Resonant Accelerometer based on Double-Ended Tuning Fork and a Force Amplification Mechanism †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
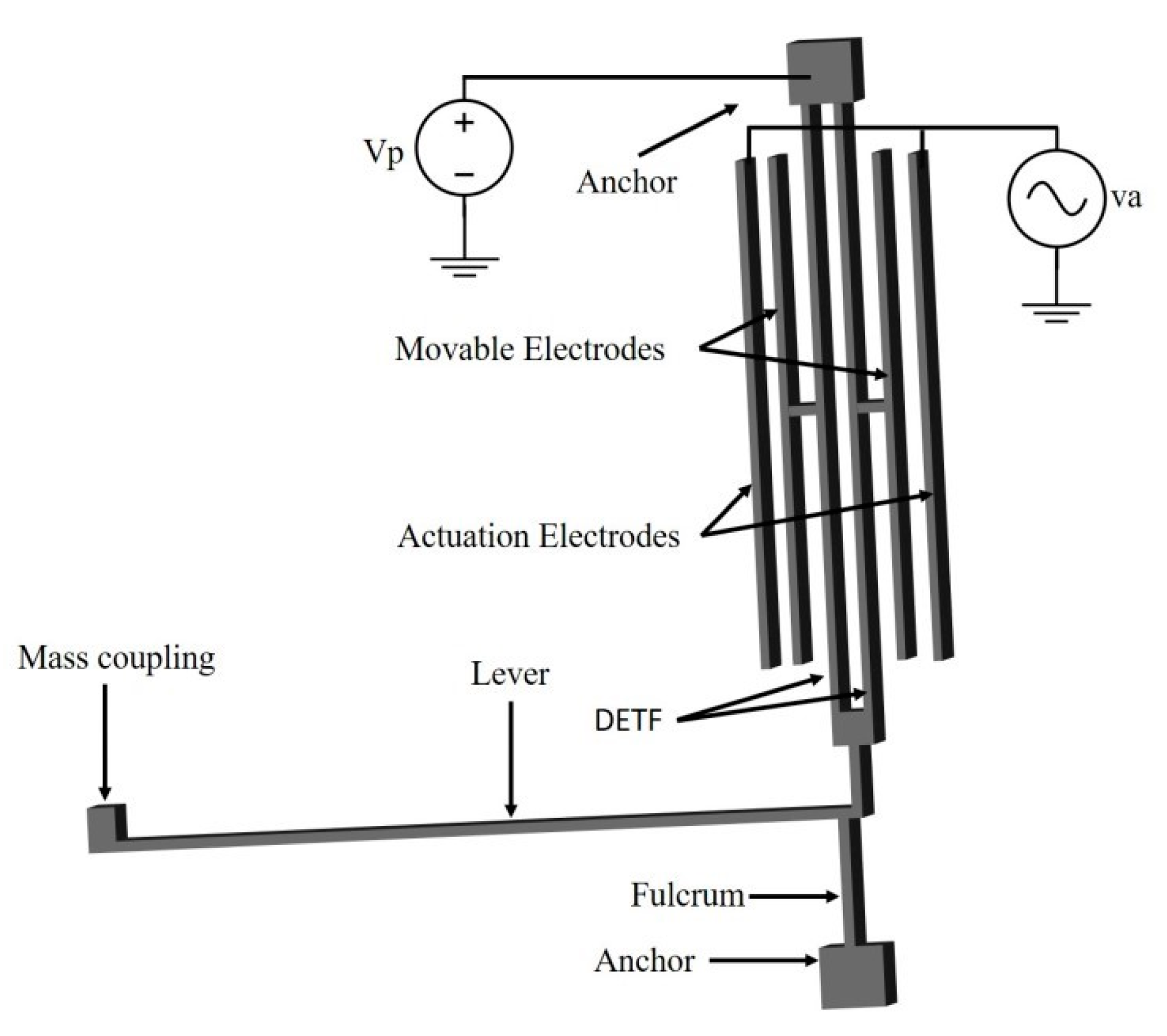
2. Accelerometer Design
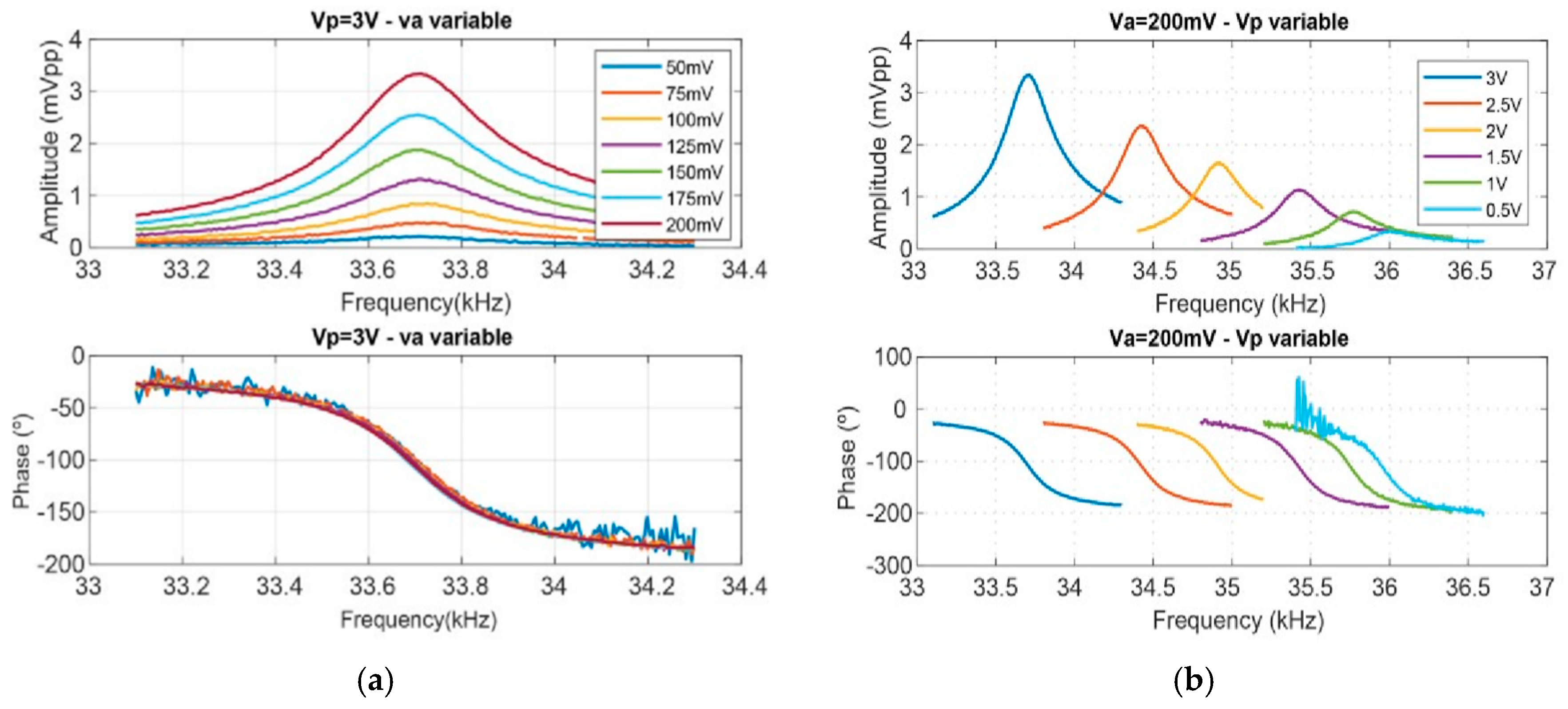
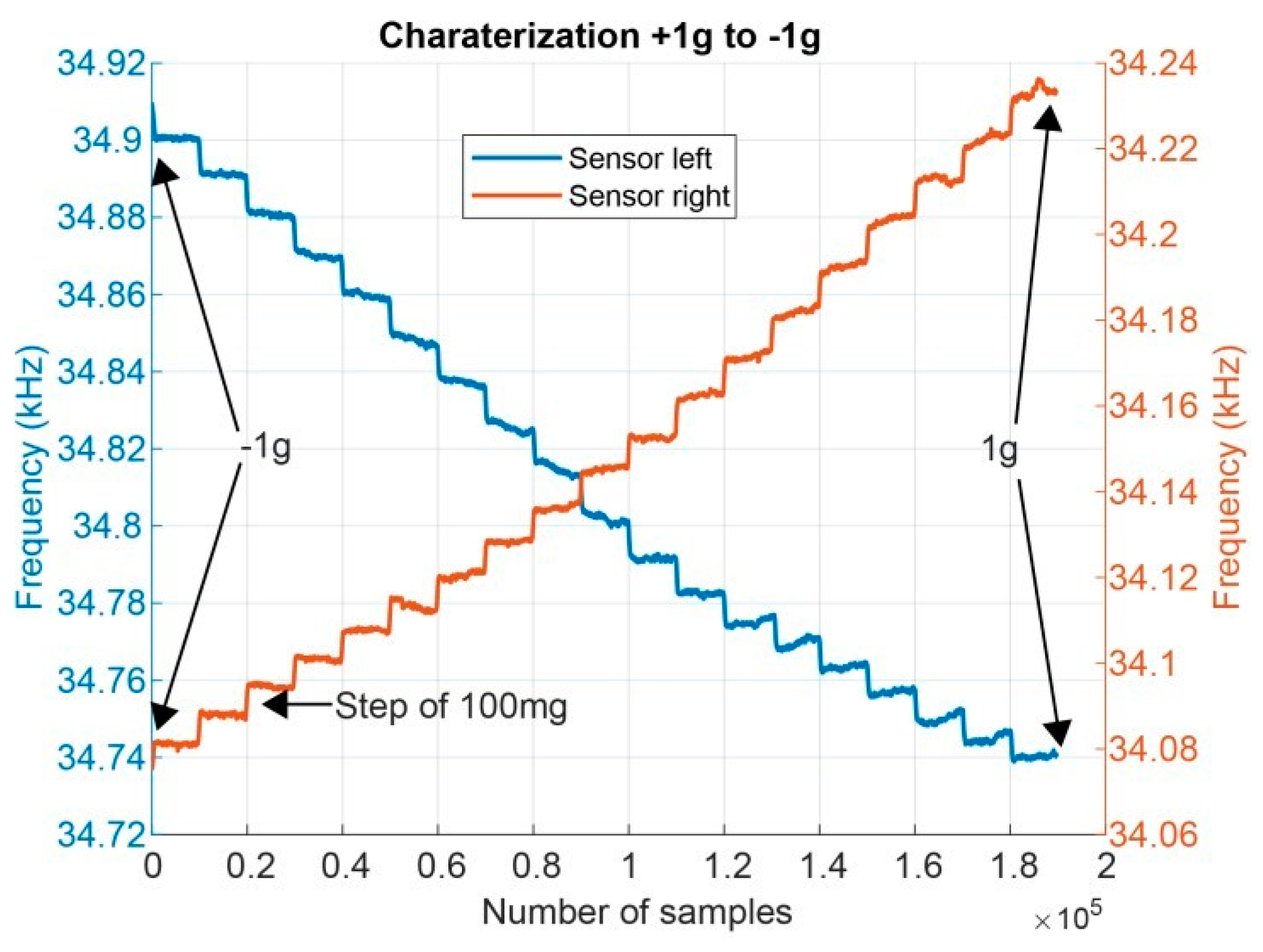
3. Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, Y.; Zwahlen, P.; Nguyen, A.M.; Frosio, R.; Rudolf, F. Ultra-high precision MEMS accelerometer. In Proceedings of the 2011 16th International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference, Beijing, China, 5–9 June 2011; pp. 695–698. [Google Scholar]
- Comi, C.; Corigliano, A.; Langfelder, G.; Longoni, A.; Tocchio, A.; Simoni, B. A Resonant microaccelerometer with high sensitivity operating in an oscillating circuit. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2010, 19, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspani, A.; Comi, C.; Corigliano, A.; Langfelder, G.; Tocchio, A. Compact biaxial micromachined resonant accelerometer. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zega, V.; Comi, C.; Minotti, P.; Langfelder, G.; Falorni, L.; Corigliano, A. A new MEMS three-axial frequency-modulated (FM) gyroscope: A mechanical perspective. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 2018, 70, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wei, X.; Weng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Z. A novel single-axis MEMS tilt sensor with a high sensitivity in the measurement range from 0° to 360°. Sensors 2018, 18, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaajakari, V. Practical MEMS: Design of Microsystems, Accelerometers, Gyroscopes, RF MEMS, Optical MEMS, and Microfluidic Systems; Small Gear Publishing: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, H.; Le, X.; Wang, W.; Xie, J. A MEMS piezoelectric in-plane resonant accelerometer based on aluminum nitride with two-stage microleverage mechanism. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 254, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.X.P.; Yang, H.S. Analytical modeling and FEM simulations of single-stage microleverage mechanism. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2002, 44, 2217–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreira, E.E.; Kuhlmann, B.; Gaspar, J.; Rocha, L.A. Resonant Accelerometer based on Double-Ended Tuning Fork and a Force Amplification Mechanism. Proceedings 2018, 2, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131030
Moreira EE, Kuhlmann B, Gaspar J, Rocha LA. Resonant Accelerometer based on Double-Ended Tuning Fork and a Force Amplification Mechanism. Proceedings. 2018; 2(13):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131030
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreira, Eurico Esteves, Burkhard Kuhlmann, João Gaspar, and Luis Alexandre Rocha. 2018. "Resonant Accelerometer based on Double-Ended Tuning Fork and a Force Amplification Mechanism" Proceedings 2, no. 13: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131030
APA StyleMoreira, E. E., Kuhlmann, B., Gaspar, J., & Rocha, L. A. (2018). Resonant Accelerometer based on Double-Ended Tuning Fork and a Force Amplification Mechanism. Proceedings, 2(13), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131030




