Abstract
This study focuses on the complex pore structure and pronounced heterogeneity of tight sandstone reservoirs in the Linxing area of the Ordos Basin and develops a multi-scale quantitative characterization approach to investigate the coupling mechanism between pore structure and reservoir properties. Six core samples were selected from the Shiqianfeng Formation (depth interval: 1326–1421 m) for detailed analysis. Cast thin sections and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) experiments were employed to characterize pore types and structural features. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments were conducted to obtain T2 spectra, which were used to classify bound and movable pores, and their corresponding fractal dimensions were calculated separately. In addition, NMR logging data from the corresponding well intervals were integrated to assess the applicability and consistency of the fractal characteristics at the logging scale. The results reveal that the fractal dimension of bound pores shows a positive correlation with porosity, whereas that of movable pores is negatively correlated with permeability, indicating that different scales of pore structural complexity exert distinct influences on reservoir performance. Mineral composition affects the evolution of pore structures through mechanisms such as framework support, dissolution, and pore-filling, thereby further enhancing reservoir heterogeneity. The consistency between logging responses and experimental observations verifies the regional applicability of fractal analysis. Bound pores dominate within the studied interval, and the vertical variation of the PMF/BVI ratio aligns closely with both the NMR T2 spectra and fractal results. This study demonstrates that fractal dimension is an effective descriptor of structural characteristics across different pore types and provides a theoretical foundation and methodological support for the evaluation of pore complexity and heterogeneity in tight sandstone reservoirs.
1. Introduction
As global demand for petroleum resources continues to rise, conventional oil and gas supplies have become increasingly strained. As a result, unconventional hydrocarbon resource exploitation has increasingly drawn attention [1,2]. Tight oil and natural gas belong to the category of non-conventional hydrocarbons present in low-permeability sandstone or shale formations, which are notoriously difficult to develop due to limited permeability and complex internal structures [3,4]. In China, such formations typically feature permeability values below 1 mD and porosity under 10% [5]. In tight sandstone, pore architecture plays a crucial role in influencing hydrocarbon accumulation and migration. The morphology, size, and connectivity of pores directly influence the migration of gas and water within coal reservoirs. Notably, pore size is significantly controlled by diagenetic processes and mineral composition, playing a pivotal role in regulating fluid migration capacity and storage behavior [5,6]. For low-permeability sandstone, considerable heterogeneity characterizes the pore framework. Therefore, the significance of pore system irregularity and intricacy lies in its impact on evaluating the enrichment prospects of hydrocarbons [7].
Fractal dimension reflects the intricate nature of pore networks within reservoirs and serves as a reliable quantitative tool to assess heterogeneity in pore architecture [8]. Greater fractal values correspond to more intricate pore geometries and enhanced heterogeneity [9,10]. Since the 1990s, researchers have progressively adopted fractal concepts to investigate pore systems in rocks and other porous substances [11]. Researchers established Scaling laws have been developed to describe the distribution of pore sizes by extracting self-similar features from experimental images and scan data using counting methods such as box counting [12,13]. Multiple analytical techniques have been employed to evaluate the pore framework in tight sandstones, such as mercury intrusion at elevated pressures (HPMI), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), nano-computed tomography, and nitrogen adsorption at cryogenic temperatures (N2-BET) [14,15,16]. With the development of these experimental techniques, scholars have begun to combine fractal theory with empirical data [17,18,19]. Among them, NMR is frequently paired with mercury intrusion testing for comprehensive analysis. High-pressure mercury experiments help determine pore dimensions, assess throat widths, and evaluate interconnectivity [20]. NMR plays a major role in determining T2 relaxation profiles and estimating fractal properties due to its non-destructive nature and fast test time [21]. Utilizing the Brooks–Corey model for capillary pressure in tubes, Li obtained the capillary tube pressure curve of the rock sample using the high-pressure mercury pressure method, combined with three fractal models to calculate the core fractal dimension, and the analysis showed a strong association between calculated fractal indices and rock physical attributes [22]. Shao et al. studied how the pore morphology, fractal behavior, and mineralogical makeup of sandstone are related based on investigations conducted using NMR techniques, indicating that fractal measurements derived from NMR have proven to be effective indicators in identifying pore characteristics within sandstone formations [23]. Teng et al. discussed how fractal attributes correlate with key parameters like porosity, permeability, and bound water saturation based on T2 spectra drawn from NMR data and interpreted using fractal analysis and found that large-sized pores primarily govern fluid transmission capabilities in reservoirs [24]. However, although some studies have conducted fractal discussions on bound pores and movable pores, no effective correlation has been established between the experimental results and the nuclear magnetic resonance logging response. Therefore, the applicability and scalability of fractal characteristics at the well section scale still have limitations, making it difficult to achieve continuous longitudinal identification and verification of pore structure characteristics.
In this study, tight sandstones from the Linxing area of the Ordos Basin were selected as the research object. Cast thin sections and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were used to identify pore types and structural features. T2 relaxation spectra obtained from laboratory-based nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments were employed to distinguish between bound and movable pores, and their corresponding fractal dimensions were calculated to quantitatively characterize pore geometry. In addition, NMR logging data from the corresponding well intervals were integrated to delineate the spatial distribution of different pore types, and the PMF/BVI ratio was analyzed to evaluate the applicability of fractal parameters at the reservoir scale. The integration of experimental and logging data effectively enhances the multi-scale applicability of fractal analysis for characterizing tight sandstone reservoirs.
2. Geological Background Study
The Linxing region lies in the northeastern sector of the Ordos Basin, structurally positioned within the Jinxi bending zone of the basin’s eastern fold belt [25], as illustrated in Figure 1a,b. The stratigraphic sequence in this zone progresses vertically from the Zhifang Formation, Shangshanggou Formation, and Liujiagou Formation, upward to the Shiqianfeng and Shangshihezi Formations [26,27]. According to Figure 1c, the Zhifang Formation primarily consists of thick-bedded medium-grained sandstone, deposited in a braided river system. The Shangshanggou Formation features grey mudstone indicative of a lacustrine depositional setting. The Liujiagou Formation, comprising interbedded siltstone and mudstone, was formed under floodplain sedimentary conditions [28,29]. In this study, most rock samples were collected from the Shiqianfeng Formation, characterized by a complex lithological composition and vertical stacking of braided channel, lake, and floodplain facies. Overlying this is the Upper Shihezhi Formation, which mainly consists of mudstone interlayered with thin sandstone beds and coal seams, reflecting the low-energy accumulation conditions of the meandering river–lake environment [30,31]. Laterally developed sand bodies across the region contributed to an effective reservoir system, while marginal fault activity further enhanced the conditions conducive to the accumulation of tight sandstone gas reservoirs [30,31].

Figure 1.
Location and stratigraphy of the Linxing area, eastern Ordos Basin. (a) Basin-scale location; (b) Structural map of the study area; (c) Lithology and sedimentary facies of the Permian sandstone-bearing formations.
3. Experimental and Analytical Methods
3.1. Source of Sandstone Samples
The sandstone samples used in this study were collected from the Linxing region of the Ordos Basin. A total of six cylindrical core samples, each with a radius of 2.5 cm, were obtained from the target interval of the Shiqianfeng Formation (1326–1421 m). Porosity and permeability measurements were performed on each core, after which the samples were sectioned into three parts for thin-section preparation, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation, and NMR testing. The experimental results were integrated with NMR logging data from the corresponding depths for combined analysis.
3.2. Rock Cast Thin Slices
Blue-dyed cast rock thin sections were prepared in accordance with the “Rock Thin Section Identification” standard (SY/T 5368-2016) [32]. Petrographic images were captured using a Leica DLC-420 microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) imaging system at a magnification of ×100. Combined with conventional petrophysical testing, the mineral composition, pore morphology, and cementation patterns of the sandstone were analyzed. This approach enables detailed microscopic characterization of the sandstone framework and pore structure, providing a robust foundation for subsequent fractal analysis and interpretation of seepage behavior.
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscope
SEM was employed to observe nanoscale pore morphology and the distribution of authigenic minerals, serving as an essential tool for characterizing the complexity of microscopic pore structures. A Quanta 400 FEG field-emission scanning electron microscope (FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR, USA) was used to image freshly fractured, gold-coated sample surfaces under an accelerating voltage of 30 kV, achieving a resolution of 1.2 nm. Mineralogical identification was carried out using secondary electron imaging (SE), backscattered electron (BSE), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) modes. All procedures were conducted in accordance with the standard “Analytical Method for Rock Samples via Scanning Electron Microscopy” (SY/T 5162-2021) [33]. The SEM approach provides high-resolution insight into pore structure heterogeneity at the nanoscale and offers a visual basis for subsequent fractal analysis.
3.4. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Experiments
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a non-destructive, rapid, and sensitive technique for characterizing pore structure, widely used to evaluate pore size distribution and the ratio of movable fluid to bound fluid. In this study, the T2 relaxation spectra of sandstone samples that had been dried, vacuumed, and saturated with brine were measured using the HD/DH2002 NMR analyzer (Beijing Heng Aode Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The experimental conditions included an echo interval of 0.20 ms, 128 scans, a wait time of 6 s, a test temperature of 35 °C, and a minimum signal-to-noise ratio of 200. Each sandstone sample was tested twice. By comparing the T2 spectra before and after centrifugation, bound and movable pores of different scales were identified. The obtained spectra are considered representative of the measurement results. In this study, the T2 spectrum served as the basis for fractal analysis and was cross validated with NMR logging data, thus bridging the characterization of pore structure between laboratory and logging scales.
3.5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Logging
NMR logging is an in situ technique based on hydrogen nuclear magnetic responses, capable of characterizing pore structures and fluid states in formations and is well-suited for identifying heterogeneity in tight reservoirs. In this study, logging data were provided by China United Coalbed Methane Corporation, and the EMPT NMR logging tool (China Oilfield Services Limited, Beijing, China) was used to perform PP6-mode measurements on representative well intervals within the study area. The tool excites hydrogen nuclei in formation fluids through a combination of static magnetic fields and radio frequency (RF) pulses and records echo train signals to invert the T2 distribution. This allows for the quantitative acquisition of total porosity, bound water (BVI), movable water (PMF), and permeability. The logged intervals cover the depths corresponding to multiple experimental samples. Logging was conducted with a cycle time of 12.4 s and an echo spacing of 0.6 ms to ensure high signal quality. Simultaneously, conventional curves such as gamma ray (GR) and resistivity were collected to assist in interpretation. This method provides essential data for validating fractal parameters at the well scale and enhances the regional applicability of the experimental results.
3.6. Fractal Method
Fractal dimension is a mathematical tool used to quantitatively characterize the complexity and heterogeneity of reservoir pore structures. It enables the multi-scale and comprehensive depiction of the geometric features of rock pore systems [34]. This parameter reflects the self-similarity between local and global pore structures, effectively representing the morphological complexity and irregular connectivity of the pore network [35], and has become one of the key indicators for evaluating heterogeneity in tight sandstone reservoirs. Typically, the fractal dimension D of sandstone pores ranges between 2.0 and 3.0. Values closer to 3.0 suggest rougher surfaces and more complex structures, while values nearer to 2.0 indicate smoother surfaces and simpler pore geometries [22,36].
In this study, the box-counting model was adopted as the foundational method for fractal analysis. This model assumes a power-law relationship between the number of objects and the scale of measurement and is suitable for calculating the two-dimensional fractal dimension of rock pore systems [37,38]. Compared to other models, the box-counting approach is well adapted to transverse relaxation time (T2) spectra acquired through NMR experiments, providing accurate insights into pore size distribution and proving especially applicable to tight sandstones with high heterogeneity [28]. During analysis, the T2 spectral data extracted from NMR tests were processed to generate cumulative distributions. A log–log plot was constructed using T2 relaxation time as the horizontal axis and the cumulative pore volume fraction (Sv) not exceeding that relaxation time as the vertical axis. The fractal dimension D was then derived from the slope of the linear portion of this plot [8] using the following formula:
where T2 is the transverse relaxation time, ms; Sv is the cumulative fraction of the pore volume whose lateral relaxation time is no greater than T2; D is the fractal dimension; and k is the slope of the line.
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Petrological and Physical Properties Characteristics
The identification results based on rock petrographic sections indicate that the sandstone composition is dominated by quartz, comprising 67% to 77%, while the clay content ranges between 5% and 13%, suggesting a strong cementation effect between clay minerals and quartz. Feldspar and mica contents range from 3% to 6% and 2% to 30%, respectively, as presented in Table 1. Regarding mineralogical components, the analyzed sandstone specimens exhibit porosity values between 6.25% and 9.74%, with a mean of 7.40%. Permeability varied from 0.08 to 0.49 mD, averaging 0.25 mD, implying a nonuniform contribution of porosity to fluid flow capacity. As burial depth increased, the stress imposed by overburden rocks intensified, gradually compacting grains within the sandstone and ultimately reducing porosity [39,40]. Early-stage compaction together with cementation involving siliceous–clay substances is considered a major contributor to low porosity and reduced permeability in tight sandstone formations [41,42].

Table 1.
Petrophysical parameters and mineral composition of six sandstone samples.
The pore categories of tight sandstone in the Linxing region are dominated by residual intergranular porosity, accompanied by a few intra-granular dissolution voids, microfractures, and intergranular openings, as illustrated in Figure 2a–f. Residual pores are derived from original interparticle voids retained after mechanical compaction and grain cementation and are typically angular with straight margins (Figure 2a,b). These intergranular voids may also originate from the chemical dissolution of soluble minerals (e.g., feldspar and lithic fragments) during late diagenesis, which may reflect moderate porosity development (Figure 2b). Additionally, such pores commonly occur between authigenic minerals and remain visible after the aggregation of clay components (Figure 2c). Microfissures are narrow cracks along grain boundaries or fractures, which may locally serve as migration paths (Figure 2d). Furthermore, some secondary voids result from the enlargement of earlier intergranular spaces via dissolution, as shown in Figure 2e. The presence of extensive cementing substances among grains lowers both porosity and permeability (Figure 2f).

Figure 2.
Microscopic characteristics of tight sandstone in the Linxing area. (a) Residual intergranular pores between framework grains; (b) Dissolved pores within grains formed by partial mineral dissolution; (c) Intercrystalline pores developed between authigenic minerals; (d) Micro-fracture cutting across quartz and feldspar grains; (e) Intergranular dissolved pores formed after dissolution of unstable minerals; (f) quartz cement occluding primary pores; (g) Quartz secondary enlargement cement and kaolinite aggregates; (h) Fibrous illite filling pore spaces; (i) Authigenic silicon crystals precipitated in pores.
Scanning electron microscopy further reveals that the sandstone matrix mainly consists of quartz, with minor occurrences of feldspar and clay minerals (kaolinite and illite), as illustrated in Figure 2g–i. Notably, quartz overgrowth is evident, and kaolinite tends to infill available intergranular space (Figure 2g). Fibrous illite crystals are observed within the interparticle voids (Figure 2h), while residual intergranular dissolution structures also appear as granular siliceous clusters (Figure 2i).
4.2. Pore Structure Characteristics Based on Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
The variation in pore sizes was analyzed using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology. A longer T2 relaxation time indicates a correspondingly larger pore radius. The parameters recorded in the experiment are detailed in Table 2. The T2 values associated with the six sandstone specimens were observed to fall within a unimodal distribution pattern (Figure 3), ranging from 100 to 1 × 106 μs. A linear conversion factor between T2 and pore size was determined as 0.0133 μm/ms [43]. Utilizing this relationship, the peak pore size range across the six samples was calculated to be 0.053–0.578 μm. The distribution was relatively narrow, suggesting that the pore system is primarily composed of micro- to nano-scale pores, while larger pores were less abundant. These findings agree with the dual pore-throat model commonly identified using high-pressure mercury intrusion tests.

Table 2.
Fractal dimensions of different pores in two NMR-based models.

Figure 3.
Saturation porosity component as a function of T2.
In the context of pore fractal analysis using NMR, the T2 threshold value (T2cutoff) serves as the dividing relaxation time between free and bound water and is defined as the projection point at which the cumulative porosity curve in the T spectrum reaches its maximum before and after centrifugation [44], as depicted in Figure 4. Variations in cumulative porosity prior to and following centrifugation were used to determine the porosity values corresponding to free and bound water, as provided in Table 2. The experimental T2 intervals for the six sandstone specimens ranged from 17.522 ms to 65.604 ms, averaging 34.911 ms, indicating significant variation. Based on the T2-derived porosity differential curves before and after centrifugal separation, the calculated free water porosity ranged from 1.088% to 3.256%, with an average of 2.217%, while bound water porosity spanned from 3.459% to 7.508%, averaging 5.564%. The free water content was markedly lower than the bound water content. This implies that bound water pores are predominant in the reservoir, indicating a compact structure in which fluid retention mainly exists in a bound condition, thereby complicating fluid extraction.

Figure 4.
S1 NMR T2 spectrum distribution.
4.3. Fractal Characteristics Based on Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Experiments
When determining the core fractal dimension through the NMR framework, the cumulative porosity distribution profile is typically segmented into confined-flow and free-flow pore regions using the T2cutoff as the boundary point [45]. The segment where T2 < T2cutoff corresponds to the bound water zone, with its fractal dimension labeled as Dc1, whereas T2 > T2cutoff defines the mobile water zone, represented by the fractal dimension D.
Based on the acquired NMR testing results, values for specific surface area Sv and T2 were obtained, and a dual-logarithmic plot of 1–Sv versus T2 was constructed following the fractal method, as illustrated in Figure 5. The plotted curves exhibit a two-phase linear pattern, which aligns with two distinct linear segments, allowing extraction of the corresponding fractal indices Dc1 and Dc2. These values are essential for quantitatively describing the structural complexity of pores across varying scales.
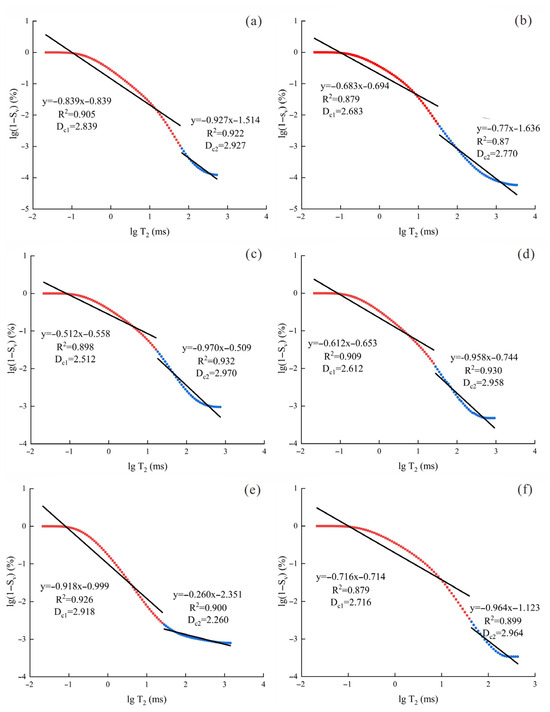
Figure 5.
Fractal curve characteristics of each sample in the NMR box model: (a) S1; (b) S2; (c) S3; (d) S4; (e) S5; (f) S6.
According to the linear regression results of the dual-logarithmic plots between 1–Sv and T2 (Figure 5), the calculated fractal values for bound and mobile pore intervals were extracted individually to represent the structural complexity of each pore type. As presented in Table 2, the fractal indices for bound pores ranged between 2.512 and 2.918, yielding an average value of 2.713. For mobile pores, the corresponding values spanned from 2.260 to 2.970, with a mean of 2.808. In general, movable pore segments exhibited greater geometric irregularity in most samples, implying a higher degree of heterogeneity, potentially associated with the presence of fractures or large conduit systems.
4.4. Pore Structure Characteristics Based on Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Logging
To further evaluate the regional-scale validity of the nuclear magnetic resonance fractal analysis conclusion, the corresponding formation interval (Well LX-46, 1362 m–1400 m) in the study area was selected for NMR logging experiments. As shown in Figure 6, the total porosity (PMT) of this well section varies between 1.708% and 14.637%, averaging 5.105%. The movable porosity (PMF) spans from 0.259% to 3.887%, with a mean value of 1.490%. The bound porosity (BVI) lies within 0.983~13.871%, with a mean of 3.615%. Porosity values exhibited noticeable fluctuations along depth, reflecting strong heterogeneity. Among the tested intervals, the bound water porosity consistently exceeded the movable one. The short relaxation time-dominated T2 spectral features aligned well with the fractal behavior observed in laboratory samples, indicating that micropores with bound water serve as the primary contributors to pore structure in tight sandstone.
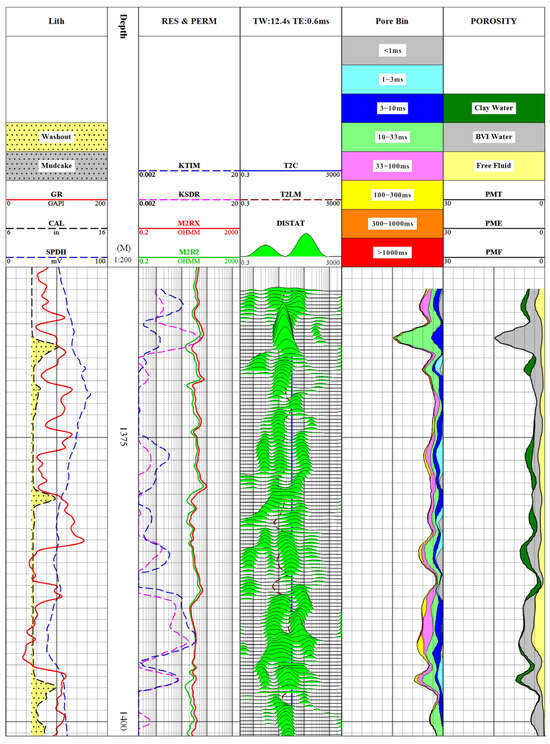
Figure 6.
Interpretation of NMR logging data in the Linxing area (1362–1400 m).
NMR logging-based KSDR and KTIM permeability inversion results ranged from 0.0010 mD to 0.5442 mD and from 0.0010 mD to 0.3685 mD, respectively, with respective average values of 0.219 mD and 0.235 mD, closely matching the experimental permeability. This supports that tight sandstone reservoirs in the Linxing block are typically marked by low permeability, notable heterogeneity, and dominant bound-pore contribution. The slightly lower mean from logging compared to the measured sample data is possibly linked to bound water prevalence and the intricate pore geometry.
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of Pore Morphology in Tight Sandstone
According to fractal geometry theory, the fractal dimension D of a pore system describes its spatial complexity and self-similarity across multiple scales. When the pore radius undergoes scaling by a certain factor, its corresponding volume is approximately transformed based on the N-th power of that scaling term. The fractal dimension serves not only as a statistical metric for describing pore structure complexity, but also partially reflects the geometric dimensionality of the system [46]. Theoretically, for a perfectly cylindrical pore, the primary spatial dimension is two, and its fractal dimension equals two. For a spherical pore, however, the scaling dimension is three, and its fractal index is accordingly three.
Experimental observations from nuclear magnetic resonance indicate that in the Linxing region, movable pore segments in tight sandstone generally display larger fractal dimensions compared to bound pores. Although the mean values of both types are similar, movable pores tend to exhibit higher spatial complexity. For all tested samples, fractal dimension values range between two and three, suggesting that pore geometries vary from irregular 2D channels to isotropic 3D networks. Their spatial arrangement shows both anisotropy and irregularity. The overall shape resembles a “badminton shuttlecock” structure (Figure 7), where expansion along the main axis is limited, while lateral growth is more pronounced—reflecting evident directional heterogeneity [47]. This morphology also plays a role in constraining seepage capacity and connectivity.
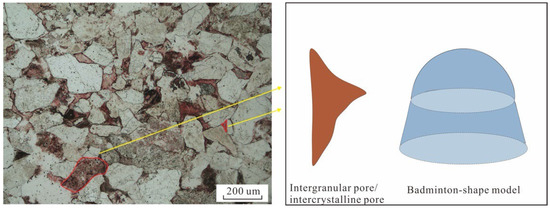
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of the pore shape of tight sandstone in the Linxing area.
5.2. The Influence of Mineral Composition on the Fractal Characteristics of Pore Structure
The fractal dimension of tight sandstone pores is influenced by both diagenetic processes and mineral composition [46]. As the primary framework mineral in tight sandstones, a higher quartz content enhances compaction resistance, which helps preserve original intergranular pores and improve pore connectivity. As shown in Figure 8a, the p-value between quartz content and the fractal dimension Dc1 of bound pores is 0.87, indicating no significant correlation. Figure 8b shows a p-value of 0.14 between quartz content and Dc2 of movable pores, suggesting a moderately positive correlation. This trend may result from increased quartz content inducing secondary quartz precipitation in some samples, which partially blocks original intergranular pores during pore-filling or cementation processes. Consequently, the structural complexity and heterogeneity of movable pores increase, leading to higher Dc2 values. As a result, the structure of movable pores becomes more irregular and geometrically complex, increasing heterogeneity and ultimately raising the Dc2 value.

Figure 8.
(a) Correlation between quartz content and Dc1; (b) Correlation between quartz content and Dc2 in the Linxing Area.
Apart from quartz, feldspar, as a typical soluble mineral, also has an impact on the pore structure. The analytical results presented in Figure 9a indicate that there is virtually no correlation between the fractal dimension Dc1 of bound pore segments and feldspar content, with a p-value of 0.58 and 4 degrees of freedom. Figure 9b demonstrates that the p-value between feldspar content and movable pore Dc2 is 0.34 with 4 degrees of freedom, suggesting that feldspar may influence the heterogeneity of movable pore structures to some extent. During the late diagenetic stage, as feldspar content increases, it becomes more susceptible to dissolution, thereby forming relatively uniform secondary dissolution pores. These dissolution pores expand the overall pore volume and enhance pore connectivity, simplifying the geometric structure of the movable pore system, which leads to a reduction in Dc2 values and a decrease in the heterogeneity of movable pores. This diagenetic evolution process not only improves pore structure but also contributes to enhancing rock permeability, thereby facilitating more efficient utilization of reservoir space. Although feldspar content across the study area varies within a narrow range, its effect on pore structure still offers valuable insight into localized reservoir quality enhancement.
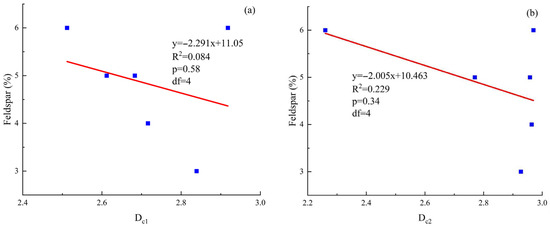
Figure 9.
(a) Correlation between feldspar content and Dc1; (b) Correlation between feldspar content and Dc2 in the Linxing Area.
As shown in Figure 10a,b, the p-value of Dc1 with clay content is 0.06 with 4 degrees of freedom, showing a positive correlation. In contrast, the p-value of Dc2 is 0.04 with 4 degrees of freedom, indicating a negative correlation. This suggests that in the tight sandstones of the Linxing area, an increase in clay mineral content leads to a more complex and irregular spatial distribution of bound pores, while movable pores tend to be relatively simplified. This may be attributed to the fine-grained nature of clay particles, which are prone to adhering to or filling pore throats. Their irregular shapes increase the roughness and tortuosity of the pore surface. Additionally, the plate-like structure and strong surface activity of clay minerals enhance capillary forces, further restricting fluid movement within bound pores and thereby increasing the Dc1 value. This reduces overall heterogeneity and consequently leads to a decrease in Dc2.
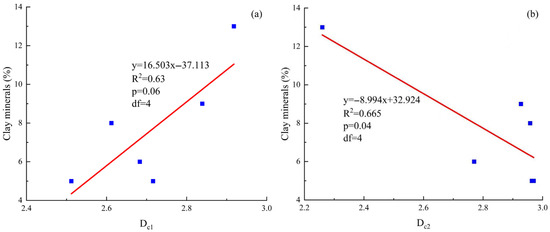
Figure 10.
(a) Correlation between clay minerals and Dc1; (b) Correlation between clay minerals and Dc2 in the Linxing Area.
During the diagenetic process, the combined effects of quartz, feldspar, and clay minerals contribute to the structural evolution of tight sandstone reservoirs in the Linxing region through mechanisms such as framework support, dissolution alteration, and pore-filling actions. These distinctions are reflected in changes to the fractal dimension, which indicates how mineral composition influences the complexity and spatial heterogeneity of the pore system. This makes it a key parameter for understanding microstructural evolution and overall reservoir performance. Further analysis reveals that fractal dimension not only captures the geometric irregularity of the pore architecture but also provides insight into the distribution behavior of fluids such as oil and gas. Samples dominated by bound pores often display higher Dc1 values, suggesting a well-sealed microporous system where hydrocarbons are largely retained in an adsorbed or bound form. In contrast, a lower Dc2 generally corresponds to samples with more continuous and regular movable pore channels, making fluid migration easier. This conclusion reinforces the applicability of fractal theory in characterizing the heterogeneity of tight reservoirs, while also serving as a useful parameter for assessing the dual behavior of oil and gas, from both microstructure and storage state perspectives.
5.3. Fractal Dimension Control of Sandstone Pore Reservoir and Seepage Characteristics
As shown in Figure 11a,b, there is a weak positive correlation between the fractal dimension Dc1 of the bound pores and the total porosity. In the tight sandstone of the Linxing area, an increase in Dc1 corresponds to an enhancement in the geometric complexity of the bound pore structure, which in turn increases the pore surface area and quantity, providing more favorable spatial conditions for fluid storage and improving the reservoir’s storage capacity. The p-value for this trend is 0.45. Although the statistical significance is not strong, it still indicates that in a compaction environment, bound pores make the main contribution to the total porosity. This conclusion is consistent with the results of nuclear magnetic resonance T2 cutoff analysis, that is, “bound pores are the main storage space for bound fluids.” Although their connectivity is limited and they are not easy to form seepage channels, their wide distribution and complex structure still constitute an important storage basis for tight reservoirs. In contrast, the fractal dimension Dc2 of movable pores shows a moderate negative correlation with porosity, with a p-value of 0.12, indicating that Dc2 has a more significant control over porosity. The more complex the structure is, the fewer the effective pores. Combined with the thin section and scanning electron microscope images, it is found that although movable pores have a large volume, they are irregular in shape and distributed discretely, which limits the formation of a highly connected reservoir system. Some movable pores formed by dissolution have a large radius and good connectivity, but their heterogeneity is strong, resulting in a still limited number of effective pores. The decrease in porosity when Dc2 increases indicates that the complexity of the movable pore structure is an important factor affecting reservoir heterogeneity.
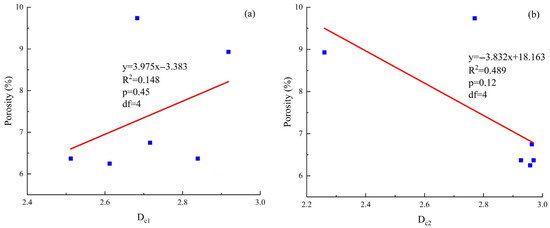
Figure 11.
(a) Correlation between porosity and Dc1; (b) Correlation between porosity and Dc2 in the Linxing area.
As shown in Figure 12a,b, the correlation between the fractal dimension Dc1 of bound pores and permeability is weak, with a p-value of 0.49. This indicates that although bound pores contribute to fluid storage and enhance reservoir capacity, their small pore size and poor connectivity limit their control over seepage paths, thereby restricting fluid mobility and having a limited impact on permeability. This result further supports the understanding that bound pores mainly influence reservoir behavior rather than seepage performance. The fractal dimension Dc2 of movable pores shows a significant negative correlation with permeability, with a p-value of 0.01. As Dc2 increases, the geometric complexity of the pore structure enhances, connectivity decreases, and seepage resistance increases, leading to a decline in permeability. This strong correlation highlights the key role of Dc2 in controlling the seepage performance of reservoirs. Overall, Dc1 mainly reflects reservoir capacity, while Dc2 is an important indicator for evaluating seepage performance.

Figure 12.
(a) Correlation between permeability and Dc1; (b) Correlation between permeability and Dc2 in the Linxing area.
Based on the nuclear magnetic resonance logging results, it can be observed that the bound porosity in the analyzed well section is generally higher than that of the movable porosity, averaging 3.615% and 1.490%, respectively. This reveals that the reservoir is primarily occupied by bound fluids and that the distribution of fluids exhibits pronounced spatial heterogeneity. This pattern is in agreement with the short T2 relaxation responses and the fractal characteristics of the spectrum acquired from NMR experiments, showing that microporous-bound pore structures play a leading role in influencing the occurrence mode of hydrocarbons. Further interpretation reveals that the fractal dimension Dc1 of bound pores has a limited linkage with permeability, whereas Dc2 of mobile pores displays a clearly inverse association. This implies that the fluid storage capacity of sandstone reservoirs is chiefly regulated by Dc1, while their transport ability is constrained by Dc2. The overall tendency of the logging outcomes aligns well with those of the experimental analysis, confirming the feasibility and consistency of using nuclear magnetic resonance data and logging methods for multi-dimensional characterization of pore structure and evaluation of reservoir performance.
6. Conclusions
- The tight sandstone samples from the Linxing region generally exhibit bimodal T2 spectra, dominated by short relaxation components, indicating that bound pores are predominant. Based on the T2cutoff classification, the fractal dimensions of bound and movable pores range from 2.512 to 2.918 and from 2.260 to 2.970, respectively, with average values of 2.713 and 2.808. This suggests that movable pores possess greater structural complexity.
- A significant correlation exists between fractal dimensions and mineral composition. An increase in quartz content is typically accompanied by a rise in Dc2, indicating enhanced complexity in the movable pore structure due to the development of secondary quartz. Conversely, an increase in feldspar content generally leads to a decrease in Dc2, primarily attributed to the dissolution of feldspar during late diagenesis, which forms secondary dissolution pores, thereby reducing the heterogeneity of movable pores.
- The results of nuclear magnetic logging indicated that the bound pores in the evaluated well interval exhibited significantly higher porosity compared to the movable pores. Furthermore, the variation trend of the PMF/BVI ratio aligned closely with the experimental data, suggesting that microporous-bound pore structures exert a major influence on the fluid occurrence conditions. The relationship between Dc1 and permeability remains weak, while Dc2 demonstrates a clear negative association. This confirms that fractal dimensions not only characterize pore complexity but also serve as effective indicators for assessing reservoir flow potential.
- This study employed the box-counting model, integrating NMR experiments and logging data to investigate pore structure and flow characteristics across multiple scales. However, the traditional fractal dimension D has limitations, especially when exceeding the theoretical threshold of 3.0, where its physical meaning becomes ambiguous. Future research is encouraged to introduce multifractal theory and incorporate methods such as CT scanning, mercury intrusion, and low-temperature gas adsorption. Combined with well logging, these approaches could build a multi-scale, coupled pore–flow characterization framework to improve the applicability and accuracy of fractal analysis in tight reservoir evaluation.
Author Contributions
Methodology, J.Q.; Investigation, H.M.; Data curation, H.F.; Writing—original draft, S.L.; Writing—review and editing, C.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the following projects: Liaoning Provincial Department of Education Project (LJKMZ20220744), Liaoning Petrochemical University Doctoral Research Project (2021XJJL-025), and the Basic Research Project of the Department of Education of Liaoning Province (LJ212510148031). We would like to thank China United Coalbed Methane Co., LTD for providing assistance for this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to confidentiality restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors state that no known competing financial interests or personal relationships were identified in this study that could have influenced the work reported.
Abbreviations
For clarity and ease of reference, the following table lists all the abbreviations and acronyms used in the introduction of this study. The full terms are provided to assist readers in understanding the technical terms throughout the manuscript.
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| T2 | Transverse Relaxation Time |
| PMF | Porosity Model Function |
| BVI | Bulk Volume Irreducible |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| HPMI | High-Pressure Mercury Intrusion |
| BET/N2-BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller Nitrogen Adsorption |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
References
- Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.X.; Liu, K.Y.; Wang, P.F.; Ji, W.M.; Gao, F.L.; Li, P.; Hu, T.; Zhang, B.; Huang, H.X. Effect of lithofacies on gas storage capacity of marine and continental shales in the Sichuan Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 36, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.X.; Li, R.X.; Jiang, Z.X.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Investigation of variation in shale gas adsorption capacity with burial depth: Insights from the adsorption potential theory. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 73, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.H.; Deng, X.Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.H.; Qiu, J.L.; Hao, L.W.; Zhao, Y.D. Densification and hydrocarbon accumulation of Triassic Yanchang Formation Chang 8 Member, Ordos Basin, NW China: Evidence from geochemistry and fluid inclusions. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.Q.; Deng, X.Y.; Du, H.Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Xu, F.M. Characterizing the heterogeneity of tight sandstone in outcropped Permian Shanxi Formation, Liujiang Basin. Pet. Geol. 2024, 44, 468–479, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.N.; Zhu, R.K.; Liu, K.Y.; Su, L.; Bai, B.; Zhang, X.X.; Yuan, X.J.; Wang, J.H. Tight gas sandstone reservoirs in China: Characteristics and recognition criteria. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 88–89, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.B.; Liu, D.M. Comparison of low-field NMR and mercury intrusion porosimetry in characterizing pore size distributions of coals. Fuel 2012, 95, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Chen, J.; Pang, X.J.; Wang, S.C.; Zhou, L.Z.; He, Z.B.; Qin, Z.Q.; Fan, X.Q. A review on pore structure characterization in tight sandstones. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 177, 436–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peta, K.; Stemp, W.J.; Stocking, T.; Chen, R.; Love, G.; Gleason, M.A.; Houk, B.A.; Brown, C.A. Multiscale Geometric Characterization and Discrimination of Dermatoglyphs (Fingerprints) on Hardened Clay—A Novel Archaeological Application of the GelSight Max. Materials 2025, 18, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yassin, M.R.; Dehghanpour, H. A modified model for spontaneous imbibition of wetting phase into fractal porous media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 543, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Jiang, Z.X.; Gong, X.; Li, C.M.; Wang, D.D.; Wu, Q.Z. The shale gas migration capacity of the Qiongzhusi Formation: Implications for its enrichment model. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 056603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.F.; He, X.J.; Feng, F.; Li, W.; Wang, M.; Zhu, W.J.; Zhu, Y.S. Fractal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Pore Structure in Tight Sandstone: A Case Study from Chang 6 Member of the Southwestern Yishan Slope. Processes 2025, 13, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Yang, Y.T.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.H. Formation Mechanism of Secondary Quartz in the Second Member of Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan Depression and Its Impact on Reservoir Physical Properties. XinJiang Pet. Geol. 2023, 44, 25–32, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, H.M.; Li, X.Z.; Hu, Z.M.; Chen, L.Q.; Shen, W.J.; Guo, W.; He, W.K.; Zhou, Y.H. Effect of Particle Size on Pore Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Deep Siliceous Shales in Southern Sichuan, China, Measured Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering and Low-Pressure Nitrogen Adsorption. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, C.R.; Freeman, M.; He, L.; Agamalian, M.; Melnichenko, Y.B.; Mastalerz, M.; Bustin, M.R.; Radliński, A.P.; Blach, T.P. Characterization of tight gas reservoir pore structure using USANS/SANS and gas adsorption analysis. Fuel 2021, 95, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.M.; Ge, H.K.; Ji, W.M.; Shen, Y.H.; Su, S. Monitor the process of shale spontaneous imbibition in co-current and counter-current displacing gas by using low field nuclear magnetic resonance method. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Li, H.Z.A. Pore structure characterization, permeability evaluation and enhanced gas recovery techniques of tight gas sandstones. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 28, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. Full-Scale Pore Structure Characterization and Its Impact on Methane Adsorption Capacity and Seepage Capability: Differences between Shallow and Deep Coal from the Tiefa Basin in Northeastern China. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Wang, Y.R.; Lin, W.; Ma, L.H.; Liu, D.X.; Liu, J.R.; Zhang, Y. Micro-pore structure and fractal characteristics of deep shale from Wufeng Formation to Longmaxi Formation in Jingmen exploration area, Hubei Province, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 7, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Li, G.; Dan, S.; Yang, Y.; He, X.; Qi, M.; Liu, G. Study of Fractal and Multifractal Features of Pore Structure in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs of the Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin, Northwest China. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 31352–31366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorddin, H.A.; Hossain, M.E.; Al-Yousef, H.; Okasha, T. Comparison of permeability models using mercury injection capillary pressure data on carbonate rock samples. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 121, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Hu, W.X.; Cao, J.; Sun, F.N.; Liu, Y.F.; Sun, Z.M. Micro/nanoscale pore structure and fractal characteristics of tight gas sandstone: A case study from the Yuanba area, northeast Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.W. Analytical derivation of Brooks-Corey type capillary pressure models using fractal geometry and evaluation of rock Heterogeneity. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 73, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.H.; Pang, X.Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, X. Fractal Analysis of Pore Network in Tight Gas Sandstones Using NMR Method: A Case Study from the Ordos Basin, China. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 10358–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Er, C.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Q.; Shen, C.; Tan, S. Pore structure characterization based on NMR experiment: A case from the Shanxi Formation tight sandstones in the Daning-Jixian area, eastern Ordos Basin. Energy Geosci. 2023, 4, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, K.X.; Zhang, H.W.; Shabbiri, K.; Hu, Q.J.; Zhang, C. The geochemical characteristics, origin, migration and accumulation modes of deep coal-measure gas in the west of Linxing block at the eastern margin of Ordos Basin. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 91, 103965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.M.; Zeng, H.; Wu, P.; Du, J.; Gao, J.X.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, Z.X. Pore Structure Differentiation between Deltaic and Epicontinental Tight Sandstones of the Upper Paleozoic in the Eastern Linxing Area, Ordos Basin, China. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.H.; Zhong, L.G.; Ning, Z.F.; Wang, Q.; Cole, D.R. Characterization of Nanoscale Pores in Tight Gas Sandstones Using Complex Techniques: A Case Study of a Linxing Tight Gas Sandstone Reservoir. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Ju, Y.W.; Cai, J.C.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, H.J.; Yu, K.; Qi, Y.; Meng, S.Z.; Li, W.Y.; Sun, Y. Micro-Nanopore Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Tight Sandstone Gas Reservoirs in the Eastern Ordos Basin, China. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 21, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Zhou, N.W.; Lu, S.F.; Liu, Y.C.; Lin, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Song, B. Generation, accumulation, and distribution of Upper Paleozoic tight sandstone gas in the northeastern margin of the Ordos Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 156, 106463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; He, J.X.; Zhang, X.L.; Wu, H.C.; Yu, Z.Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, T.T.; Wang, W. Fractal analysis of pore structures in transitional shale gas reservoirs in the Linxing area, Ordos Basin. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 979039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ren, D.Z.; Sun, H.P.; Wang, H.; Tian, T.; Li, Q.H.; Yan, Z. Imbibition Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Fracturing Fluid in a Tight Sandstone Reservoir. Acs Omega 2024, 9, 17204–17216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SY/T 5368-2016; Rock Thin Section Identification. Code of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- SY/T 5162-2021; Analytical Method for Rock Samples via Scanning Electron Microscopy. Code of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Li, P.; Zheng, M.; Bi, H.; Wu, S.T.; Wang, X.R. Pore throat structure and fractal characteristics of tight oil sandstone: A case study in the Ordos Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 149, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ji, Y.L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, C.L.; Chen, S. Pore structure and fractal characteristics of a tight gas sandstone: A case study of Sulige area in the Ordos Basin, China. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2018, 36, 1438–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Z.; Liu, G.D.; Yang, W.W.; Zou, H.Y.; Sun, M.L.; Wang, X.L. Multi-fractal distribution analysis for pore structure characterization of tight sandstone-A case study of the Upper Paleozoic tight formations in the Longdong District, Ordos Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 92, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y. Characterization and Typeification Evaluation of Pore Structure in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs of Shahejie Formation in Szechwan Szechwan Dongying Sag; Chengdu University of Technology: Chengdu, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Tang, X.Y. Pore Structure Characteristics and Typeification Evaluation of High-Pressure Low-Permeability Clastic Rock Reservoirs: A Case Study of the Huangliu Formation in Yinggehai Basin. J. Northeast Pet. Univ. 2024, 48, 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.D.; Wang, Y.B.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Ni, X.M.; Wu, X.; Zhao, S.H. Characteristics of Tight Sandstone Reservoirs and Controls of Reservoir Quality: A Case Study of He 8 Sandstones in the Linxing Area, Eastern Ordos Basin, China. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2019, 93, 637–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Jiang, Z.X.; Lu, J.M.; Zhang, C.J.; Shi, L.; Sun, L.; Yang, L.; Shang, P. Hydrocarbon Source and Relationship between Hydrocarbon Charging Process and Reservoir Tight Period of the Denglouku Formation Tight Sandstone Gas Reservoirs in the Xujiaweizi Fault Depression, Songliao Basin. Nat. Resour. Res. 2024, 33, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, K.; Shi, W.Z.; Qin, S.; Zhang, W.; Qi, R.; Xu, L.T. Reservoir Densification, Pressure Evolution, and Natural Gas Accumulation in the Upper Paleozoic Tight Sandstones in the North Ordos Basin, China. Energies 2022, 15, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Meng, X.H.; Wang, X.; Dong, Y.X.; Li, X.W.; Zhang, C.H.; Li, Z.Q.; Ma, T.; Wei, W.; Guo, J. Geochemical characteristics of diagenetic fluid and densification model of tight gas sandstone reservoirs in Linxing Area, the eastern margin of Ordos Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 138, 105496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.J.; Fan, Y.R.; Hu, F.L.; Li, C.X.; Yu, J.; Liu, Z.C.; Wang, F.Y. Characterization of Pore Throat Size Distribution in Tight Sandstones with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and High-Pressure Mercury Intrusion. Energies 2019, 12, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Weller, A. Fractal dimension of pore-space geometry of an Eocene sandstone formation. Geophysics 2014, 79, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golsanami, N.; Sun, J.M.; Zhang, Z.Y. A review on the applications of the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology for investigating fractures. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 133, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.B.; Du, Z.W.; Qiang, X.L.; Lei, T.; Jiang, T.T.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.S. Binary pore structure and fractal characteristics of tight sandstone: A case study of Chang 7 Member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin. Pet. Geol. Recovery Effic. 2024, 31, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, R.Y.; Wang, L.N.; Qu, Z.Y.; Ding, X.Y.; Gao, C.L.; Meng, W.C. Pore Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Tight Sandstones Based on Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: A Case Study in the Triassic Yanchang Formation of the Ordos Basin, China. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 16284–16297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).