A Planar Electrochromic Device using WO3 Nanoparticles and a Modified Paper-Based Electrolyte †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
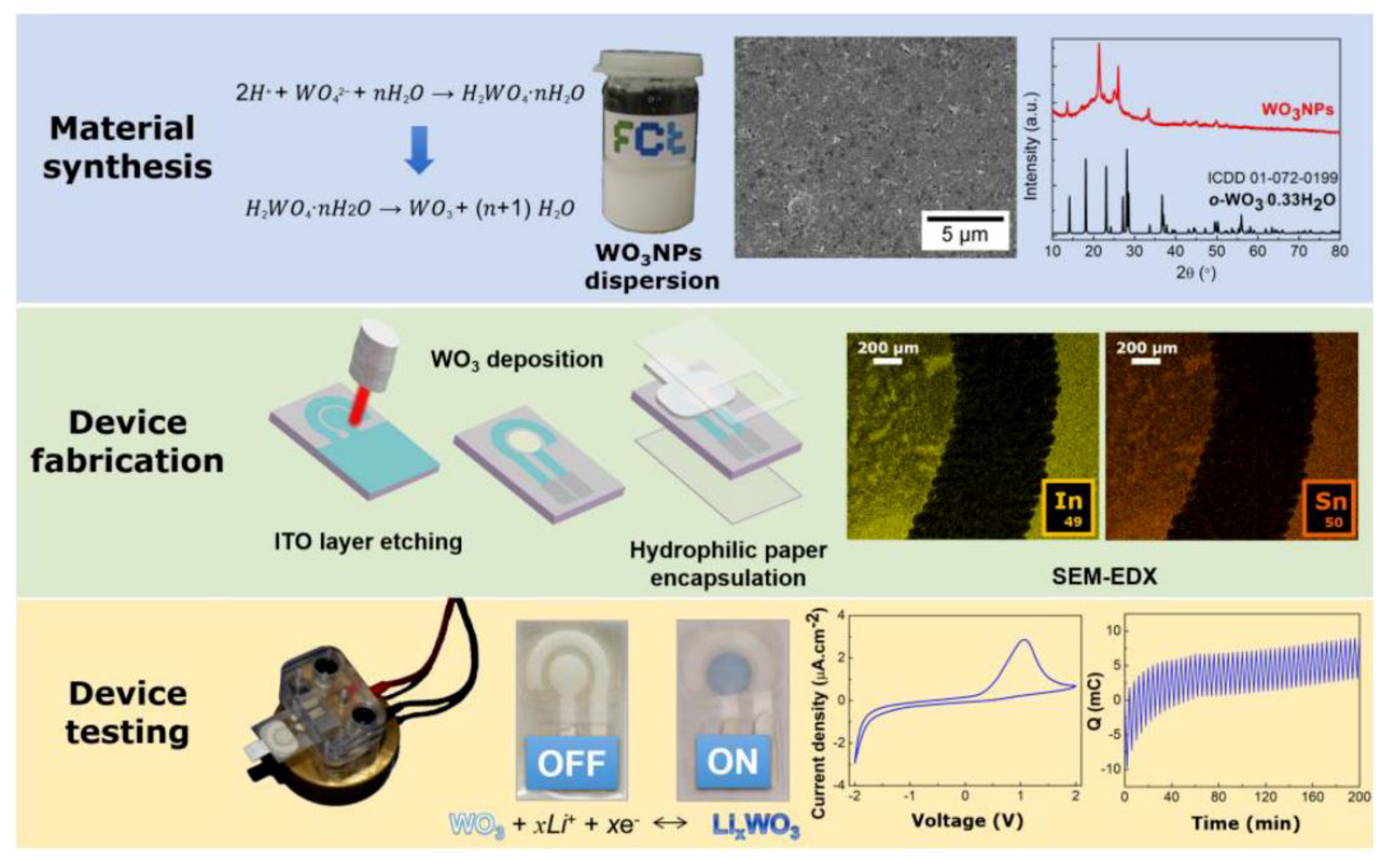
2.1. Material Production and Characterization
2.2. Device Production and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Granqvist, C. Oxide Electrochromics: Why, How, and Whither. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granqvist, C.; Azens, A.; Heszler, P.; Kish, L.; Osterlund, L. Nanomaterials for Benign Indoor Environments: Electrochromics for “Smart Windows”, Sensors for Air Quality, and Photo-Catalysts for Air Cleaning. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2007, 91, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Wojcik, P.; Pinto, J.V.; Elangovan, E.; Viegas, J.; Pereira, L.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Structure and Morphologic Influence of WO3 Nanoparticles on the Electrochromic Performance of Dual-Phase a-WO3 /WO3 Inkjet Printed Films. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1400002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Ou, J.Z.; Strano, M.S.; Kaner, R.B.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-zadeh, K. Nanostructured Tungsten Oxide—Properties, Synthesis, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 2175–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquinha, P.; Pereira, S.; Pereira, L.; Wojcik, P.; Grey, P.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Flexible and Transparent WO3 Transistor with Electrical and Optical Modulation. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, P.; Pereira, L.; Pereira, S.; Barquinha, P.; Cunha, I.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Solid State Electrochemical WO3 Transistors with High Current Modulation. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1500414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.C.; Santos, L.; Costa, M.N.; Dantas, J.M.; Duarte, P.; Gonçalves, A.; Martins, R.; Salgueiro, C.A.; Fortunato, E. Office Paper Platform for Bioelectrochromic Detection of Electrochemically Active Bacteria Using Tungsten Oxide Nanoprobes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Matteis, V.; Cannavale, A.; Blasi, L.; Quarta, A.; Gigli, G. Chromogenic Device for Cystic Fibrosis Precocious Diagnosis: A “Point of Care” Tool for Sweat Test. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 225, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Sun, P.; Mai, W. Electrochromic Energy Storage Devices. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Neto, J.P.; Crespo, A.; Nunes, D.; Costa, N.; Fonseca, I.M.; Barquinha, P.; Pereira, L.; Silva, J.; Martins, R.; et al. WO3 Nanoparticle-Based Conformable PH Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 13, 12226–12234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granqvist, C.G. Handbook of Inorganic Electrochromic Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Deepa, M.; Saxena, T.K.; Singh, D.P.; Sood, K.N.; Agnihotry, S.A. Spin Coated versus Dip Coated Electrochromic Tungsten Oxide Films: Structure, Morphology, Optical and Electrochemical Properties. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 1974–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Khoo, E.; Lee, P.S.; Ma, J. Synthesis, Assembly, and Electrochromic Properties of Uniform Crystalline WO3 Nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 14306–14312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondalkar, V.V.; Kharade, R.R.; Mali, S.S.; Mane, R.M.; Patil, P.B.; Patil, P.S.; Choudhury, S.; Bhosale, P.N. Nanobrick-like WO3 Thin Films: Hydrothermal Synthesis and Electrochromic Application. Superlattices Microstruct. 2014, 73, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Y.; Li, N.; Lv, H.; Hou, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. Highly Robust and Flexible WO3·2H2O/PEDOT Films for Improved Electrochromic Performance in near-Infrared Region. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 163, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marques, A.; Santos, L.; Pereira, S.; Emanuele, U.; Sinopoli, S.; Igreja, R.; Sales, G.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. A Planar Electrochromic Device using WO3 Nanoparticles and a Modified Paper-Based Electrolyte. Proceedings 2018, 2, 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131065
Marques A, Santos L, Pereira S, Emanuele U, Sinopoli S, Igreja R, Sales G, Martins R, Fortunato E. A Planar Electrochromic Device using WO3 Nanoparticles and a Modified Paper-Based Electrolyte. Proceedings. 2018; 2(13):1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131065
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarques, Ana, Lídia Santos, Sónia Pereira, Umberto Emanuele, Stefano Sinopoli, Rui Igreja, Goreti Sales, Rodrigo Martins, and Elvira Fortunato. 2018. "A Planar Electrochromic Device using WO3 Nanoparticles and a Modified Paper-Based Electrolyte" Proceedings 2, no. 13: 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131065
APA StyleMarques, A., Santos, L., Pereira, S., Emanuele, U., Sinopoli, S., Igreja, R., Sales, G., Martins, R., & Fortunato, E. (2018). A Planar Electrochromic Device using WO3 Nanoparticles and a Modified Paper-Based Electrolyte. Proceedings, 2(13), 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131065








