Abstract
Economic use of organic and inorganic fertilizers following their availability is necessary for livestock-based Nepalese farming systems. However, how best to integrate these fertilizers in an appropriate manner is not yet clear. Thus, this study was conducted in the horticulture farm of the Agriculture and Forestry University (AFU), Rampur, Chitwan, Nepal from November 2018 to February 2019 to evaluate the effect of organic and inorganic sources of nitrogen (N) on growth, yield, and quality of beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.) varieties. The experiment was laid out in a two factorial randomized complete block design with four replications consisting of two beetroot varieties, i.e., Madhur and Ruby Red, and five N source combinations, i.e., N1: 100% poultry manure (PM), N2: 50% PM + 50% urea, N3: 100% farmyard manure (FYM), N4: 50% FYM + 50% urea, and N5: 100% urea (120:80:40 kg NPK ha−1). Results of this study indicated a significant impact of N sources and varieties on the assessed parameters. During harvest, a significantly higher plant height (41.84 cm), number of leaves per plant (14.68), leaf length (34.56 cm), leaf width (11.38 cm), and beetroot diameter (72.15 mm) were observed in the N2 treatment. Likewise, higher economic (49.78 t ha−1) and biological yields (78.69 t ha−1) were also recorded in the N2 compared to other N sources. Out of the two varieties, the Madhur variety was significantly better in most growth and yield parameters. Similarly, the Madhur variety showed a significantly higher economic (44.49 t ha−1) and biological yields (69.79 t ha−1) compared to the Ruby Red variety. However, the physiological weight loss was higher in the Ruby Red variety. Therefore, the current study suggests that an integration of poultry manure along with the combination of N fertilizer and the Madhur variety is the best combination for quality beetroot production in the Terai region of Nepal.
1. Introduction
Beetroot is one of the major root vegetables grown throughout the world and is mainly consumed as a salad vegetable, though the leaves can also be eaten as spinach [1]. Recently, beetroot has been gaining popularity as a “super food” due to its beneficial value for health. It can be consumed in a variety of states from raw to heavily processed. It is a rich source of protein, carbohydrates, calcium, and phosphorous; therefore, it is an ideal vegetable for health-conscious individuals [2]. From the cultivation point of view, beetroot is easy to cultivate in the field. It grows quickly, is highly productive, and is usually free of pests and diseases [3]. Though it is a cool season crop, it grows well in warm weather and thus can be grown during winter all across the plains of Nepal. However, the growth, development, and yield of beetroot depend greatly on soil conditions. Soils supplied with nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P), and potassium (K) through the addition of organic and inorganic fertilizers influence the growth and harvest of the beetroot crop [4]. Nevertheless, application of chemical fertilizers by farmers without sufficient knowledge of soil fertility status and crop nutrient requirements affects the soil as well as the crop. As a result, the inappropriate use of inorganic fertilizers has led to a drastic reduction in the fertility status of Nepalese soils [5,6]. Among the many constraints to increasing the productivity of beetroot, application of inorganic nutrients (mainly N) is the most limiting factor [7]. Optimum application of N fertilizers promotes growth and in turn increases both yield and quality; however, excessive application of N fertilizer negatively impacts the soil ecosystem and can reduce yield [8,9,10]. Therefore, the substitution of inorganic fertilizers with organic manure or a reduction in chemical fertilizer usage is necessary for the sustainability of agriculture production [4]. Organic manure such as PM and FYM is easily available in Nepalese farming communities. Organic manure is regarded as especially important for root crops, as it improves the physical, chemical, and biological conditions of soil and ultimately favors better root growth [11]. Farmyard manure is highly used organic manure that supplies some essential plant nutrients (N, P, and K) and other macronutrients and micronutrients. Poultry manure is another important organic source of nutrients, and it contains relatively higher amount of plant nutrients compared to other organic manures [12]. However, application of the appropriate amount of animal manure itself cannot meet crop requirements, as the direct application of organic manure is bulky and takes longer to decompose in the soil, which may not be possible during the crop growing period and may lead to poor yield [4]. In this regard, the combined use of organic and inorganic fertilizers has been reported to be the best alternative for better root growth and production of root crops such as beets [13].
Many studies have also reported positive effect of fertilization with inorganic and/or organic fertilizers on the yield of vegetables such as carrot [14], radish [15], cabbage [16], and tomato [17]. Adopting appropriate fertilizer management strategies results in significant economic benefits to producers [18]. Agriculture, as an economic sector, should operate profitably while adhering to the fundamental principles of sustainable agricultural production, with minimal environmental effect and judicious application of fertilizers [19]. In addition to the nutrient requirements, the genetic characteristics of a variety determine the amount of yield. The variety should be selected as per the growing environment and season. However, only one variety (i.e., Madhur) is registered in Nepal [20] and all other varieties such as Ruby Red and Ruby Queen are imported from abroad and sold by private seed companies. Further, there has been limited research carried out on the available beetroot varieties as per the growing environment. To achieve more returns per unit area, the selection of a suitable variety as well as the good fertilization strategy combining the use of organic and inorganic nutrients is necessary [21]. By taking the above-mentioned criteria into account, we carried out this study to explore the effect of organic and inorganic sources of N on growth, yield, and quality of beetroot along with appropriate variety selection in the Terai region of Nepal.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
The current experiment was conducted at the horticulture farm of Agriculture and Forestry University, Rampur, Chitwan District, Narayani Zone, Nepal from November 2018 to February 2019. The experimental site is located at 27°31′ N latitude and 84°25′ E longitude with elevation of 228 masl and is about 10 km west from district headquarter Bharatpur. The location lies in the Terai of Central Development Region of Nepal.
2.2. Climate
The experimental site was situated in the humid subtropical region characterized by three distinct seasons, summer or spring season (March to May), rainy or monsoon season (June to September), and winter season (November to February). The maximum winter temperature rises up to 27 °C. The hottest part of the year is April/May and June when the maximum temperature ranges between 37 °C to 42 °C.
The weekly average data on different weather parameters, i.e., maximum and minimum temperature, relative humidity, and total rainfall during the growing season of beetroot, were collected from nearby station, National Maize Research Programme (NMRP), Rampur, Chitwan and is presented in Figure 1. The maximum temperature ranged from 22.66 °C (4th week of December 2018) to 29.46 °C (1st week of November 2018). The minimum temperature ranged from 7.18 °C (1st week of January 2019) to 16.52 °C (1st week of November 2018). Likewise, the average relative humidity during cropping season was 91.73%. Rainfall occurred only once during 4th week of January2019 (11 mm).
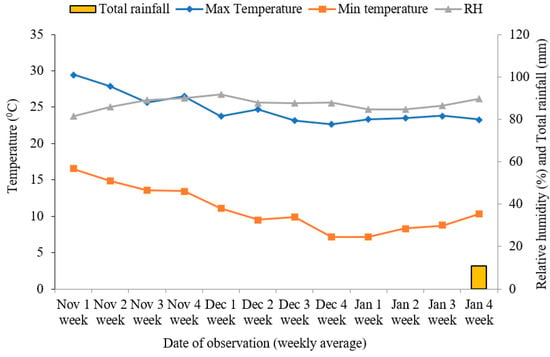
Figure 1.
The weekly average meteorological data of the experimental site (Horticulture farm, AFU, Rampur, Chitwan from November 2018 to January 2019.
2.3. Soil Characteristics of Research Site
Soil samples were taken from the top (0 to 30 cm) layer before the commencement of the experiment and analyzed for its some physical and chemical properties. Three composite soil samples were then prepared by mixing the collected subsamples before sowing. Each composite sample represented each block of the experimental design. Total N was determined by Macro–Kjeldahl method [22], available P by Olsen’s bio-carbonate method, and available K by ammonium acetate method [23]. Organic matter was determined by Walkely and Black method [24], pH by Beckman Glass Electrode pH [25], and soil texture by hydrometer method at Soil and Fertilizer Testing Laboratory of Ministry of Land Management, Hetauda, Makwanpur District, Nepal. The soil in the study site is loamy sand with initial soil chemical properties of 5.7 pH, 3.9% organic matter, 0.14% total N, 30.3 kg ha−1available P, and 397.3 kg ha−1 available K.
2.4. Experimental Details
A randomized complete block design including two treatment factors was used in this study and replicated four times. The first treatment factor was N sources at five levels: N1: 100% N from poultry manure (PM, i.e., 13.11 t ha−1), N2: 50% N from PM (6.55 t ha−1) + 50% N from urea (60 kg N ha−1), N3: 100% N from farmyard manure (FYM, 25.80 t ha−1), N4: 50% N from FYM (12.90 t ha−1) + 50% N from urea (130.43 kg N ha−1), and N5: 100% N from urea (260.86 kg N ha−1). All the organic and inorganic fertilizers were applied as per the recommended dose, i.e., 120:80:40 kg NPK ha−1 [20]. The dose of organic manure and inorganic fertilizer was calculated based on their nutrient content and required amount of N was supplied through those sources. However, P(as 500 kg P2O5 ha−1) and K (66.67 kg K2O ha−1) doses were made constant and added as single superphosphate (SSP) and muriate of potash (MOP), respectively, equally in all plots at seed sowing time. The second treatment factor was variety at two levels: Madhur and Ruby Red, which are both open-pollinated varieties. There were a total of 40 plots, each of which was 1.8 m × 1.0 m in size. The N content of FYM and PM used in this study was 0.9 and 1.8%, respectively. After precise calculations, the required amount of manure was applied well before seed sowing.
2.5. Sowing and Cultural Management
The whole experimental field was ploughed by tractor, and harrowing was done to make the soil pulverized and smooth. The organic manures and chemical fertilizers were applied after final field preparation and before sowing. Beetroot seeds were primed over a night before sowing and were sown in line, two seeds per hill on 3 November 2018at a spacing of 45 × 10 cm. All the intercultural operations such as thinning, weeding, and irrigation were performed during the life stages of the beetroot crop. Both varieties were harvested at 80 days after sowing (DAS).
2.6. Data Collection
For data collection, a set of 10 random plants from each plot excluding the border plants was taken during the crop growing period and after harvesting. The observations recorded during the crop growing period were plant height (cm), number of leaves per plant, leaf length (cm), leaf breadth (cm), and canopy diameter (cm). Similarly, after harvest, the measured parameters were beetroot diameter (mm), beetroot length (cm), root and leaf fresh weight (g), economic yield (t ha−1), biological yield (t ha−1), root and leaf dry matter %, and physiological weight loss (%),
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data entry and tabulation was done on MS-Excel and data analysis was done using GENSTAT 18th edition software. The effects of treatments (N source and variety) on measured variables were tested by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The means were compared using Duncan’s multiple range test (DMRT) at 5% level of significance.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Variety and Nitrogen Source on Growth Parameters
3.1.1. Plant Height
The results of ANOVA showed that the plant height was significantly affected by the variety and nitrogen (N) source at different stages of beetroot (p ≤ 0.05) (Table 1). However, the interaction effect exhibited no significant variation on plant height of beetroot. Significantly higher plant heights were recorded in the Madhur variety than the Ruby Red variety from 60 DAS till harvest. Similarly, beetroot plant height did not differ significantly due to N sources at 30, 40, and 50 DAS, but highly significant variation was observed at 60 DAS, 70 DAS, and final harvest. At harvest, the N2 treatment had significantly taller plant height (41.84 cm), while lower (34.77 cm) was in the N3 treatment (p ≤ 0.01).

Table 1.
Effect of variety and nitrogen source on plant height at different stages of beetroot at AFU, Rampur, Chitwan in 2018/19.
3.1.2. Number of Leaves per Plant
Statistically, no significant variation in number of leaves per plant was recorded between the two varieties of beetroot at 30, 40, and 50 DAS (Table 2). In contrast, the number of leaves was significantly higher in the Madhur variety at 60 DAS (10.34), 70 DAS (12.31), and at harvest (13.96) compared to the Ruby Red variety (9.91, 11.99, and 12.99, respectively).

Table 2.
Effect of variety and nitrogen source on number of leaves at different stages of beetroot at AFU, Rampur, Chitwan in 2018/19.
The number of leaves of beetroot at all stages varied significantly among the different N sources (Table 2). At harvest, a significantly higher number of leaves (14.68) was observed in the N2 treatment (p ≤ 0.001). In addition, the number of leaves in the N5 (13.53) and N1 (13.36) treatments were statistically similar.
3.1.3. Canopy Diameter
The results of ANOVA depicted that the main effect of variety and N source had a significant effect on canopy diameter of beetroot at all stages except 40 and 50 DAS (Table 3). At 60 DAS (35.97 cm), 70 DAS (38.15 cm), and 80 DAS (40.51 cm), canopy diameter was higher in the Madhur variety than in the Ruby Red variety (p ≤ 0.05). Likewise, among N sources, beetroot had a higher canopy diameter (39.54 cm) in the N1 treatment compared to the other N sources at 60 DAS (p ≤ 0.01). The observations at 70 and 80 DAS exhibited a similar pattern.

Table 3.
Effect of variety and nitrogen source on canopy diameter at different stages of beetroot at AFU, Rampur, Chitwan in 2018/19.
3.1.4. Leaf Length
The effect of variety and nitrogen source on leaf length of beetroot at different stages is presented in Table 4. Between the two varieties, a significantly (p ≤ 0.05) longer leaf was recorded in Madhur (33.70 cm) compared to Ruby Red (32.07 cm) at harvest. Regarding the different N sources, the N2 treatment had a significantly longer leaf at all growth stages compared to all other N sources. In contrast, leaf length was significantly lower in the N3 treatment (31.58 cm) among the N sources.

Table 4.
Effect of variety and nitrogen source on leaf length of beetroot at different stages at AFU, Rampur, Chitwan in 2018/19.
3.1.5. Leaf Breadth
According to the results of ANOVA, the leaf breadth of beetroot was not significantly different between varieties during the early growth period (i.e., 30, 40, and 50 DAS) except at 60 DAS, 70 DAS, and at harvest (Table 5). At 60 DAS, 70 DAS, and at harvest, the Madhur variety had a significantly (p ≤ 0.05) wider leaf (9.8 cm, 10.36 cm, and 10.81 cm, respectively), while narrower leaf (9.32 cm, 9.62 cm, and 10.31 cm, respectively) was produced by the Ruby Red variety. Likewise, among N sources, a significantly greater leaf breadth was observed in the N2 treatment compared to the other treatments from 30 DAS until harvest, while a significantly narrower leaf was recorded in the N3 treatment (Table 5).

Table 5.
Effect of variety and nitrogen source on leaf breadth of beetroot at different stages at AFU, Rampur, Chitwan in 2018/19.
3.2. Effect of Variety and Nitrogen Source on Yield and Quality Attributing Parameters
3.2.1. Root Diameter and Length
The ANOVA results showed that the root diameter and length was significantly affected by the variety as well as the nitrogen source at harvest (Table 6). However, they did not differ significantly by the interaction effect of the two factors (Table 6). Generally, root diameter and total root length was higher in the Madhur variety (69.88 mm and 22.08 cm, respectively) than the Ruby Red variety (66.07 mm and 20.86 cm, respectively) (p ≤ 0.05). The varietal effect on edible root length was, however, non-significant. Among the combinations of different N sources, the N2 treatment had a significantly highest root diameter (72.15 mm) (p ≤ 0.05), while the lowest root diameter (64.32 mm) was found in the N3 treatment. In addition, total root length was found to be significantly greater in the N1 treatment followed by the N3 (21.84 cm) treatment (p ≤ 0.001). Likewise, the N1 treatment had significantly higher edible root length (11.05 cm) among all the other treatments (p ≤ 0.05).

Table 6.
Effect of variety and nitrogen source on beetroot diameter and length at AFU, Rampur, Chitwan in 2018/19.
3.2.2. Average Root and Leaf Fresh Weight
The effect of variety and N source on root and leaf fresh weight is presented in Table 7. According to the ANOVA results, the Madhur variety had significantly highest root weight (200.20 gm) (p ≤ 0.05) and leaf weight (113.80 gm) (p ≤0.01) compared to the Ruby Red variety (177.10 gm and 95.60 gm, respectively). Among the N sources, the N2 treatment had a significantly greater (p ≤ 0.01) average root weight per plant (224.00 g) compared to the N4 (207.50 g) treatment. However, the root weight in the N1, N3, and N5 treatments did not differ significantly. Likewise, the N2 treatment had the greater leaf weight (130.10 g), which was statistically at par with the N4 (121.40 g) treatment (p ≤ 0.01), on the other hand, lowest leaf fresh weight was recorded in the N3 treatment (79.70 g).

Table 7.
Effect of variety and nitrogen source on root and leaf fresh weight of beetroot at AFU, Rampur, Chitwan in 2018/19.
3.2.3. Economic and Biological Yields
The ANOVA results demonstrated that the economic (root) and biological yields of beetroot were both significantly influenced by the variety and N source (Table 8).The Madhur variety had a significantly higher economic (44.49 t ha−1) and biological yield (69.79 t ha−1) compared to the Ruby Red variety (39.35 t ha−1 and 60.59 t ha−1, respectively). Among N sources, a significantly higher (p ≤ 0.01) economic yield (49.78 t ha−1) was recorded in the N2 treatment compared to the N4 treatment (46.12 t ha−1). The observations on biological yield also exhibited a similar pattern. A significantly higher (p ≤ 0.01) biological yield (78.69 t ha−1) was observed in the N2 treatment compared to the other treatments. Meanwhile, economic (35.76 t ha−1) and biological yields (53.47 t ha−1) were lowest in the N3 treatment. However, the interaction effect of variety and N source did not show significant differences on the economic and biological yield of beetroot.

Table 8.
Effect of variety and nitrogen source on economic (root) and biological yield of beetroot at AFU, Rampur, Chitwan in 2018/19.
3.2.4. Root and Leaf Dry Matter Percentage
The main effect of variety and nitrogen source demonstrated a significant effect on root and leaf dry matter percentage (p ≤ 0.05) (Table 9). Higher root and leaf dry matter percentage was recorded in variety Madhur (10.47% and 9.10% respectively) than that of Ruby Red variety. Among N sources, significantly higher root dry matter % was observed in N1 treatment (10.94%) followed by N2 (10.75%). Similarly, higher leaf dry matter % was recorded in treatment N2 (9.19%) followed by treatment N5(8.94%).

Table 9.
Effect of varieties and nitrogen sources on root dry matter % and leaf dry matter of beetroot at AFU, Rampur, Chitwan in 2018/19.
3.2.5. Physiological Loss in Weight (PLW)
Between the two varieties, the Ruby Red variety lost significantly more fresh weight than that of the Madhur variety from the 3rd day of storage up to the 11th day of storage (Table 10). When beetroots were stored under ordinary room conditions, the highest percentage of fresh weight loss was found in the N5 followed by the N3 treatmentsfrom the 3rd day of storage up to the 11th day of storage (Table 10). Weight loss was significantly lower in the N2 treatment followed by the N1 and N3 treatments from the 3rd day to the 11th day of storage (Table 10).

Table 10.
Effect of variety and nitrogen source on physiological weight loss (%) of beetroot at different days of storage at AFU, Rampur, Chitwan in 2018/19.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Variety on Beetroot Growth, Yield, and Quality Attributes
4.1.1. Effect of Variety on Beetroot Growth
The current study revealed a higher plant height in the Madhur variety compared to the Ruby Red variety from 60 DAS till harvest. Such differences in plant height between the two varieties could be attributed to the genetic makeup of the beetroot plants and their response to the soil growing and environmental conditions. A variation in plant height among different varieties of radish was also reported by Chapagain et al. [26], Dongarwar et al. [27], and Subedi et al. [11]. Similarly, during the early phase of growth (30, 40, and 50 DAS), no significant effect of variety on number of leaves per plant was observed. This could be attributed to the fact that the varieties might not have expressed their genetic potential at the early growth stages. However, a significant difference in the number of leaves between the varieties was observed from 60 DAS till harvest. A greater number of leaves per plant was recorded in the Madhur variety compared to the Ruby Red variety. This might be due to the developing beetroot plants’ need for more carbohydrates, which encouraged the Madhur plants to produce a greater number of leaves. Similar results were obtained by Chapagain et al. [26] and Kumar et al. [28] in radish.
In addition, both varieties showed a significant effect on leaf length, leaf breadth, and canopy diameter at the different stages of beetroot. The longest and widest leaves were produced by the Madhur variety compared to the Ruby Red variety. Significantly higher canopy spread was also observed in the Madhur variety from 60 DAS till harvest. Thus, having longer and wider leaves in addition to a higher canopy spread might have aided in more photosynthate accumulation, which produced maximum yield [27]. The variation in these vegetative traits between varieties is probably due to genetic differences.
4.1.2. Effect of Variety on Yield and Quality of Beetroot
Root diameter, total root length, and economic and biological yield were recorded significantly higher in the Madhur variety. Root diameter is primarily a cultivar characteristic, as different cultivars have different root shapes and sizes [13]. These results are in accordance with the findings of Ijoyah et al. [29], who reported significant variation in root diameter and length among four different cultivars of beetroot, viz., Moronia, Lola, Crosby, and Detroit-243. A similar variation in diameter and length of root among different varieties was also reported by Dongarwar et al. [27] in radish. As the number of leaves, leaf length, and leaf breadth were higher in the Madhur variety, it also exhibited the highest leaf fresh weight as well as leaf dry matter. The present results conform to the findings of Singh et al. [15], who reported a significant difference among radish cultivars to root weight.
Likewise, the economic/root yield of beetroot was found to be significantly higher in the Madhur variety compared to the Ruby Red variety. A significant increase in root yield might be due to the cumulative effect of all of the growth parameters, viz., plant height, leaf length, leaf breadth, leaf fresh and dry weight, and yield components, viz., root length, root diameter, and root fresh weight. Moreover, a significant increase in root yield could be attributed to the genetic structure of the evaluated beetroot varieties. The root yield was also the result of translocation of more carbohydrates from source to sink [27]. Similar results were also recorded by Ijoyah et al. [29] among different cultivars of beetroot, viz., Moronia, Lola, Crosby, and Detroit-243, where the Crosby variety was superior to all others in terms of root yield. The result on root yield was also in accordance with the findings of Singh and Taj [30] in radish.
4.2. Effect of Nitrogen Source on Beetroot Growth, Yield, and Quality Attributes
4.2.1. Effect of Nitrogen Source on Beetroot Growth
Results revealed that all of the vegetative parameters of beetroot were significantly enhanced with the combined use of urea and poultry manure. The integrated use of nutrients resulted in rapid cell division, multiplication, and elongation in the meristematic region of plants, which promoted vegetative growth [31]. The N also synthesized into amino acids, which built complex proteins and helped in promoting luxurious growth [31]. Kiran et al. [32] also recorded similar findings in radish.
4.2.2. Effect of Nitrogen Source on Beetroot Yield and Quality Parameters
Significantly higher root diameter and length were produced by either PM alone or in combination with urea, which ultimately resulted in higher root (economic) yield in the same treatment. The increased root length in poultry manure applied to plots might be due to the presence of phosphorous (1.2%) in poultry manure. Phosphorus stimulates root growth, allowing for greater absorption and translocation of nutrients [8]. Moreover, application of organic manure helps soil microorganisms to produce polysaccharides and thus leads to better soil structure useful for root growth [33]. According to Gajeswki et al. [34], the application of poultry manure allows for easy root penetration, erosion resistance, and good soil moisture properties such as available water holding capacity and permeability, combined with adequate aeration. Likewise, significantly higher root diameter in poultry manure plus urea-treated plots might be due to the sufficient availability of phosphorous from poultry manure affecting the root diameter of root crops. It could also be due to the adequate supply of macro- and micronutrients for the metabolic activities of the plants. Similar results were reported by Kanauija [35], who recorded maximum values for carrot root diameter (4.14 cm) when a combination of urea and organic manure was used.
The highest root diameter was recorded in the N2 (50% N from PM + 50% N from urea) treatment, which ultimately led to higher root yield in the same treatment. This might be due to the corresponding response of increased growth and yield attributing characteristics attained previously under this treatment. Furthermore, an increment in root yield as a result of the integration of organic and inorganic fertilizer might be due to the reduction in nutrient losses, improved fertilizer use efficiency, and increased soil nutrient availability to plants, resulting in higher root yield [32]. The maximum biological yield was also found in the N2 (50% N from PM + 50% N from urea) treatment and the minimum yield in the N3 (100% N from FYM) treatment. The biological yield is directly influenced by leaf number, leaf length, leaf fresh weight, root length, root diameter, and root weight of plants. Further, solubilization of plant nutrients through the addition of inorganic fertilizers and organic manure results in an increased uptake of N and biological yield of the plant. Similar results were obtained by Subedi et al. [11] in radish.
5. Conclusions
Our study concluded that the Madhur variety of beetroot performed better than the Ruby Red variety in terms of overall growth, yield, and quality attributes in the Chitwan district of Nepal. The current study also indicated that application of 50% N through poultry manure and 50% N through urea can produce a higher yield than either of these applications alone. Therefore, the integrated application of organic and inorganic N sources is suggested for the optimum production and quality of beetroot in the Terai region of Nepal. However, further research should be carried out in different agro-climatic locations of the country including different varieties before the dissemination of these findings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization—A.S. and M.D.S.; Methodology—A.S.; Investigation—A.S.; Data curation—A.S., H.N.G. and B.S.; Formal Analysis—A.S., H.N.G. and D.P.; Visualization—A.S., M.D.S., D.P.; Supervision—M.D.S., H.N.G. and B.S.; Software—A.S. and H.N.G.; Validation—A.S., M.D.S., H.N.G., B.S. and D.P.; Writing—Original draft preparation—A.S.; Writing—Review and Editing—A.S., M.D.S., H.N.G., B.S. and D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Agriculture and Forestry University, Rampur, Nepal for their assistance during the research period. Our sincere thanks to Ian Rogers for professional English editing service during the preparation of the manuscript. Finally, we would like to thank anonymous reviewers and an academic editor for their valuable comments and suggestions which helped us on improving this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lock, M.; Grubben, G.J.H.; Denton, O.A. Plant Resources of Tropical Africa 2. Vegetables. Kew Bull. 2004, 59, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deuter, P.; Grundy, T. Beetroot commercial production and processing. Agency Food Fibre Sci. Holl. Hortic. Ltd. Partn. 2004, 14, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nottingham, S. Beetroot. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/21542519/Beetroot (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Deshika, V.; Karunarathna, B. Effect of integrated plant nutrient management on growth and yield of radish (Raphanus sativas L.) in sandy regosol. Res. J. Agric. For. Sci. 2019, 7, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sapkota, A.; Shrestha, R.K.; Chalise, D. Response of maize to the soil application of nitrogen and phosphorous fertilizers. Intl. J. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 5537–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, S.; Bhatta, N.P.; Paudel, P.; Pariyar, R.; Maskey, K.H.; Khadka, J.; Thapa, T.B.; Rijal, B.; Panday, D. Improving fertilizer recommendations for Nepalese farmers with the help of soil-testing mobile van. J. Crop Improv. 2018, 32, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagadeesh, C.; Madhavi, M.; Siva-Prasad, M.; Padmaja, V.V. Effect of organic manures on growth and yield attributes of beetroot cv. Crimson Globe. Intern. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 3538–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodlass, G.; Rahn, C.; Shepherd, M.A.; Chalmers, A.G.; Seeney, F.M. The nitrogen requirement of vegetables: Comparisons of yield response models and recommendation systems. J. Hort. Sci. 1997, 72, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzluebbers, A.J. Integrated crop-livestock systems in the southeastern USA. Agric. J. 2007, 99, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickhout, B.; Bouwman, A.P.; VanZeijts, H. The role of nitrogen in world food production and environmental sustainability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 116, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, S.; Srivastava, A.; Sharma, M.D.; Shah, S.C. Effect of organic and inorganic nutrient sources on growth, yield and quality of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) varieties in Chitwan, Nepal. SAARC J. Agric. 2018, 16, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J. Composting Chicken Manure. WSU cooperative extension. King County Master Gardner and Cooperative Extension Livestock Advisor, Washington State University, Pullman. 2005. Available online: hppt://www.scirp.org (accessed on 26 August 2021).
- Ahmed, A.; Sambo, B.E.; Arunah, U.L.; Odion, E.C. Response of farm yard manure and inorganic fertilizers for sustainable growth of carrot (Daucus carota L.) in Northern Nigeria. J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2014, 7, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Horlacher, D.; Liebig, H.P. Effects of different nitrogen rates on open-field vegetable growth and nitrogen utilization in the north China plain. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2004, 35, 1725–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Gandhi, N.; Singh, K.; Tinna, D.; Singh, S. Effect of the organic manure, inorganic fertilizers and their combination on growth, yield and quality of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) cv.R33. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, SP4, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Jakse, M.; Mihelic, R. The influence of organic and mineral fertilization on vegetable growth and N availability in soil: Preliminary results. Acta Hortic. 1999, 506, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ayeni, L.S.; Omole, T.O.; Adeleye, E.O.; Ojeniyi, S.O. Integrated application of poultry manure and NPK fertilizer on performance of tomato in derived savannah transition zone of southwest Nigeria. Sci. Nat. J. 2010, 8, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Escalante, H.J.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, S.; Jiménez-Lizárraga, M.; Morales-Reyes, A.; DeLaCalleja, J.; Vazquez, R. Barley yield and fertilization analysis from UAV imagery: A deep learning approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2493–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petek, M.; Toth, N.; Pecina, M.; Karažija, T.; Lazarević, B.; Palčić, I.; Veres, S.; Ćustić, M.H. Beetroot mineral composition affected by mineral and organic fertilization. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AITC. Agriculture Information and Training Center/Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development. Hariharbhawan, Lalitpur, Nepal (2018/19). Available online: http://www.aitc.gov.np (accessed on 2 November 2018).
- Devkota, S.; Panthi, S.; Shrestha, J. Response of rice to different organic and inorganic nutrient sources at Parwanipur, Bara district of Nepal. J. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2019, 2, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Prentice Hall of India: New Delhi, India, 1967; 498p. [Google Scholar]
- Black, C.A. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1. Physical and mineralogical Properties; Agronomy Series No.9; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottenie, A.; Veriso, M.; Kilkens, L.; Velghe, G.; Camerlynck, R. Chemical Analysis of Plants and Soillaboratory of Analytical and Agrochemistry; State University: Ghent, Belgium, 1982; pp. 100–129. [Google Scholar]
- Chapagain, T.R.; Piya, S.; Dangal, N.K.; Mandal, J.L.; Chaudhary, B.P. Comparison of commercial and local varieties of radish at different levels of manures and fertilizers. Nepal J. Sci. Technol. 2010, 11, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongarwar, L.N.; Kashiwar, S.R.; Ghawade, S.M.; Dongarwar, U.R. Varietal performance of radish (Raphanus sativus L.)varieties in black soils of Vidharbha-Maharashtra, India. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2018, 7, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Baishaya, L.K.; Ghosh, D.C.; Gupta, V.K.; Dubey, S.K.; Das, A.; Patel, D.P. Productivity and soil health of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) field as influenced by organic manures, inorganic fertilizers and bio-fertilizers under high altitudes of eastern Himalayas. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 223. [Google Scholar]
- Ijoyah, M.O.; Sophie, V.L.; Rakotomavo, H. Yield performance of four beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.) varieties compared with the local variety under open field conditions in Seychelles. Agro-Science 2008, 7, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.B.; Taj, R.K. Evaluation of radish cultivars under rainfed conditions of Nagaland. Prog. Horti. 2005, 37, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, M.R.; Sreedhar, D. Growth and yield response of radish cv. Pusa Himani to integrated nutrient management practices. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Bio-Res. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, M.; Jilani, M.S.; Waseem, K.; Khan, M.S.; Haq, F.; Nadim, M.A.; Ullah, G.; Shaheen, S. Integrated use of organic and inorganic fertilizers on the growth and yield of radish. Sarhad J. Agric. 2019, 35, 933–941. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, A.; Siddaramappa, R.; Rangaswami, G. Effect of organic manuring on the activities of the enzymes hydrolyzing sucrose and urea and on soil aggregation. Plant Soil 1972, 37, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajewski, M.; Weglarz, Z.; Serdea, A.; Bajer, M.; Kuczkowska, A.; Majewski, M. Carotenoid accumulation by carrot storage roots in relation to nitrogen fertilizer level. Not. Bot. Horti. Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2010, 38, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Kanaujia, S.P. Integrated nutrient management on productivity of carrot and fertility of soil. SAARC J. Agric. 2013, 11, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).