Abstract
Whey proteins are highly valued food ingredients. This study examines the health benefits to muscle cells of six individual whey peptides known to cross the intestinal barrier. Results indicate that peptides KVPQ, NLPPL, VAGT, VGIN and PVPQ protect undifferentiated C2C12 myoblasts from free radical damage.
1. Introduction
By 2050, 22% of the global population approximately 2 billion people will be over 60. Frailty is a common aliment of the elderly and a large proportion of this cohort have considerable loss of sketelal muscle mass and function, impairing their mobility. Muscle loss can be reversed or delayed by a combination of dietary protein and exercise [1]. Bovine whey proteins (β-Lactoglobulin, α-Lactalbumin, Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) and Lactoferrin) are high quality proteins that contain all essential amino acids, are rich in branched chain amino acids, are noted for their bioactive peptides and are readily digested [2]. Branched chain amino acids play an essential role in muscle cell health not least of which includes metabolism, protein synthesis, mitochondrial biogenesis and redox balance [3]. There is a plethora of evidence from intervention trials that consumption of whey has positive benefits on muscle [4]. Recent studies in our laboratory have identified 31 peptides from whey capable of surviving the hydrolytic conditions of the upper gastrointestinal tract and crossing the intestinal barrier in vitro. Of these, 6 peptides (TKIPA, NLPPL, PVPQ, VGIN, VAGT and KVPQ) were selected for cellular assays with the murine myoblast cell line, C2C12. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of these 6 bioavailable whey peptides on cell growth and protection of C2C12 from free radical damage.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Arklow, Ireland) unless otherwise specified. The peptides TKIPA, NLPPL, PVPQ, VGIN, VAGT and KVPQ were synthesized and purified by the method previously described [5]. The murine myoblast cell line C2C12 (ATCC CRL-1772TM) was sourced from the American Type Culture Collection (Virginia, USA).
2.2. Cell Lines
C2C12 cells were grown to 80% confluency in a 75 cm2 tissue culture flask with Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) plus 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and antibiotics (100 U/mL penicillin and 100 µg/mL streptomycin) at 37 °C with 5% CO2. Experiments were performed at passage number 8–17.
2.3. Alamar Blue Assay
C2C12 were seeded at 8 × 104 cells/well in 96 well plates in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% antibiotics. Cells were incubated for 24 h. Cells were then washed twice with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and treated with 100 µL of each peptide (final concentration 2.5 mM or 5 mM). Cells were then incubated for a further 24 h. Alamar Blue reagent (10 µL) was added. The plate was incubated for 4 h at 37 °C. Absorbance was read at 570 nm and 600 nm, fluorescence excitation at 560 nm and emission at 590 nm. Controls included untreated cells with media alone and cells treated with leucine (final concentration 2.5 mM and 5 mM).
2.4. Cellular Antioxidant Activity
C2C12 were seeded at 8 × 104 cells/well in 96 well plates in DMEM plus 10% FBS and 1% antibiotics. After 24 h, cells were then washed with PBS. Cells were treated with 50 µL of each peptide (final concentration 2.5 mM or 5 mM, reconstituted in Hanks Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS)) and 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin di-acetate (DCFH-DA) (50 µL, final concentration 25 µM) for 1 h. Cells were then washed with PBS. 2,2′-azobis (2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride (ABAP) (100 µl final concentration 600 µM) was added. Fluorescence was read every minute for 1 h with excitation at 485 nm and emission at 535 nm. Cells treated with HBSS; and DCFH-DA (untreated) acted as the negative control. Another control included cells treated with free radical in the absence of peptides (Radical). N-acetylcysteine (NAC) (2.5 mM and 5 mM final concentration) acted as the positive control.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Cellular assays were performed three times on 2 different days. One way ANOVA using a Bonferroni’s comparison test was used to compare results using SigmaPlot software. P value < 0.5 determined statistical significance. Results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Alamar Blue
Six whey peptides present in the basolateral side of differentiated Caco2-HT-29 co-cultures, after exposure to gastrointestinal digested whey protein isolate, were selected for further investigation. Peptides TKIPA and VAGT were derived from β-Lactoglobulin, VGIN from α-Lactalbumin, NLPPL and KVPQ from BSA and PVPQ from β-casein. Each of the 6 peptides contained at least one branched chain amino acid. To investigate if these whey peptides promoted cell growth in muscle cells, undifferentiated C2C12 myoblasts were exposed to synthesized peptides at 2.5 mM and 5 mM concentration for 24 h and Alamar Blue test performed (Figure 1). Alamar Blue functions as a health indicator by using the reducing capacity of living cells to quantitatively measure cell proliferation. Only peptide VAGT (5 mM) significantly (p < 0.05) increased the growth of undifferentiated C2C12 compared to leucine at 2.5 mM. Peptides TKIPA (2.5 mM), NLPPL (2.5 mM and 5 mM), VGIN (2.5 mM) and KVPQ (5 mM) retarded growth compared to leucine at 2.5 mM and 5 mM (p < 0.05).

Figure 1.
Cell viability of C2C12 (8 × 104 cells/well) treated with synthesized peptides for 24 h, measured with the Alamar Blue assay. Experiments were performed in triplicate. Different letters indicate significant difference (p < 0.05).
3.2. Protection against Free Radicals
To investigate if the peptides protected undifferentiated C2C12 myoblasts from free radicals, free radical ABAP was added to C2C12 pretreated with synthesized peptides (Figure 2). Data indicates that the peptides KVPQ (5 mM), NLPPL (5 mM), VAGT (5 mM), VGIN (5 mM) and PVPQ (5 mM) were as effective as N-acetylcysteine (5 mM) at inhibiting the free radical in C2C12 cells compared to radical control (p < 0.05). In contrast, peptide TKIPA (2.5 mM or 5 mM) did not provide a protective effect.
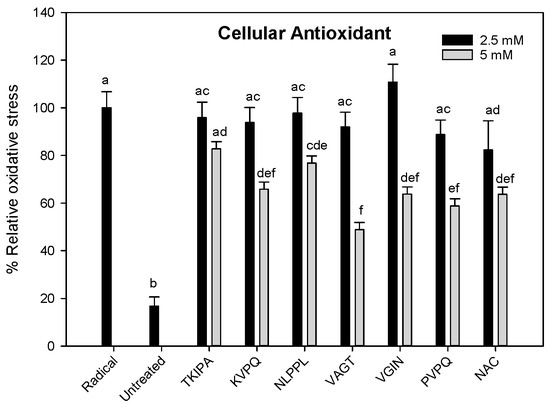
Figure 2.
Relative oxidative stress in C2C12 (8 × 104 cells/well) after 1 h exposure to synthesized peptides. Radical = cells treated with DMEM + DCFH-DA + ABAP, Untreated = cells treated with DMEM + DCFH-DA, NAC = cells treated with DMEM + N-acetylcysteine + DCFH-DA + ABAP. Experiments were performed in triplicate. Different letters indicate significant difference (p < 0.05).
Results indicate that 5 of the 6 peptides protect C2C12 from free radicals. In agreement, other studies have demonstrated that peptides or hydrolysates from whey have positive effects on redox balance [6,7]. However it is important to note that there are some limitations to our study namely, the peptide concentrations used are not physiological, C2C12 cells are not differentiated nor do they represent an ageing muscle. It would therefore be prudent to repeat these assays with a range of antioxidant markers (GSH, catalase), a panel of cell metabolic biomarkers and using differentiated and ageing C2C12 cells.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, drafting, analysis and funding, N.O.B and L.G.; methodology, drafting and analysis, S.G., E.A. and S.K.
Funding
This work was funded by Teagasc Project MDBY0015. Sarah Gilmartin is in receipt of a Teagasc Walsh Fellowship.
Acknowledgments
This work is based upon work from COST Action NutRedOx-CA16112 supported by COST (European Cooperation in Science and Technology).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Naseeb, M.A.; Volpe, S.L. Protein and exercise in the prevention of sarcopenia and aging. Nutr. Res. 2017, 40, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrochano, A.R.; Arranz, E.; De Noni, I.; Stuknyte, M.; Ferraretto, A.; Kelly, P.M.; Buckin, V.; Giblin, L. Intestinal health benefits of bovine whey proteins after simulated gastrointestinal digestion. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 49, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, A.; D’Antona, G.; Nisoli, E. Branched-chain amino acids, mitochondrial biogenesis, and healthspan: An evolutionary perspective. Aging-Us 2011, 3, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, R.W.; Bass, J.J.; Carson, B.P.; Norton, C.; Kozior, M.; Brook, M.S.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Atherton, P.J.; Smith, K.; Jakeman, P.M. The Effect of whey protein supplementation on the recovery of contractile function following resistance training. Med. Sci. Sport Exer. 2018, 50, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarga, T.; Aluko, R.E.; Rai, D.K.; O’Connor, P.; Hayes, M. Identification of bioactive peptides from a papain hydrolysate of bovine serum albumin and assessment of an antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Res. Int. 2016, 81, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrochano, A.R.; Buckin, V.; Kelly, P.M.; Giblin, L. Invited review: Whey proteins as antioxidants and promoters of cellular antioxidant pathways. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4747–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basilicata, M.G.; Pepe, G.; Adesso, S.; Ostacolo, C.; Sala, M.; Sommella, E.; Scala, M.C.; Messore, A.; Autore, G.; Marzocco, S.; et al. Antioxidant properties of buffalo-milk dairy products: A beta-Lg peptide released after gastrointestinal digestion of buffalo ricotta cheese reduces oxidative stress in intestinal epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).