Treatment of Wastewater from the Confectionery Industry Using Pressure Membrane Processes †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
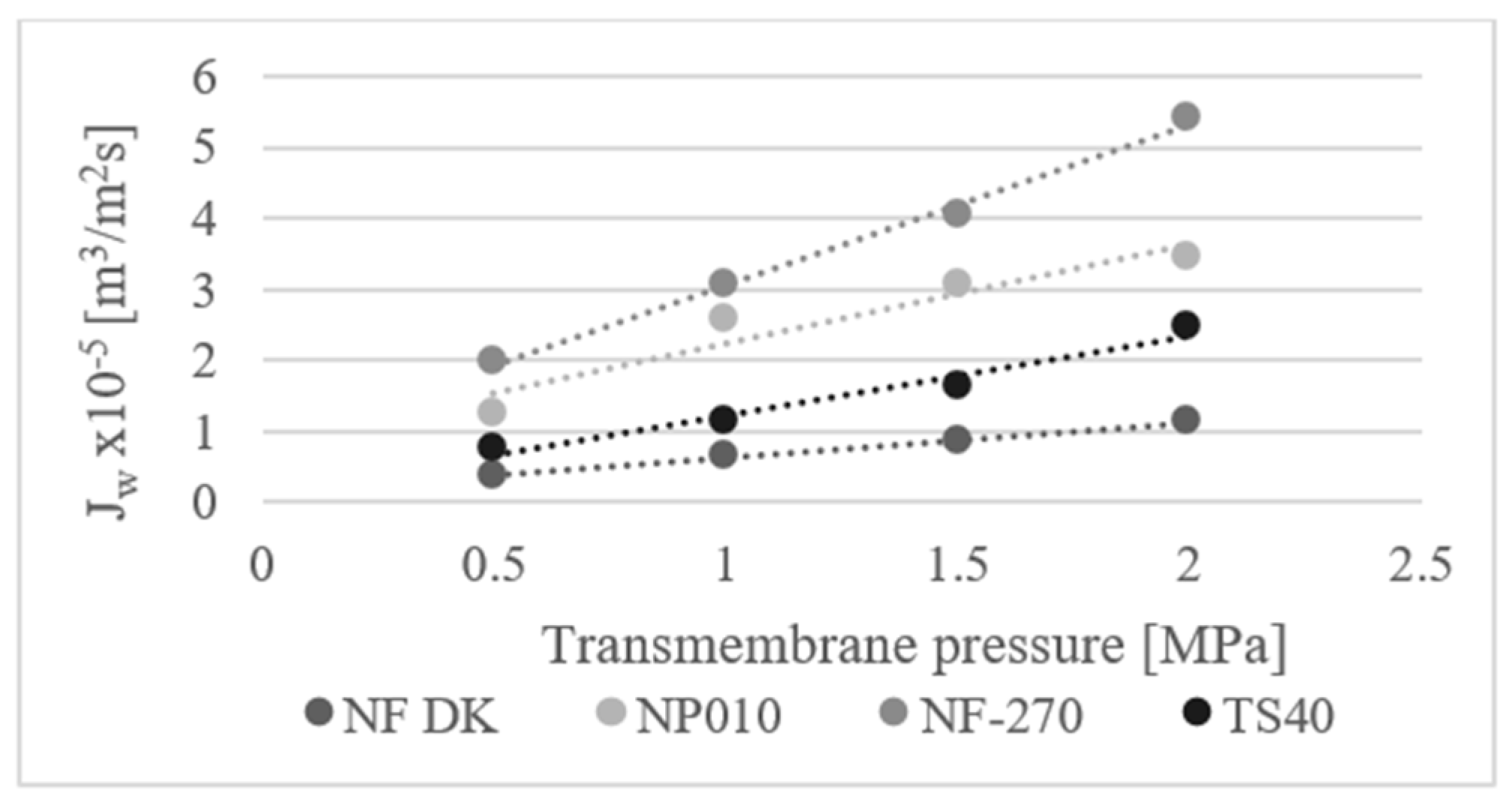
3. Results and Conclusions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abou-Elela, S.I.; Nasr, F.A.; El-Shafai, S.A. Wastewater management in small- and medium-size enterprises: Case studies. Environmentalist 2008, 28, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgun, H.; Karagul, N.; Dereli, R.K.; Ersahin, M.E.; Coskuner, T.; Ciftci, D.I.; Ozturk, I.; Altinbas, M. Confectionery industry: A case study on treatability-based effluent characterization and treatment system performance. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, O.P.; Chaudhari, P.K. Electrochemical treatment of sugar industry wastewater: COD and color removal. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 739, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzanowski, S.; Wałęga, A.; Paśmionka, I. Oczyszczanie ścieków z wybranych zakładów przemysłu spożywczego; Infrastruktura i ekologia terenów wiejskich: Kraków, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bunani, S.; Yörükoğlu, E.; Sert, G.; Yüksel, Ü.; Yüksel, M.; Kabay, N. Application of nanofiltration for reuse of municipal wastewater and quality analysis of product water. Desalination 2013, 315, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea-Corbacho, A.; Gutiérrez, S.; Quiroga, J.M. Removal of emerging contaminants from wastewater using nanofiltration for its subsequent reuse: Fullescale pilot plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, K.; Karunagaran, K.; Sharma, D.C. Recycling of wastewaters of textile dyeing industries using advanced treatment technology and cost analysis—Case studies. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2007, 50, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Sugar wastewater |
|---|---|
| COD (mg/L) | 8170 |
| BOD (mg/L) | 2600 |
| N-NO3− (mg/L) | 49.5 |
| N-NH4+ (mg/L) | 12 |
| P-PO43− (mg/L) | 17.4 |
| pH | 7.00 |
| Symbol | DK | TS40 | NF-270 | NP010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Producer | GE | Trisep | Dow Filmtec | Microdyn Nadir |
| Material | Polyamide skin layer | Amide polipiperazine | Polyamide skin layer | Polyethersulfone |
| MWCO (Da) | 150–300 | 200 | 200 | 1000 |
| pH | 2–10 | 2–11 | 2–10 | 0–14 |
| Parameter | Real wastewater | Wastewater after UF | Wastewater after NF |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD (mg/L) | 8170 | 8060 | 100.1 |
| BOD (mg/L) | 2600 | 1500 | 20 |
| N-NO3− (mg/L) | 49.5 | 49.5 | 18.3 |
| N-NH4+(mg/L) | 12 | 12 | 7 |
| P-PO4−3 (mg/L) | 17.4 | 6.2 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puszczało, E.; Marszałek, A. Treatment of Wastewater from the Confectionery Industry Using Pressure Membrane Processes. Proceedings 2019, 16, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019016027
Puszczało E, Marszałek A. Treatment of Wastewater from the Confectionery Industry Using Pressure Membrane Processes. Proceedings. 2019; 16(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019016027
Chicago/Turabian StylePuszczało, Ewa, and Anna Marszałek. 2019. "Treatment of Wastewater from the Confectionery Industry Using Pressure Membrane Processes" Proceedings 16, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019016027
APA StylePuszczało, E., & Marszałek, A. (2019). Treatment of Wastewater from the Confectionery Industry Using Pressure Membrane Processes. Proceedings, 16(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019016027




