Borosilicate Glass MEMS Lorentz Force Magnetometer †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
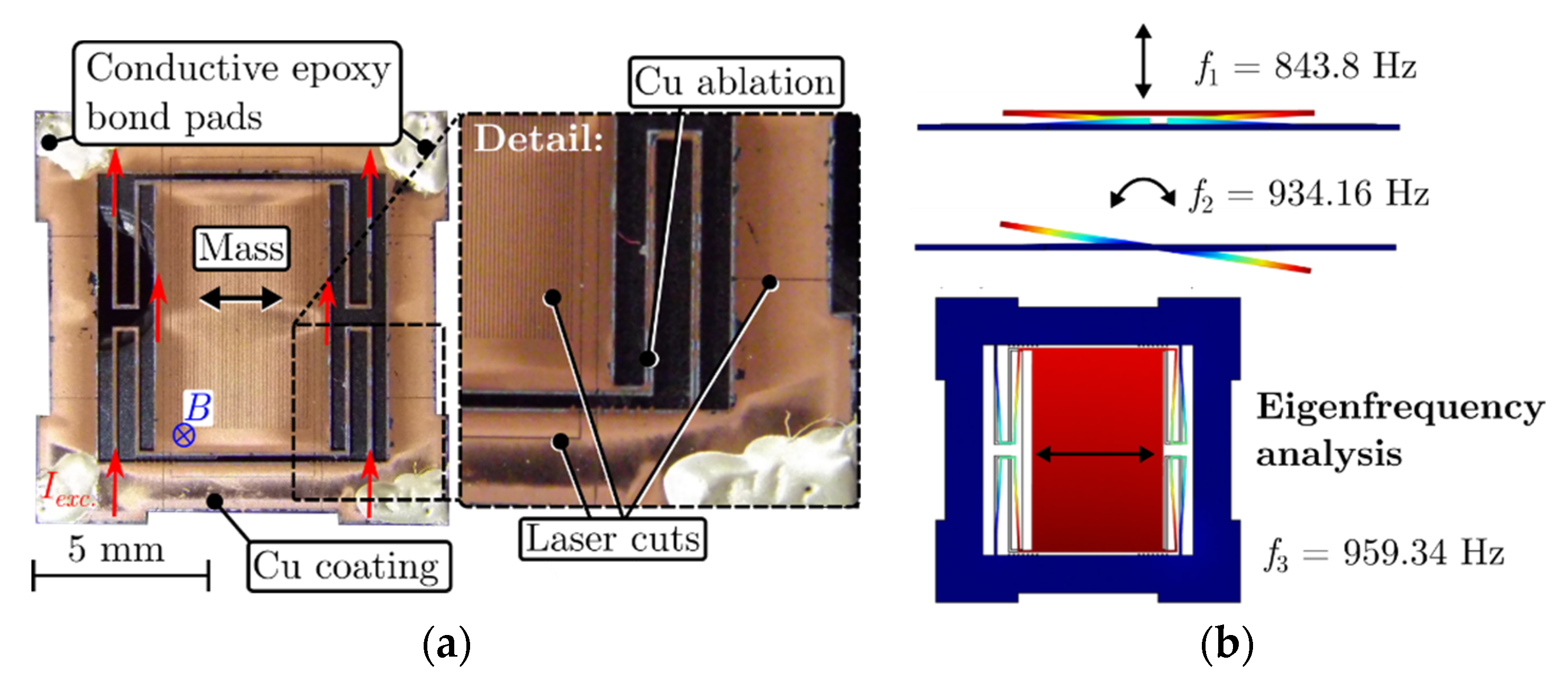
2. Sensing Principle & Fabrication
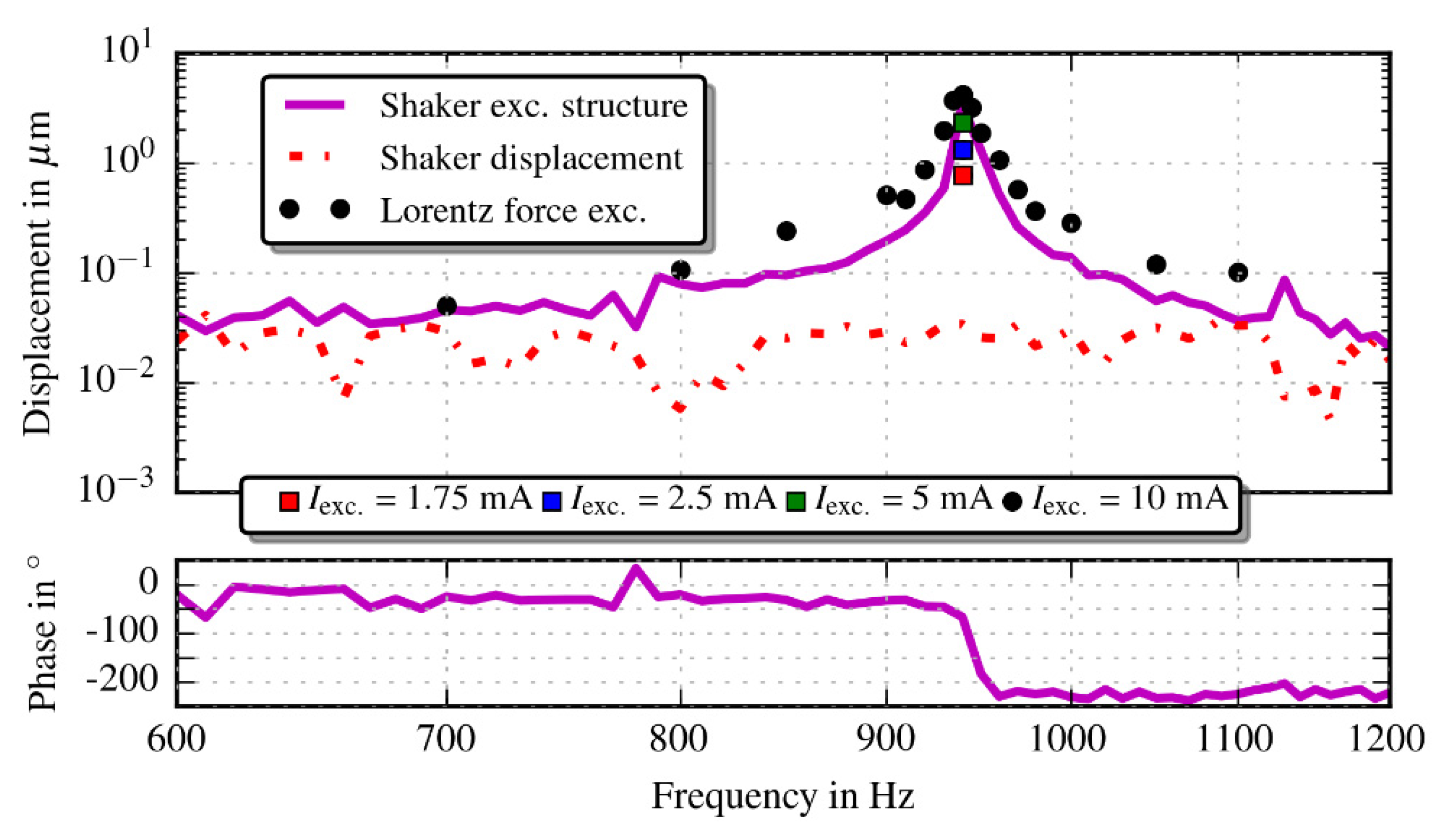
3. Measurement Set-Up
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bourhis, E.L. Glass Mechanics and Technology, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-527-67944-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bellouard, Y.; Said, A.A.; Dugan, M.; Bado, P. High Accuracy Micro-Displacement Sensor With Integrated Optics-based Detection Means. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripka, P.; Janosek, M. Advances in magnetic field sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domke, M.; Egle, B.; Piredda, G.; Stroj, S.; Fasching, G.; Bodea, M.; Schwarz, E. Ultrashort pulse laser dicing of thin Si wafers: the influence of laser-induced periodic surface structures on the backside breaking strength. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 26, 115004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortschitz, W.; Steiner, H.; Stifter, M.; Kainz, A.; Kohl, F.; Siedler, C.; Schalko, J.; Keplinger, F. Novel MOEMS Lorentz Force Transducer for Magnetic Fields. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortschitz, W.; Steiner, H.; Sachse, M.; Stifter, M.; Kohl, F.; Schalko, J.; Jachimowicz, A.; Keplinger, F.; Sauter, T. Robust Precision Position Detection with an Optical MEMS Hybrid Device. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 4855–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainz, A.; Schalko, J.; Jachimowicz, A.; Keplinger, F.; Steiner, H.; Kohl, F.; Stifter, M.; Beigelbeck, R.; Hortschitz, W. Distortion-free measurement of electric field strength with a MEMS sensor. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kahr, M.; Domke, M.; Steiner, H.; Hortschitz, W.; Stifter, M. Borosilicate Glass MEMS Lorentz Force Magnetometer. Proceedings 2018, 2, 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130788
Kahr M, Domke M, Steiner H, Hortschitz W, Stifter M. Borosilicate Glass MEMS Lorentz Force Magnetometer. Proceedings. 2018; 2(13):788. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130788
Chicago/Turabian StyleKahr, Matthias, Matthias Domke, Harald Steiner, Wilfried Hortschitz, and Michael Stifter. 2018. "Borosilicate Glass MEMS Lorentz Force Magnetometer" Proceedings 2, no. 13: 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130788
APA StyleKahr, M., Domke, M., Steiner, H., Hortschitz, W., & Stifter, M. (2018). Borosilicate Glass MEMS Lorentz Force Magnetometer. Proceedings, 2(13), 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130788




