Abstract
In this work, we investigate the effect of HNO3 anodizing solution concentration ranging from 1.5 to 3 M on H2-sensing performance of 2D WO3 nanostructures prepared by anodizing sputtered tungsten films. The thickness of WO3 nanosheets was found to reduce while the crystallinity degraded with increasing HNO3 concentration. However, the nanosheets anodized in 2 M HNO3 exhibited the highest response of 43.4 to 1 vol % H2, which was one order of magnitude larger than those fabricated with other concentrations at the optimal operating temperature of 350 °C. In addition, the optimal nanostructures displayed good H2 selectivity against NO2, CH4, C2H2 and C2H5OH.
1. Introduction
Two-dimensional (2D) nanostructures of metal oxides, particularly ultrathin nanosheets, have recently attracted substantial attention in gas-sensing applications due its large specific surface area, 2D-quantum effects and unique electronic properties [1,2,3,4,5]. Recently, 2D tungsten oxide (WO3) nanosheets have been fabricated by a facile anodization method and demonstrated promising gas-sensing performance [5]. It is thus compelling to further optimize its performance by varying anodization parameters. In this work, 2D WO3 nanostructures were prepared by anodization of sputtered tungsten (W) films with varying concentrations of HNO3 anodizing solution and systematically characterized for gas-sensing towards hydrogen.
2. Materials and Methods
Firstly, 1 µm-thick W films were deposited on alumina substrates by radio-frequency (rf) sputtering in Ar at 2.6 × 10−3 Torr with an rf power of 100 W. The W films were then anodized in HNO3 solutions with different concentrations ranging from 1.5 to 3.0 M at 60 °C. An anode voltage of 50 V was applied between the W film and Pt wire for 5 h. Next, Cr/Au intergitated electrodes were sputtered onto the WO3 film on alumina substrates. Lastly, the sensors were annealed in air at 450 °C for 3 h. The annealed material was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD).
Gas sensing tests have been carried out by the flow through method in a sealed stainless steel chamber with controlled temperature and humidity with the setup reported earlier [6]. Dry air certified bottles have been used as gas source and certified mass flow controllers to reproduce desired gaseous composition inside the test chamber. The sensors were tested toward hydrogen (H2) at 200–350 °C. Nitrogen dioxide (H2), methane (CH4), acetylene (C2H2) and ethanol (H2) were also tested as possible interfering species.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Results
Typical morphology of anodized WO3 films as shown in Figure 1 illustrates polygonal sheet structures having small thickness of below 50 nm. In addition, it was found that the thickness of nanosheets tended to reduce with increasing HNO3 concentration. XRD patterns (Figure 2) confirm that the anodized films are nanocrystalline with reducing grain size and crystallinity as HNO3 concentration increases.
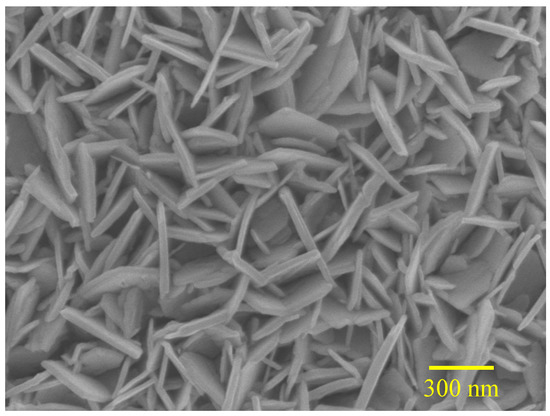
Figure 1.
Typical SEM image of 2D WO3 nano-structures prepared by anodization with 2 M HNO3.
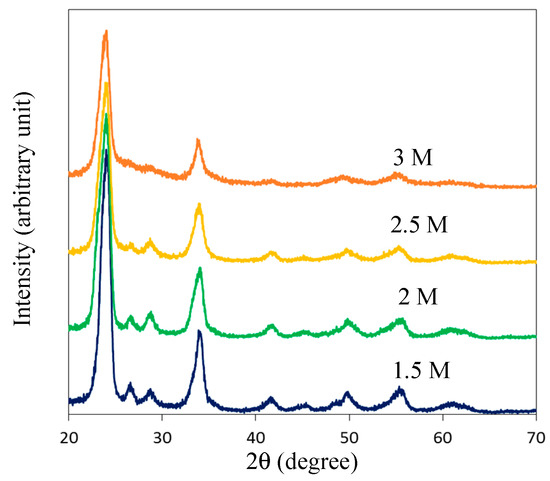
Figure 2.
Typical XRD patterns of 2D WO3 nanostructures prepared by anodization with different HNO3 concentrations.
3.2. Gas-Sensing Results
Gas-sensing results towards various concentrations (0.015–1 vol %) of H2 in Figure 3 showed that 2D WO3 nanosheets exhibit typical n-type sensing behaviors with large resistance change at an optimal HNO3 concentration of 2 M. The response variations as functions of concentration and temperature as demonstrated in Figure 4 and Figure 5 shows that the 2D WO3 nanosheets prepared in 2 M HNO3 exhibited the highest response of 43.4 to 1 vol % H2 at the optimal operating temperature of 350 °C, which was more than one order of magnitude larger than those anodized with other HNO3 concentrations. Moreover, the optimal 2D WO3 nanosheets displayed good H2 selectivity against NO2, CH4, C2H2 and C2H5OH as displayed in Figure 6. The results might be ascribed to the moderate HNO3 concentration that leads to optimally etched 2D WO3 nanostructures with large surface area and good crystallinity.
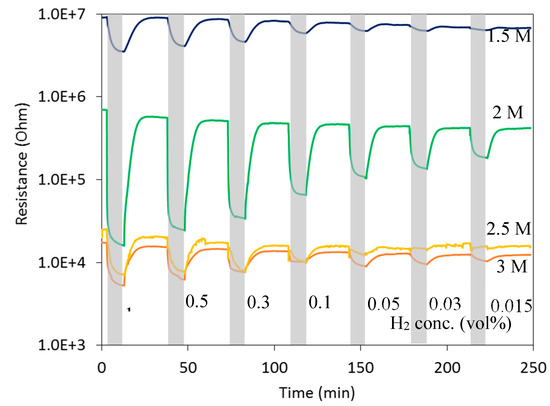
Figure 3.
Resistance vs. time of 2D WO3 nano-structures prepared by anodization with different HNO3 concentrations subjected to various H2 pulses at 350 °C.
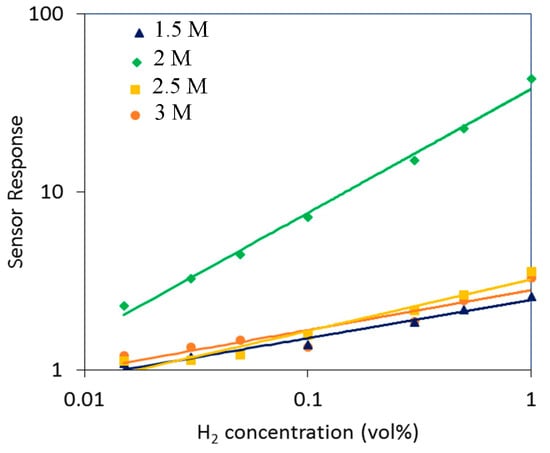
Figure 4.
Response vs. H2 concentration of 2D WO3 nanostructures prepared by anodization with different HNO3 concentrations at 350 °C.
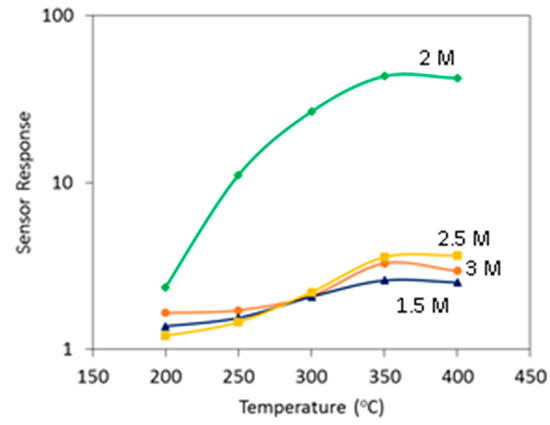
Figure 5.
Response vs. operating temperature of 2D WO3 nanostructures prepared by anodization with different HNO3 concentrations at 1 vol % H2.
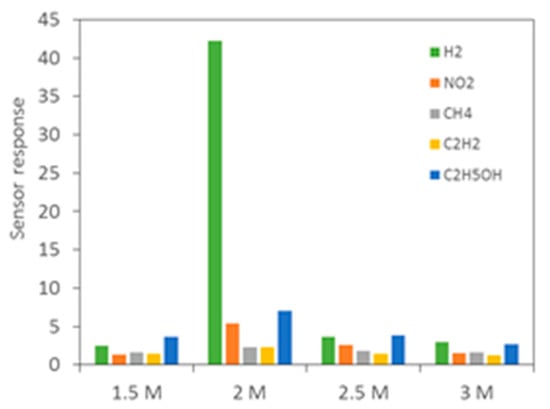
Figure 6.
Selectivity histogram of 2D WO3 nanostructures prepared by anodization with different HNO3 concentrations at 1 vol %.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, 2D WO3 nanostructures prepared by anodizing sputtered tungsten films and the effect of HNO3 anodizing solution concentration ranging from 1.5 to 3 M on H2-sensing performance were systematically investigated. SEM and XRD analyses indicate that the thickness of WO3 nanosheets tended to reduce while the crystallinity degraded with increasing HNO3 concentration. However, the nanosheets anodized in 2 M HNO3 exhibited the highest response of 43.4 to 1 vol % H2, which was one order of magnitude larger than those fabricated with other concentrations at the optimal operating temperature of 350 °C. Moreover, the optimal nanostructures displayed good H2 selectivity against NO2, CH4, C2H2 and C2H5OH.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
References
- Alsaif, M.M.Y.A.; Field, M.R.; Daeneke, T.; Chrimes, A.F.; Zhang, W.; Carey, B.J.; Berean, K.J.; Walia, S.; van Embden, J.; Zhang, B.; et al. Exfoliation Solvent Dependent Plasmon Resonances in Two-Dimensional Sub-Stoichiometric Molybdenum Oxide Nanoflakes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3482–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balendhran, S.; Walia, S.; Alsaif, M.; Nguyen, E.P.; Ou, J.Z.; Zhuiykov, S.; Sriram, S.; Bhaskaran, M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Field Effect Biosensing Platform Based on 2D α-MoO3. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9753–9760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaif, M.M.Y.A.; Chrimes, A.F.; Daeneke, T.; Balendhran, S.; Bellisario, D.O.; Son, Y.; Field, M.R.; Zhang, W.; Nili, H.; Nguyen, E.P.; et al. High-Performance Field Effect Transistors Using Electronic Inks of 2D Molybdenum Oxide Nanoflakes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.B.; Mishra, R.K.; Sahay, P.P. Structural and alcohol response characteristics of Sn-doped WO3 nanosheets. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Sadek, A.Z.; Zheng, H.; Bansal, V.; Bhargava, S.K.; Wlodarski, W.; Zhu, J.; Yu, L.; Hu, Z. Nanostructured WO3 films using high temperature anodization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 142, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horprathum, M.; Srichaiyaperk, T.; Samransuksamer, B.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Eiamchai, P.; Limwichean, S.; Chananonnawathorn, C.; Aiempanakit, K.; Nuntawong, N.; Patthanasettakul, V.; et al. Ultrasensitive Hydrogen Sensor Based on Pt-Decorated WO3 Nanorods Prepared by Glancing-Angle dc Magnetron Sputtering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22051–22060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).