Abstract
Most cyanide-containing industrial effluents also contain other cyano-derivatives and high amounts of metals and metal-cyanide compounds. For this reason, the biotreatment of these wastes requires the use of microorganisms capable to degrade all these different cyano-compounds and to tolerate metals. Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344 is a cyanotrophic bacterium capable of metabolize cyanide in its free form, but it is not very efficient at degrading metal-cyanide complexes. Therefore, for the optimization of the cyanide biodegradation process it is essential to find and characterize new bacterial strains, capable of assimilating metal cyanide-complexes, to complement the capacities of P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344.
1. Introduction
The Cyanide, one of the known most toxic chemicals, is widely used in several industries including plastics, electroplating, organic chemicals production, photographic developing, and pharmaceuticals. In gold and silver mining, cyanide is used to recover these metals through the leaching process. Cyanide leaching remains the only viable chemical lixivant for the recovery of gold, accounting for 90% of world production [1]. As consequence, cyanide-containing wastes are accumulated in the environment becoming a risk to human health and ecosystems. The toxicity of cyanide arises from its affinity for metals and the inhibition of cytochrome C oxidase in the electron transport chain as well as many other metalloenzymes by binding metal ions critical to the proteins’ functions [2]. The global consumption of cyanide is over 1.5 million metric tons per year. The use that created the largest environmental threat of cyanide is as a lixiviant in gold leach mining. Up to 90% of gold is extracted from ore utilizing some form of cyanide leaching. These mining practices generate large volumes of cyanide-laden effluent, which when not properly contained and remediated, have had catastrophic impacts on downstream environments and human communities [3]. Conventional chemical treatments of cyanide wastewaters can be effective at reducing the toxicity from cyanide; they can be costly, require significant infrastructure, need long-term storage or transportation, and involve reagents that pose their own environmental hazards [1]. Thus, cyanide biodegradation has become an efficient economically interesting alternative to the physical-chemical treatments of cyanide-containing industrial residues [4]. Despite the toxicity of cyanide, cyanotrophic microorganisms such as the alkaliphilic bacterium Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes CECT5344 may use cyanide and its derivatives as a nitrogen source for growth, making biodegradation of cyanurated industrial waste possible [5]. P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT5344, isolated after an enrichment cultivation procedure, has the ability to use cyanide as the sole nitrogen source under alkaline conditions that avoid hydrogen cyanide volatilization [5]. Most cyanide-containing industrial effluents also contain other cyano-derivatives and high amounts of metals and metal–cyanide compounds. For this reason, the biotreatment of these wastes requires the use of microorganisms capable to degrade all these different cyano-compounds and to tolerate metals [1] P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344 is a cyanotrophic bacterium capable of metabolize cyanide in its free form, but it is not very efficient at degrading metal-cyanide complexes [5]. Therefore, for the optimization of the cyanide biodegradation process it is essential to find and characterize new bacterial strains, capable of assimilating metal cyanide-complexes, to complement the capacities of P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344.
2. Materials and Methods
Bacterial isolation. Bacterial strains were isolated after an enrichment cultivation procedure. The medium used was the M9 minimal medium [6] prepared at pH 9.5, with with 2 mM of potassium ferrocyanide (K4[Fe(CN)6]) or potassium ferricyanide (K3[Fe(CN)6]) or sodium cyanide (NaCN) or residue from the electroplating industry (called residue) as the sole added nitrogen source and 50 mM acetate as the sole carbon source. The medium was inoculated with sludges collected in the surroundings of Rio Tinto (Huelva) and incubated in an Erlenmeyer flask at 37 °C in a rotatory shaker. After 2 weeks, the process was repeated 6 times by reinoculation in fresh medium with 1% of the previously grown culture. Samples of the enriched culture were plated on Luria-Bertani (LB) medium solidified with 1.8% Bacto agar (Difco, Hampton, NH, USA), and individual colonies were purified and tested for axenic growth in liquid cultures with cyanide as the sole nitrogen source. 5 types of colonies were able to assimilate cyanide compounds, thus producing an axenic culture from which a single colony was selected, obtained in pure culture, and kept for further analysis. Culture media. The bacterial strains were grown either in M9 minimal medium (without ammonium and citrate) adjusted to pH 9.5 on a rotatory shaker at 230 rpm and 30 °C. Unless otherwise stated, 50 mM acetate was used as the carbon source. The appropriate nitrogen sources were added from sterilized stocks at the indicated concentrations. Bacterial growth was monitored by determining the absorbance at 600 nm. The free cyanide concentration was determined colorimetrically [5]. Taxonomic position and analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequence of isolates. Genomic DNA from the bacterial strains was obtained by using a Puregene kit B (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the instructions of the manufacturer. Gene encoding the small ribosome subunit (16S rRNA) was sequenced using services provided by Sistemas Genómicos (Valencia, Spain). After a BLAST analysis of the sequences, the isolates were tentatively identified.
3. Results
In this work, we report for the isolation of five bacterial strains able to degrade metal-cyanide complexes as the sole nitrogen source in minimal medium with acetate as carbon source and under alkaline conditions and aerobic conditions. The strains ware isolated by enrichment cultivation in selective media at pH 9.5 with 2 mM of potassium ferrocyanide (K4[Fe(CN)6]) or potassium ferricyanide (K3[Fe(CN)6]) or sodium cyanide (NaCN) or residue from the electroplating industry as the sole nitrogen source as described in Materials and Methods. The bacteria have been classified as Microbacterium testaceum, Achromobacter piechaudii, Achromobacter xylosoxidans, Microbacterium kitamiense and Achromobacter sp. by comparison of the 16S RNA gene sequence with existing sequences.
In order to know what kind of substrates the isolated bacterial strains can metabolize, bacterial isolates were aerobically cultured in M9 minimal medium (pH 9.5) with DL-malate as carbon source. Several cyanide-compounds were used as the sole nitrogen source: KCN, K4Fe(CN)6, K3[Fe(CN)6] or Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3. A. piechaudii, A. xylosoxidans, M. kitamiense y Achromobacter sp. were not able to grow with 2 or 4 mM KCN. Only M. testaceum was able to use KCN 2 mM as the sole nitrogen source to grow. None of the isolated bacteria grew in media with Fe4[Fe(CN)6]. However A. piechaudii, A. xylosoxidans y M. kitamiense were able to use potassium ferrocyanide (K4Fe(CN)6) as the sole source of nitrogen for their growth. Only M. kitamiense y A. xylosoxidans showed cell growth in media with potassium ferricyanide, whereas A. piechaudii was unable to use this complex, although it did it in the case of ferrocyanide. M. kitamiense assimilated more efficiently the cyanide of both metallic complexes. In addition, all bacterial strains were cultured in media with cyanide residue (2 mM free cyanide as final concentration) from the jewelery industry. All bacterial strains were able to use the cyanide residues as nitrogen source for their growth, being Achromobacter sp. the most efficient.
The degradation of cyanide present in the jewelry cyanide residues from by mixed cultures was also studied. The co-cultures were constituted by different mixtures of 2 bacterial strains; Achromobacter sp./P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344 R1, M. kitamiense/P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344 R1, and Achromobacter sp./M. kitamiense. Mixed cultures of Achromobacter sp./P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344 R1 and Achromobacter sp./M. kitamiense were not more efficient that of the pure strains. However, when P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344 y M. kitamiense were inoculated together with cyanide residues, the mixed culture reached a maximum cell growth of 0.75 (O.D. 600 nm) (Figure 1c), much higher than the growth shown by P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344 R1 (Figure 1a) and slightly higher than that of M. kitamiense (Figure 1b). The results obtained could indicate that both species use different cyanide substrates existing in the jewellery residues.
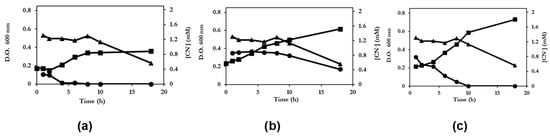
Figure 1.
Growth of P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344 R1 (a), M. kitamiense (b) in pure cultures and growth of P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344 and M. kitamiense in co-cultures (c) with cyanide residue (2 mM free cyanide as final concentration) from the jewellery industry as the sole nitrogen source. Cells were inoculated in media at pH 9.5 containing DL-malate (4 g/L) as the carbon source. At the indicated times, the increments of cell growth of the culture growing with cyanide with respect to the control culture (  ) and the cyanide concentration in the culture supernatant (
) and the cyanide concentration in the culture supernatant (  ) were measured. The concentration of cyanide in a noninoculated flask containing culture medium (
) were measured. The concentration of cyanide in a noninoculated flask containing culture medium (  ) was measured at the same time.
) was measured at the same time.
 ) and the cyanide concentration in the culture supernatant (
) and the cyanide concentration in the culture supernatant (  ) were measured. The concentration of cyanide in a noninoculated flask containing culture medium (
) were measured. The concentration of cyanide in a noninoculated flask containing culture medium (  ) was measured at the same time.
) was measured at the same time.
4. Discussion
Achromobacter sp. and M. kitamiense grew quite efficiently in media with cyanide residues from the jewelery industry, although in the case of Achromobacter sp. this process was much more advantageous. In contrast, M. kitamiense assimilated both ferrocyanide and ferricyanide much more efficiently. Also, P. pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344 is able to use cyanide-metal complexes as nitrogen sources although in a very limited way [5]. That is, these three bacterial strains exhibit different assimilating competences, and therefore the addition of the degradative capacities of the three bacterial strains opens the possibility of the use of mixed cultures, instead of pure strains, as a good alternative for a more effective elimination of cyanide, both free and complexed, existing in cyanide residues. From a biotechnological point of view, the treatment of cyanide residues, coming from the jewelery industry using microorganisms, can be treated in a more efficient way with co-cultures of bacterial strains. In this sense the joint inoculation of M. kitamiense and Achromobacter sp. was the most promising since there was greater degradation of cyanide in its different forms, except for cyanide in free form.
Acknowledgments
Funded by IB16062, Junta de Extremadura (Consejería de Economía e Infraestructuras), Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional, European Union.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Akcil, A. Destruction of cyanide in gold mill effluents: Biological versus chemical treatments. Biotechnol. Adv. 2003, 21, 501–511. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0734975003000995 (accessed on 16 October 2018). [CrossRef]
- Vogel, S.N.; Sultan, T.R.; Ten Eyck, R.P. Cyanide Poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 1981, 18, 367–383. Available online: https://doi.org/10.3109/15563658108990043 (accessed on 16 October 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico, M.; Benito, G.; Salgueiro, A.R.; Díez-Herrero, A.; Pereira, H.G. Reported tailings dam failures: A review of the European incidents in the worldwide context. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 846–852. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389407010837 (accessed on 16 October 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.M.; Trevor Sewell, B.; Benedik, M.J. Cyanide bioremediation: The potential of engineered nitrilases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3029–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque-Almagro, V.M.; Huertas, M.J.; Martínez-Luque, M.; Moreno-Vivián, C.; Roldán, M.D.; García-Gil, L.J.; Castillo, F.; Blasco, R. Bacterial degradation of cyanide and its metal complexes under alkaline conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 940–947. Available online: http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-13644269308&partnerID=40&md5=c1165cb3147cce49650bed7731dcac1d (accessed on 16 October 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Rusell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).