Variation in Leaf C, N, and P Stoichiometric Characteristics of Populus euphratica Communities in a Desert Riparian Ecosystem of Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Field Investigation and Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
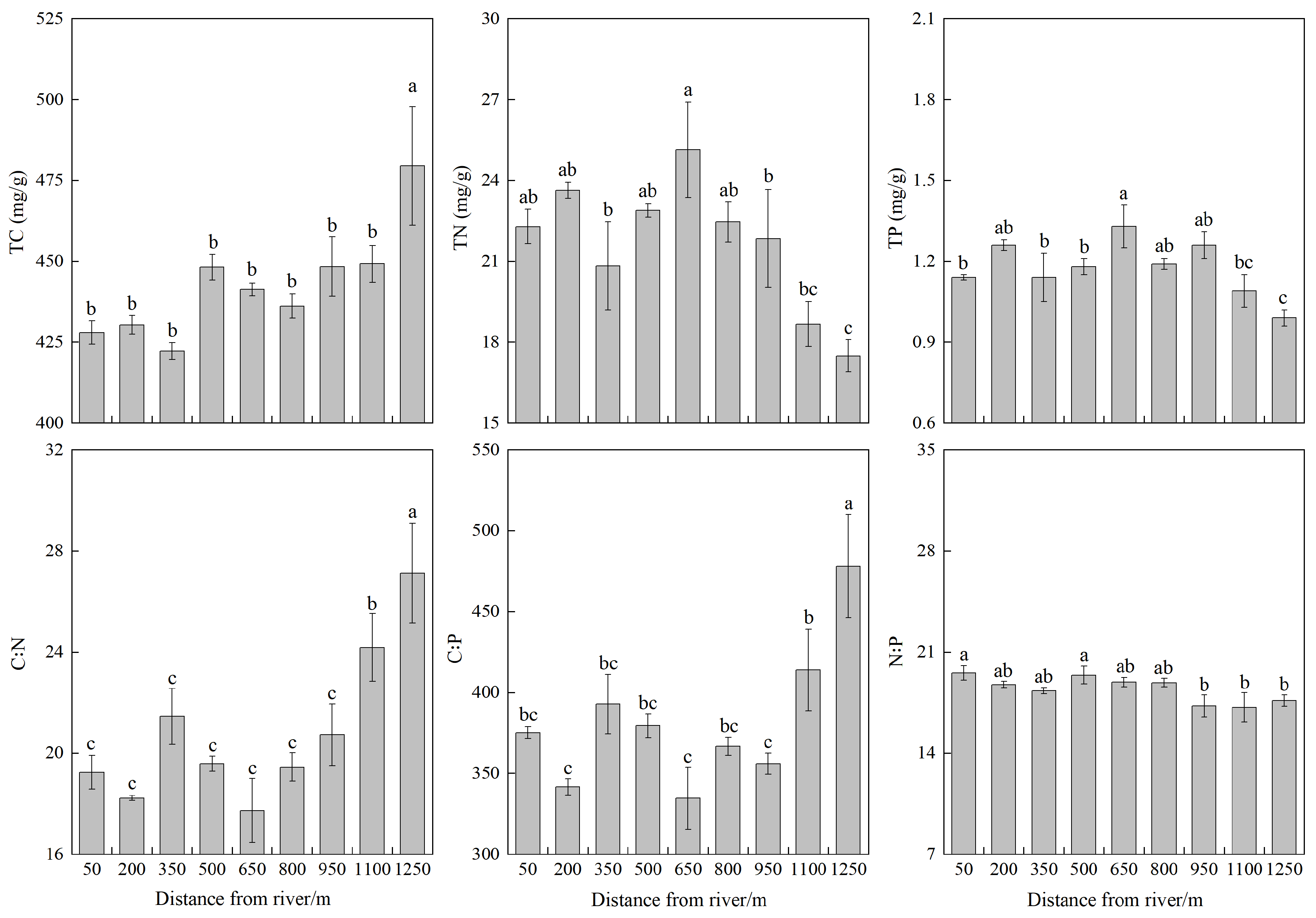
3.1. Leaf TC, TN, and TP Stoichiometric Characteristics of Populus euphratica Community
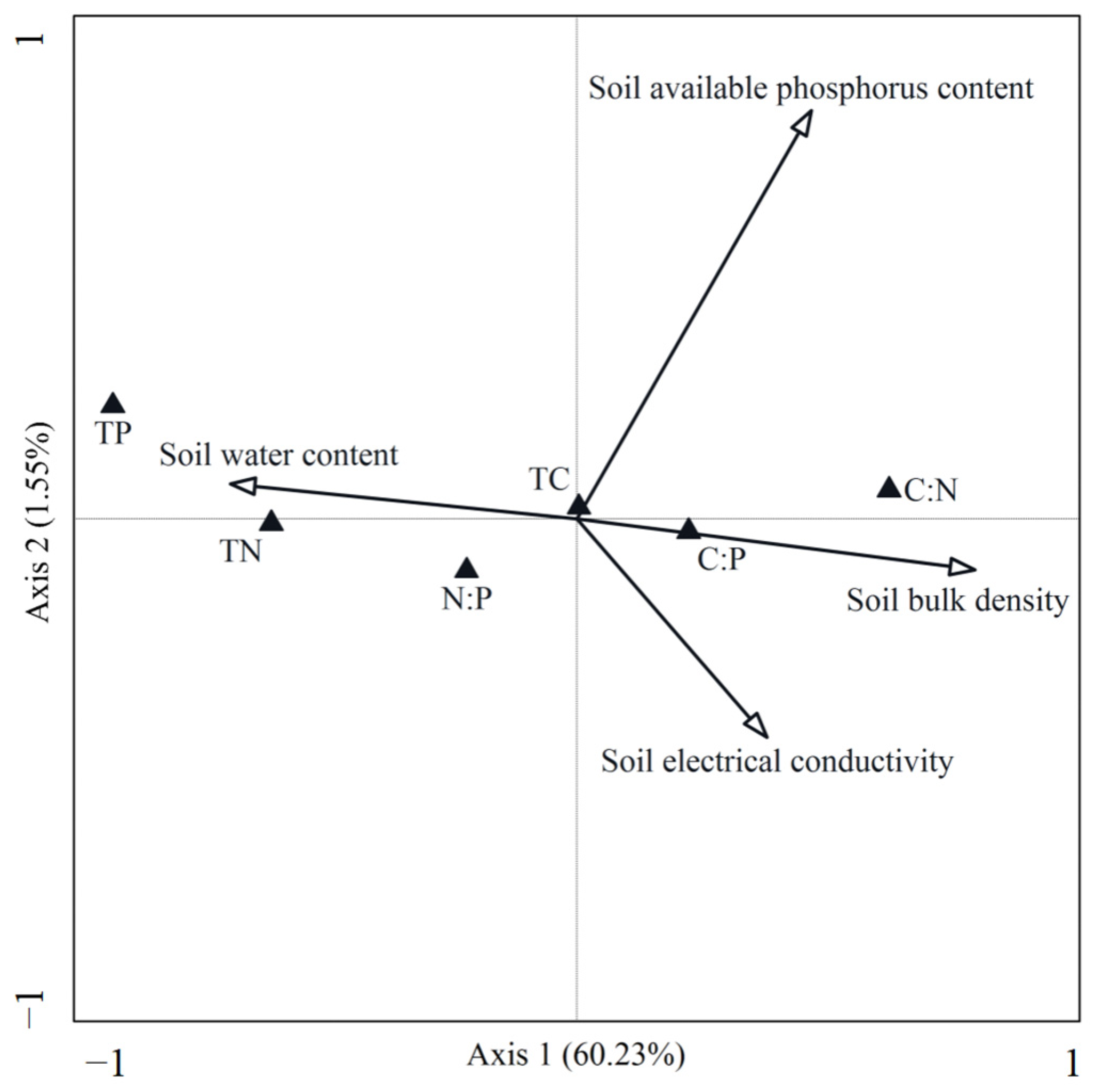
3.2. Relationship Between Community Leaf Stoichiometry Characteristics and Environmental Factors
3.3. Key Environmental Drivers of Community Leaf Stoichiometric Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Variations of Leaf C:N:P Stoichiometry at the Community Level
4.2. Patterns and Drivers of Leaf C:N:P Stoichiometry at the Community Level
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wright, I.J.; Reich, P.B.; Westoby, M.; Ackerly, D.D.; Baruch, Z.; Bongers, F.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Chapin, T.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Diemer, M.; et al. The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature 2004, 428, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.Z.; Crowther, T.W.; Mo, L.D.; Maynard, D.S.; Renner, S.S.; van den Hoogen, J.; Zou, Y.; Liang, J.; De-Miguel, S.; Nabuurs, G.-J.; et al. The global biogeography of tree leaf form and habit. Nat. Plants 2003, 9, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chi, X.L.; Ji, C.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Ma, W.H.; Mohhammat, A.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Yue, M.; et al. Variations of leaf N and P concentrations in shrubland biomes across northern China: Phylogeny, climate, and soil. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 4429–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.Y.; Xu, W.T.; Zhou, G.Y.; Bai, Y.F.; Li, J.X.; Tang, X.L.; Chen, D.; Liu, Q.; Ma, W.; Xiong, G.; et al. Patterns of plant carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus concentration in relation to productivity in China’s terrestrial ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4033–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Yan, Z.B.; Niklas, K.J.; Han, W.X.; Kattge, J.; Reich, P.B.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Z.; Hu, H.; et al. Global leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry and their scaling exponent. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.J.; Cieraad, E.; Armstrong, J.; Armstrong, W.; Clarkson, B.R.; Colmer, T.D.; Pedersen, O.; Visser, E.J.W.; Voesenek, L.A.C.J.; van Bodegom, P.M. Global patterns of the leaf economics spectrum in wetlands. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, P.B.; Oleksyn, J. Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11001–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.X.; Fang, J.Y.; Reich, P.B.; Woodward, F.I.; Wang, Z.H. Biogeography and variability of eleven mineral elements in plant leaves across gradients of climate, soil and plant functional type in China. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruelheide, H.; Dengler, J.; Purschke, O.; Lenoir, J.; Jiménez-Alfaro, B.; Hennekens, S.M.; Botta-Dukát, Z.; Chytrý, M.; Field, R.; Jansen, F.; et al. Global trait-environment relationships of plant communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1906–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Denno, R.F.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Folarin, A.; Huberty, A.; Interlandi, S.; Kilham, S.S.; McCauley, E.; Schulz, K.L.; et al. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 2000, 408, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, R.; Chapin, F.S.I. The mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: A re-evaluation of processes and patterns. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2000, 30, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Niklas, K.J.; Cobb, E.D. N, P, and C stoichiometry of Eranthis hyemalis (Ranunculaceae) and the allometry of plant growth. Am. J. Bot. 2005, 92, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, E.; Navas, M.L.; Grigulis, K. Plant Functional Diversity–Organism Traits, Community Structure, and Ecosystem Properties; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre-Gutiérrez, J.; Díaz, S.; Rifai, S.W. Tropical forests in the Americas are changing too slowly to track climate change. Science 2025, 387, eadl5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.X.; Shangguan, Z.P. Spatial patterns of leaf nutrient traits of the plants in the Loess Plateau of China. Trees-Struct. Funct. 2007, 21, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.H.; Chen, Y.N.; Ren, L.L.; Lü, H.S.; Zhao, W.Z.; Yuan, F.; Xu, M. Ecosystem restoration and conservation in the arid inland river basins of Northwest China: Problems and strategies. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.H.; Liang, W.Z.; Han, L.; Wang, H.Z. Leaf functional traits of Populus euphratica and its response to groundwater depths in Tarim extremely arid area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 5368–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.Y.; Zhao, W.W.; Daryanto, S.; Wang, L.X.; Fan, H.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Y.P. The spatial distribution and temporal variation of desert riparian forests and their influencing factors in the downstream Heihe River basin, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2405–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhao, C.Y.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lv, G.H. Distribution pattern of tugai forests species diversity and their relationship to environmental factors in an arid area of China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.S.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.H.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, W.H. Water use strategies of the desert riparian forest plant community in the lower reaches of Heihe River Basin, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Zhou, J.H.; Guan, T.Y.; Cai, W.T.; Jiang, L.H.; Lai, L.M.; Gao, N.N.; Zheng, Y.R. Spatial variation in leaf nutrient traits of dominant desert riparian plant species in an arid inland river basin of China. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Guan, T.Y.; Zhou, J.H.; Cai, W.T.; Gao, N.N.; Du, H.; Jiang, L.H.; Lai, L.M.; Zheng, Y.R. Groundwater depth and soil properties are associated with variation in vegetation of a desert riparian ecosystem in an arid area of China. Forests 2018, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, T.F.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, C.Y. Sap flow characteristics and their response to environmental variables in a desert riparian forest along lower Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemery, G.E.; Savill, P.S.; Pryor, S.N. Applications of the crown diameter-stem diameter relationship for different species of broadleaved trees. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 215, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.T.; Mcintosh, R.P. An upland forest continuum in the prairie forest border region of Wisconsin. Ecology 1951, 32, 476–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Islam, W.; Zeng, F.J. Film mulching counteracts the adverse effects of mild moisture deficiency, and improves the quality and yield of Cyperus esculentus. L grass and tuber in the oasis area of Tarim Basin. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1296641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.D.; Arif, M.; Liu, M.H.; Li, J.J.; Hu, X.; Geng, Q.W.; Yin, F.; Li, C.X. Plant-soil interactions and C:N:P stoichiometric homeostasis of plant organs in riparian plantation. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 979023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.A.; Wang, S.K.; Lv, P.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhang, J. Plant functional diversity enhances associations of soil fungal diversity with vegetation and soil in the restoration of semiarid sandy grassland. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorel, S.; Grigulis, K.; Mcintyre, S.; Williams, N.S.G.; Garden, D.; Dorrough, J.; Berman, S.; Quétier, F.; Thébault, A.; Bonis, A. Assessing functional diversity in the field-methodology matters. Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination; Version 5.0; Microcomputer Power, Ithaca: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, M.X.; Ma, X.X. Stoichiometric characteristics of leaves of Populus euphratica with different stand ages and soil. Arid Zone Res. 2017, 34, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.M.; Flexas, J.; Pinhiro, C. Photosynthesis under drought and salt stress: Regulation mechanisms from whole plant to cell. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahnama, A.; James, R.A.; Poustini, K.; Munns, R. Stomatal conductance as a screen for osmotic stress tolerance in durum wheat growing in saline soil. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCree, K. Whole-plant carbon balance during osmotic adjustment to drought and salinity stress. Funct. Plant Biol. 1986, 13, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.X.; Fang, J.Y.; Guo, D.L.; Zhang, Y. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Zhao, G.X.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.T.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, X.F.; An, L.; Xu, S.J. C:N:P stoichiometry and leaf traits of halophytes in an arid saline environment, Northwest China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Wu, Y.; He, J.S. Relationship between leaf phosphorus concentration and soil phosphorus availability across Inner Mongolia grassland. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balba, A.M. Management of Problem Soils in Arid Ecosystems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.Z.; Zhang, H.; Song, C.P.; Zhu, J.K.; Shabala, S. Mechanisms of plant responses and adaptation to soil salinity. Innovation 2020, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Wang, L.; He, W.L.; An, L.Z.; Xu, S.J. Nutrient resorption or accumulation of desert plants with contrasting sodium regulation strategies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerselman, W.; Meuleman, A.F.M. The vegetation N: P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Zhou, J.H.; Lai, L.M.; Jiang, L.H.; Zheng, Y.R. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometric characteristics of Tamarix ramosissima Ledeb. shrubland and their influencing factors in a desert riparian area of China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Gou, W.; Wang, H.; Wu, G.Q.; Su, P.X. Characteristics of C, N, P, and their response to soil water and salt in leaves of Lycium ruthenicum in the lower reaches of the Heihe River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7189–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.X.; Wu, X.; Gong, L. Leaf characteristics of typical desert plants in the upper reaches of Tarim River and their relationship with soil factors. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 5360–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
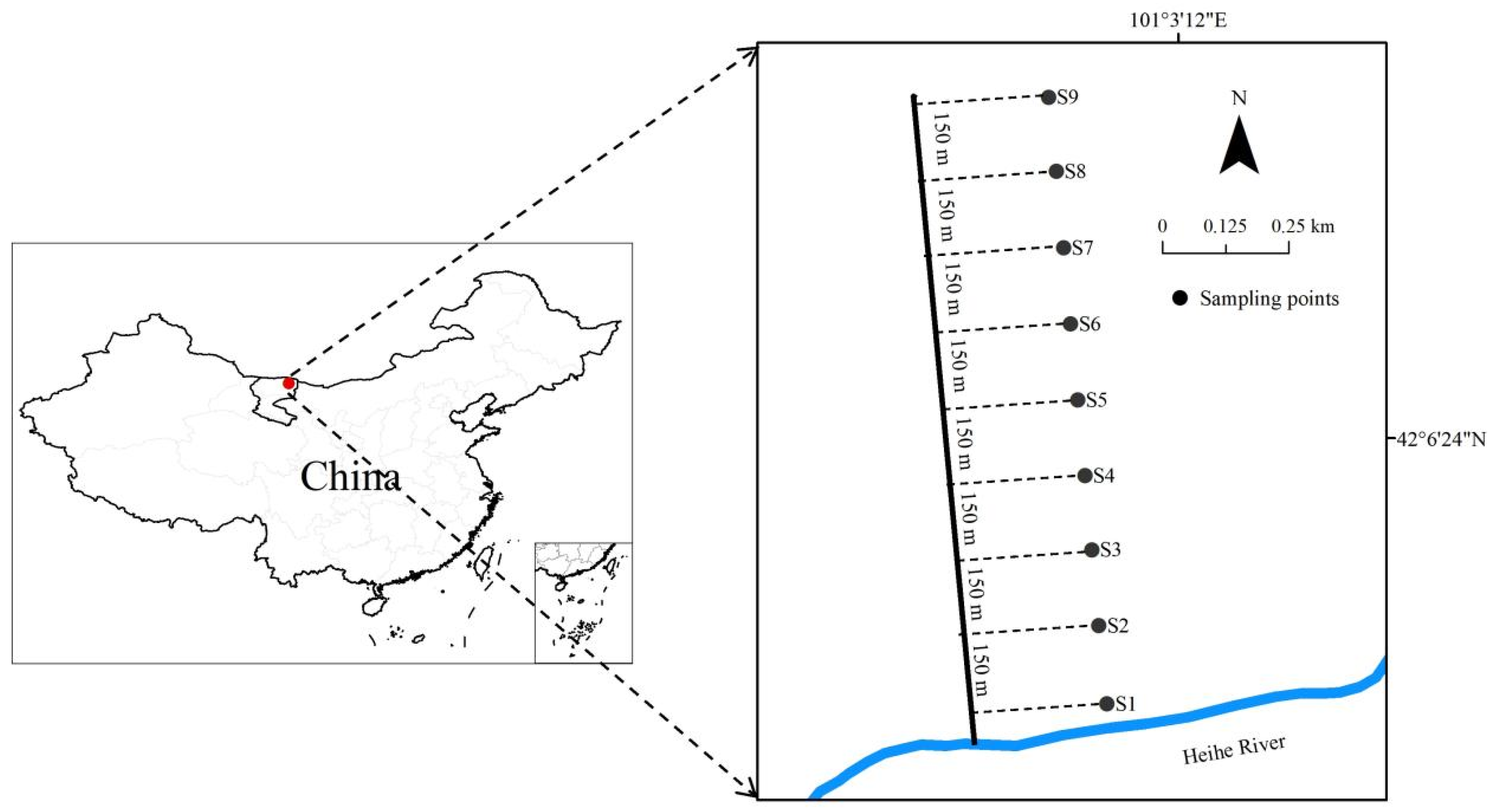

| Site | Distance/m | Altitude/m | Structure | Main Species | Dominant Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 50 | 916 | Arbor–shrub–herb | Populus euphratica, Sophora alopecuroides, Tamarix ramosissima | P. euphratica |
| S2 | 200 | 917 | Arbor–shrub–herb | P. euphratica, S. alopecuroides, T. ramosissima | P. euphratica |
| S3 | 350 | 914 | Arbor–shrub–herb | P. euphratica, S. alopecuroides, T. ramosissima, Alhagi sparsifolia | P. euphratica |
| S4 | 500 | 914 | Arbor–shrub–herb | P. euphratica, S. alopecuroides, T. ramosissima, A. sparsifolia, Peganum harmala | P. euphratica |
| S5 | 650 | 913 | Arbor–shrub–herb | P. euphratica, S. alopecuroides, T. ramosissima, A. sparsifolia | P. euphratica |
| S6 | 800 | 913 | Arbor–shrub–herb | P. euphratica, S. alopecuroides, T. ramosissima, P. harmala | P. euphratica |
| S7 | 950 | 912 | Arbor–herb | P. euphratica, S. alopecuroides | P. euphratica |
| S8 | 1100 | 916 | Arbor–herb | P. euphratica, S. alopecuroides | P. euphratica |
| S9 | 1250 | 915 | Arbor–herb | P. euphratica, S. alopecuroides | P. euphratica |
| Parameter | Mean Value | SD | CV | Minimum | Maximum | Df | F Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC (mg/g) | 442.58 | 21.77 | 0.05 | 377.08 | 508.69 | 8 | 2.839 | 0.031 |
| TN (mg/g) | 21.69 | 2.80 | 0.13 | 16.37 | 27.57 | 8 | 4.555 | 0.004 |
| TP (mg/g) | 1.18 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.94 | 1.45 | 8 | 4.328 | 0.005 |
| C:N | 20.81 | 3.45 | 0.17 | 16.00 | 31.69 | 8 | 8.442 | 0.001 |
| C:P | 381.03 | 50.85 | 0.13 | 303.34 | 550.78 | 8 | 7.722 | 0.001 |
| N:P | 18.43 | 1.17 | 0.06 | 15.24 | 20.63 | 8 | 2.569 | 0.046 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, F.; Qin, H.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y. Variation in Leaf C, N, and P Stoichiometric Characteristics of Populus euphratica Communities in a Desert Riparian Ecosystem of Northwest China. Nitrogen 2025, 6, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6020035
Zhang X, Liu X, Shi L, Zhang Y, Wang J, Gao F, Qin H, Shi M, Wang Y, Zheng Y. Variation in Leaf C, N, and P Stoichiometric Characteristics of Populus euphratica Communities in a Desert Riparian Ecosystem of Northwest China. Nitrogen. 2025; 6(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaolong, Xianmeng Liu, Lijiang Shi, Yinbo Zhang, Jingwei Wang, Feng Gao, Hao Qin, Min Shi, Yongji Wang, and Yuanrun Zheng. 2025. "Variation in Leaf C, N, and P Stoichiometric Characteristics of Populus euphratica Communities in a Desert Riparian Ecosystem of Northwest China" Nitrogen 6, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6020035
APA StyleZhang, X., Liu, X., Shi, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Gao, F., Qin, H., Shi, M., Wang, Y., & Zheng, Y. (2025). Variation in Leaf C, N, and P Stoichiometric Characteristics of Populus euphratica Communities in a Desert Riparian Ecosystem of Northwest China. Nitrogen, 6(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6020035








