Abstract
Energy management is a key issue in the design of long-lived wireless sensor networks. (WSNs). Energy is used to collect data by sensors and to communicate it to other nodes and to the gateways. The energy management procedures aim at minimizing the energy consumption of both the data acquisition and transmission activities. A careful design is crucial when the devices are powered by energy harvesting techniques, such as solar power. This paper describes a device architecture for a WSN node designed to monitor the habit of pink iguanas: a recently discovered species living in remote locations at the Galápagos Islands. The few individuals of this species live in a relatively small area (around 25 km2 on top of Volcano Wolf, Isla Isabela) that lacks of any available communication infrastructure. The design combines an ultra low power sleep mode and a long range communication capability that requires a very high power consumption.
1. Introduction
Pink Land Iguana (Conolophus marthae) is a recently discovered species of iguana [1]. The species is assessed as Critically Endangered in the IUCN Red List, that establishes priorities of research needed and conservation actions. Among high priority researches needed are those that attempt to (i) clarify the area of distribution of C. marthae; (ii) clarify times and usage patterns of the area; (iii) provide crucial data to develop habitat suitability models; (iv) identify nesting sites; (v) monitor a feral cat population impacting the area. The application of long-term animal-tracking techniques would greatly aid in accomplishing such tasks. However, prior attempts proved ineffective due to a combination of the difficulty of the terrain and hard logistics that limit the duration of field trips, lack of suitable tracking devices, and absence of a network infrastructure. To this aim we developed a dedicated sensor node able to create a delay tolerant Wireless Sensor Network (WSN), integrating several sensors, a GPS receiver and storage capabilities. The sensor node uses an energy harvesting circuit composed of a small solar cell and a supercapacitor that allows the node to support long range communication capability and feeds the energy-hungry GPS sensor [2].
In this paper we presents the device describing three main aspects: (i) the novel harvesting architecture that includes an high drain line able to power an RF booster; (ii) a refined power management solution that allows the definition of several power consumption states; (iii) the device sticking solution directly tested on the field on a real animals.
2. Device Description
Each WSN device integrates the following components:
- the Texas Instrument CC1310 wireless controller;
- a sensor subsystem including an accelerometer (ADXL345), a digital humidity sensor with integrated temperature sensor (HDC1008) and a UV light sensor (VEML6070);
- the Global Top PA6C GPS receiver;
- 1GB NOR flash (N25Q00AA13G1240E)
- the Skyworks SE2435L including a power amplifier and a low noise amplifier.
3. Energy Harvesting Architecture
The harvesting architecture is depicted in Figure 1. As we can see from the picture, solar cell micro panels harvest energy from solar light to the supercapacitor through the harvester (BQ25570).
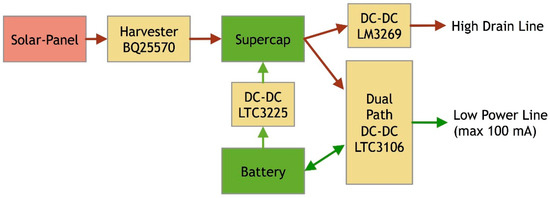
Figure 1.
Harvesting Architecture.
The BQ25570 is able to extract very small amount of power (up to microwatt) generated by solar panels and LTC3225 is designed to charge two supercapacitors in series to a selectable fixed output voltage. Automatic cell balancing prevents overvoltage damage to the supercapacitors.
Through software control it is possible to decide to charge the battery from the supercapacitor or viceversa, through the dual path DC-DC (LTC3106).
Without any load, the LTC3106 generates an output voltage up to 5V from the input sources with very low power stand-by consumption. If the solar power is unavailable, the LTC3106 can switch to the other available power sources as the battery. The supercapacitor has been used as the primary power source and LTC3106 can also charge the backup battery whenever an energy surplus is available.
Using this design we found out empirically that the linear LTC3106 produces a ripple in the power supply as shown by our measurement instruments in Figure 3. This power noise feeds the microcontroller that in turn feeds the RF oscillator, ultimately producing a noise. This noise is evident using a continuous wave and it is shown in Figure 2. To overcome this shortcoming a possible solution is the introduction of an LDO (such as the LCP170) that introduces a small voltage drop from 3.3V to 3V.
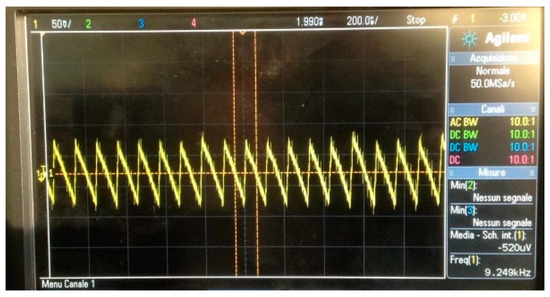
Figure 3.
Power supply ripple.
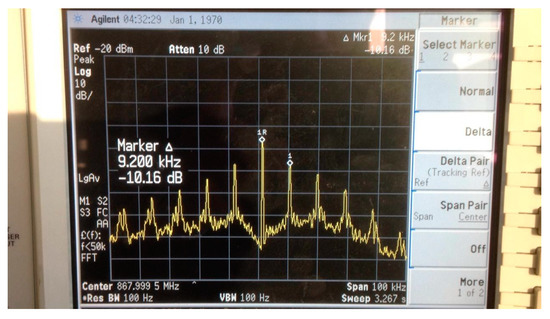
Figure 2.
Spurious frequencies from a continuous wave due to the linear power noise.
4. Power Architecture and Design
The activation of the different functions is ruled by a power management block. Figure 4 shows the architecture of the power management system.
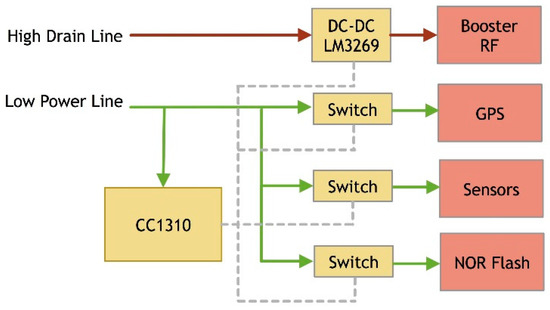
Figure 4.
Power management architecture.
As already seen the system integrates solar panels and supercapacitors (for energy storage) as the key enabler to “perpetual” WSN operations. In this respect the node controlling several DC-DC is able to operate from the range of nanowatt, in the deep sleep mode, up to Watt in the long range transmission mode (the SE2435L absorbs 250 mA with 23 dB of gain). Moreover, the multi-sensor system includes the Wake-on Radio technology that allows a low power receiving mode that can be used to implement the discovery functionality of the WSN [3].
The high drain line is dedicated to the high-power RF module, and the other is used for the micro-controller and sensors activities. The rationale of this line split is the presence of a booster that in turn calls for a high current drain (long range transmission).
In Table 1 we report the measurements of the average power consumption in the various device states together with a short description.

Table 1.
Average power consumptions.
5. Application on the Field
Special attention has been devoted to the connection of the sensor system to the animal. The use of special glues or microsurgical approaches have been considered to minimize the animal stress and to prevent accidental removal of the device.
Based on prior experience, we preferred gluing the board on iguanas as show in Figure 5. Epoxide glue ensures that the device remains attached the time between two shedding events, that is at least one year. For future applications and longer monitoring, anatomical microsurgical attachments will be evaluated. Other methods based on fastened jackets or similar forms are not considered as they proved dangerous to animal health when applied in long-term studies [4].
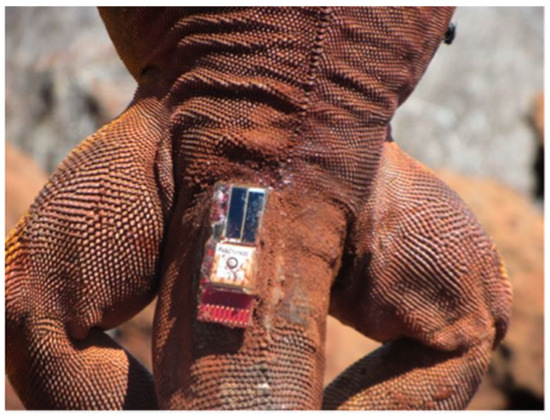

Figure 5.
Animal with the device glued.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gentile, G.; Fabiani, A.; Marquez, C.; Snell, H.L.; Snell, H.M.; Tapia, W.; Sbordoni, V. An overlooked pink species of land iguana in the Galápagos. PANS 2009, 106, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracciale, L.; Catini, A.; Gentile, G.; Loreti, P. Delay tolerant wireless sensor network for animal monitoring: The Pink Iguana case. Lect. Notes Electr. Eng. 2017, 429, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bracciale, L.; Loreti, P.; Bianchi, G. The sleepy bird catches more worms: revisiting energy efficient neighbor discovery. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2016, 15, 1812–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.M.; Knapp, C.R.; Bradley, K.A.; Gerber, G.P.; Alberts, A.C. Review of radio transmitter attachment methods for West Indian rock iguanas (genus Cyclura). Appl. Herpetol. 2009, 6, 151–170. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).