Desorption and Electrical Conductivity Studies of Indium Tin Oxide Powders and Thick Films †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
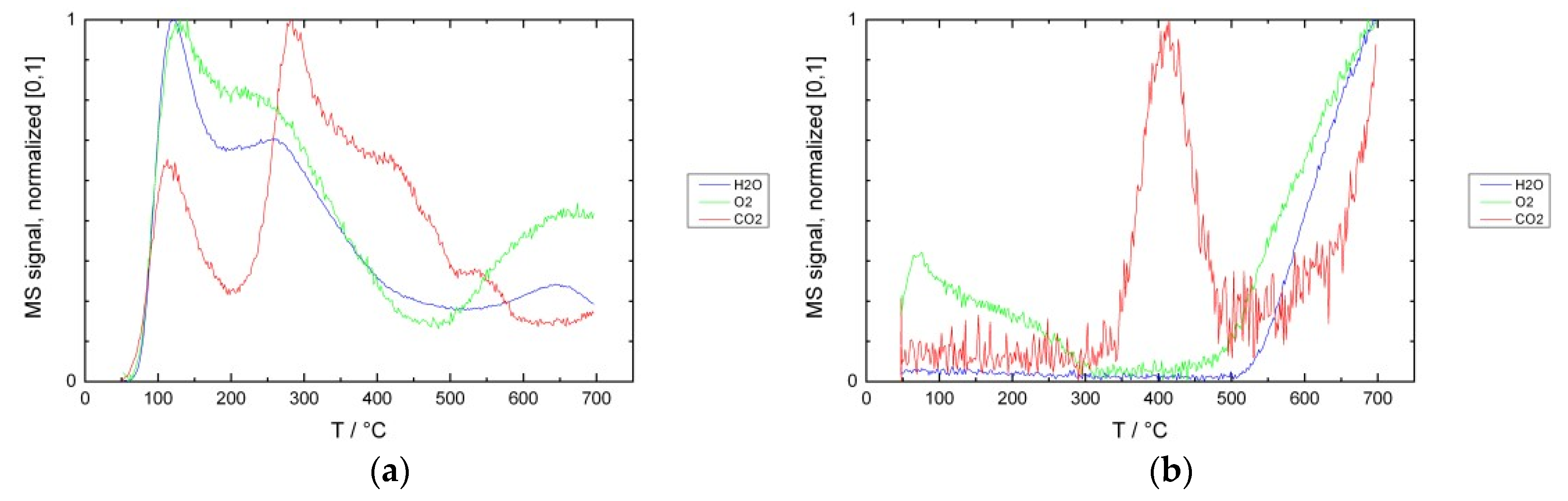
3.1. Desorption Measurements
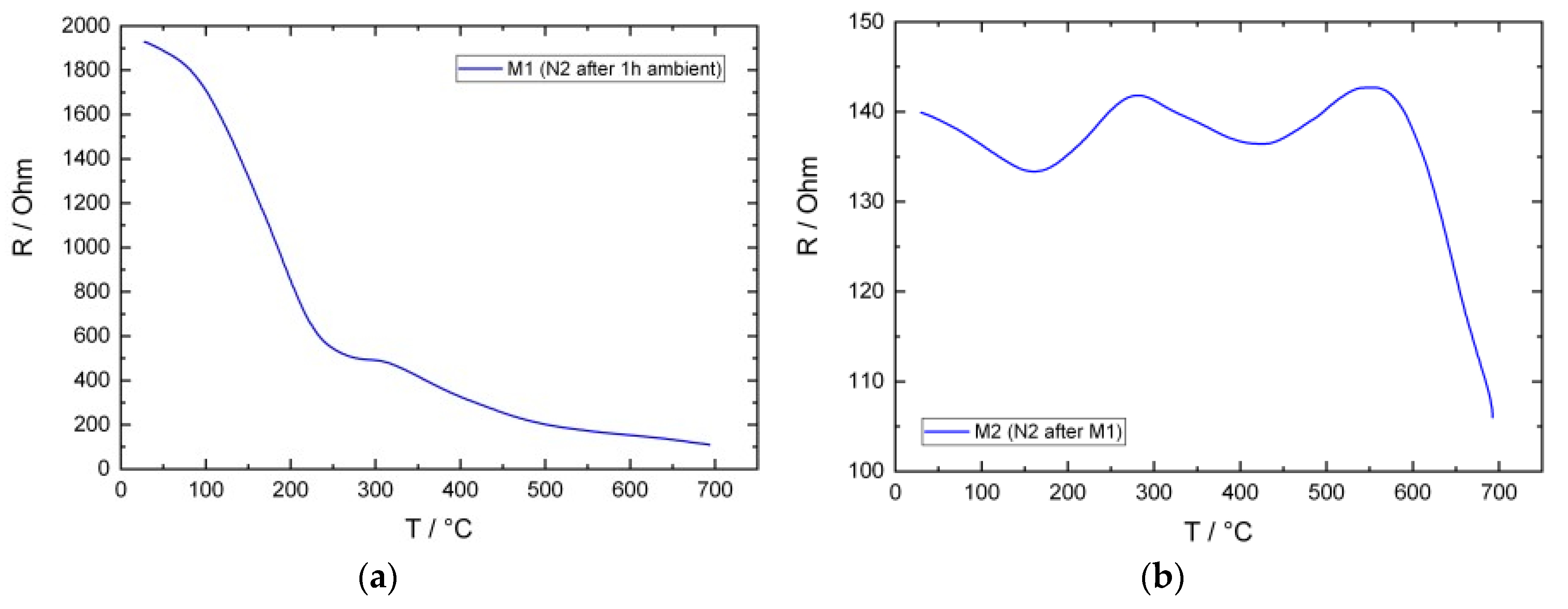
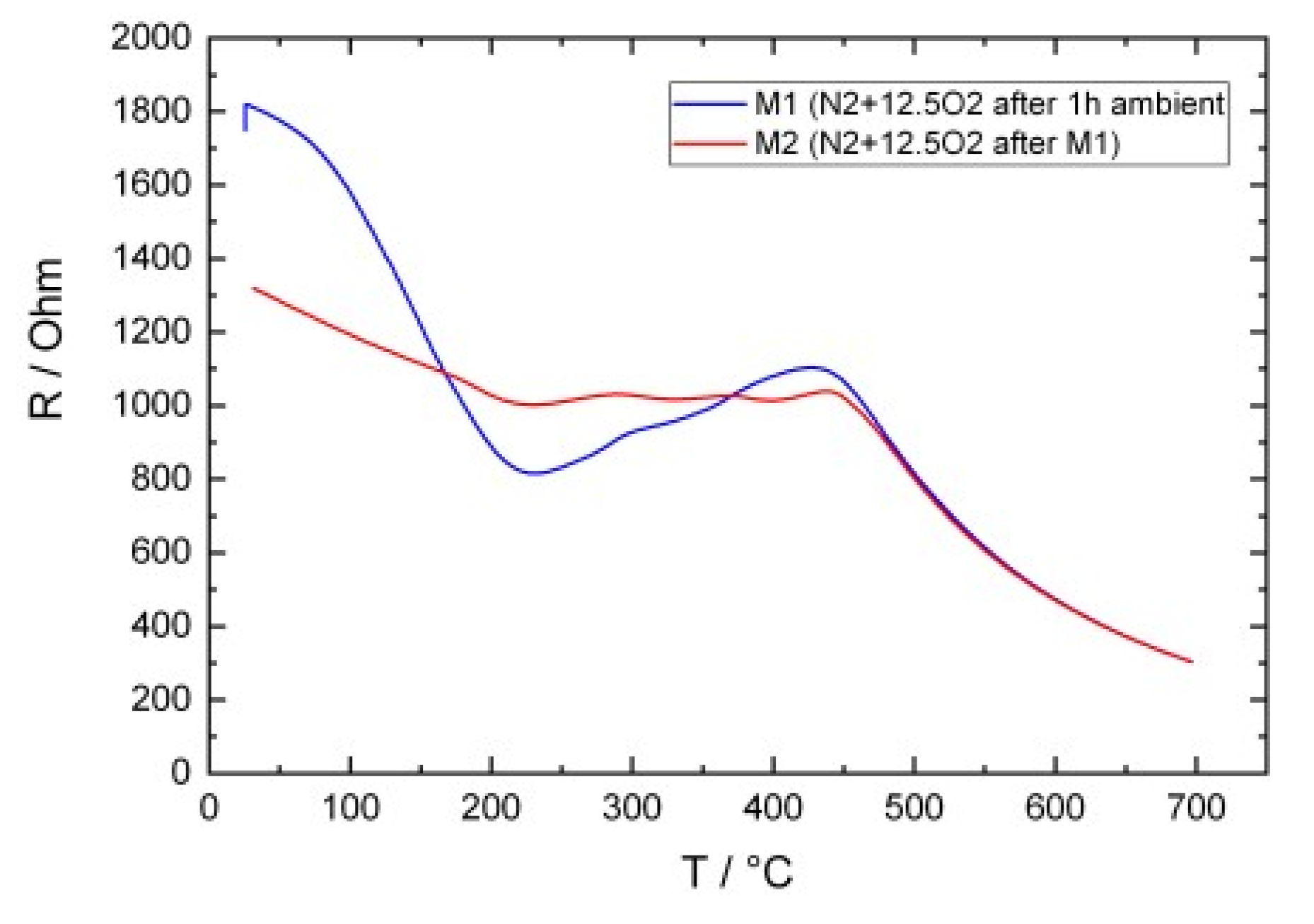
3.2. Electrical Conductivity Measurements
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mbarek, H.; Saadoun, M. Screen-printed Tin-doped indium oxide (ITO) films for NH3 gas sensing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2006, 26, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.G.; Makhija, K.K. Fabrication of carbon dioxide gas sensor and its alarm system using indium tin oxide (ITO) thin films application. Sens. Actuators B 1994, 21, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.C.; Kaushlendra, A. Fabrication and characterization of nanostructured indium tin oxide film and its application as humidity and gas sensors. J. Mater Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 4172–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, G.M. Solid-state mixed-potential sensor employing tin-doped indium oxide sensing electrode and scandium oxide-stabilised zirconia electrolyte. Adv. Powder Technol. 2009, 20, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, I.; Meddeb, W. Effect of temperature and NO2 surface adsorption on electricalproperties of screen printed ITO thin film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 355, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donley, C.; Dunphy, D. Characterization of Indium-Tin Oxide Interfaces Using X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Redox Processes of a Chemisorbed Probe Molecule: Effect of Surface Pretreatment Conditions. Langmuir 2002, 18, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, M.; Preiss, E.M. Indium-tin-oxide single-nanowire gas sensor fabricated via laserwriting and subsequent etching. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 215, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaney, J.A.; Koh, S.E. Surface chemistry of carbon removal from indium tin oxide by base and plasma treatment, with implications on hydroxyl termination. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 218, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detweiler, Z.; Wulfsberg, S.N. The oxidation and surface speciation of indium and indium oxides exposed to atmospheric oxidants. Surf. Sci. 2015, 684, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Z. Low-temperature catalysis for VOCs removal in technology andapplication: A state-of-the-art review. Catal. Today 2016, 264, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dietrich, S.; Kusnezoff, M. Desorption and Electrical Conductivity Studies of Indium Tin Oxide Powders and Thick Films. Proceedings 2018, 2, 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130901
Dietrich S, Kusnezoff M. Desorption and Electrical Conductivity Studies of Indium Tin Oxide Powders and Thick Films. Proceedings. 2018; 2(13):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130901
Chicago/Turabian StyleDietrich, Stefan, and Mihails Kusnezoff. 2018. "Desorption and Electrical Conductivity Studies of Indium Tin Oxide Powders and Thick Films" Proceedings 2, no. 13: 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130901
APA StyleDietrich, S., & Kusnezoff, M. (2018). Desorption and Electrical Conductivity Studies of Indium Tin Oxide Powders and Thick Films. Proceedings, 2(13), 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130901



