Zero-Cost Agricultural Wastes as Sources for Activated Carbons Synthesis: Lead Ions Removal from Wastewaters †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Activated Carbons by Hydrothermal Treatment
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
Equations (Isotherm, Kinetic, Thermodynamic)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations
3.2. Adsorption Evaluation
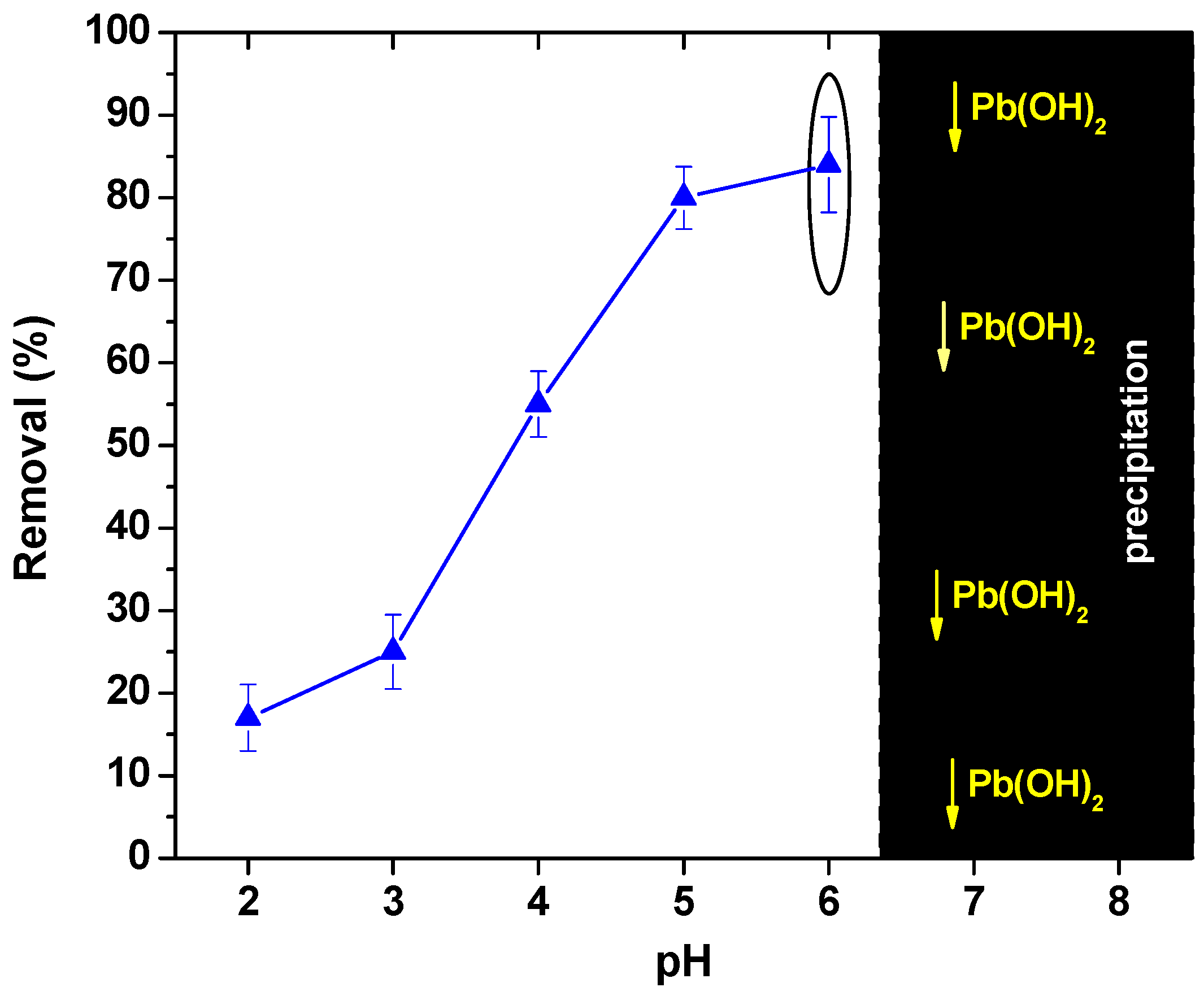
3.2.1. Effect of pH
3.2.2. Effect of Initial Pb(II) Concentration and Temperature
3.2.3. Thermodynamics
3.3. Cost-Effectiveness of Agricultural-Based Activated Carbons
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, W.H.; Mazlee, M.N.; Ahmad, Z.A.; Ishak, M.A.M.; Shamsul, J.B. The development of low cost adsorbents from clay and waste materials: A review. J. Mater. Cycle Waste Manag. 2017, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habineza, A.; Zhai, J.; Ntakirutimana, T.; Qiu, F.P.; Li, X.; Wang, Q. Heavy metal removal from wastewaters by agricultural waste low-cost adsorbents: Hindrances of adsorption technology to the large scale industrial application—A review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 78, 192–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, M.I.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zimmerman, A.; Mosa, A.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Cao, X. A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 406–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Kyzas, G.Z. Agricultural peels for dye adsorption: A review of recent literature. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 200, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z. Green Adsorbents; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kyzas, G.Z. Coffee wastes as adsorbents. In Agricultural Wastes: Characteristics, Types and Management; Foster, C.N., Ed.; NOC: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 215–229. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Wan, W.; Qian, K.; Xie, J. Constructing graphite-like carbon nitride modified hierarchical yolk-shell tio2 spheres for water pollution treatment and hydrogen production. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1806–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, A.; Khan, M.A.; Hameed, B.H.; AlOthman, Z.A.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Ahmed, A.Y.B.H.; Alsohaimi, I.H. Development of activated carbon from phoenix dactylifera fruit pits: Process optimization, characterization, and methylene blue adsorption. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 62, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottipati, R.; Mishra, S. Preparation of microporous activated carbon from aegle marmelos fruit shell and its application in removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous phase. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 36, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, F.S.; Amin, M.S. Adsorption of methylene blue by activated carbon derived from various fruit peels. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 22573–22584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Sabar, S.; Benhouria, A.; Khanday, W.A.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H. Nanoporous activated carbon prepared from karanj (Pongamia pinnata) fruit hulls for methylene blue adsorption. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Arshad, S.H.; Ngadi, N.; Aziz, A.A.; Amin, N.S.; Jusoh, M.; Wong, S. Preparation of activated carbon from empty fruit bunch for hydrogen storage. J. Energy Storage 2016, 8, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Kyzas, G.Z. Progress in batch biosorption of heavy metals onto algae. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Kyzas, G.Z. Composts as biosorbents for decontamination of various pollutants: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliyanni, E.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Matis, K.A. Activated carbons for the removal of heavy metal ions: A systematic review of recent literature focused on lead and arsenic ions. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z. A decolorization technique with spent “greek coffee” grounds as zero-cost adsorbents for industrial textile wastewaters. Materials 2012, 5, 2069–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z. Commercial coffee wastes as materials for adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Materials 2012, 5, 1826–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Deliyanni, E.A. Modified activated carbons from potato peels as green environmental-friendly adsorbents for the treatment of pharmaceutical effluents. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 97, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Deliyanni, E.A.; Lazaridis, N.K. Magnetic modification of microporous carbon for dye adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Deliyanni, E.A.; Matis, K.A. Activated carbons produced by pyrolysis of waste potato peels: Cobaltions removal by adsorption. Colloid Surf. A 2016, 490, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Karamesouti, M.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. A review for coffee adsorbents. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 229, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donia, A.M.; Atia, A.A.; Elwakeel, K.Z. Selective separation of mercury(II) using magnetic chitosan resin modified with schiff’s base derived from thiourea and glutaraldehyde. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Over the adsorption in solution. Z. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.M.; Van Ness, H.C. Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; Steele, P.H. Single, binary and multi-component adsorption of copper and cadmium from aqueous solutions on kraft lignin—A biosorbent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 297, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upendra, U.; Manas, M. Sorption of cadmium from aqueous solution using pretreated rice husk. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Kostoglou, M.; Lazaridis, N.K. Copper and chromium(VI) removal by chitosan derivatives-equilibrium and kinetic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 152, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Miguel, G.; Lambert, S.D.; Graham, N.J.D. The regeneration of field-spent granular-activated carbons. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, E.; González, E.; González, J.F.; González-Garcı́a, C.M.; Ramiro, A.; Gañan, J. Thermal regeneration of activated carbon saturated with p-nitrophenol. Carbon 2004, 42, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, P.M.; Beltrán, F.J.; Gómez-Serrano, V.; Jaramillo, J.; Rodrı́guez, E.M. Comparison between thermal and ozone regenerations of spent activated carbon exhausted with phenol. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.; Hawkes, F.R.; Hawkes, D.L.; Lourenco, N.D.; Pinheiro, H.M.; Delee, W. Colour in textile effluents—Sources, measurement, discharge consents and simulation: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1999, 74, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.W. Industrial Wastewater Treatment Technology, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]


| Langmuir Equation | Freundlich Equation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | T (°C) | Qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/g) | R2 (-) | KF (mg1−1/n L1/n g−1) | n (-) | R2 (-) |
| PAC | 20 | 217 | 0.01782 | 0.994 | 26.27 | 3.09 | 0.951 |
| 30 | 235 | 0.01778 | 0.992 | 28.28 | 3.07 | 0.952 | |
| 40 | 236 | 0.01965 | 0.991 | 30.53 | 3.17 | 0.954 | |
| 50 | 262 | 0.01819 | 0.991 | 31.45 | 3.06 | 0.964 | |
| Sample | C0 (mg/L) | T (K) | Qe (mg/g) | Kc | ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | ΔH0 (kJ/mol) | ΔS0 (kJ/mol K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAC | 10 | 293 | 9.32 | 13.29 | −6.30 | +13.82 | +0.068 |
| 303 | 9.41 | 15.67 | −6.93 | ||||
| 313 | 9.44 | 15.67 | −7.16 | ||||
| 323 | 9.65 | 24.00 | −8.54 | ||||
| 100 | 293 | 75.01 | 3.00 | −2.68 | +10.79 | +0.046 | |
| 303 | 78.23 | 3.55 | −3.19 | ||||
| 313 | 80.12 | 4.00 | −3.61 | ||||
| 323 | 82.34 | 4.56 | −4.07 | ||||
| 300 | 293 | 150.15 | 1.00 | 0.00 | +8.46 | +0.029 | |
| 303 | 161.17 | 1.14 | −0.34 | ||||
| 313 | 165.09 | 1.22 | −0.52 | ||||
| 323 | 175.81 | 1.40 | −0.90 | ||||
| 700 | 293 | 200.34 | 0.40 | 2.23 | +5.99 | +0.013 | |
| 303 | 221.31 | 0.46 | 1.97 | ||||
| 313 | 215.62 | 0.44 | 2.12 | ||||
| 323 | 240.24 | 0.52 | 1.75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kyzas, G.Z.; Mitropoulos, A.C. Zero-Cost Agricultural Wastes as Sources for Activated Carbons Synthesis: Lead Ions Removal from Wastewaters. Proceedings 2018, 2, 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110652
Kyzas GZ, Mitropoulos AC. Zero-Cost Agricultural Wastes as Sources for Activated Carbons Synthesis: Lead Ions Removal from Wastewaters. Proceedings. 2018; 2(11):652. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110652
Chicago/Turabian StyleKyzas, George Z., and Athanasios C. Mitropoulos. 2018. "Zero-Cost Agricultural Wastes as Sources for Activated Carbons Synthesis: Lead Ions Removal from Wastewaters" Proceedings 2, no. 11: 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110652
APA StyleKyzas, G. Z., & Mitropoulos, A. C. (2018). Zero-Cost Agricultural Wastes as Sources for Activated Carbons Synthesis: Lead Ions Removal from Wastewaters. Proceedings, 2(11), 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110652






