Multi-Objective Optimization of a Fractional-Order Lorenz System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Optimization Methodology
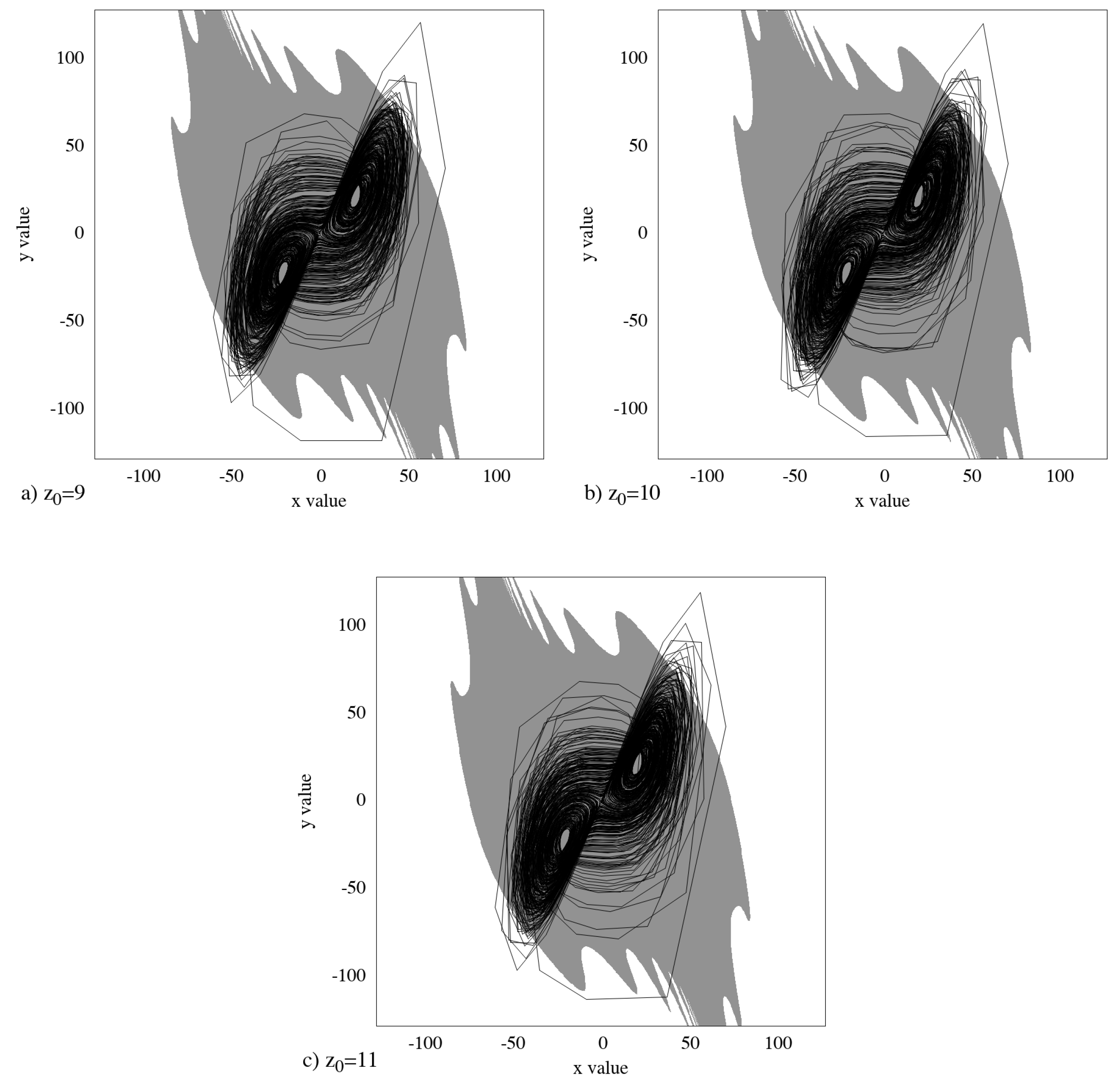
2.1. The Fractional Lorenz System
2.2. The M2sFRK Method for Fractional Integration
2.3. The Optimization of the Fractional Lorenz System
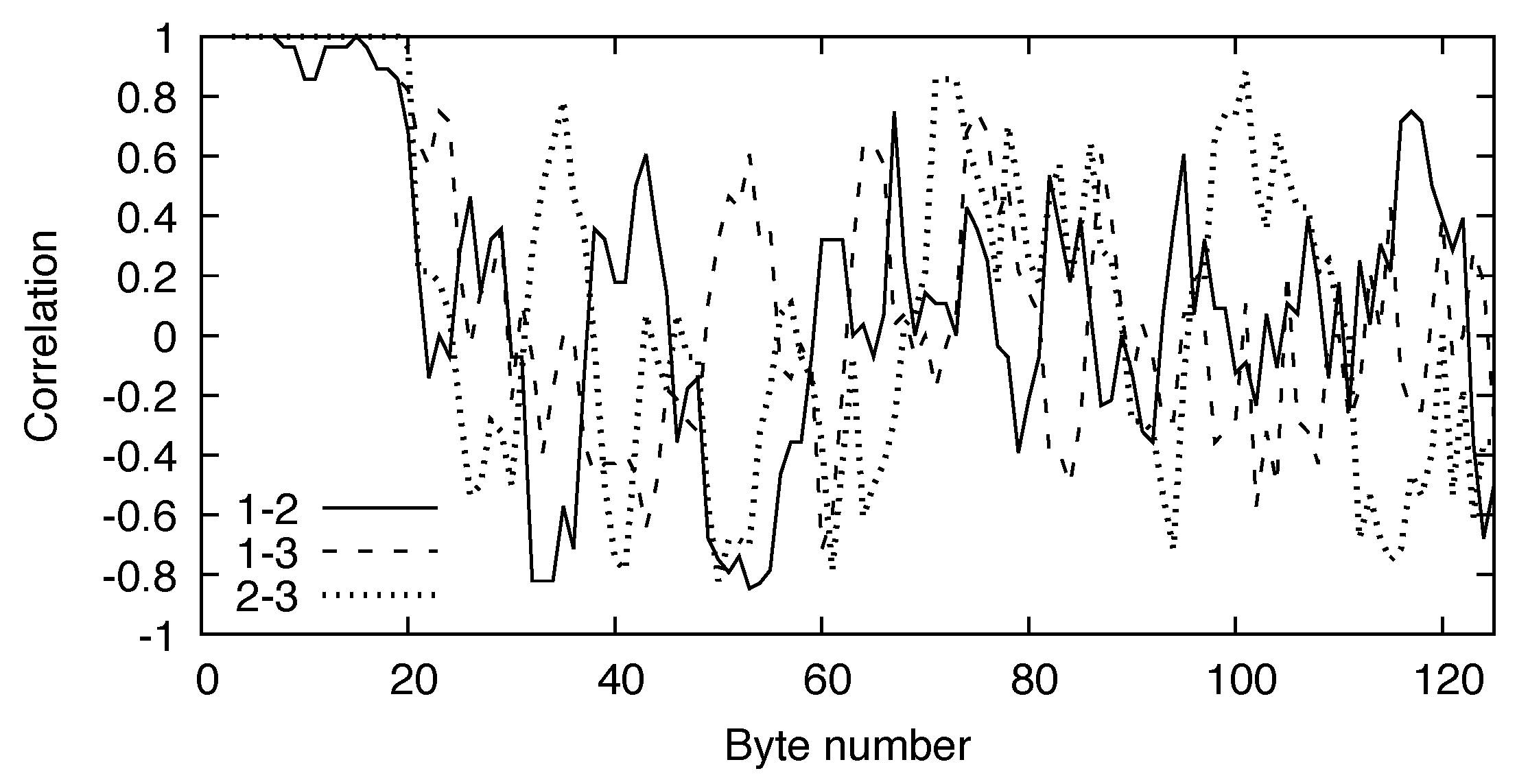
3. Pseudo-Random Number Generator
Digital image processing is the use of a digital computer to process digital images through an algorithm [1][2]. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing. It allows a much wider range of algorithms to be applied to the input data and can avoid problems such as the build-up of noise and distortion during processing
4. Optimization of Fractional Arneodo System
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, C.H.; Lee, J.D.; Tam, L.M.; Cheng, S.C. FPGA Implementation of Image Encryption by Adopting New Shimizu–Morioka System-Based Chaos Synchronization. Electronics 2025, 14, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Taralova, I.; El Assad, S.; Loiseau, J. Image encryption based on fractional chaotic pseudo-random number generator and DNA encryption method. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 109, 2103–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén-Fernández, O.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; de la Fraga, L.; Sandoval-Ibarra, Y.; Nuñez-Perez, J.C. An Image Encryption Scheme Synchronizing Optimized Chaotic Systems Implemented on Raspberry Pis. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; de la Fraga, L.; Guillén-Fernández, O.; Silva-Juárez, A. Optimization of Integer/Fractional Order Chaotic Systems by Metaheuristics and their Electronic Realization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Lu, R.; Zhang, H. Dynamical behaviors of the simple chaotic system with coexisting attractors and its synchronous application. Integration 2025, 102, 102368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonny, M.A.T.; Sambas, A.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Al Nassan, W.; Zhang, S.; Obaideen, K.; Mamat, M.; Kamal, M. A Speech Cryptosystem Using the New Chaotic System with a Capsule-Shaped Equilibrium Curve. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 75, 5987–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdELHaleem, S.H.; Abd-El-Hafiz, S.K.; Radwan, A.G. Analysis and Guidelines for Different Designs of Pseudo Random Number Generators. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 115697–115715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fraga, L.G.; Ovilla-Martínez, B. Generating pseudo-random numbers with a Brownian system. Integration 2024, 96, 102135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhang, S.; Su, D.; Wu, Y.; Musoya Gracia, Y.; Yin, H. Dynamic Analysis and Implementation of FPGA for a New 4D Fractional-Order Memristive Hopfield Neural Network. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.; Singh, U. A Review on Applications of Chaotic Maps in Pseudo-Random Number Generators and Encryption. Ann. Data Sci. 2024, 11, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Min, R.; Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Y. Hyperchaotic hashing: A chaotic hash function based on 2D linear cross-coupled map with parallel feedback structure. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassef, A.; Abdelkareem, M.; Maghrabie, H.; Baroutaji, A. Metaheuristic-Based Algorithms for Optimizing Fractional-Order Controllers—A Recent, Systematic, and Comprehensive Review. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.; Suhail Hussain, S.; Chandra Das, D.; Selim Ustun, T.; Iqbal, A. A review on fractional order (FO) controllers’ optimization for load frequency stabilization in power networks. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 4009–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai Lekshmi, A.; Balakumar, V. Numerical investigation of fractional order chaotic systems using a new modified Runge-Kutta method. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 105225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; González-Zapata, A.; Díaz-Muñoz, J.; de la Fraga, L.; Cruz-Vega, I. Optimization of fractional-order chaotic cellular neural networks by metaheuristics. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2022, 231, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Juárez, A.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; de la Fraga, L.; Li, R. Optimization of the Kaplan-Yorke dimension in fractional-order chaotic oscillators by metaheuristics. Appl. Math. Comput. 2021, 394, 125831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, R.; Saad, N. Fractional Order Runge–Kutta Methods. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcerzak, M.; Pikunov, D.; Dabrowsk, A. The fastest, simplified method of Lyapunov exponents spectrum estimation for continuous-time dynamical systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 94, 3053–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, T.; Chua, L. Practical Numerical Algorithms for Chaotic Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ecuyer, L.; Simard, R.; TestU01: A C Library for Empirical Testing of Random Number Generators. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software. 2007, Volume 33. Available online: http://simul.iro.umontreal.ca/testu01/tu01.html (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E.; Leigh, S.; Levenson, M.; Vangel, M.; Banks, D.; Heckert, A.; et al. A Statistical Test Suite for the Validation of Random Number Generators and Pseudo Random Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications. 27 April 2010. Available online: http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/ST/toolkit/rng/documentation_software.html (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Yates, R. Fixed-point arithmetic: An introduction. Digit. Sig. Labs 2009. Available online: https://www.cpplab.net/web/dsp/fp.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- AbdElHaleem, S.H.; Abd-El-Hafiz, S.K.; Radwan, A.G. Secure blind watermarking using fractional-order Lorenz system in the frequency domain. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2024, 173, 154998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
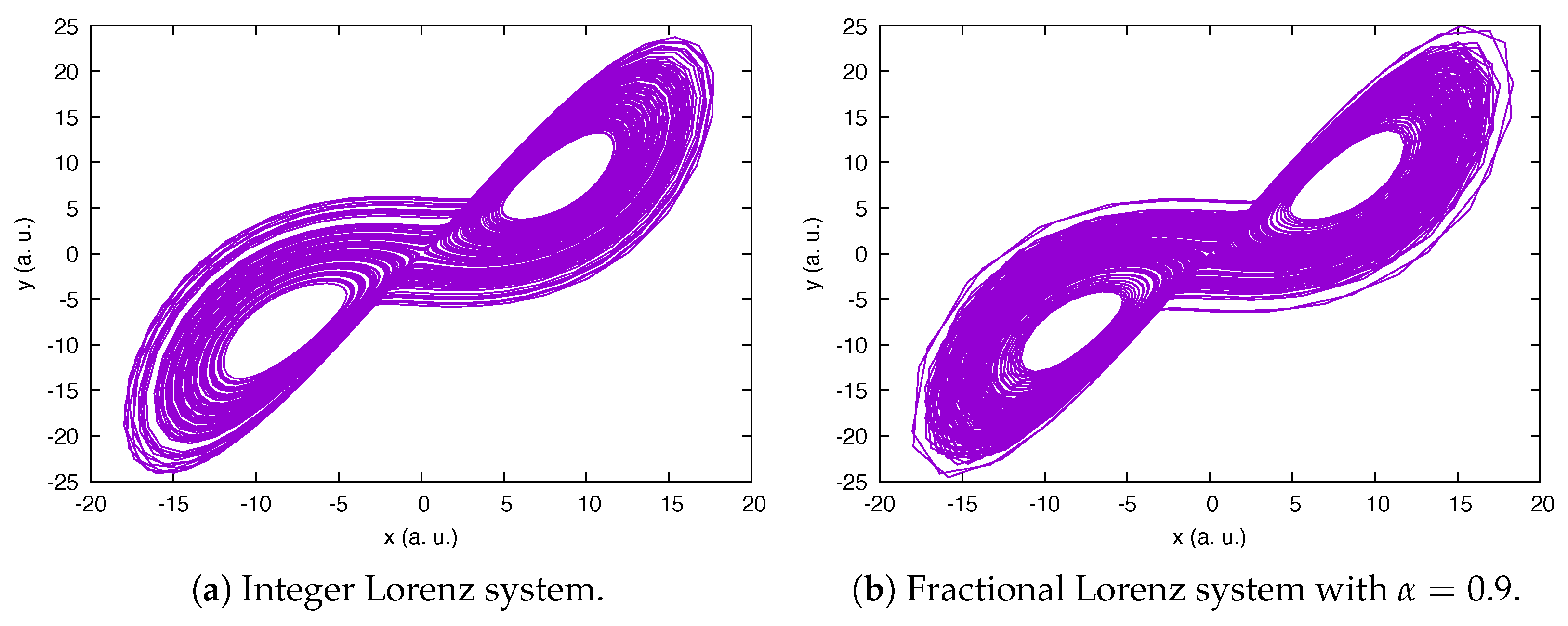

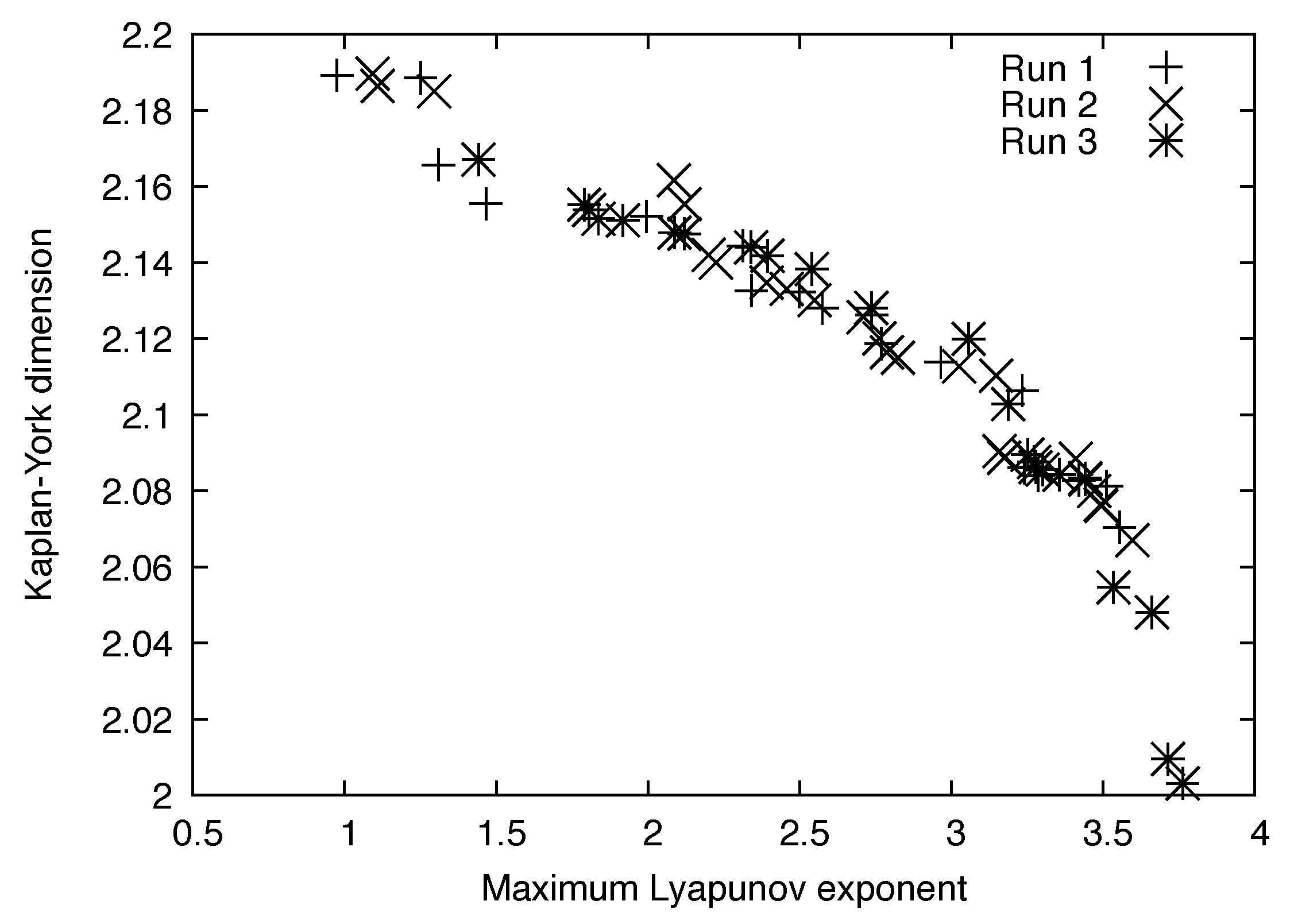
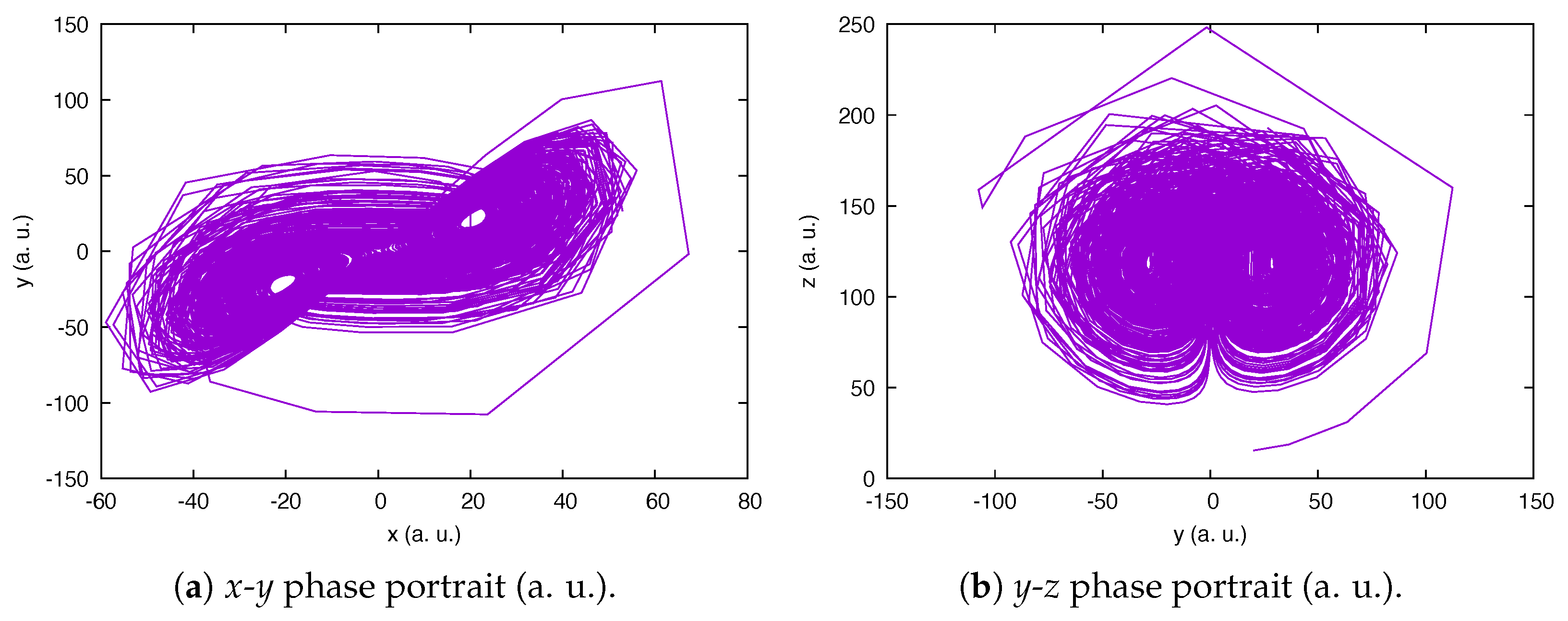

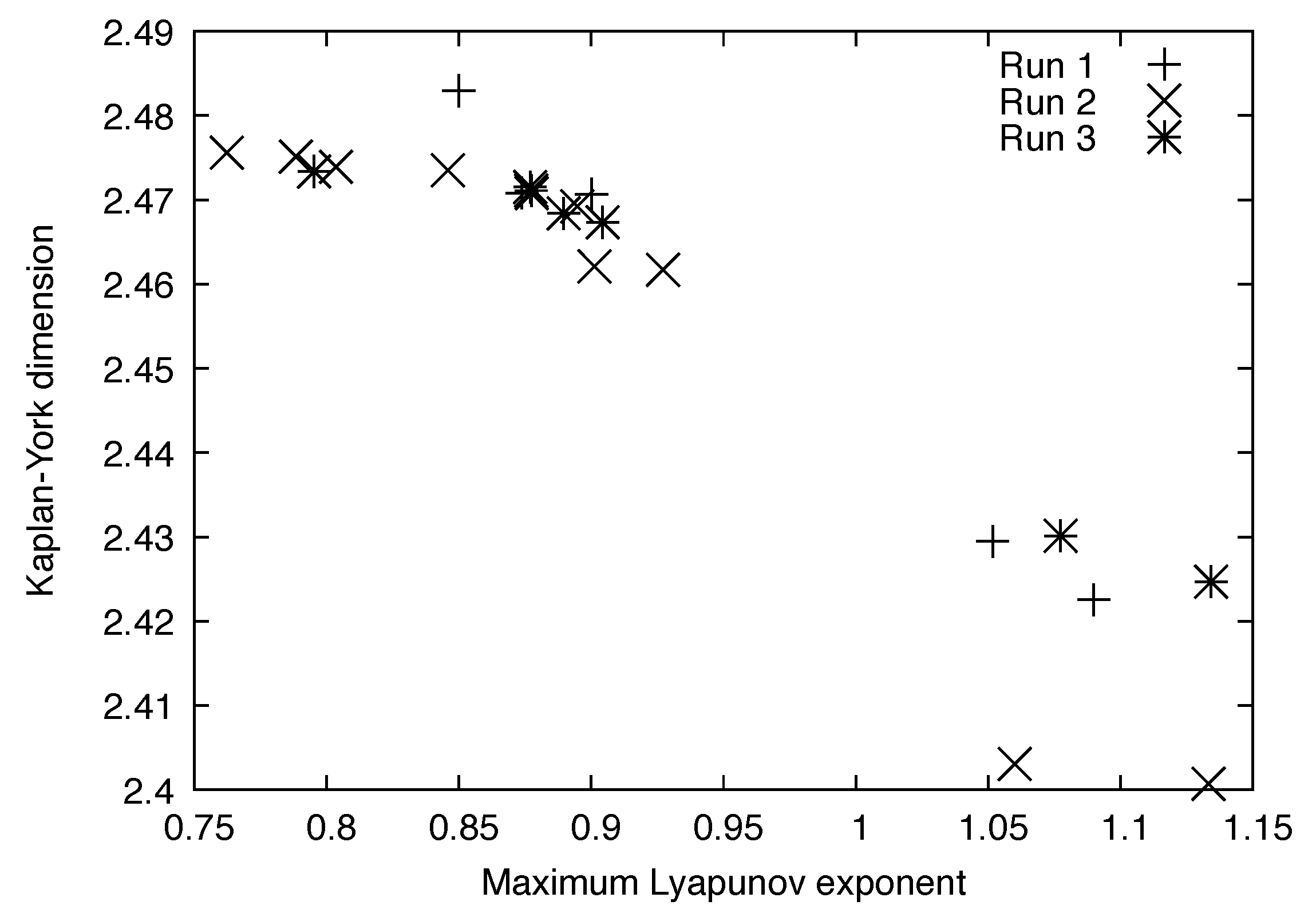

| MLE | KYD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.714313 | 2.009484 | 32.5167 | 118.9399 | 7.7136 |
| 3.661470 | 2.048009 | 29.8022 | 118.9523 | 6.0606 |
| 3.534711 | 2.054591 | 26.8531 | 119.4898 | 5.8574 |
| 3.512003 | 2.081190 | 23.1857 | 117.3934 | 4.4772 |
| 3.440673 | 2.083289 | 23.1105 | 116.9628 | 4.1644 |
| 3.420663 | 2.082792 | 23.1857 | 117.3934 | 4.1344 |
| 3.286999 | 2.083993 | 23.1857 | 117.0897 | 4.1344 |
| 3.174116 | 2.088680 | 21.9799 | 119.9868 | 3.2355 |
| 3.159071 | 2.090405 | 17.9290 | 119.3225 | 4.1486 |
| 3.147922 | 2.110244 | 17.9290 | 117.9841 | 2.8672 |
| PRNG with Real | PRNG with Fixed | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numbers | Point Arithmetic | ||||
| TestU01 test name | – | ||||
| 1 | Rabbit | All 40 tests passed | All 40 tests passed | ||
| 2 | Alphabit | All 17 tests passed | All 17 tests passed | ||
| 3 | Block Alphabit | All 6 repetitions of | All 6 repetitions of | ||
| Alphabit tests passed | Alphabit tests passed | ||||
| NIST test name | p-value | Proportion | p-value | Proportion | |
| 4 | Frequency | 0.455937 | 98 | 0.759756 | 99 |
| 5 | BlockFrequency | 0.514124 | 98 | 0.759756 | 97 |
| 6 | CumulativeSums | 0.674343 | 98 | 0.656132 | 99 |
| 7 | Runs | 0.304126 | 100 | 0.574903 | 100 |
| 8 | LongestRun | 0.699313 | 100 | 0.115387 | 98 |
| 9 | Rank | 0.002559 | 98 | 0.319084 | 99 |
| 10 | FFT | 0.971699 | 99 | 0.191687 | 98 |
| 11 | NonOverlappingTemplate | 0.487699 | 99 | 0.494655 | 99 |
| 12 | OverlappingTemplate | 0.911413 | 98 | 0.978072 | 97 |
| 13 | Universal | 0.262249 | 99 | 0.678686 | 98 |
| 14 | ApproximateEntropy | 0.637119 | 100 | 0.739918 | 99 |
| 15 | RandomExcursions | 0.349123 | 100 | 0.391268 | 99 |
| 16 | RandomExcursionsVariant | 0.261833 | 99 | 0.350938 | 99 |
| 17 | LinearComplexity | 0.334538 | 100 | 0.595549 | 97 |
| 18 | Serial | 0.539942 | 99 | 0.523809 | 100 |
| MLE | KYD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.133314 | 2.400701 | −94.9042 | 28.0987 | 1.6709 |
| 1.089930 | 2.422546 | −96.0482 | 29.8352 | 1.4881 |
| 1.060094 | 2.403057 | −94.5423 | 28.0987 | 1.6641 |
| 1.051732 | 2.429479 | −95.6548 | 29.8352 | 1.4881 |
| 0.927153 | 2.461696 | −94.4014 | 34.6392 | 1.0057 |
| 0.894752 | 2.469233 | −94.7296 | 34.6336 | 1.0010 |
| 0.877517 | 2.470804 | −98.4468 | 35.9923 | 1.0031 |
| 0.849975 | 2.482956 | −95.1019 | 34.8128 | 1.0017 |
| 0.803558 | 2.473915 | −94.3803 | 34.6342 | 1.0032 |
| 0.788414 | 2.475124 | −94.3867 | 34.6337 | 1.0031 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de la Fraga, L.G. Multi-Objective Optimization of a Fractional-Order Lorenz System. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030171
de la Fraga LG. Multi-Objective Optimization of a Fractional-Order Lorenz System. Fractal and Fractional. 2025; 9(3):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030171
Chicago/Turabian Stylede la Fraga, Luis Gerardo. 2025. "Multi-Objective Optimization of a Fractional-Order Lorenz System" Fractal and Fractional 9, no. 3: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030171
APA Stylede la Fraga, L. G. (2025). Multi-Objective Optimization of a Fractional-Order Lorenz System. Fractal and Fractional, 9(3), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030171






