Abstract
Caffeine is an alkaloid belonging to the methylated xanthine family. It is found in various foods of plant origin, including tea leaves, guarana berries, and coffee beans. Due to its stimulating effect on the central nervous system and the associated increase in alertness and reduction in tiredness, caffeine is specifically added to some foods, such as food supplements. Claims about the positive physiological effects of caffeine are health claims within the definition of the European Union (EU) Health Claims Regulation and must be authorised before use. Despite a positive opinion from the European Food Safety Authority, regulation of the authorisation of caffeine claims was rejected due to a veto by the European Parliament. As a result, health claims are currently not regulated for caffeine in all EU member states, and the transitional on-hold status also no longer applies for most claims. Therefore, products with health claims regarding caffeine are still observed within the context of governmental food-control activities. To investigate how these are currently used on the market, internet research (n = 188) was carried out. The sample included foods that naturally contain caffeine or to which it is frequently added, namely coffee, tea, non-alcoholic soft drinks and mixed drinks, as well as food supplements, including sports nutrition products. Furthermore, the labelling of official samples that were conspicuous in relation to caffeine in the years 2019–2023 (n = 136) was included in the evaluation. The products most frequently advertised with unregulated health claims for caffeine were food supplements (31% of 135 products). On the other hand, health claims were least frequently used for coffee (4% of 77 products) and tea (18% of 33 products). For all product groups, health claims were mainly made regarding improved concentration and performance/energy. The individual effects the health claims referred to differed between the product groups. In the case of coffee and tea, the advertised effects are mainly limited to increased energy and performance in the form of a “kick” or “boost”. A wider range of different health claims are used for food supplements and alcohol-free beverages, including claims relating to stamina and alertness. In general, the tendency was observed for health claims to be advertised more frequently on the internet than on the product labelling itself. This study exposes a critical issue: while scientific evidence supports some health claims for caffeine, they still remain unregulated, complicating enforcement and creating public confusion. Prompt regulatory revision is needed to align these claims with scientific validations, ensuring both accuracy and regulatory compliance.
1. Introduction
Caffeine is an alkaloid from the methylated xanthine family and occurs naturally in various foods of plant origin such as tea, guarana, and coffee. Due to its stimulating effect on the central nervous system and the associated increase in alertness and reduction in the feeling of tiredness, caffeine is also deliberately added to some foods [1]. In the European Union (EU), claims about the physiological effects of caffeine are treated as so-called health claims within the definition of Regulation (EC) No. 1924/2006 (Health Claims Regulation) [2]. These claims must be approved prior to use on food labels or in advertising. Despite a positive opinion from the European Food Safety Authority, the approval regulation for four caffeine claims was withdrawn due to a veto by the European Parliament. The primary reason for the rejection was the concern that the use of health claims about caffeine would encourage the consumption of energy drinks by adolescents, which are characterised by high levels of both sugar and caffeine [3]. Indeed, the presence of health claims regarding caffeine and the declaration of caffeine content may encourage consumption [4]. For example, the average caffeine intake via natural sources from coffee and tea is already very high, estimated at about 240 mg per day for German consumers [5]. This is already more than half of the 400 mg/day considered safe by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) for healthy adults [1]. In a small proportion of young adults (less than 5%), the maximum recommended caffeine intake is consistently exceeded [6], so there might be some justification for the standpoint of the European Parliament not to further decrease the safety margin with health-based advertising.
At present, no health claims for caffeine are approved, and most of the transitional measures for certain on-hold health claims no longer apply. As products with caffeine health claims had repeatedly come into focus in the course of previous official food control measures, an internet search was carried out to investigate how these are currently used on the market. Samples examined for official control purposes, which were conspicuous in connection with caffeine analytically and/or in the labelling, were also retrospectively taken into account.
2. Materials and Methods
In the search for products with health claims related to caffeine, the product categories beverages and food supplements, including sports nutrition, were considered. Within beverages, the focus was on coffee, tea, non-alcoholic soft drinks, and mixed drinks, as these often contain caffeine.
The research was conducted exclusively online, employing both a targeted and a non-targeted search strategy. In the targeted search strategy, well-known brands associated with caffeine were examined for the presence of health claims. In order to achieve this, the websites of the brands were searched for any caffeine-related claims. In the event that the brands in question did not possess their own website with an online store, the search was conducted on retailer websites. In certain instances, the manufacturers themselves advertised sales on alternative platforms, such as by using hyperlinks. In the non-targeted search strategy, caffeine health claims and product categories were searched for individually or in combination in various search engines. The objective was to identify brands with lower sales, in order to ensure that they would not be overlooked due to the limited awareness of them. In the event of conspicuous hits, the product groups and/or the associated brands were subjected to further examination.
Furthermore, the CVUA Karlsruhe laboratory information system (LIMS) database was queried to identify samples that were analysed for caffeine and were objected to in relation to caffeine between the years 2019 and 2023. The labelling of those samples was subsequently reviewed with a view to identify any health claims regarding caffeine. In order to achieve this, both the archived product images and the websites that were saved at the time of the sampling were subjected to examination.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Prevalence of Caffeine Health Claims across Product Categories
Within the product groups evaluated, health claims for caffeine were most frequently used for food supplements, including those intended for sports nutrition, and beverages (Figure 1). Among the internet products evaluated, food supplements were significantly more affected (63%) than beverages, where the proportion of products with health claims for caffeine was 38%. In the food supplements and beverages analysed for caffeine between the years 2019 and 2023 (n = 136), the proportion of samples advertised with health claims was similar in both product groups at 15% and 19%, respectively.
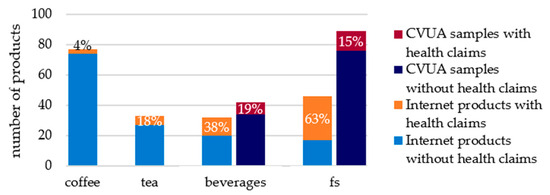
Figure 1.
Percentage of samples evaluated for caffeine health claims. fs: food supplements.
For coffee and tea, health claims for caffeine were less common. Among internet products (n = 188), 18% of tea products and 4% of coffee products were promoted with health claims. Between 2019 and 2023, only one coffee and four tea samples of the CVUA samples analysed for caffeine were objected to in relation to caffeine. The number of samples was too small to make a representative statement. Therefore, those samples were not evaluated for health claims.
3.2. Distribution of Caffeine Health Claims: Product Labels vs. Websites
In the internet samples where the product label was fully visible on the internet pages, it is notable that health claims were more frequently stated exclusively on the websites (14%) than exclusively on the products (8%); see Figure 2. In 78% of the products, health claims regarding caffeine were advertised on the product itself and on the websites. It can be concluded that websites serve as a significant platform for the promotion of products with health claims.
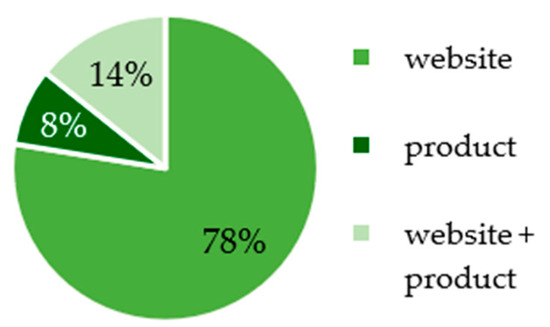
Figure 2.
Placement of advertising with health claims for caffeine in the products from the internet search.
3.3. Categories and Frequency of Caffeine-Related Health Claims
The health claims relating to caffeine can be differentiated according to the type of health claim in question. The relative proportions of the identified categories of health claims per product group are illustrated in Figure 3. In the case of coffee and tea products, health claims are predominantly employed to promote energy (33% of health claims for coffee products, 46% for tea products) and energy-related parameters, such as a “kick” or “boost” (33% of health claims for coffee products, 15% for tea products). A greater variety of health claims are identified in the advertising of beverages and food supplements, which are represented in similar proportions. In the case of beverages, the largest proportion of health claims relate to energy, accounting for 25% of all claims. In the case of food supplements, the largest proportion of health claims relate to concentration and focus, accounting for 17% of all claims. In the case of tea products, beverages, and food supplements, health claims were also made that do not fall into the areas of concentration, performance, or energy. These claims extend beyond the scientifically confirmed effects of caffeine, such as the promotion of fat burning.
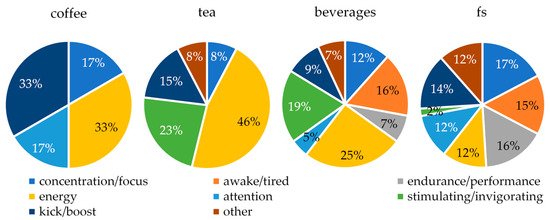
Figure 3.
Types of health claims for caffeine identified in the products evaluated. fs: food supplements.
3.4. Evaluation of the “On-Hold” Status of Caffeine Health Claims
The objective of the Health Claims Regulation is to establish a unified legal framework for nutrition and health claims within the EU, with the aim of protecting consumers from misleading or false claims. The positive nutritional or physiological effects must be proven for all nutrition and health claims on the basis of generally recognised scientific evidence. In consequence of the considerable number of health claims submitted by the Member States that were required to be evaluated by EFSA, a list was compiled in 2012 comprising more than 2000 health claims on botanicals. The aforementioned health claims may continue to be used under certain conditions as on-hold claims under the purview of the food business operators until a final decision is made regarding their status. The use of the claims is contingent upon compliance with the Health Claims Regulation and national provisions. The evaluation of further health claims for botanicals has been temporarily halted [7].
On-hold claims must comply with the requirements set forth by the Health Claims Regulation, as outlined in Article 28(5). In particular, the evidence must be based on generally accepted scientific principles. It is the responsibility of the food business operator to prove their case. In accordance with the ruling of the Court of Justice of the EU on 10 September 2020 (C-363/19), the food business operator may rely on the evidence contained within the dossiers submitted to EFSA [8]. Therefore, a positive assessment by EFSA, such as for the claims ‘caffeine contributes to an increase in endurance performance’ and ‘caffeine contributes to an increase in endurance capacity’, may be used as evidence of beneficial effects. On the other hand, claims with a negative opinion from EFSA will be placed on the non-authorised list and the on-hold status will no longer apply [9].
In accordance with Article 28(6) of the Health Claims Regulation, health claims regarding psychological and behavioural functions and claims regarding slimming or weight-control or a reduction in the sense of hunger (Article 13(1) b and c) may only be used as on-hold claims if their use was permitted prior to the entry into force of the Health Claims Regulation, or if an application was made before 19 January 2008. It is necessary to consider the legislation of the individual countries. Prior to the Health Claims Regulation, there were no health claims in accordance with Article 13(1) b and c that were permitted in Germany. Consequently, the on-hold status does not apply to health claims with a psychological function reference or for weight reduction in Germany, because the transitional period for these health claims under Article 28(6) of the Health Claims Regulation has expired.
Taking into account the requirements for the authorisation of health claims and the utilisation of the on-hold status, the authors agree with Meyer and Baumgärtner [3] and Sadler [9,10] that the claims about physical performance may still be on hold, while the authors do not agree that the mental performance claims are still on hold. This illustrates the lack of clarity surrounding the categorisation of health claims that have been placed on hold. Therefore, the Appendix A Table A1 presents a comprehensive list of all health claims pertaining to caffeine, accompanied by their status within the EU register, the information whether they were rejected, and the status of the evaluation conducted by the EFSA. Additionally, the authors have provided their assessment of whether they consider the claim to be still on hold (last column of Table A1).
3.5. Comparison to Previous Studies
In 2015, a total of 43 food supplements and sports nutrition products containing caffeine were evaluated. At that time, 5 of the 17 (12%) objected samples were objected to due to deficiencies in relation to unauthorised health claims in general [11]. The proportion of complaints is comparable to the proportion of food supplements with caffeine health claims in the samples from 2019 to 2023 (15%). It should be noted that only the claims ‘caffeine contributes to an increase in endurance performance’ and ‘caffeine contributes to an increase in endurance capacity’ are potentially permitted as on-hold.
4. Conclusions
Despite the legal uncertainty surrounding the use of health claims relating to caffeine in advertising, such claims are frequently used for the promotion of numerous products. Such claims are employed with greater frequency in the case of products containing added caffeine than in the case of products naturally containing caffeine. The type of health claims made vary according to the product group. In the context of distance selling, health claims are employed with greater frequency on websites than on the product itself.
Although some caffeine health claims are scientifically supported, they are still not regulated, which makes them difficult to communicate and enforce under food law. The considerable number of caffeine claims identified in the products under review, coupled with the wide range of different types of claims, indicates that this is a prevalent advertising strategy, despite the absence of regulatory approval. A prompt revision of European regulations is required to guarantee a high level of consumer protection based on scientifically validated and approved caffeine claims.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ICC2024-18172/s1, poster file (in PDF format) presented at ICC 2024.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, D.W.L.; methodology, Y.K. and K.S.; formal analysis, K.H., V.K., Y.K. and K.S.; investigation, K.H., V.K., Y.K. and K.S.; data curation, K.H., V.K., Y.K. and K.S.; writing—original draft preparation, K.H. and V.K.; writing—review and editing, D.W.L., V.B., A.-K.K., Y.K. and K.S.; visualisation, K.H. and V.K.; supervision, D.W.L., V.B. and A.-K.K.; project administration, D.W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The laboratory teams of the plant-based foods and beverages departments at CVUA Karlsruhe are thanked for excellent technical assistance. The authors would like to acknowledge the assistance of DeepL (https://www.deepl.com/) for providing support in German-English translation and English language improvement.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Overview of Health Claims Related to Caffeine and Caffeine-Containing Foods in the EU Register and the Open European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Database, Including Their Current Status (as of 26 June 2024).
Table A1.
Overview of Health Claims Related to Caffeine and Caffeine-Containing Foods in the EU Register and the Open European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Database, Including Their Current Status (as of 26 June 2024).
| EFSA Question No. | EFSA Opinion Ref. | ID EU Register/Dossier No. | Nutrient Substance, Food, or Food Category | Claim 1 | Status EU Register [12] | Status Per EU Regulation | Status Open EFSA (Positive/Negative Opinion) [13] | Status On-Hold 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q-2008-2221 | [14] | 1484 | Caffeine | Contributes to the mobilisation of fat stores. Contributes to the stimulation of fat release. Helps to increase fat burning. Contributes to the oxidation of stored fats. Helps generate a negative energy balance. Contributes to increased calorie burning. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-2226 | [15] | 1489 | Caffeine | Enhances physical performance. Provides a performance edge. Can delay the onset of fatigue. Can increase exercise intensity/work rate. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-2224 | [14] | 1487 | Caffeine | Caffeine can increase resting metabolic rate. Caffeine supports thermogenesis and energy oxidation. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2013-00399 | [16] | 0393_UK | Caffeine | Caffeine helps to increase alertness (>40 mg, <75 mg). 3 | non-authorised | EU Regulation 2016/1411 [12] | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-1522 | [14] | 735 | Caffeine (from tea/coffee/chocolate or added in pure form) | Contributes to the mobilisation of fat stores. Contributes to the stimulation of fat release. Helps to increase fat burning. Contributes to the oxidation of stored fats. Helps generate a negative energy balance. Contributes to increased calorie burning. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-1524 Q-2008-2223 | [15] | 737, 1486 | Caffeine (from tea/coffee/chocolate or added in pure form) | Improves physical performance. 4 EFSA proposed wording: Caffeine contributes to an increase in endurance performance. | non-authorised | n/a | published (positive) | possibly on hold 6 |
| Q-2008-1330 | [17] | 543 | Caffeine and carbohydrate | Helps increase carbohydrate availability during endurance exercise. Combination of caffeine and carbohydrate improves endurance performance. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-2764 | [18] | 2031 | CoffeeSLENDER® tablets made from an extract from green coffee beans (Svetol®) the active principle of which is: 5-caffeoylquinic acid (chlorogenic acid) = 45%, caffeine = 2%, 3- caffeoylquinic acid = 10% | As an aid to weight loss and weight control as part of a calorie-controlled diet. Acts by reducing absorption of sugar (glucose) from the digestive tract. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-2533 | [19] | 1800 | Epigallocatechin gallate (ECGC) + caffeine | Increases burning of calories. Stimulates your metabolism to burn calories. Stimulates your body to enhance the calorie burning process. Stimulates your metabolism. Three servings per day have been shown to increase calorie burning by approximately 106 calories. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-2668 | [20] | 1935 | L-Theanine | Caffeine antagonist. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-1400 | [21] | 613 | Taurine | It supports proper metabolism (uptake of glucose/caffeine). | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-3884 | [18] | 3152 | Coffee | Antioxidants in coffee helps protect our cells against free radicals. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-1838 | [18] | 1099 | Coffee | Coffee is a major dietary source of antioxidants. Antioxidants from dietary sources: protect you from free radicals. Protect your cells and tissues from oxidation. Antioxidants help strengthen our body’s natural defences against oxidative stress. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-1839 | [18] | 1100 | Coffee | Coffee contributes to healthy blood glucose levels. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2011-00783 | [22] | n/a | Coffee C21 | Regular consumption of Coffee C21 contributes to the maintenance of DNA integrity in cells of the body. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2014-00624 | [23] | n/a | Coffee C21 (coffee standardised by its content of caffeoylquinic acids, trigonelline, and N-methylpyridinium) | Regular consumption of Coffee C21 contributes to the maintenance of DNA integrity in cells of the body. | non-authorised | EU Regulation 2016/1411 [12] | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2019-00423 | [24] | 0487_DE | Coffee C21, a blend of pure Arabica roast coffees (Coffea arabica L.) without any non-coffee ingredients | Regular consumption of Coffee C21 contributes to the maintenance of DNA integrity in cells of the body. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2010-00254 | [18] | 4301 | Coffee, not covered by specific food legislation | Coffee naturally contains antioxidants that may support the body’s natural cell defences. Coffee is a major dietary source of antioxidants. Antioxidants from dietary sources: protect from free radicals, which cause cell damage. Protects body tissues, lipids, cells and DNA from oxidative damage. Help strengthen the body’s natural defences against oxidative stress. | non-authorised | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-2225 | [15] | 1488 | Caffeine | Supports exercise performance (reduction in perceived exertion, improve time to exhaustion and exercise capacity). 4 EFSA proposed wordings: Caffeine contributes to an increase in endurance capacity. Caffeine contributes to a reduction in the rated perceived exertion/effort during exercise. | not listed | n/a | published (positive) | possibly on-hold 6 |
| Q-2008-2228 | [14] | 1491 | Caffeine (with or without carbohydrates) | Enhances mental performance. Enhances focus, alertness and concentration. Enhances reaction time. Stay sharper for longer. 5 EFSA proposed wordings: Caffeine helps to increase alertness. Caffeine helps to improve concentration. | not listed | n/a | published (positive) | no 7 |
| Q-2008-2222 | [14] | 1485 | Caffeine (from tea/coffee/chocolate or added in pure form) | Contributes to mental performance. Helps maintain and improve alertness. Aids concentration. Helps make you feel more energetic. Helps revive you. Helps keep you alert. 5 EFSA proposed wordings: Caffeine helps to increase alertness. Caffeine helps to improve concentration. | not listed | n/a | published (positive) | no 7 |
| Q-2008-1926 | [14] | 1187 | Coffee drink/caffeine | Coffee helps you stay alert. Coffee invigorates. | not listed | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-2227 | [15] | 1490 | Caffeine (with or without carbohydrates) | Reduces the perception of effort. 5 EFSA proposed wording: Caffeine contributes to a reduction in the rated perceived exertion/effort during exercise. | not listed | n/a | published (positive) | no 7 |
| Q-2008-1523 | [14] | 736 | Caffeine (from tea/coffee/chocolate or added in pure form) | Contributes to mental performance. Helps maintain and improve alertness. Aids concentration. Helps make you feel more energetic. Helps revive you. Helps keep you alert. Helps improve how you feel. 5 EFSA proposed wordings: Caffeine helps to increase alertness. Caffeine helps to improve concentration. | not listed | n/a | published (positive) | no 7 |
| Q-2008-1840 | [14] | 1101 | Coffea arabica L. and other spp. (common name: coffee) | Cognitive and physical performance. | not listed | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-4914 | n/a | 4204 | Food supplement green tea extract rich in EGCG, vitamin C, caffeine, carnitine | Helps to slim body by fat burning. | not listed | n/a | application withdrawn | no |
| Q-2008-4913 | n/a | 4203 | Food supplement green tea extract rich in EGCG, vitamin C, caffeine, carnitine | Helps promote thermogenic effect. | not listed | n/a | application withdrawn | no |
| Q-2008-1908 | n/a | 1169 | Energy drinks containing 0.032% caffeine, 0.4% taurine, and 0.24% glucuronolactone | Contains natural caffeine to stimulate your mind. Delivers fresh physical energy while enhancing performance, endurance and concentration. | not listed | n/a | application withdrawn | no |
| Q-2008-2010 | [25] | 1272 | Caffeinated carbohydrate containing energy drinks | Enhances mental performance, reaction time, alertness, focus, and memory. Energises. Gives you an energy boost. Enhances mental energy. Enhances alertness quickly. | not listed | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2010-00376 | n/a | 4423 | Ilex paraguariensis-mate-leaves | Invigorating action due to polyphenols, catechins, theobromine, caffeine, and mate content. 5 | not listed | n/a | intake | no 7 |
| Q-2008-1843 | [20] | 1104 | Camelia sinensis (common name: tea) | Tea helps refresh body and mind. Tea helps to revive you. Tea helps keeping you alert. | not listed | n/a | published (negative) | no |
| Q-2008-2871 | n/a | 2138 | standardised Guarana extract PC102 Dry extract from seeds of Paullinia cupana H. B. et Kunth, drug-to-native extract ratio (4.5–7):1, solvent of extraction ethanol/water, 11.0–13.0% caffeine | For mental performance. 5 | not listed | n/a | intake | no 7 |
| Q-2010-00487 | n/a | 4534 | Cassia angustifolia folium, Camellia sinensis folium (senna leaves, tea bush leaves) | Maintain weight control because of anthraquinone, catechins, polyphenols and caffeine, constituents present in this plants combination. 5 | not listed | n/a | intake | no 7 |
| Q-2008-4915 | n/a | 4205 | Food supplement green coffee extract rich in chlorogenic acids, vitamin B8, chromium, green tea extract | Helps promote weight loss. | not listed | n/a | application withdrawn | no |
| Q-2008-1944 | n/a | 1206 | Food supplement of plants (meadowsweet, birch, green tea, green coffee, yerba mate), concentrated fruits juices, and pectin | Three-in-one slimming action, adopt the slimming action, relax. Specially formulated for those who wish to refine their thighs, cuts and hips. Product plants: Meadowsweet and birch support the hydric elimination of the kidneys. Green tea helps in weight control. Yerba mate is traditionally used to contribute to lipid degradation. | not listed | n/a | application withdrawn | no |
Abbreviations: EGCG, epigallocatechin gallate; n/a, not available; EU, European Union; EFSA, European Food Safety Authority. 1 Submitted wording. 2 Judgment based on the authors’ expert opinion and interpretation of available data, considering commentaries for classification of claims according to Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 [26,27]. 3 The caffeine content was too low for substantiation of the health claim. 4 Health claim within the definition of Article 13(1)(a) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 related to the role of a nutrient or substance in bodily functions (authors’ judgement). 5 Health claim within the definition of Article 13(1)(b) and (c) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 related to psychological functions and weight management (authors’ judgement). 6 Transitional measures for certain on-hold health claims under Article 28(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, potentially possible pending further review. 7 Transitional period for these health claims under Article 28(6) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 has expired as neither the Member States’ communication of claims by 31 January 2008, nor the Commission’s subsequent decision-making process, were completed as stipulated; additionally, there were no national provisions for caffeine-related claims for psychological functions and weight management in Germany prior to the regulation’s entry into force.
References
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Safety of Caffeine. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 2006 on Nutrition and Health Claims Made on Foods. Off. J. Europ. Union 2006, L404, 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, A.H.; Baumgärtner, K. Koffein–Health Claims. Weiter “on Hold”–Geht’s Noch! Dtsch. Lebensm. Rundsch. 2017, 113, 171–173. [Google Scholar]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Winkler, G. Caffeine Content Labeling: A Prudent Public Health Policy? J. Caffeine Res. 2013, 3, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maixner, S.; Plato, L.; Mahler, M.; Ruge, W.; Lachenmeier, D. Koffein in Nahrungsergänzungsmitteln und Sportlernahrung–eine unterschätzte Aufnahmequelle? Aktuel. Ernahrungsmed. 2016, 41, P42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Wegert, K.; Kuballa, T.; Schneider, R.; Ruge, W.; Reusch, H.; Alexy, U.; Kersting, M.; Winkler, G. Caffeine Intake from Beverages in German Children, Adolescents, and Adults. J. Caffeine Res. 2013, 3, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbrüster, N. Health Claims für Lebensmittel—Was geschieht mit den Botanicals? Z. Phytother. 2020, 41, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voß, L. “Claims on hold”—EuGH äußert sich zur Beweislast. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/claims-hold-eugh-äußert-sich-zur-beweislast-meyer-rechtsanwalts-gmbh/ (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Sadler, M. Regulatory Developments with European Health Claims. In Foods, Nutrients and Food Ingredients with Authorised EU Health Claims: Volume 2; Sadler, M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition: Number 286; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–27. ISBN 978-1-78242-382-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sadler, M.J. European Health Claims: Regulatory Developments. In Foods, Nutrients and Food Ingredients with Authorised EU Health Claims; Sadler, M.J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1–16. ISBN 978-0-08-100922-2. [Google Scholar]
- Plato, L.; Lachenmeier, D.; Maixner, S.; Mahler, M.; Ruge, W. Koffein in Nahrungsergänzungsmitteln Und Sportlernahrung—Eine Unterschätzte Aufnahmequelle. Available online: https://www.ua-bw.de/pub/beitrag_printversion.asp?subid=2&Thema_ID=2&ID=2212&Pdf=No&lang=DE (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- European Commission. Food and Feed Information Portal Database (FIP). Health Claims. EU Register. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/food-feed-portal/screen/health-claims/eu-register (accessed on 14 July 2024).
- EFSA. Open EFSA. Available online: https://open.efsa.europa.eu (accessed on 14 July 2024).
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of Health Claims Related to Caffeine and Increased Fat Oxidation Leading to a Reduction in Body Fat Mass (ID 735, 1484), Increased Energy Expenditure Leading to a Reduction in Body Weight (ID 1487), Increased Alertness (ID 736, 1101, 1187, 1485, 1491, 2063, 2103) and Increased Attention (ID 736, 1485, 1491, 2375) Pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of Health Claims Related to Caffeine and Increase in Physical Performance during Short-Term High-Intensity Exercise (ID 737, 1486, 1489), Increase in Endurance Performance (ID 737, 1486), Increase in Endurance Capacity (ID 1488) and Reduction in the Rated Perceived Exertion/Effort during Exercise (ID 1488, 1490) Pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of a Health Claim Related to Caffeine and Increased Alertness Pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/20061. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion Part II on the Substantiation of Health Claims Related to Various Food(s)/Food Constituent(s) Not Supported by Pertinent Human Data (ID 406, 462, 472, 543, 659, 678, 696, 858, 1381, 1403, 1437, 1438, 1513, 1536, 1537, 1538, 1539, 1540, 1543, 1613, 1627, 1855, 1860, 1981, 2126, 2514, 3127, 4038, 4501, 4672, 4712, 4718) Pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of Health Claims Related to Coffee, Including Chlorogenic Acids from Coffee, and Protection of DNA, Proteins and Lipids from Oxidative Damage (ID 1099, 3152, 4301), Maintenance of Normal Blood Glucose Concentrations (ID 1100, 1962), and Contribution to the Maintenance or Achievement of a Normal Body Weight (ID 2031, 4326) Pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of Health Claims Related to Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) in Combination with Caffeine, and Contribution to the Maintenance or Achievement of a Normal Body Weight (ID 1800) Pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of Health Claims Related to L-Theanine from Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze (Tea) and Improvement of Cognitive Function (ID 1104, 1222, 1600, 1601, 1707, 1935, 2004, 2005), Alleviation of Psychological Stress (ID 1598, 1601), Maintenance of Normal Sleep (ID 1222, 1737, 2004) and Reduction of Menstrual Discomfort (ID 1599) Pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of Health Claims Related to Taurine and “Immune System Protection” (ID 611), “Metabolism Processes” (ID 613), Contribution to Normal Cognitive Function (ID 1659), Maintenance of Normal Cardiac Function (ID 1661), Maintenance of Normal Muscle Function (ID 1949) and Delay in the Onset of Physical Fatigue during Exercise (ID 1958) Pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of a Health Claim Related to Coffee C21 and Reduction of Spontaneous DNA Strand Breaks Pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of a Health Claim Related to Coffee C21, a Coffee Standardised by Its Content of Caffeoylquinic Acids, Trigonelline and N-Methylpyridinium, and Reduction of DNA Damage by Decreasing Spontaneous DNA Strand Breaks Pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition; Novel foods and Food Allergens (NDA); Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Ildico Hirsch-Ernst, K.; Kearney, J.; Knutsen, H.K.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; et al. Coffee C21 and Protection of DNA from Strand Breaks: Evaluation of a Health Claim Pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of Health Claims Related to: Flavonoids and Ascorbic Acid in Fruit Juices, Including Berry Juices (ID 1186); Flavonoids from Citrus (ID 1471); Flavonoids from Citrus Paradisi Macfad. (ID 3324, 3325); Flavonoids (ID 1470, 1693, 1920); Flavonoids in Cranberry Juice (ID 1804); Carotenoids (ID 1496, 1621, 1622, 1796); Polyphenols (ID 1636, 1637, 1640, 1641, 1642, 1643); Rye Bread (ID 1179); Protein Hydrolysate (ID 1646); Carbohydrates with a Low/Reduced Glycaemic Load (ID 476, 477, 478, 479, 602) and Carbohydrates Which Induce a Low/Reduced Glycaemic Response (ID 727, 1122, 1171); Alfalfa (ID 1361, 2585, 2722, 2793); Caffeinated Carbohydrate-Containing Energy Drinks (ID 1272); and Soups (ID 1132, 1133) Pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte-Salinas, N.; Konnertz-Häußler, C. Gesundheitsbezogene Angaben zu psychischen Funktionen oder Verhaltensfunktionen, VO (EG) 1924/2006, Art. 13, Rn. 31-36. In Health-Claims-Verordnung: HCVO; Holle, M., Hüttebräuker, A., Konnertz-Häußler, C., Conte-Salinas, N., Guttau, T., Eds.; C.H. Beck oHG: Munich, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rathke, K.-D.; Hahn, A. Psychische und Verhaltensfunktionen, VO (EG) 1924/2006, Art. 13, Rn. 24, 25. In Lebensmittelrecht; Sosnitza, O., Meisterernst, A., Eds.; C.H. Beck oHG: Munich, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).