Greater Application of Nitrogen to Soil and Short-Term Fumigation with Elevated Carbon Dioxide Alters the Rhizospheric Microbial Community of xTriticocereale (Triticale): A Study of a Projected Climate Change Scenario
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
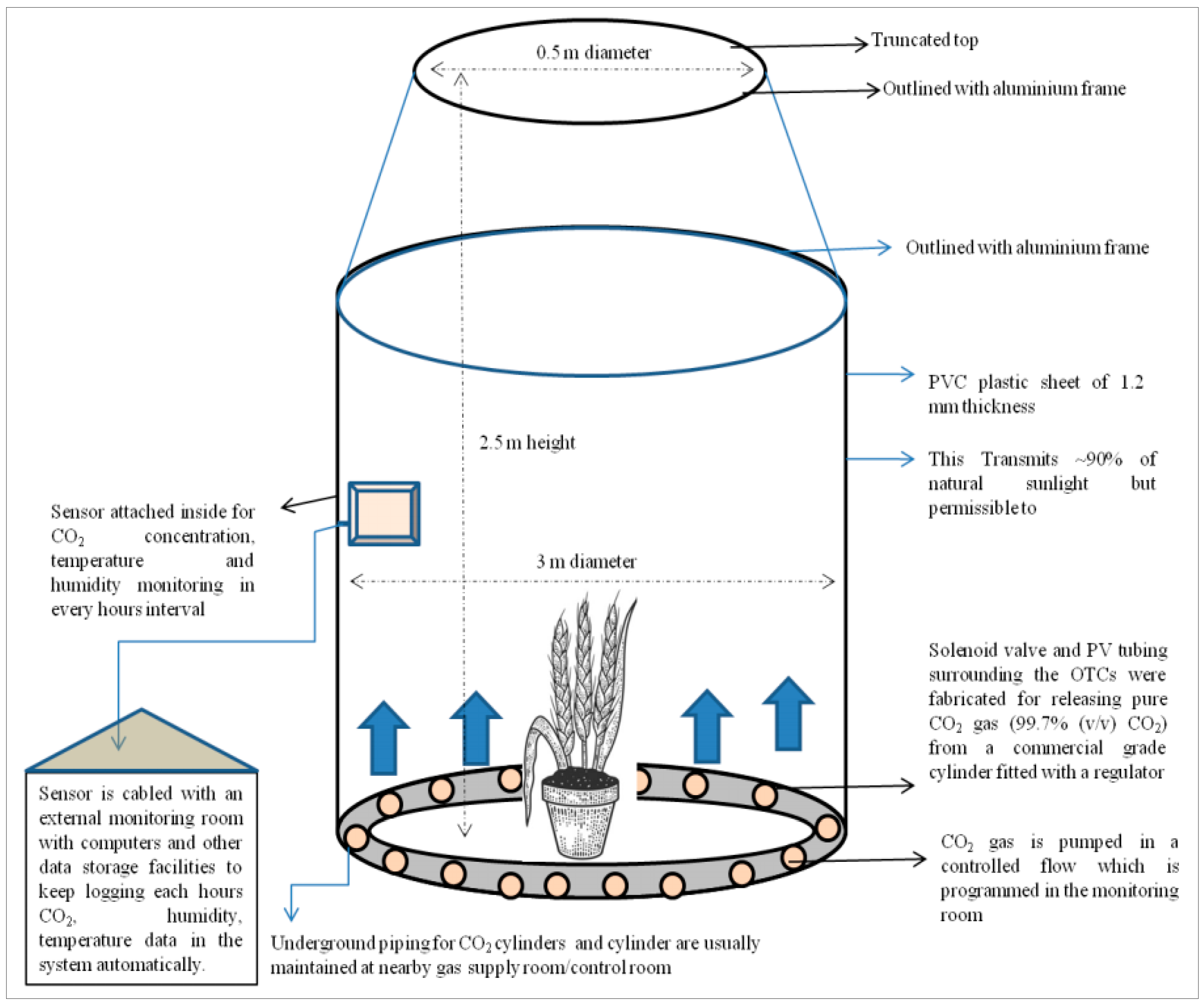
2.2. Open-Top Chamber Experiment Details
2.3. Crop Management and Treatments
2.4. Soil Sampling
2.5. Soil Microbial Composition/Structural Analysis UsingPhospholipid Fatty Acid (PLFA) Composition and Content
2.6. Shannon–Weiner Diversity Index (H’)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
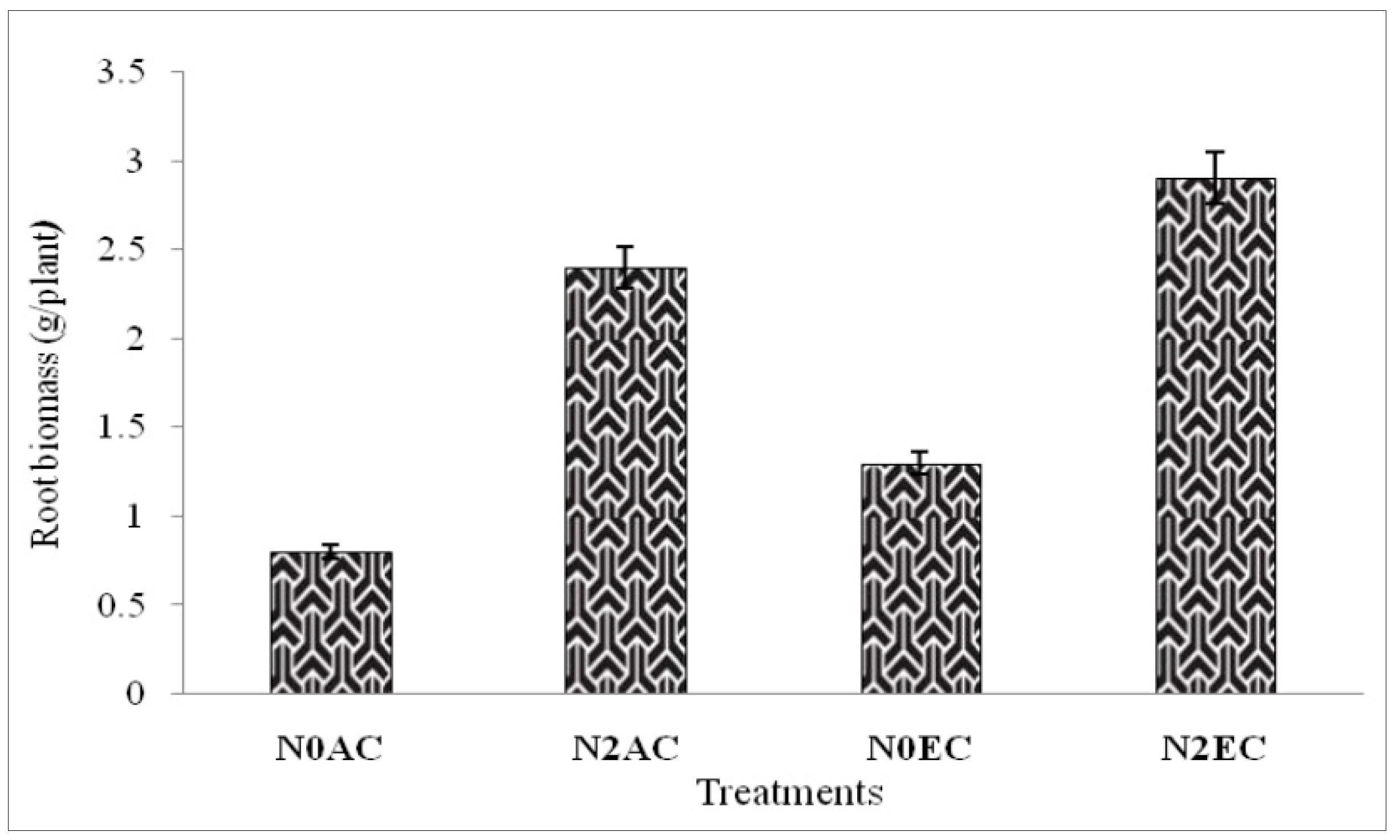
3. Results
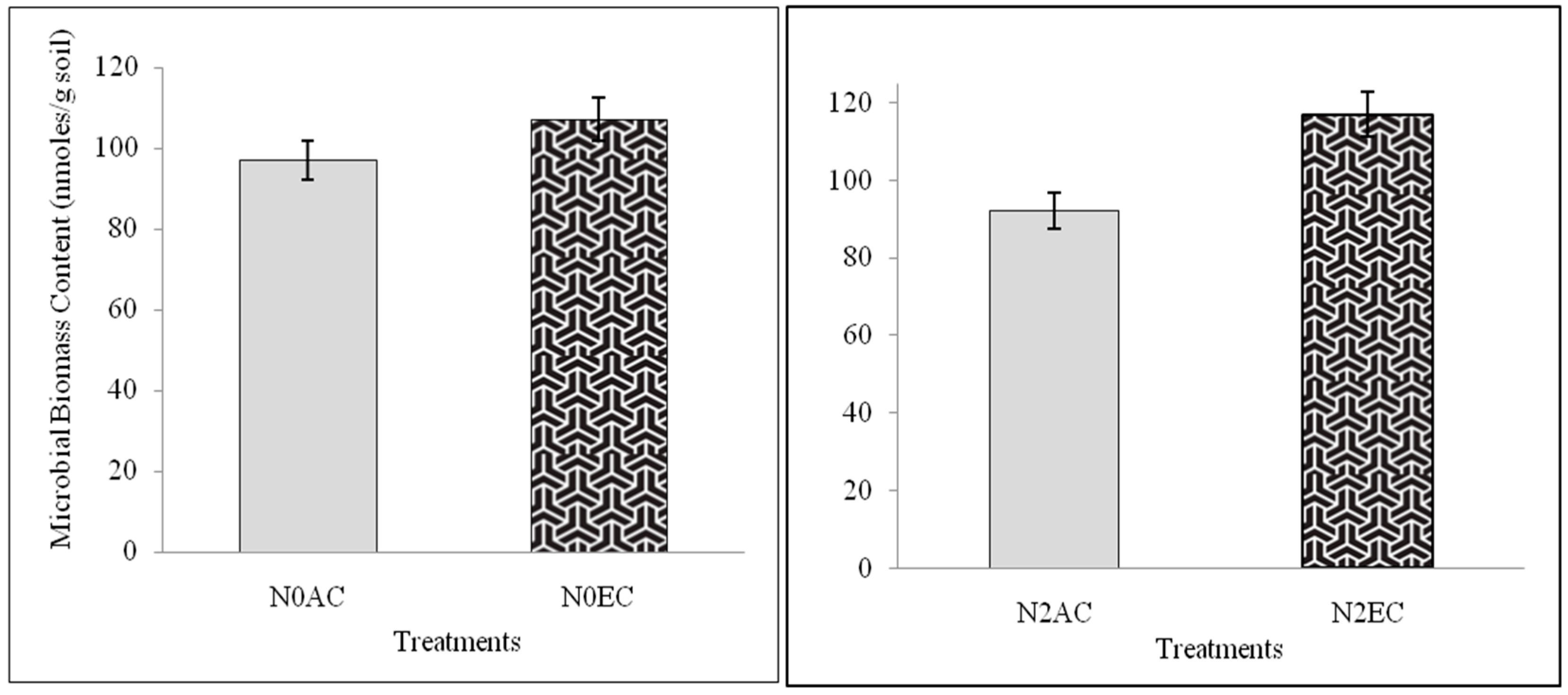
3.1. Microbial Biomass Content (MBC) During CO2 Enrichment and Differential Doses of Nitrogen Application Experiment of xTriticocereale (Triticale)
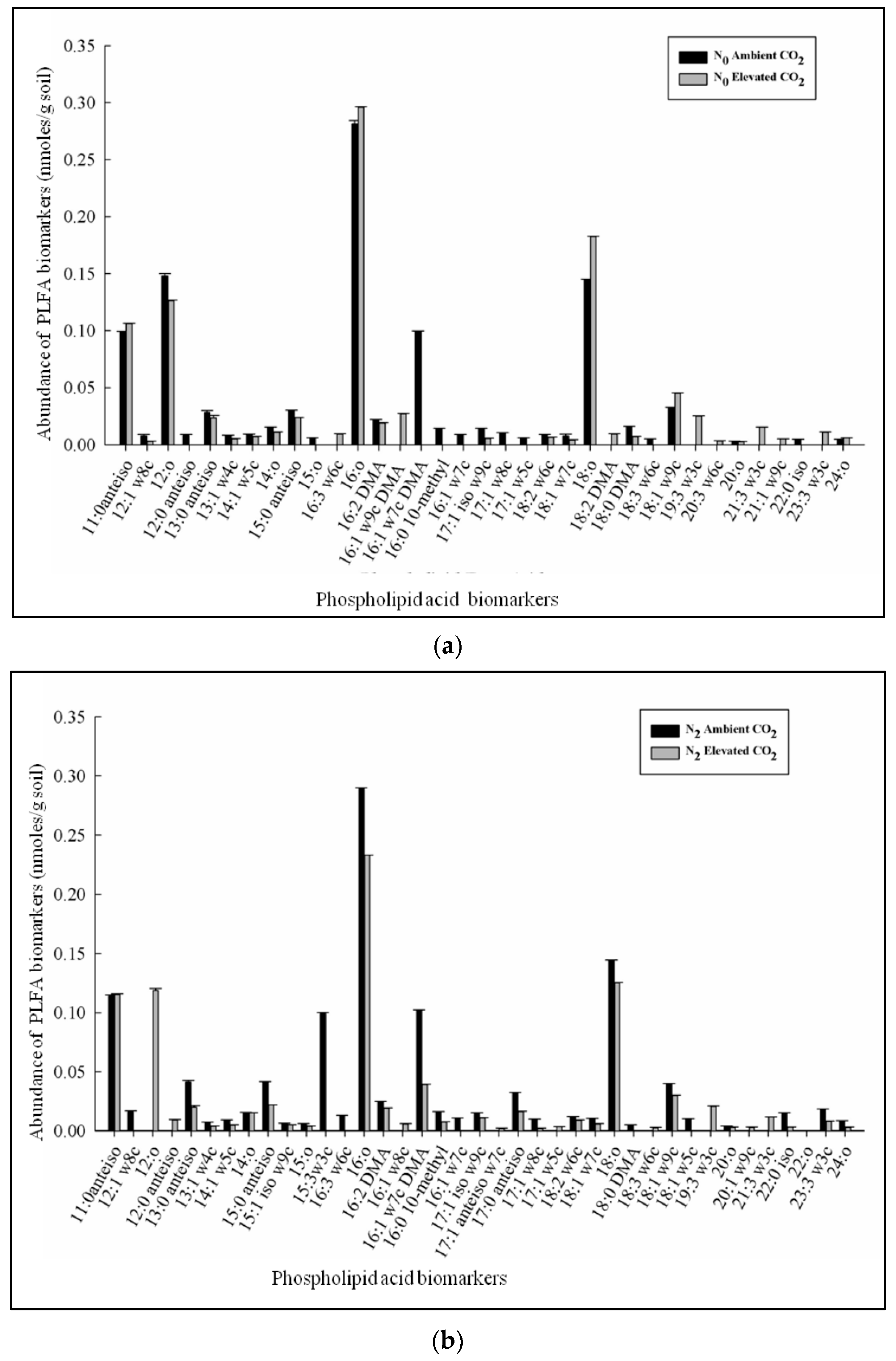
3.2. Phospholipid Fatty Acid (PLFA) Profiles Affected by CO2 Enrichment and Differential Doses of Nitrogen Application in xTriticocereale (Triticale)
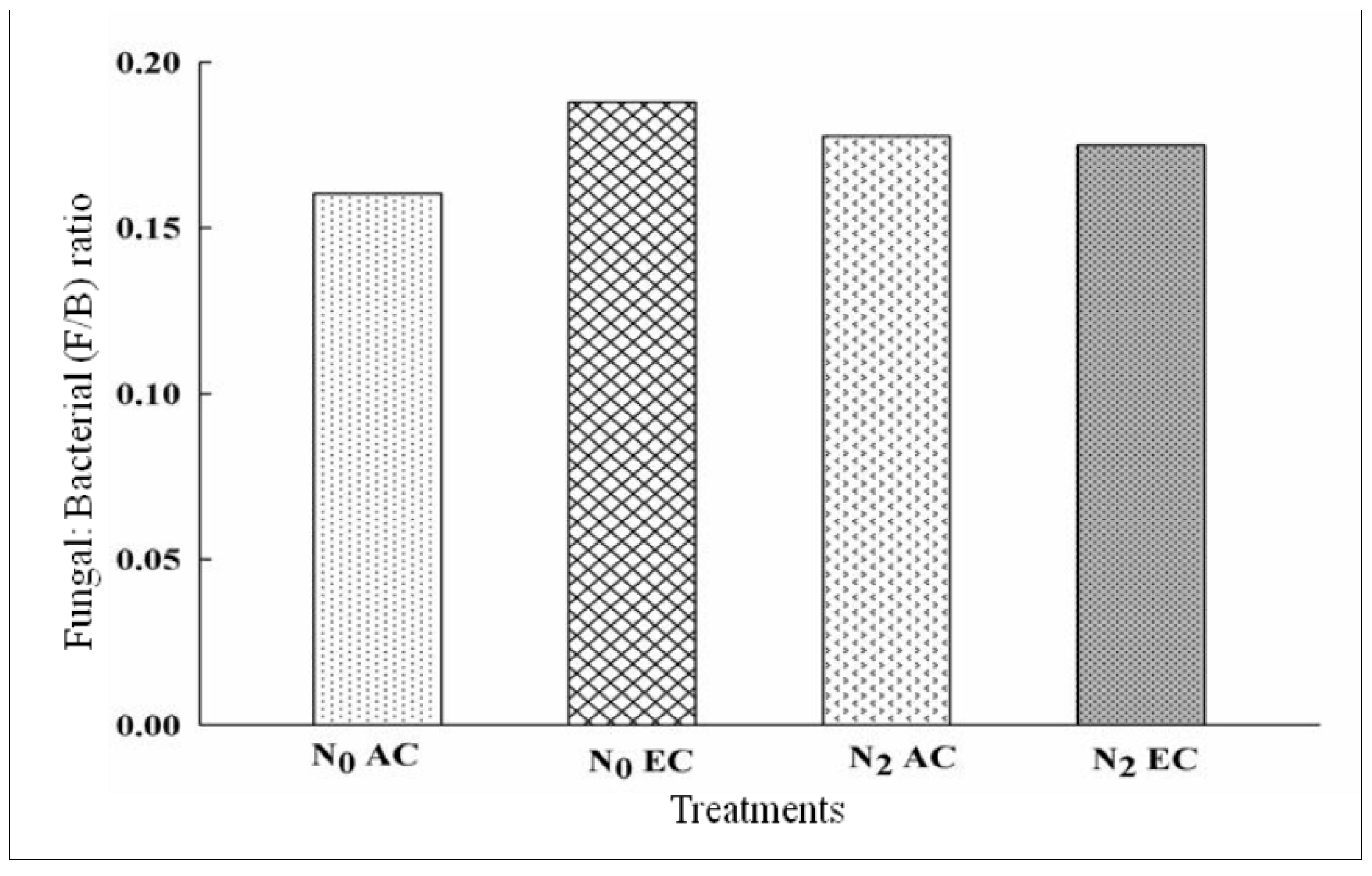
3.3. Fungal/Bacterial Ratio Affected by CO2 Enrichment and Nitrogen Application in xTriticocereale (Triticale)
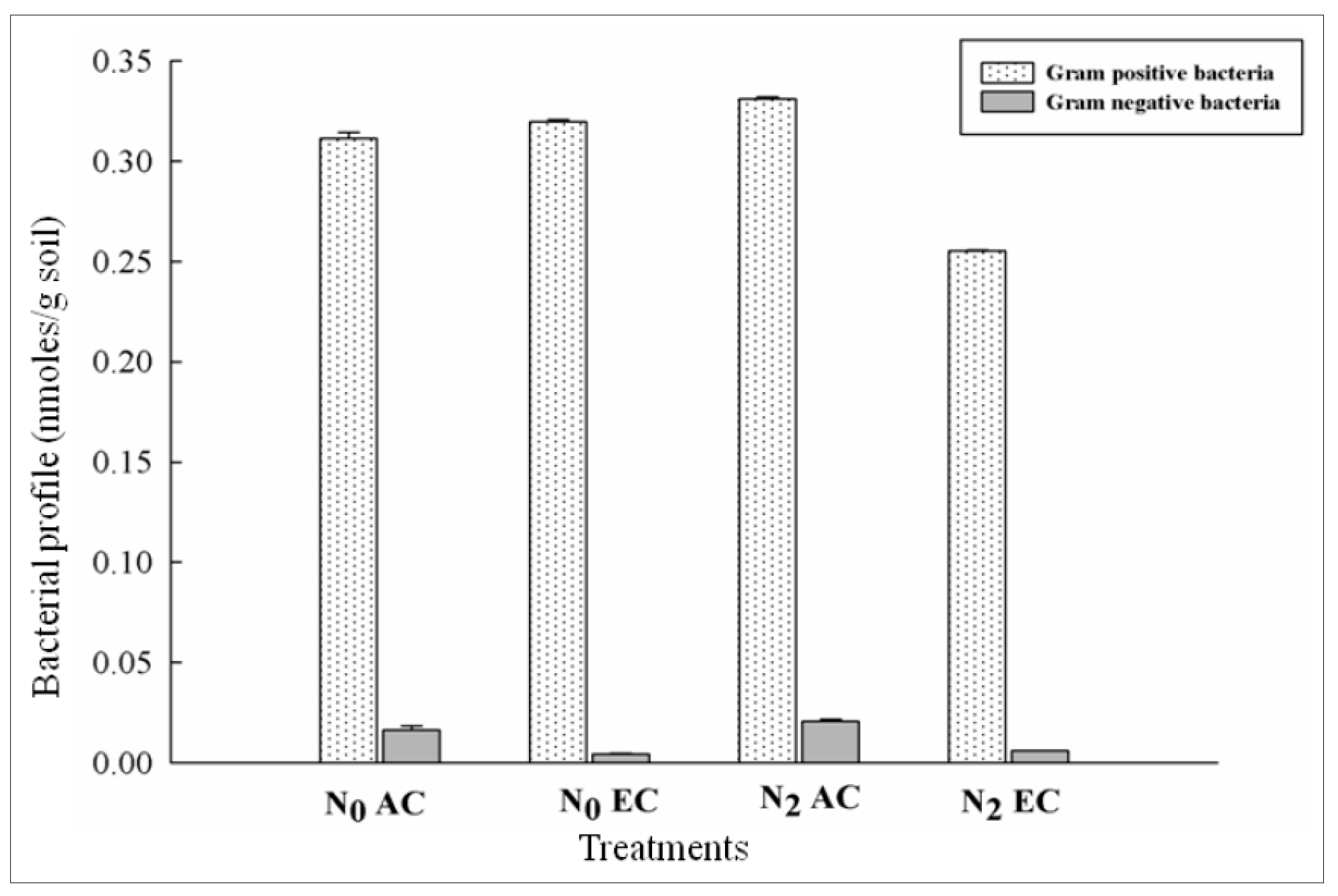
3.4. Responses in Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacterial Distribution in CO2 Enrichment and Differential Doses of Nitrogen Application in xTriticocereale (Triticale)
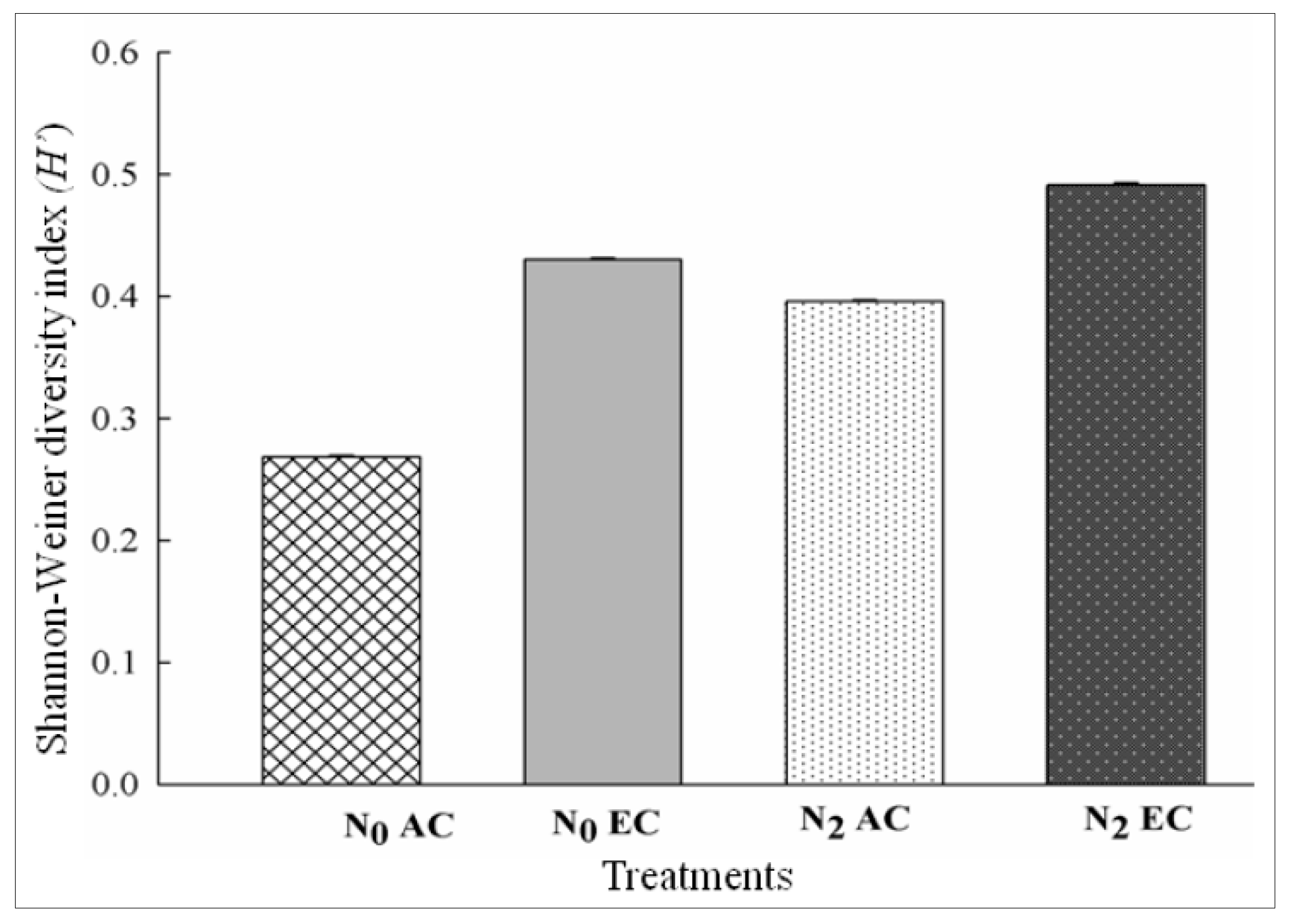
3.5. Shannon–Weiner Diversity Index (H’) as Influenced by CO2 Enrichment and Differential Doses of Nitrogen in xTriticocereale (Triticale)
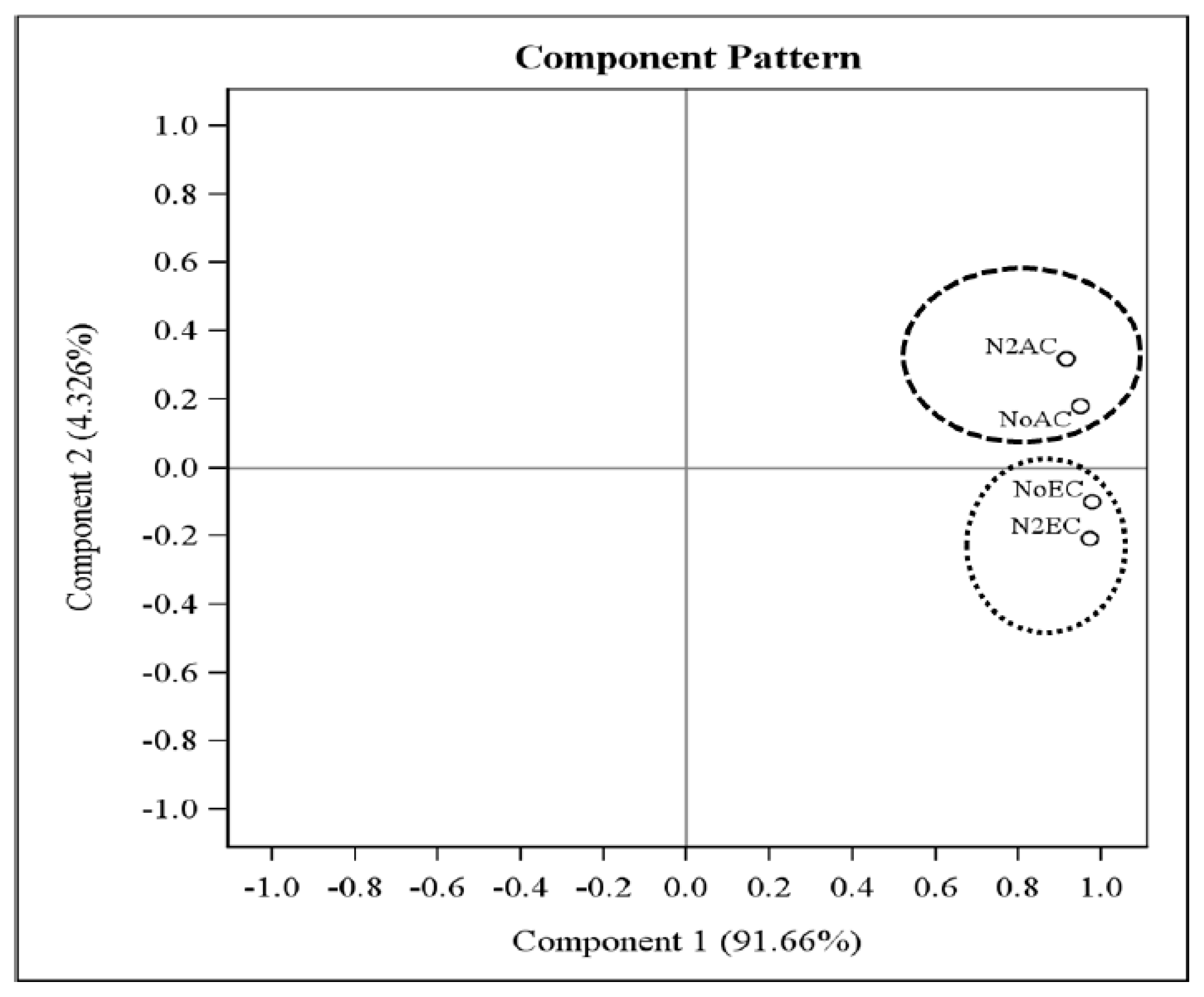
3.6. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of PLFA Responses Using xTriticocereale (Triticale) Soil Microbial Community as Influenced by Ambient and Elevated Levels of CO2 and Varying Nitrogen Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. AR6 Synthesis Report: Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nasa.gov2025 Carbon Dioxide Vital Signs—Climate Change: Vital Signs of the Planet. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Gruber, N.; Galloway, J.N. An earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 2008, 451, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thilakarathne, C.L.; Tausz-Posch, S.; Cane, K.; Norton, R.M.; Tausz, M.; Seneweera, S. Intra specific variation in growth and yield response to elevated CO2 in wheat depends on the differences of leaf mass per unit area. Funct. Plant Biol. 2013, 40, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drigo, B.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; VanVeen, J.A. Climate change goes under ground: Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on microbial community structure and activities in the rhizosphere. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2008, 44, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Bardgett, R.D.; Smith, P.; Reay, D.S. Microorganisms and climate change: Terrestrial feedbacks and mitigation options. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, M.; Reichstein, M. Terrestrial ecosystem carbon dynamics and climate feed backs. Nature 2008, 451, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgeway, J.R.; Morrissey, E.M.; Brzostek, E.R. Plant litter traits control microbial decomposition and drive soil carbon stabilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 175, 108857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xing, W.; Liu, J. Litter chemical traits, microbial and soil stoichiometry regulate organic carbon accrual of particulate and mineral-associated organic matter. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Ineson, P.; Rowland, A.P. Decomposition of tree leaf litters grown under elevated CO2: Effect of litter quality. Plant Soil. 1994, 163, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungate, B.A.; Holland, E.A.; Jackson, R.B.; Chapin, F.S.; Mooney, H.A.; Field, C.B. The fate of carbon in grasslands under carbon dioxide enrichment. Nature 1997, 388, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, D.S.; Dentener, F.; Smith, P.; Grace, J.R.; Feely, A. Global nitrogen deposition and carbon sinks. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, K.S.; Craine, J.M.; Fierer, N. Consistent effects of nitrogen amendments on soil microbial communities and processes across biomes. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finzi, A.C.; DeLucia, E.H.; Hamilton, J.G.; Richter, D.D.; Schlesinger, W.H. The nitrogen budget of a pine forest under free air CO2 enrichment. Oecologia 2002, 132, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Gu, J.D. Higher diversity of ammonia/ammonium-oxidizing prokaryotes in constructed freshwater wetland than natural coastal marine wetland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 97, 7015–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyer, J.S.; Sasser, M. High throughput phospholipid fatty acid analysis of soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 61, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelles, L. Fatty acid patterns of phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides in the characterisation of microbial communities in soil: A review. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1999, 29, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegård, Å.; Tunlid, A.; Bååth, E. Phospholipid fatty acid composition, biomass, and activity of microbial communities from two soil types experimentally exposed to different heavy metals. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 3605–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grayston, S.J.; Griffith, G.S.; Mawdsley, J.L.; Campbell, C.D.; Bardgett, R.D. Accounting for variability in soil microbial communities of temperate upland grassland ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 533–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Hobbs, P.J.; Frostegård, Å. Changes in soil fungal: Bacterial biomass ratios following reductions in the intensity of management of upland grassland. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1996, 22, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, P.A.; Larsson, L.; Bago, B.; Wallander, H.; VanAarle, I.M. Ergosterol and fatty acids for biomass estimation of mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 2003, 159, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Kaur, A.; Choudhary, R.; Kaushik, R. Phospholipid fatty acid—A bioindicator of environment monitoring and assessment in soil ecosystem. Curr. Sci. 2005, 89, 1103. [Google Scholar]
- Hungate, B.A.; Canadell, J.; Chapin, F.S. Plant species mediate changes in soil microbial N in response to elevated CO2. Ecology 1996, 77, 2505–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, D.R.; Pregitzer, K.S.; Curtis, P.S.; Teeri, J.A.; Fogel, R.; Randlett, D.L. Elevated atmospheric CO2 and feedback between carbon and nitrogen cycles. Plant Soil 1993, 151, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginkel Van, J.H.; Gorissen, A.; Polci, D. Elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration: Effects of increased carbon input in a Lolium perennes oil on microorganisms and decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, K.M.; Hungate, B.A.; Drake, B.G.; Megonigal, J.P. Altered soil microbial community at elevated CO2 leads to loss of soil carbon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4990–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drissner, D.; Blum, H.; Tscherko, D.; Kandeler, E. Nine years of enriched CO2 changes the function and structural diversity of soil microorganisms in a grassland. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 58, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Simpson, A.J.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Simpson, M.J. Altered microbial community structure and organic matter composition under elevated CO2 and N fertilization in the duke forest. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 2104–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treseder, K.K. A meta-analysis of mycorrhizal responses to nitrogen, phosphorus, and atmospheric CO2 in field studies. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, S.A.; Ziegler, S.E. Altered patterns of soil carbon substrate usage and heterotrophic respiration in a pine forest with elevated CO2 and N fertilization. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringelberg, D.B.; Stair, J.O.; Almeida, J.; Norby, R.J.; O’Neill, E.G.; White, D.C. Consequences of rising atmospheric carbon dioxide levels for the below ground microbiota associated with white oak. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 26, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drigo, B.; Pijl, A.S.; Duyts, H.; Kielak, A.M.; Gamper, H.A.; Houtekamer, M.J.; Boschker, H.T.; Bodelier, P.L.; Whiteley, A.S.; vanVeen, J.A.; et al. Shifting carbon flow from roots in to associated microbial communities in response to elevated atmospheric CO2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10938–10942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montealegre, C.M.; VanKessel, C.; Russelle, M.P.; Sadowsky, M.J. Changes in microbial activity and composition in a pasture ecosystem exposed to elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide. Plant Soil 2002, 243, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Soil Properties | Values/Inferences |
|---|---|
| pH (soil/water1/2.5) | 7.9 |
| Electrical conductivity (EC) (dSm−1) | 0.64 |
| Textual class | Sandy loam |
| Soil type | Typic Haplustept |
| Bulk density (Mg m−3) | 1.61 |
| Water-holding capacity (%) | 32.6 |
| Available N (g kg−1) | 0.30 |
| Available P (kg ha−1) | 11.7 |
| Available K (kg ha−1) | 225 |
| Oxidizable soil organic carbon (g kg−1) | 3.7 |
| Nitrogen (N) Doses | Carbon Dioxide | Notation Used |
|---|---|---|
| N0 (Normal recommended dose of N: 0.0533 g N/kg of soil) | Ambient CO2 (384 ± 13 ppm) | N0AC |
| N2 Twice of N0, (0.107 g N/kg soil) | Ambient CO2 (384 ± 13 ppm) | N2AC |
| N0 (Normal recommended dose of N: 0.0533 g N/kg of soil) | Elevated CO2 (580 ± 20 ppm) | N0EC |
| N2 Twice of N0, (0.107 g N/kg soil) | Elevated CO2 (580 ± 20 ppm) | N2EC |
| Treatments | Microbial Biomass Content (nmoles/g of Dry Soil) | Gram-Positive Bacteria (nmoles/g of Dry Soil) | Gram -Negative Bacteria (nmoles/g of Dry Soil) | F:B Ratio | Straight-Chain Fatty Acids (nmoles/g of Dry Soil) | Branched Fatty Acids (nmoles/g of Dry Soil) | MUFA (nmoles/g of Dry Soil) | PUFA (nmoles/g of Dry Soil) | DMA (nmoles/g of Dry Soil) | 18:1 ω9c (nmoles/g of Dry Soil) | 18:2 ω6,9c (nmoles/g of Dry Soil) | 10-Methyl (nmoles/g of Dry Soil) | Shannon–Weiner Diversity Index (H’) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0AC | 96 | 0.3 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.61 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.005 | 0.043 | 0.037 | 0.01 | 0.015 | 0.27 |
| N2AC | 88 | 0.3 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.49 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.032 | 0.044 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.4 |
| N0EC | 101 | 0.3 | 0.004 | 0.19 | 0.63 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.038 | 0.051 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.43 |
| N2EC | 112 | 0.26 | 0.006 | 0.17 | 0.51 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.021 | 0.034 | 0.01 | 0.008 | 0.49 |
| LSD at 5% | 0.0172 *** | 0.00190 *** | 0.00190 *** | 0.0188 ** | 0.0014 *** | 0.0013 *** | 0.0014 *** | 0.00135 *** | 0.00135 *** | 0.00136 *** | 0.001 *** | 0.0014 *** | 0.0085 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gadpayle, K.A.; Saha, N.D.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Pal, M. Greater Application of Nitrogen to Soil and Short-Term Fumigation with Elevated Carbon Dioxide Alters the Rhizospheric Microbial Community of xTriticocereale (Triticale): A Study of a Projected Climate Change Scenario. Nitrogen 2025, 6, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6030067
Gadpayle KA, Saha ND, Bhattacharyya R, Pal M. Greater Application of Nitrogen to Soil and Short-Term Fumigation with Elevated Carbon Dioxide Alters the Rhizospheric Microbial Community of xTriticocereale (Triticale): A Study of a Projected Climate Change Scenario. Nitrogen. 2025; 6(3):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6030067
Chicago/Turabian StyleGadpayle, Kritika Adesh, Namita Das Saha, Ranjan Bhattacharyya, and Madan Pal. 2025. "Greater Application of Nitrogen to Soil and Short-Term Fumigation with Elevated Carbon Dioxide Alters the Rhizospheric Microbial Community of xTriticocereale (Triticale): A Study of a Projected Climate Change Scenario" Nitrogen 6, no. 3: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6030067
APA StyleGadpayle, K. A., Saha, N. D., Bhattacharyya, R., & Pal, M. (2025). Greater Application of Nitrogen to Soil and Short-Term Fumigation with Elevated Carbon Dioxide Alters the Rhizospheric Microbial Community of xTriticocereale (Triticale): A Study of a Projected Climate Change Scenario. Nitrogen, 6(3), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6030067







