Assessing Liquid Inoculant Formulation of Biofertilizer (Sinorhizobium meliloti) on Growth, Yield, and Nitrogen Uptake of Lucerne (Medicago sativa)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Liquid Inoculant
2.2. Experimental Location
2.3. Analysis of Soil and Biofertilizer Application
2.4. Trial Design and Treatment
2.5. Data Collection
Growth and Yield Parameters
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Lucerne Growth, Yield and N Uptake Parameters
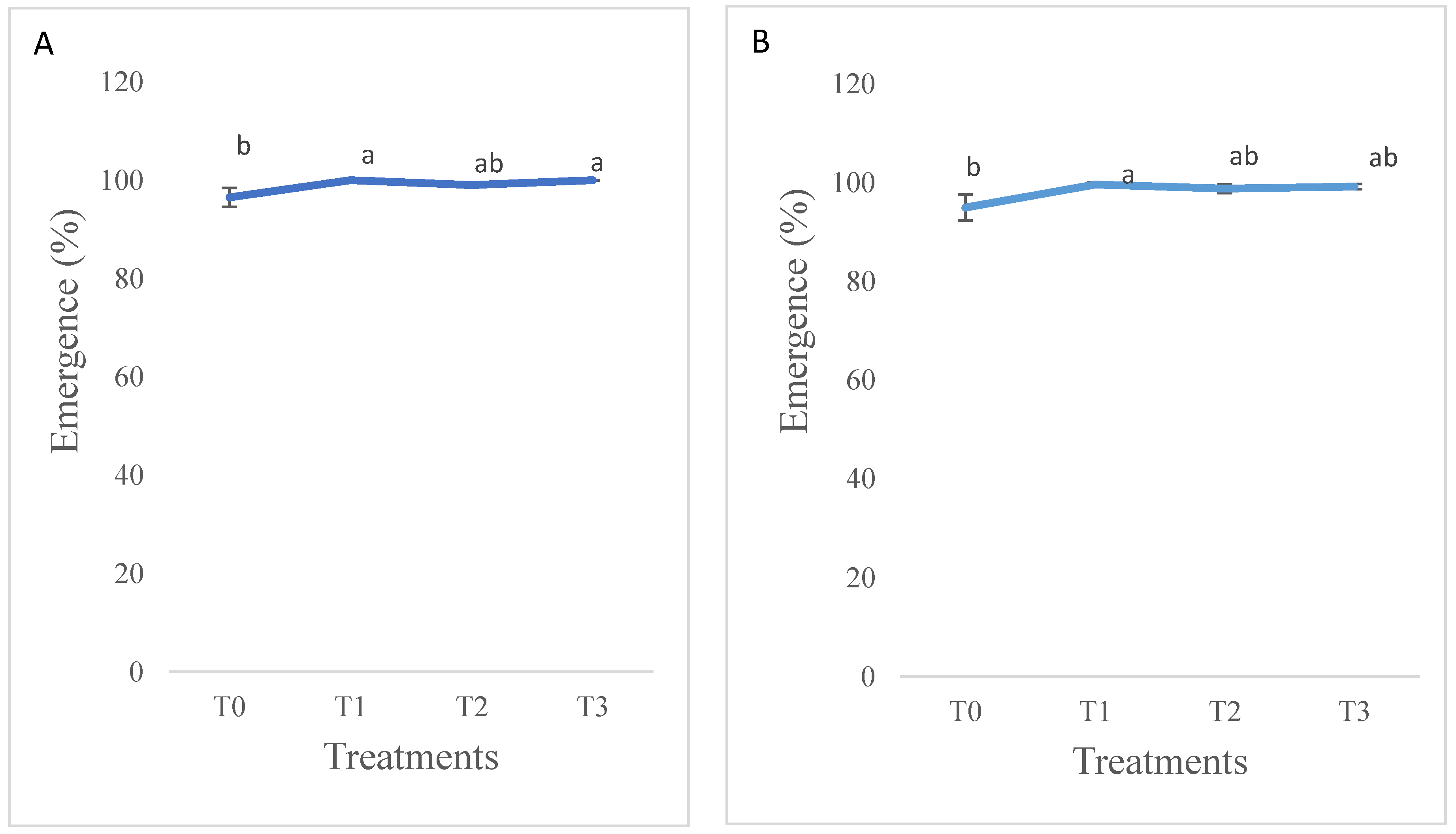
3.1.1. Lucerne Emergence
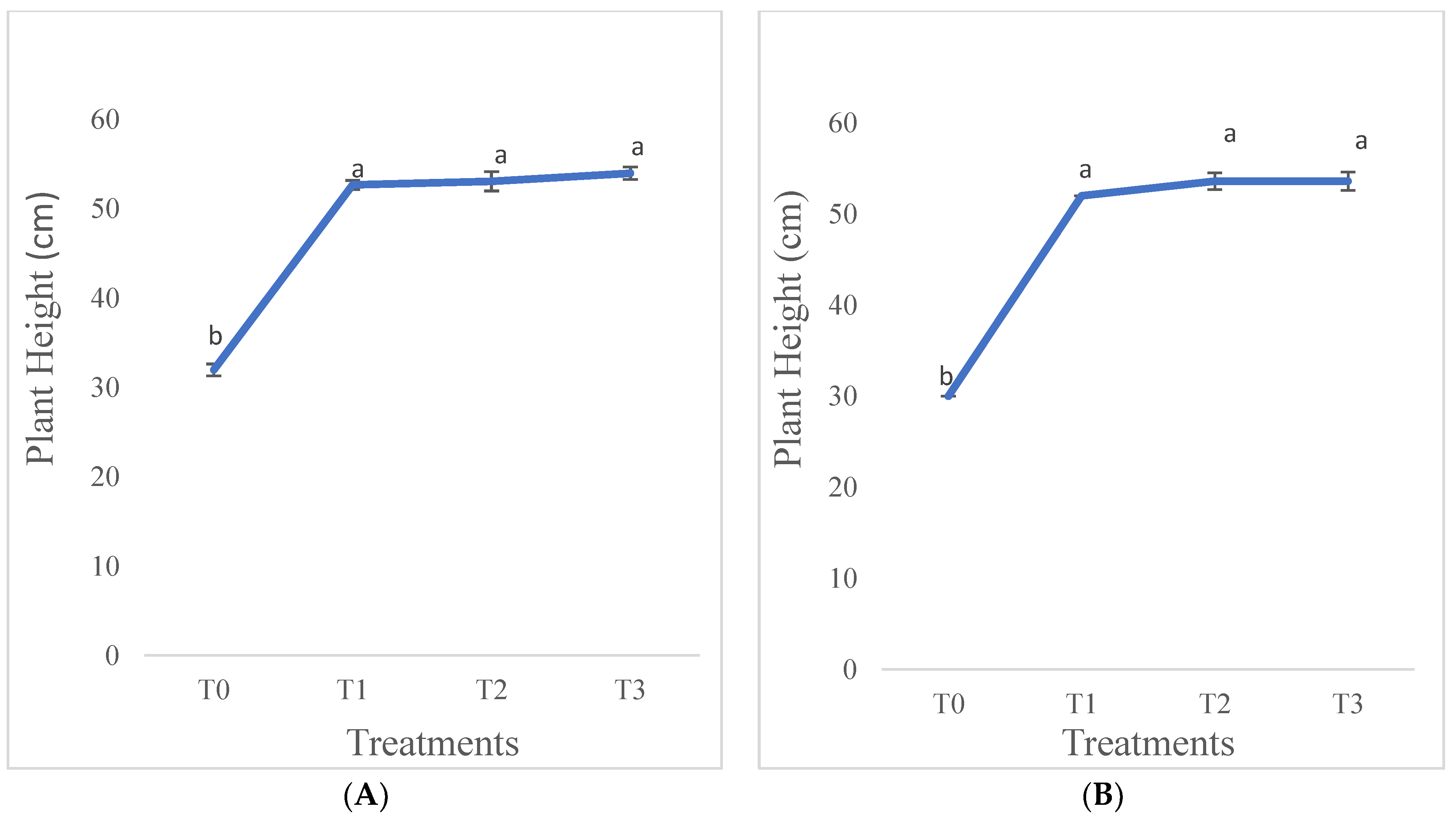
3.1.2. Plant Height
3.1.3. Root Length
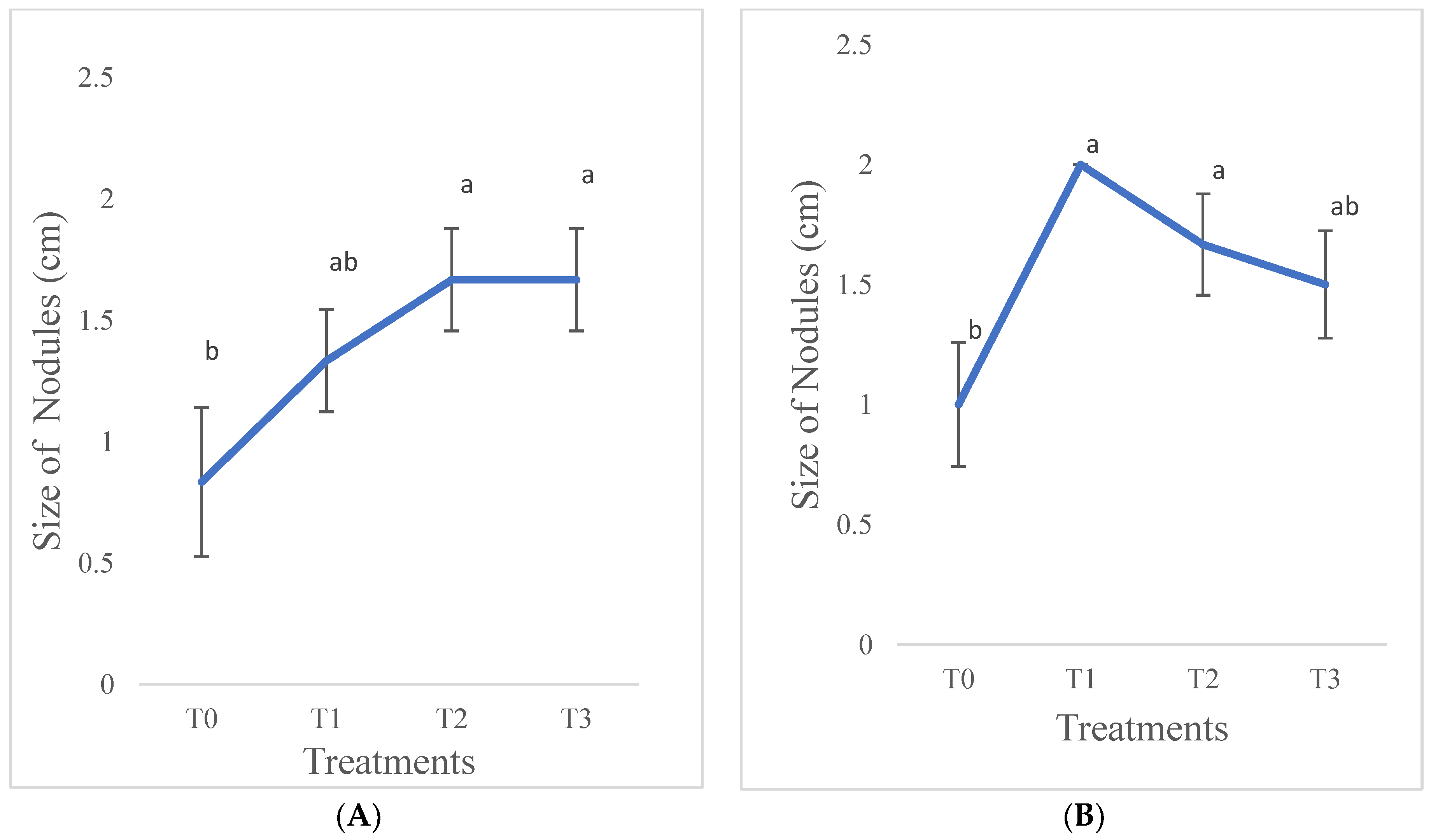
3.1.4. Size of Nodules
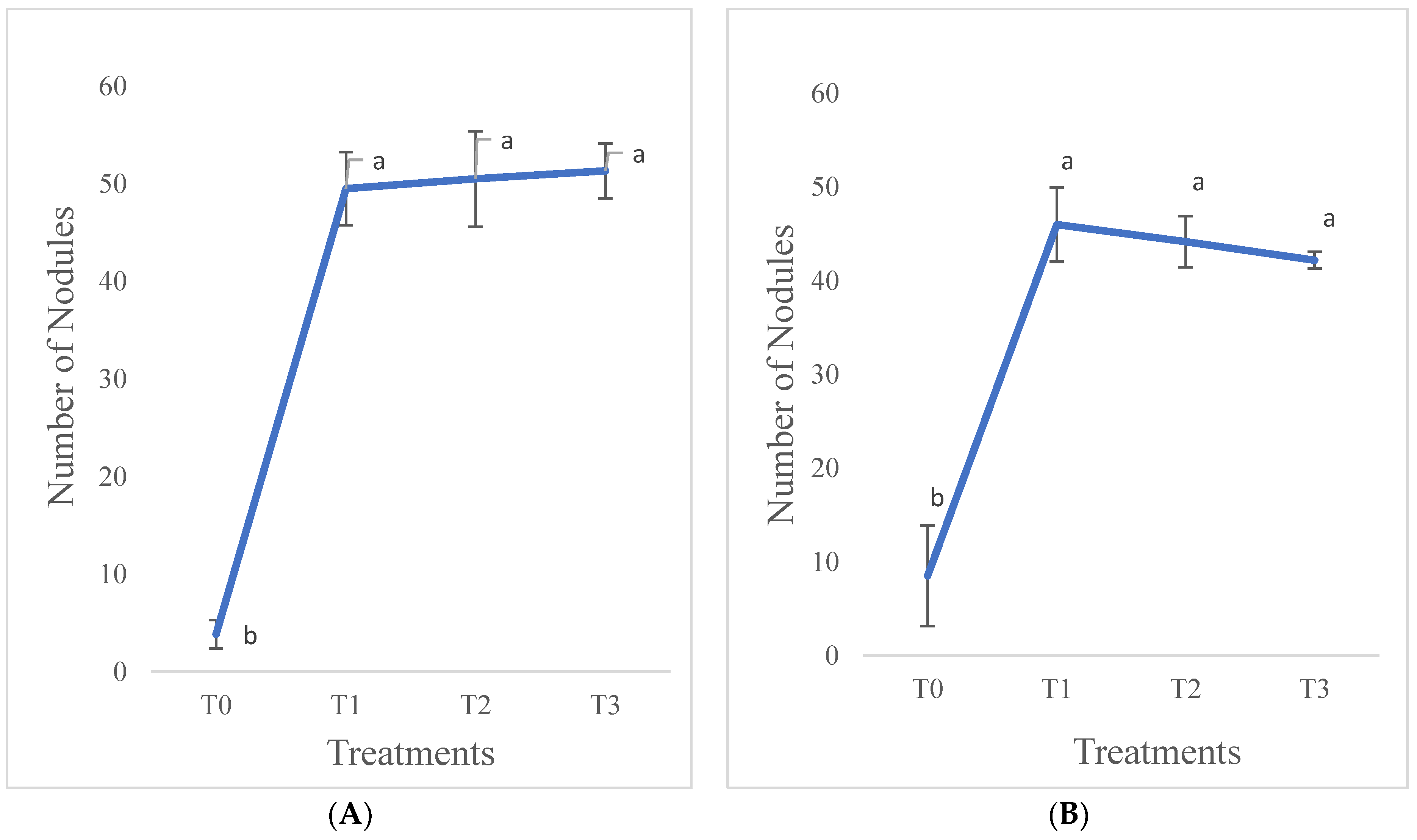
3.1.5. Number of Nodules
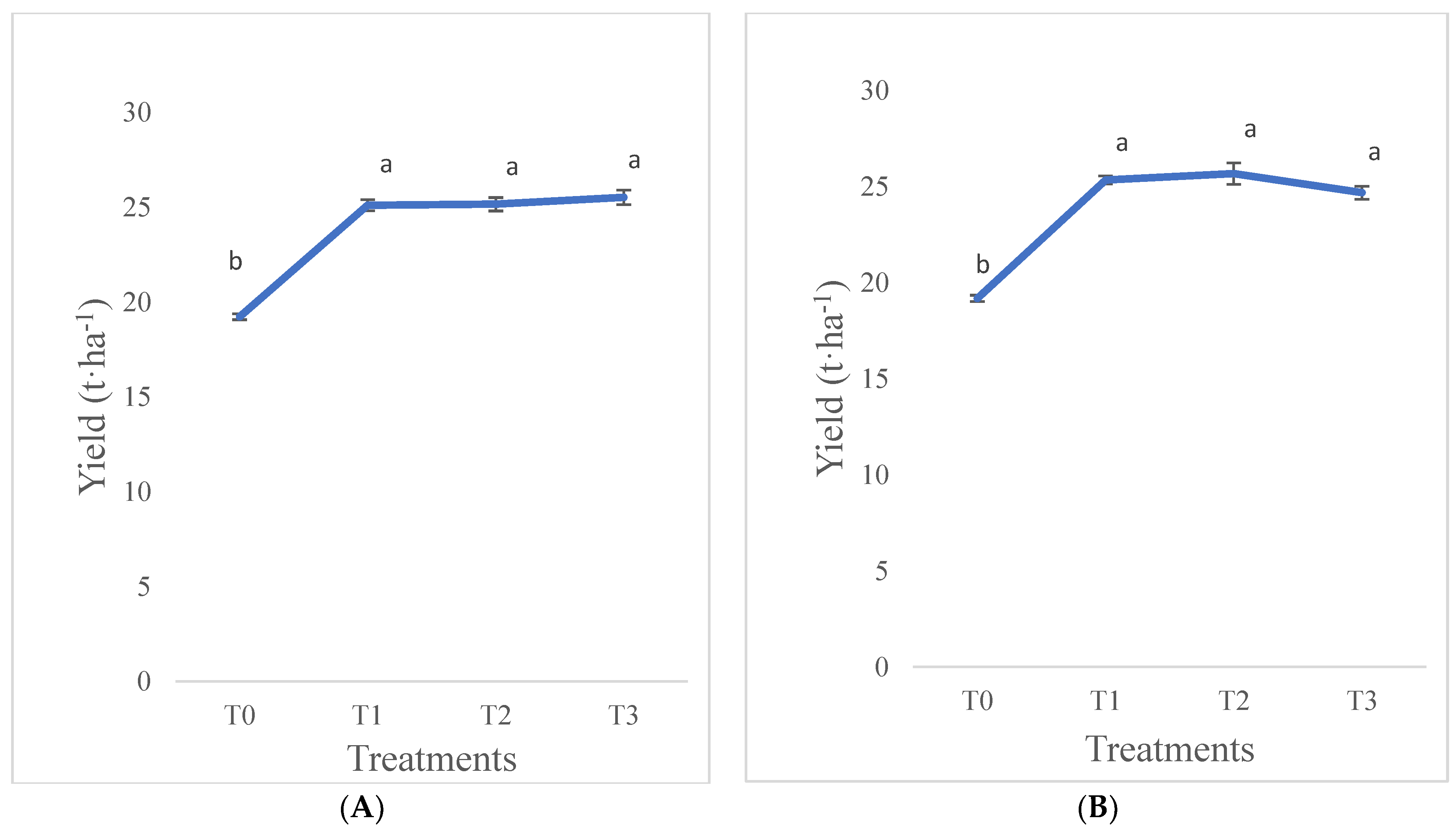
3.1.6. Yield
3.1.7. Nitrogen Content
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Note
- Truter, W.; Sehoole, O.; Murphy, M.; Fessehazion, M.; Annandale, J.; Jarmain, C.; Dlamini, M.; Everson, C. Irrigation Guidelines for Mixed Pastures and Lucerne. Water Comm. Rep. 2016, 31, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, E.B.; Hyam, G.F.S.; Breytenbach, W.A.S.; Metcalf, H.D.; Basson, W.D.; Williams, F.R.; Scheepers, L.F.; Plint, A.P.; Smith, H.R.H.; Smith, P.J.; et al. Pasture Handbook, 5th ed.; Kejafa Knowledge Works: Pretoria, South Africa, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Makuni, J. Direct and Indirect Methods of Estimating Lucerne (Medicago sativa) Yield. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2019; pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Truter, W.F.; Botha, P.R.; Dannhauser, C.S.; Maasdorp, B.V.; Miles, N.; Smith, A.; Snyman, H.A.; Tainton, N.M. Southern African pasture and forage science entering the 21st century: Past to present. Afr. J. Range Forage Sci. 2015, 32, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassermann, V.D.; Kruger, A.J.; van den Berg, M. Herbage yield and stand persistence of lucerne cultivars of varying winter dormancy under irrigation in the Transvaal Middleveld. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 1992, 9, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Bailly, X.; Giuntini, E.; Sexton, M.C.; Lower, R.P.J.; Harrison, P.W.; Kumar, N.; Young, J.P.W. Population genomics of Sinorhizobium medicae based on low coverage sequencing of sympatric isolates. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigley, K. Lucerne (Medicago sativa L.) Establishment after Inoculation with Different Carriers of Ensifer meliloti on Five Sowing Dates. Ph.D. Thesis, Lincoln University, Lincoln, NB, USA, 2011; pp. 1–86. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.M.; Kobayashi, H.; Davies, B.W.; Taga, M.E.; Walker, G.C. How rhizobial symbionts invade plants: The Sinorhizobium-Medicago model. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drizo, A.; Johnston, C.; Guðmundsson, J. An Inventory of Good Management Practices for Nutrient Reduction, Recycling and Recovery from Agricultural Runoff in Europe’s Northern Periphery and Arctic Region. Water 2022, 14, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnie, N.; Gweta, M.; Gweyi-Onyango, J.; Machage, B.; Mutegi, J.; Nziguheba, G.; Masso, C. Assessment of the 2006 Abuja fertilizer declaration with emphasis on Nitrogen use efficiency to reduce yield gaps in maize production. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 5, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IFPRI. Short-Term Policy Considerations to Respond to Russia-Ukraine Crisis Disruptions in Fertilizer Availability and Affordability; IFPRI International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Egamberdiyeva, D.; Qarshieva, D.; Davranov, K. Growth and yield of soybean varieties inoculated with Bradyrhizobium spp in N-deficient calcareous soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2004, 40, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, R.K.; Bhardwaj, D.; Tuteja, N. Bio-fertilizers: A sustainable eco-friendly agricultural approach to crop improvement. In Plant Acclimation to Environmental Stress; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 403–432. [Google Scholar]
- Ruzzi, M.; Aroca, R. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria act as bio-stimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htwe, A.Z.; Moh, S.M.; Soe, K.M.; Moe, K.; Yamakawa, T. Effects of biofertilizer produced from Bradyrhizobium and Streptomyces griseoflavus on plant growth, nodulation, nitrogen fixation, nutrient uptake, and seed yield of mung bean, cowpea, and soybean. Agronomy 2019, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatabazi, A.; Vorster, B.J.; Mvondo-She, M.A.; Mangwende, E.; Mangani, R.; Hassen, A.I. Efficacy of Peat and Liquid Inoculant Formulations of Bradyrhizobium japonicum Strain WB74 on Growth, Yield and Nitrogen Concentration of Soybean (Glycine max L.). Nitrogen 2021, 2, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frame, J.; Charlton, J.F.L.; Laidlaw, A.S. Temperate Forage Legumes, 1st ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wigley, K.; Liu, W.Y.Y.; Khumalo, Q.; Moot, D.J.; Brown, D.S.; Ridgway, H.J. Effectiveness of three inoculation methods for lucerne (Medicago sativa L.) in two Canterbury soils. N. Zeal. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 58, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biradar, B.P.; Santhosh, G.P. Role of Polymeric Additives in Formulation, Shelf-life and Bioefficacy of Liquid Inoculant of Pseudomonas fluorescens. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2018, 6, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World Map of the Koppen-Gieger Climate Classification Updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soil Classification Working Group, 1991, South Africa: Cited [16].
- Jackson, M.C. Soil Chemical Analysis; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Zhou, X.; Smith, D.L. Enhanced soybean plant growth resulting from co-inoculation of Bacillus strains with Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, J.C.; Ladha, J.K.; Dazzo, F.B.; Yanni, Y.G.; Rolfe, B.G. Rhizobial Inoculation Influences Seedling vigor and Yield of Rice. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souleimanov, A.; Prithiviraj, B.; Smith, D.L. The major Nod factor of Bradyrhizobium japonicum promotes early growth of soybean and corn. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamptey, S.; Ahiabor, B.D.K.; Yeboah, S.; Osei, D. Effect of rhizobium inoculants and reproductive growth stages on shoot biomass and yield of soybean (Glycine max (L.) merril). J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argaw, A. Evaluation of co-inoculation of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Phosphate solubilizing Pseudomonas spp. effect on soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) in Assossa Area. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2012, 14, 213–224. [Google Scholar]
- Tairo, E.V.; Ndakidemi, P.A. Yields and economic benefits of soybean (Glycine max L.) as affected by Bradyrhizobium japonicum inoculation and phosphorus supplementation. Am. J. Res. Commun. 2013, 1, 159–172. [Google Scholar]
- Soe, K.M.; Yamakawa, T. Evaluating the effects of Streptomyces griseoflavus P4 on dry weight of different crops and examine phytohormones activity in term of indole acdic acid (IAA) production. Myanmar Agric. Res. J. 2018, 4, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Patten, C.L.; Glick, B.R. Role of Pseudomonas putida indoleacetic acid in development of the host plant root system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3795–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, A.I.; Fadaka, A.O.; Gokul, A.; Bakare, O.O.; Aina, O.; Fisher, S.; Klein, A. Biofertilizer: The future of food security and food safety. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gatabazi, A.; Botha, M.; Mvondo-She, M.A. Assessing Liquid Inoculant Formulation of Biofertilizer (Sinorhizobium meliloti) on Growth, Yield, and Nitrogen Uptake of Lucerne (Medicago sativa). Nitrogen 2023, 4, 125-134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen4010009
Gatabazi A, Botha M, Mvondo-She MA. Assessing Liquid Inoculant Formulation of Biofertilizer (Sinorhizobium meliloti) on Growth, Yield, and Nitrogen Uptake of Lucerne (Medicago sativa). Nitrogen. 2023; 4(1):125-134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen4010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleGatabazi, Auges, Martin Botha, and Mireille Asanzi Mvondo-She. 2023. "Assessing Liquid Inoculant Formulation of Biofertilizer (Sinorhizobium meliloti) on Growth, Yield, and Nitrogen Uptake of Lucerne (Medicago sativa)" Nitrogen 4, no. 1: 125-134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen4010009
APA StyleGatabazi, A., Botha, M., & Mvondo-She, M. A. (2023). Assessing Liquid Inoculant Formulation of Biofertilizer (Sinorhizobium meliloti) on Growth, Yield, and Nitrogen Uptake of Lucerne (Medicago sativa). Nitrogen, 4(1), 125-134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen4010009





