LED-Based Tomographic Imaging for Live-Cell Monitoring of Pancreatic Islets in Microfluidic Channels †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
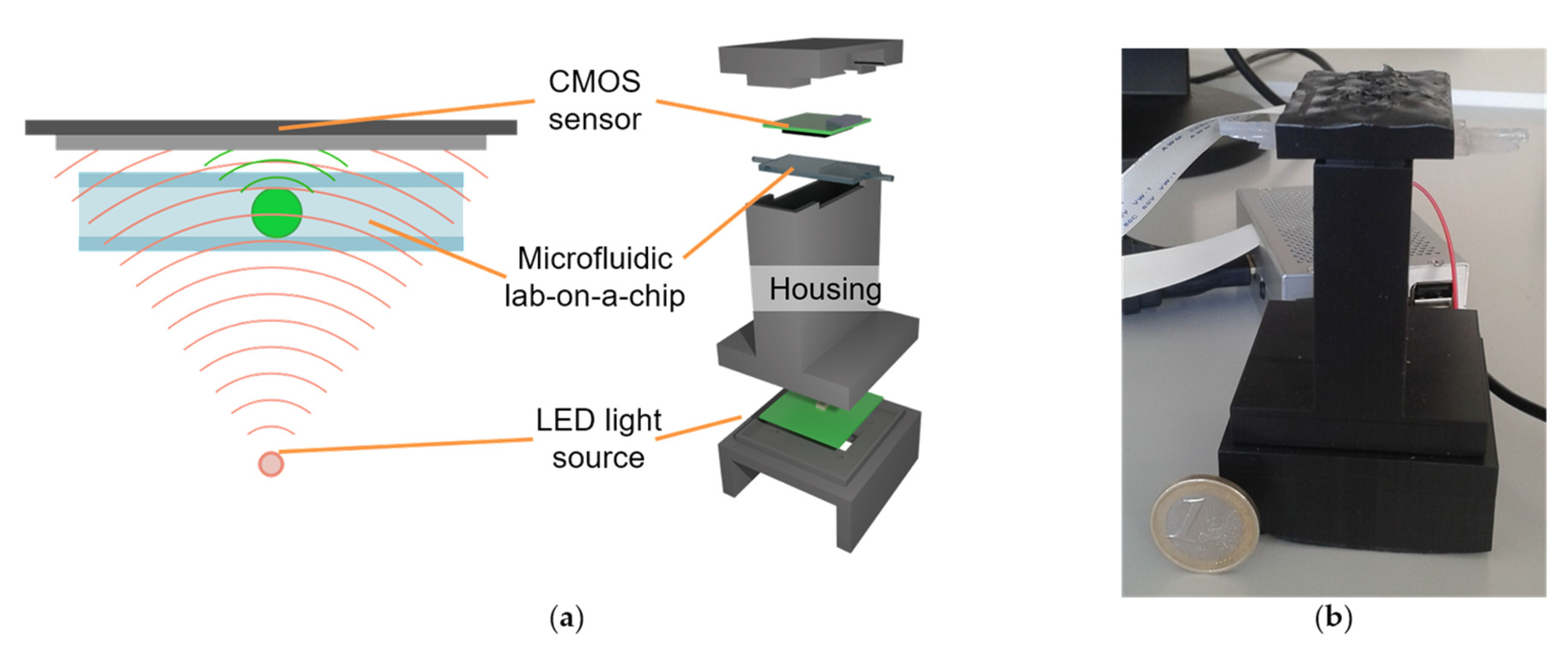
2.1. Digital Holographic Microscope
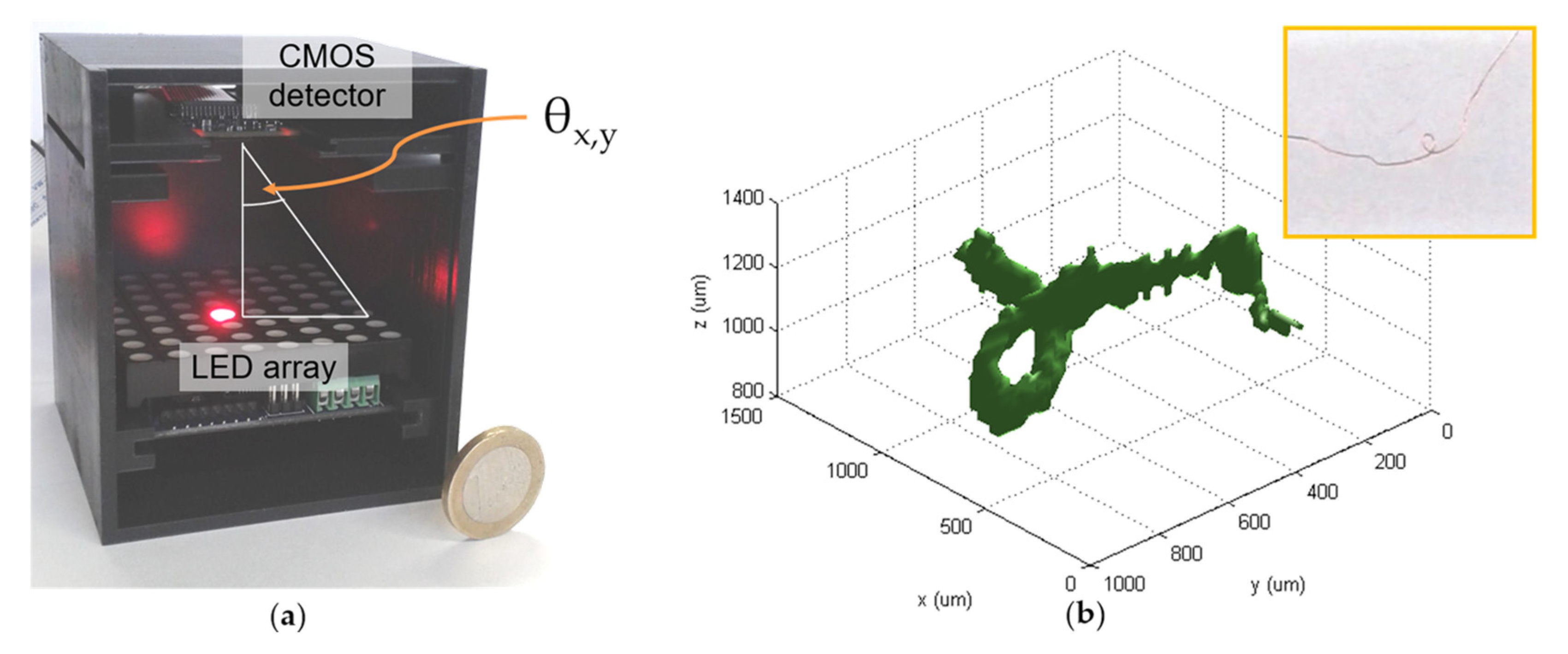
2.2. Optical Tomographic 3D Microscope
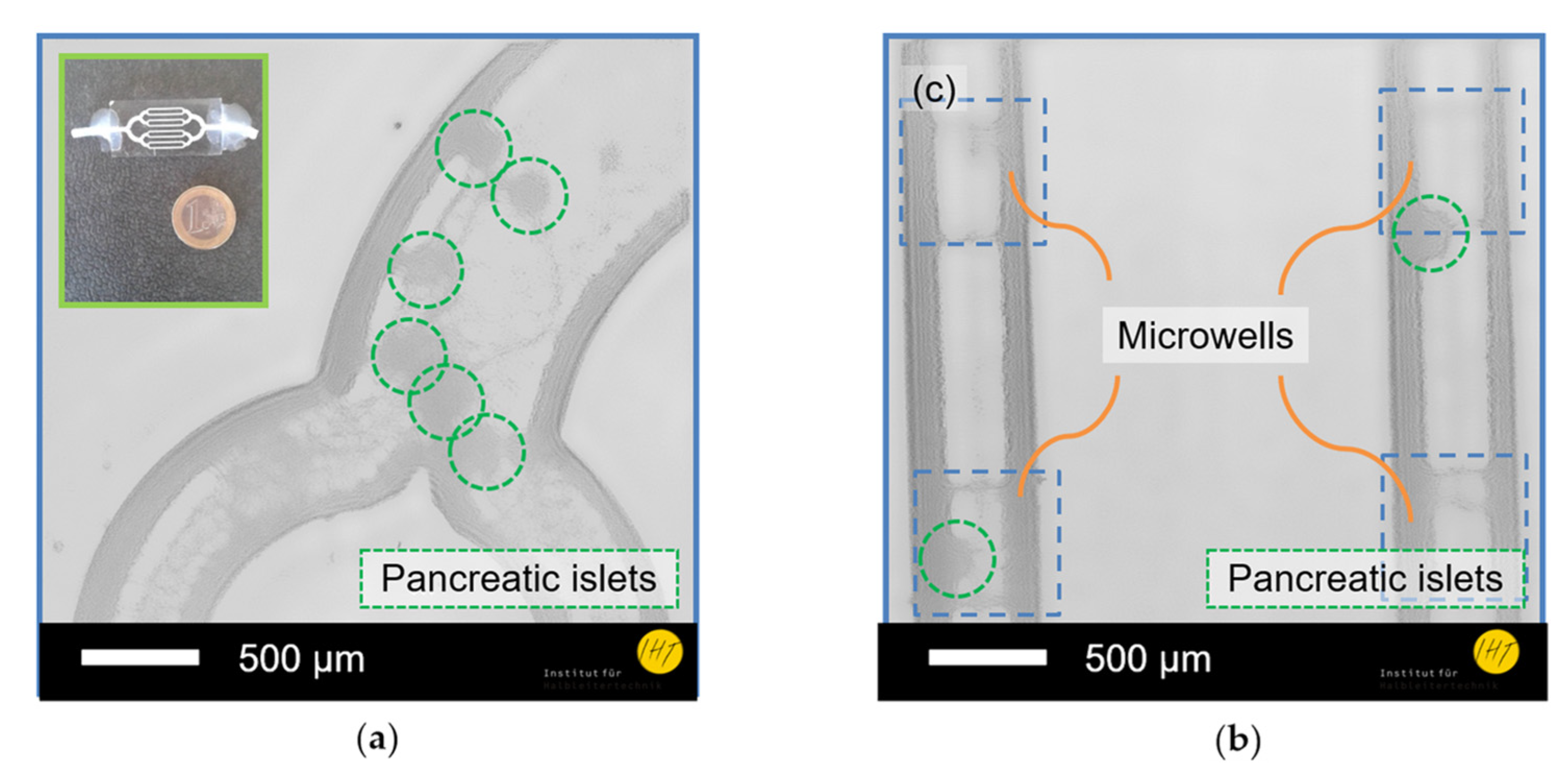
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaw, J.E.; Sicree, R.A.; Zimmet, P.Z. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 87, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, F.M.; Rorsman, P. Diabetes Mellitus and the β Cell: The Last Ten Years. Cell 2012, 148, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak, A.; Cohrs, C.M.; Tsata, V.; Chouinard, J.A.; Selck, C.; Stertmann, J.; Reichelt, S.; Rose, T.; Ehehalt, F.; Weitz, J.; et al. Using pancreas tissue slices for in situ studies of islet of Langerhans and acinar cell biology. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2809–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, T.; Mattern, K.; Früh, E.; Hecht, L.; Rustenbeck, I.; Dietzel, A. A 3D microfluidic perfusion system made from glass for multiparametric analysis of stimulus-secretioncoupling in pancreatic islets. Biomed. Microdevices 2017, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latychevskaia, T.; Fink, H.-W. Practical algorithms for simulation and reconstruction of digital in-line holograms. Appl. Opt. 2014, 54, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latychevskaia, T.; Fink, H.-W. Solution to the Twin Image Problem in Holography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 233901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.; Nehmetallah, G.; Banerjee, P.P. Digital tomographic compressive holographic reconstruction of three-dimensional objects in transmissive and reflective geometries. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, T.; Morsi, M.; Reckers, K.; Brüning, D.; Seemann, N.; Panten, U.; Rustenbeck, I. Metabolic amplification of insulin secretion is differentially desensitized by depolarization in the absence of exogenous fuels. Metabolism 2017, 67, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scholz, G.; Xu, Q.; Schulze, T.; Boht, H.; Mattern, K.; Hartmann, J.; Dietzel, A.; Scherneck, S.; Rustenbeck, I.; Prades, J.D.; et al. LED-Based Tomographic Imaging for Live-Cell Monitoring of Pancreatic Islets in Microfluidic Channels. Proceedings 2017, 1, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040552
Scholz G, Xu Q, Schulze T, Boht H, Mattern K, Hartmann J, Dietzel A, Scherneck S, Rustenbeck I, Prades JD, et al. LED-Based Tomographic Imaging for Live-Cell Monitoring of Pancreatic Islets in Microfluidic Channels. Proceedings. 2017; 1(4):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040552
Chicago/Turabian StyleScholz, Gregor, Qifeng Xu, Torben Schulze, Heidi Boht, Kai Mattern, Jana Hartmann, Andreas Dietzel, Stephan Scherneck, Ingo Rustenbeck, Joan Daniel Prades, and et al. 2017. "LED-Based Tomographic Imaging for Live-Cell Monitoring of Pancreatic Islets in Microfluidic Channels" Proceedings 1, no. 4: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040552
APA StyleScholz, G., Xu, Q., Schulze, T., Boht, H., Mattern, K., Hartmann, J., Dietzel, A., Scherneck, S., Rustenbeck, I., Prades, J. D., Fündling, S., Wasisto, H. S., & Waag, A. (2017). LED-Based Tomographic Imaging for Live-Cell Monitoring of Pancreatic Islets in Microfluidic Channels. Proceedings, 1(4), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040552





