use (MWh) | Generation (MWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tehran | A | 1354.45 | 26,469.47 | 58,551.60 | 7078.02 |
| B | 1531.33 | 23,730.39 | 55,905.04 | 7047.71 | |
| C | 1684.23 | 22,886.90 | 55,190.84 | 7030.89 | |
| D | 1843.92 | 22,072.80 | 54,513.95 | 6968.22 | |
| Tabriz | A | 8107.58 | 14,496.55 | 53,171.22 | 5474.40 |
| B | 8570.56 | 12,705.65 | 51,789.56 | 5451.37 | |
| C | 8957.80 | 12,142.08 | 51,601.92 | 5440.31 | |
| D | 9355.89 | 11,593.97 | 51,441.91 | 5396.33 | |
| Kish island | A | 0.97 | 47,154.91 | 78,320.38 | 6977.47 |
| B | 1.90 | 43,557.72 | 74,619.19 | 6952.68 | |
| C | 2.96 | 42,569.03 | 73,602.45 | 6933.36 | |
| D | 4.36 | 41,639.13 | 72,646.52 | 6869.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fazelpour, F.; Soltani, N.; Markarian, E.; Khezerloo, H. Impact of Multiple Parameters on Energy Performance of PV-DSF Buildings. Proceedings 2018, 2, 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2231487
Fazelpour F, Soltani N, Markarian E, Khezerloo H. Impact of Multiple Parameters on Energy Performance of PV-DSF Buildings. Proceedings. 2018; 2(23):1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2231487
Chicago/Turabian StyleFazelpour, Farivar, Nima Soltani, Elin Markarian, and Hamed Khezerloo. 2018. "Impact of Multiple Parameters on Energy Performance of PV-DSF Buildings" Proceedings 2, no. 23: 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2231487
APA StyleFazelpour, F., Soltani, N., Markarian, E., & Khezerloo, H. (2018). Impact of Multiple Parameters on Energy Performance of PV-DSF Buildings. Proceedings, 2(23), 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2231487




