A POD-Based Reduced-Dimension Method for Solution Coefficient Vectors in the Crank–Nicolson Mixed Finite Element Method for the Fourth-Order Parabolic Equation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The CNMFE Method for the Fourth-Order Variable Coefficient Parabolic Equation
2.1. The CNMFE Scheme
2.2. The Uniqueness, Stability, and Error Estimates of the CNMFE Solutions
3. The POD-Based RDCNMFE Method for the Fourth-Order Variable Coefficient Parabolic Equation
3.1. Structure of POD Bases
3.2. The RDCNMFE Scheme
3.3. The Uniqueness, Stability, and Error Estimate of the RDCNMFE Solutions
- (1)
- Demonstrate the uniqueness.(i) When .The uniqueness of the solutions for Problem 3 is guaranteed through Theorem 1.Consequently, the corresponding solutions, , derived from the first and fourth expressions of Problem 4, also have uniqueness.(ii) When .Through the application of and , the last three equations of Problem 4 are reformulated asFor , the uniqueness of the solutions for Problem 3 is guaranteed. (72)–(74) adhere to the identical structure, as presented in Problem 3. Thus, the solutions for (72)–(74) have uniqueness.
- (2)
- Analyze the stability.(i) When .When applying Theorem 2 and considering the orthonormality of the vectors in and , it follows that(ii) When .From the positive definite symmetry of matrix , (72) can be reformulated asSubstituting (73) into (76), and since is positive definite, we obtainLetting , and taking the inner product of (77) and , we haveThen, two sides of (78) are such thatandSimilar to (25), we obtainCombining (79), (80), and (81), we haveMultiplying (82) by and summating from 2 to n, it follows thatNoting thatputting (84) into (83), we haveUsing the Gronwall inequality for (85),AndSo, we getBecause of , we getBased on (75) and (89), the solutions exhibit unconditional stability.
- (3)
- Discuss the error estimates. (i) For .According to (68) and (69), and considering , we obtain(ii) For .Defining and , and combining (20), (76), and (73), we obtainPutting (92) into (91), and since is positively definite, we haveLetting , we obtainTaking the inner product of (94) and ,Then, two sides of (95) are such thatandUsing Lemma 1, (31), and (86), we can estimate the first term of (97) as follows:Combining (96), (97), and (98), we haveMultiplying (99) by and summating from to , we deriveNoting thatPutting (101) into (100), from (68) and (69), we haveWhen applying the Gronwall’s inequality for (102),Andthus, we getBecause of , we haveCombining Theorems 3 and 4 and formula (90) and (106), and utilizing the triangle inequality, we derive
4. The Numerical Experiments for the Fourth-Order Parabolic Equations
4.1. The Fourth-Order Variable Coefficient Parabolic Equation
- Step 1:
- In order to generate the snapshot matrices and , the initial CNMFE solution vectors are calculated via Problem 3.
- Step 2:
- Calculate the eigenvalues and the corresponding eigenvectors of the matrix . Sort the eigenvalues in descending order.
- Step 3:
- Through calculation, it is observed that . From the matrix , the first 6 eigenvectors can be selected. Applying the formula , we construct the POD bases .
- Step 4:
- Inserting the result into Problem 4 and calculating the RDCNMFE solutions.
4.2. The Time-Fractional Fourth-Order Parabolic Equation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| POD | proper orthogonal decomposition |
| CNMFE | Crank–Nicolson mixed finite element |
| RDCNMFE | reduced-dimension Crank–Nicolson mixed finite element |
| PDEs | partial differential equations |
References
- Zhang, T. Finite element analysis for Cahn-Hilliard equation. Math. Numer. Sin. 2006, 28, 281–292. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chai, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zou, Y. A C0 weak Galerkin method for linear Cahn-Hilliard-Cook equation with random initial condition. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 414, 126659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danumjaya, P.; Pani, A.K. Mixed finite element methods for a fourth order reaction diffusion equation. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 2012, 28, 1227–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; He, M.; Sun, P. Energy-stable finite element method for a class of nonlinear fourth-order parabolic equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2024, 438, 115576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, R.; Qi, R.J.; Sun, H. Energy stability and convergence of variable-step L1 scheme for the time fractional Swift-Hohenberg model. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2024, 27, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.W.; Blowey, J.F.; Garcke, H. Finite element approximation of a fourth order nonlinear degenerate parabolic equation. Numer. Math. 1998, 80, 525–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Cheng, Y.; Li, M. High order spline finite element method for the fourth-order parabolic equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 2023, 184, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Li, H.; He, S.; Gao, W. A coupling method based on new MFE and FE for fourth-order parabolic equation. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2013, 43, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; He, S.; Gao, W.; Fang, Z.C. H1-Galerkin mixed element method and numerical simulation for the fourth-order parabolic partial differential equations. Math. Numer. Sin. 2012, 34, 259–274. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.Y.; Shi, Y.H.; Wang, F.L. Supercloseness and the optimal order error estimates of H1-Galerkin mixed element method for fourth order parabolic equation. Math. Numer. Sin. 2014, 36, 363–380. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Guo, Y. The space-time mixed finite element method for fourth order parabolic problems. J. Inn. Mong. Univ. (Natural Sci. Ed.) 2006, 37, 19–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Li, H. The mixed discontinuous space-time finite element method for the fourth order linear parabolic equation with generalized boundary condition. Math. Numer. Sinica. 2009, 31, 167–178. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; He, S. A two-grid mixed finite element method for a nonlinear fourth-order reaction-diffusion problem with time-fractional derivative. Comput. Math. Appl. 2015, 70, 2474–2492. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; He, S.; Wang, J. TGMFE algorithm combined with some time second-order schemes for nonlinear fourth-order reaction diffusion system. Results. Appl. Math. 2019, 4, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, W. Weak Galerkin finite element methods for a fourth order parabolic equation. Numer. Methods Partial. Differ. Equ. 2019, 35, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, F.; Liu, B. Finite difference discretization of a fourth-order parabolic equation describing crystal surface growth. Appl. Anal. 2015, 94, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, R.K.; Kaur, D.; Singh, S. A class of two- and three-level implicit methods of order two in time and four in space based on half-step discretization for two-dimensional fourth order quasi-linear parabolic equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 352, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Mohanty, R.K. Highly accurate compact difference scheme for fourth order parabolic equation with Dirichlet and Neumann boundary conditions: Application to good Boussinesq equation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 378, 125202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Z. Pointwise error estimate of the compact difference methods for the fourth-order parabolic equations with the third Neumann boundary conditions. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 2023, 47, 634–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Mohanty, R.K. High-order half-step compact numerical approximation for fourth-order parabolic PDEs. Numer. Algorithms 2024, 95, 1127–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, N. A fast computational technique to solve fourth-order parabolic equations: Application to good Boussinesq, Euler-Bernoulli and Benjamin-Ono equations. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2024, 101, 194–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishige, K.; Miyake, N.; Okabe, S. Blowup for a Fourth-Order Parabolic Equation with Gradient Nonlinearity. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 2020, 52, 927–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhou, J. Infinite Time Blow-Up of Solutions to a Fourth-Order Nonlinear Parabolic Equation with Logarithmic Nonlinearity Modeling Epitaxial Growth. Mediterr. J. Math. 2021, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Tang, G. Blow-up phenomena for a class of fourth order parabolic equation. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2021, 505, 125445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, B.; Wang, J. Global existence and blow-up of weak solutions for a fourth-order parabolic equation with gradient nonlinearity. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 2024, 75, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.D. Finite Element and Reduced Dimension Methods for Partial Differential Equations; Springer: Singapore; Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.D.; Chen, G. Proper Orthogonal Decomposition Methods for Partial Differential Equations; Academic Press of Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, W.; Chen, C. A fourth order Runge-Kutta type of exponential time differencing and triangular spectral element method for two dimensional nonlinear Maxwell’s equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 2025, 207, 348–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, A. Sparse grid time-discontinuous Galerkin method with streamline diffusion for transport equations. Partial. Differ. Equ. Appl. 2023, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Y. Generalized multiscale finite element method and balanced truncation for parameter-dependent parabolic problems. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, X.; Ji, D. A Reduced High-Order Compact Finite Difference Scheme Based on POD Technique for the Two Dimensional Extended Fisher-Kolmogorov Equation. IAENG Int. J. Appl. Math. 2020, 50, 474–483. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. A proper orthogonal decomposition-compact difference algorithm for plate vibration models. Numer. Algorithms 2023, 94, 1489–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Piao, G.R. A reduced Galerkin finite element formulation based on proper orthogonal decomposition for the generalized KDV-RLW-Rosenau equation. J. Inequal. Appl. 2023, 2023, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Archilla, B.; John, V.; Novo, J. Second order error bounds for POD-ROM methods based on first order divided differences. Appl. Math. Letters 2023, 146, 108836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, A.; Singler, R.J. A new proper orthogonal decomposition method with second difference quotients for the wave equation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2025, 457, 116279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. A POD based extrapolation DG time stepping space-time FE method for parabolic problems. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2024, 539, 128501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Qi, Q. A POD based reduced-order local RBF collocation approach for time-dependent nonlocal diffusion problems. Appl. Math. Letters 2025, 160, 109328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.D.; Li, L.; Sun, P. A reduced-order MFE formulation based on POD method for parabolic equations. Acta. Math. Sci. 2013, 33B, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Teng, F.; Luo, Z.D. A reduced-order extrapolation algorithm based on CNLSMFE formulation and POD technique for two-dimensional Sobolev equations. Appl. Math. Ser. B. 2014, 29, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.D.; Zhou, Y.J.; Yang, X.Z. A reduced finite element formulation based on proper orthogonal decomposition for Burgers equation. Appl. Numer. Math. 2009, 59, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Rui, H. A reduced-order characteristic finite element method based on POD for optimal control problem governed by convection-diffusion equation. Comput. Meth. Appl. M 2022, 391, 114538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Rui, H. Reduced-order finite element approximation based on POD for the parabolic optimal control problem. Numer. Algorithms 2024, 95, 1189–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.D. A POD-Based Reduced-Order Stabilized Crank-Nicolson MFE Formulation for the Non-Stationary Parabolized Navier-Stokes Equations. Math. Model. Anal. 2015, 20, 346–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.D. A POD-based reduced-order TSCFE extrapolation iterative format for two-dimensional heat equations. Bound. Value. Probl. 2015, 2015, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.D. The reduced-order extrapolating method about the Crank-Nicolson finite element solution coefficient vectors for parabolic type equation. Mathematics. 2020, 8, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Luo, Z.D. The reduced-dimension technique for the unknown solution coefficient vectors in the Crank-Nicolson finite element method for the Sobolev equation. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2022, 513, 126207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Luo, Z.D. A reduced-order extrapolation technique for solution coefficient vectors in the mixed finite element method for the 2D nonlinear Rosenau equation. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2020, 485, 123761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.D. The dimensionality reduction of Crank-Nicolson mixed finite element solution coefficient vectors for the unsteady Stokes equation. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Teng, F.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, Z. Two-grid dimension reduction method of Crank-Nicolson mixed finite element solution coefficient vectors for the fourth-order extended Fisher-Kolmogorov equation. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2024, 536, 128168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Li, H. The reduced-dimension method for Crank-Nicolson mixed finite element solution coefficient vectors of the extended Fisher-Kolmogorov equation. Axioms 2024, 13, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Cai, Y.; Luo, Z. The dimension reduction method of two-grid Crank-Nicolson mixed finite element solution coefficient vectors for nonlinear fourth-order reaction diffusion equation with temporal fractional derivative. Commun. Nonlinear. Sci. 2024, 133, 107962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.A. Sobolev Spaces; Academic Press: New York, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.D. The Founfations and Applications of Mixed Finite Element Methods; Chinese Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, H.; He, S.; Gao, W.; Liu, Y. A new linearized Crank-Nicolson mixed element scheme for the extended Fisher-Kolmogorov equation. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 756281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

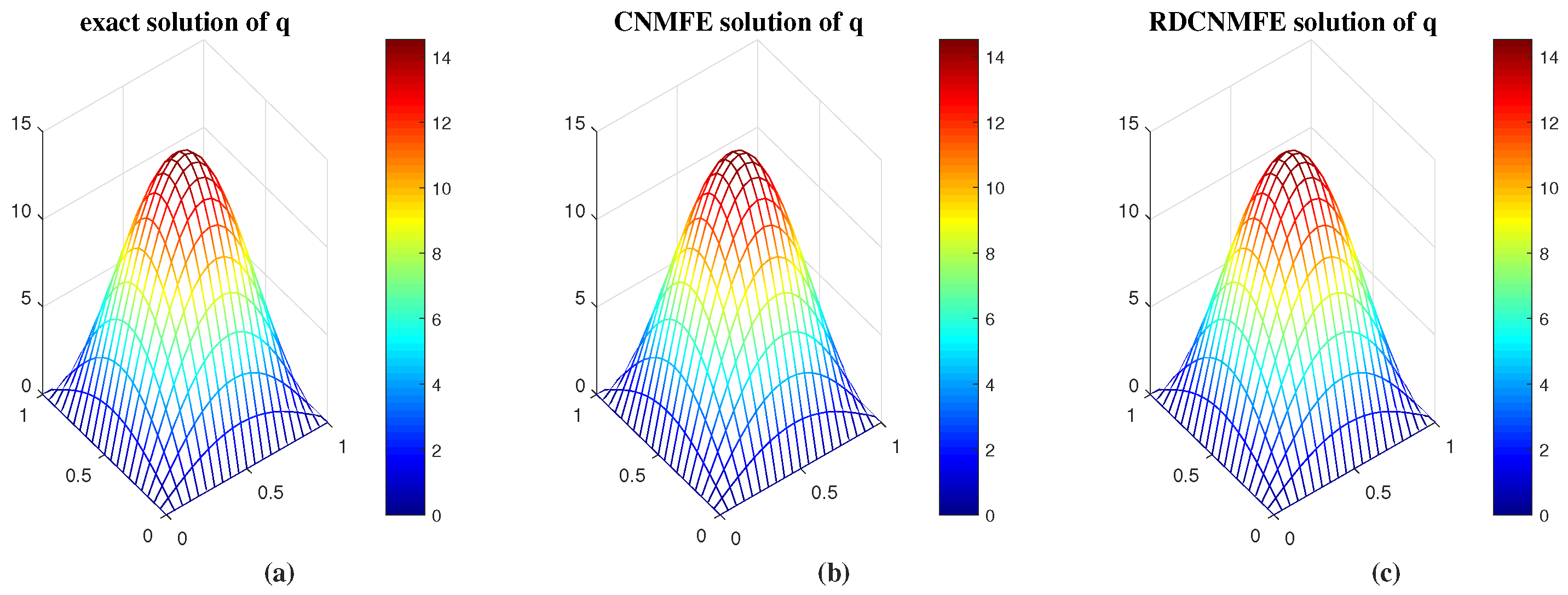
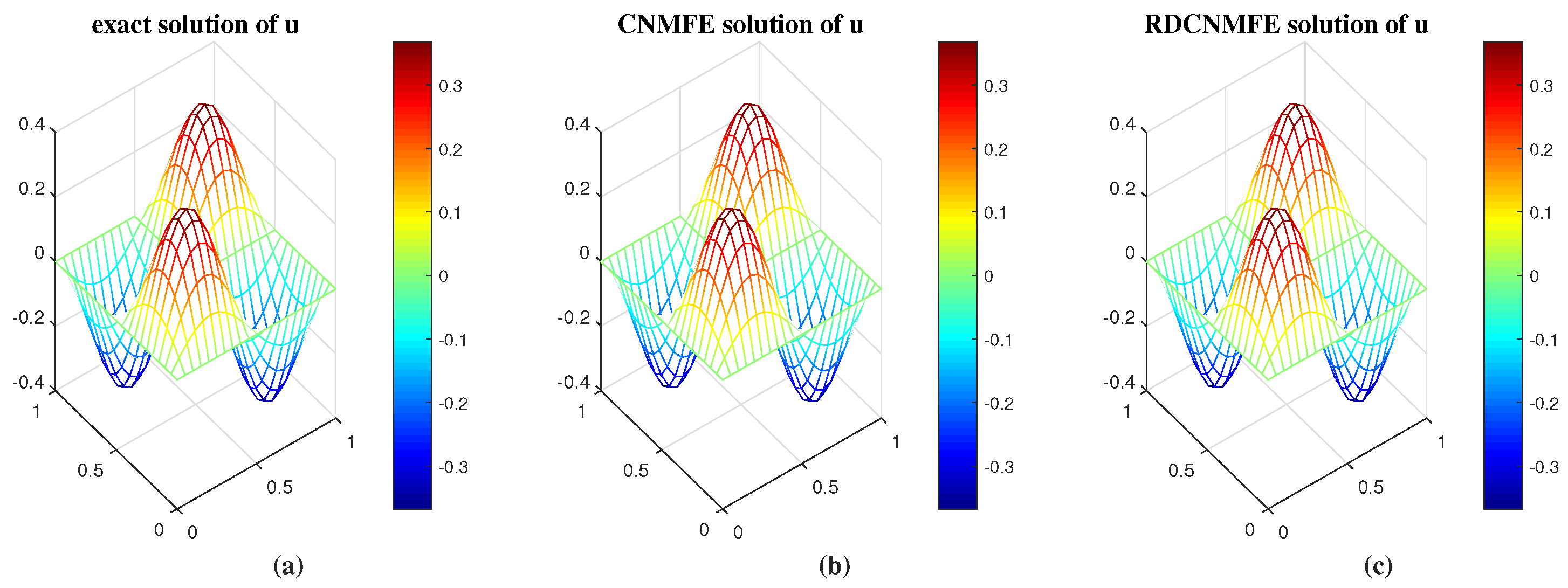
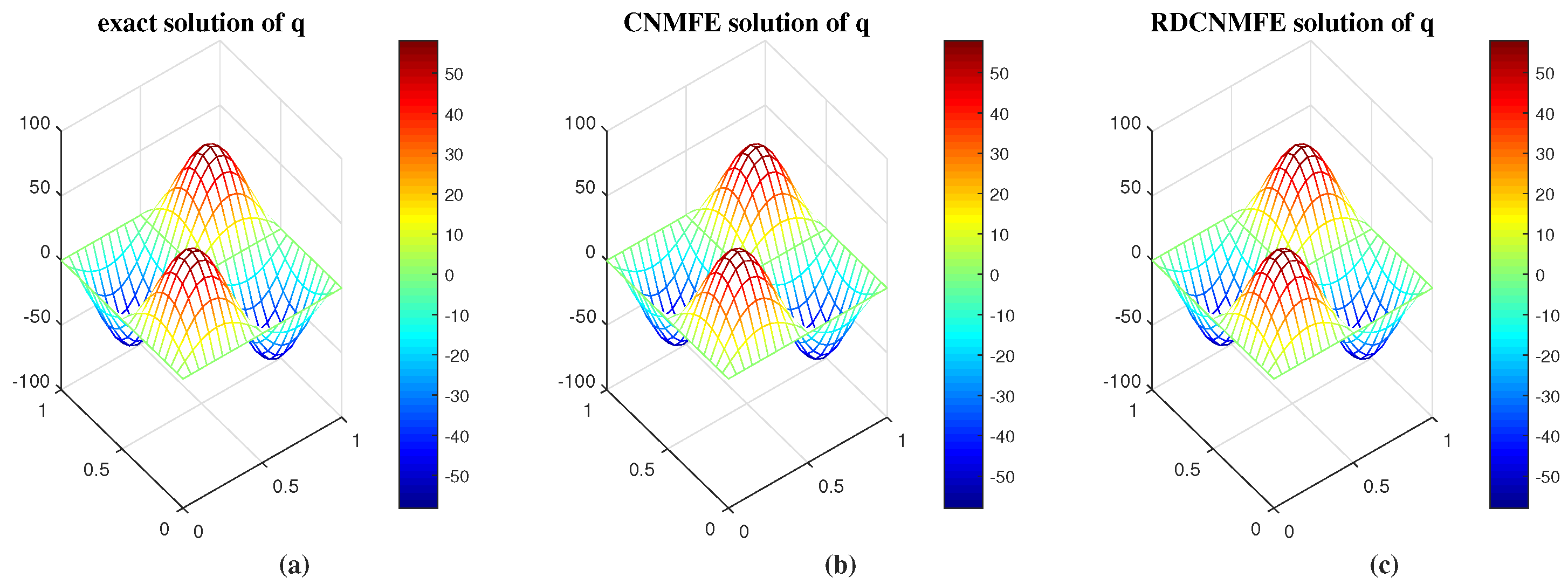
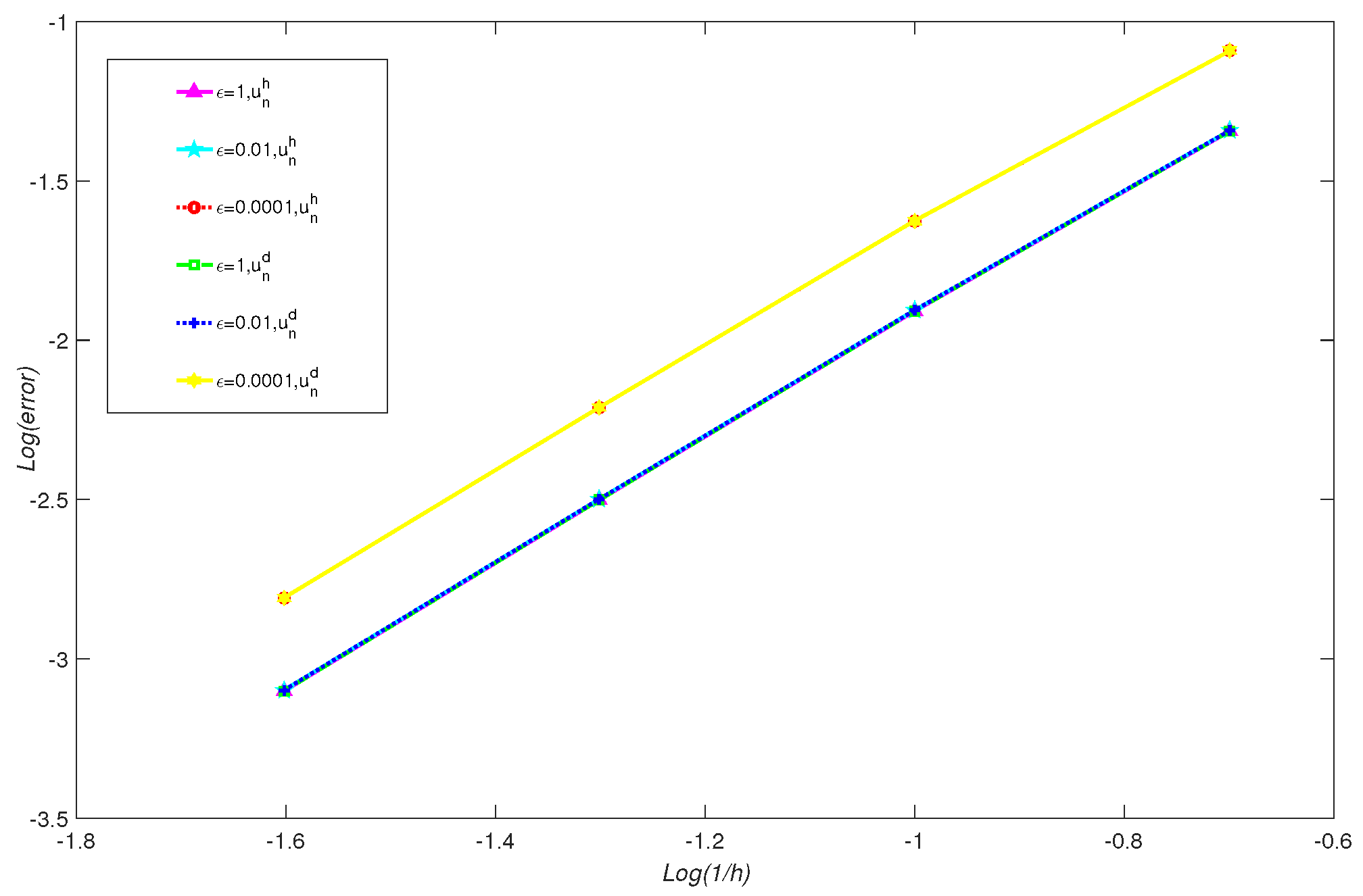
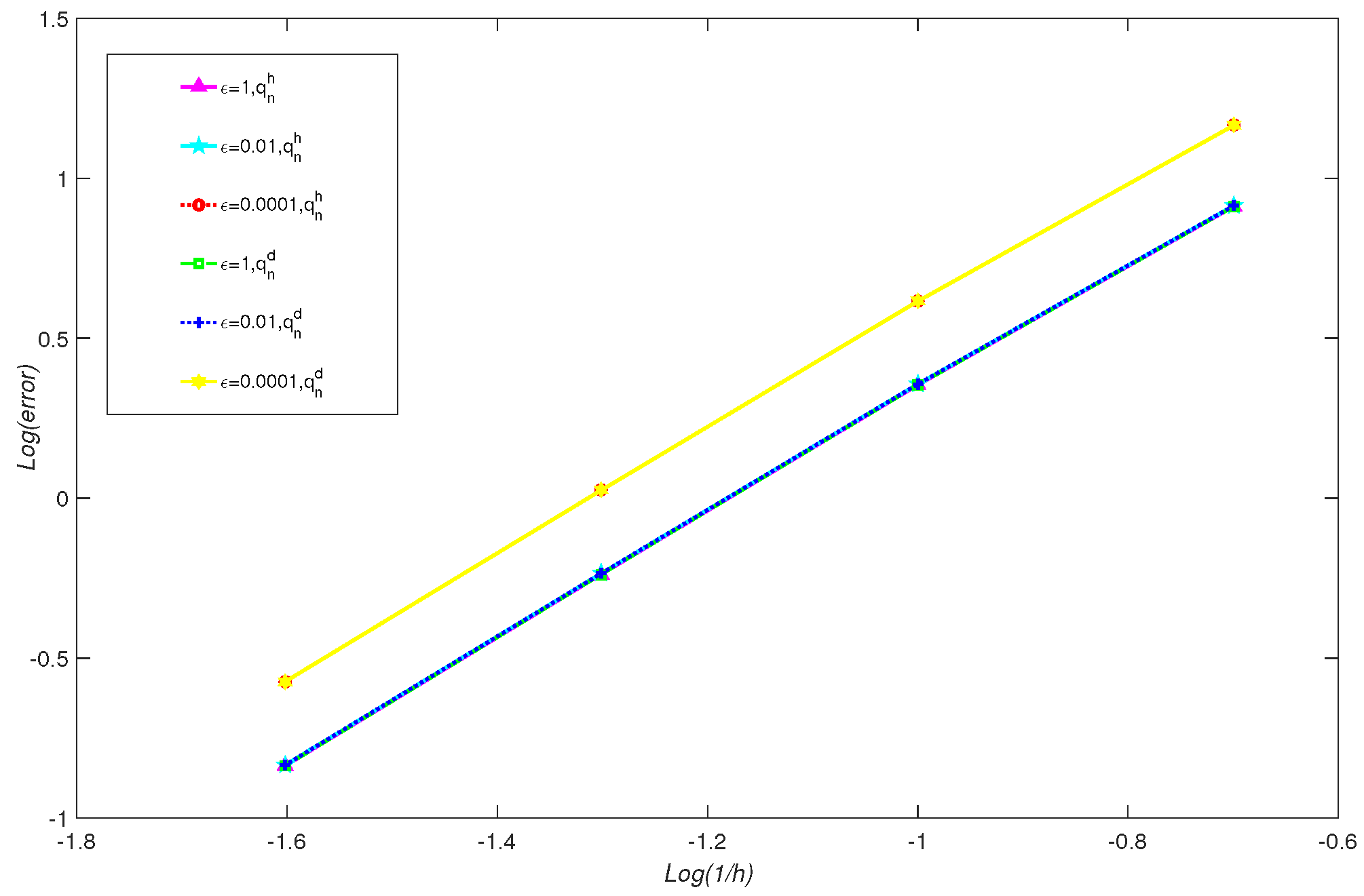

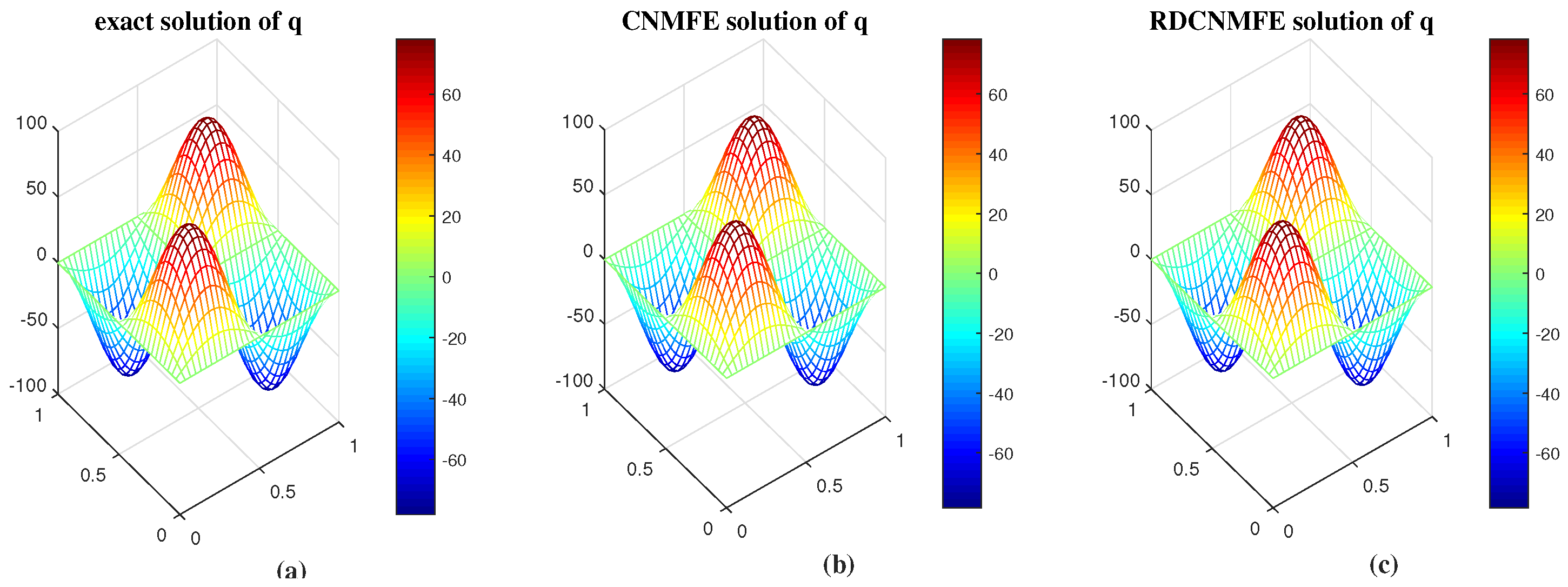
| CNMFE Method | RDCNMFE Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Order | Order | |||
| 4.0880 × 10−3 | 4.0880 × 10−3 | ||||
| 1.1926 × 10−3 | 1.7773 | 1.1926 × 10−3 | 1.7773 | ||
| 3.1003 × 10−4 | 1.9436 | 3.1003 × 10−4 | 1.9436 | ||
| 7.7556 × 10−5 | 1.9991 | 7.7556 × 10−5 | 1.9991 | ||
| CNMFE Method | RDCNMFE Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Order | Order | |||
| 1.9183 × 10−1 | 1.9183 × 10−1 | ||||
| 5.5050 × 10−2 | 1.8010 | 5.5050 × 10−2 | 1.8010 | ||
| 1.4248 × 10−2 | 1.9500 | 1.4248 × 10−2 | 1.9500 | ||
| 3.5645 × 10−3 | 1.9990 | 3.5645 × 10−3 | 1.9990 | ||
| Real Time | CNMFE Method | RDCNMFE Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU Runtime | CPU Runtime | |||||
| 1.9848 × 10−4 | 9.1218 × 10−3 | 257.785 s | 1.9848 × 10−4 | 9.1218 × 10−3 | 61.542 s | |
| 7.2804 × 10−5 | 8.7617 × 10−3 | 518.493 s | 7.2804 × 10−5 | 8.7617 × 10−3 | 71.464 s | |
| 2.6836 × 10−5 | 7.7620 × 10−3 | 776.562 s | 2.6836 × 10−5 | 7.7620 × 10−3 | 88.742 s | |
| CNMFE Method | RDCNMFE Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Order | Order | |||
| 4.5306 × 10−2 | 4.5306 × 10−2 | ||||
| 1.2336 × 10−2 | 1.8768 | 1.2336 × 10−2 | 1.8768 | ||
| 3.1509 × 10−3 | 1.9691 | 3.1509 × 10−3 | 1.9691 | ||
| 7.9192 × 10−4 | 1.9923 | 7.9192 × 10−4 | 1.9923 | ||
| 4.5542 × 10−2 | 4.5542 × 10−2 | ||||
| 1.2420 × 10−2 | 1.8746 | 1.2420 × 10−2 | 1.8746 | ||
| 3.1736 × 10−3 | 1.9684 | 3.1736 × 10−3 | 1.9684 | ||
| 7.9778 × 10−4 | 1.9921 | 7.9778 × 10−4 | 1.9921 | ||
| 8.0912 × 10−2 | 8.0912 × 10−2 | ||||
| 2.3697 × 10−2 | 1.7717 | 2.3697 × 10−2 | 1.7717 | ||
| 6.1544 × 10−3 | 1.9450 | 6.1544 × 10−3 | 1.9450 | ||
| 1.5541 × 10−3 | 1.9856 | 1.5541 × 10−3 | 1.9856 | ||
| CNMFE Method | RDCNMFE Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Order | Order | |||
| 8.1734 × 100 | 8.1734 × 100 | ||||
| 2.2583 × 100 | 1.8557 | 2.2583 × 100 | 1.8557 | ||
| 5.7873 × 10−1 | 1.9643 | 5.7873 × 10−1 | 1.9643 | ||
| 1.4557 × 10−1 | 1.9911 | 1.4557 × 10−1 | 1.9911 | ||
| 8.2168 × 100 | 8.2168 × 100 | ||||
| 2.2721 × 100 | 1.8546 | 2.2721 × 100 | 1.8546 | ||
| 5.8240 × 10−1 | 1.9639 | 5.8240 × 10−1 | 1.9639 | ||
| 1.4651 × 10−1 | 1.9910 | 1.4651 × 10−1 | 1.9910 | ||
| 1.4643 × 101 | 1.4643 × 101 | ||||
| 4.1238 × 100 | 1.8281 | 4.1238 × 100 | 1.8281 | ||
| 1.0595 × 100 | 1.9605 | 1.0595 × 100 | 1.9605 | ||
| 2.6680 × 10−1 | 1.9896 | 2.6680 × 10−1 | 1.9896 | ||
| Real Time | CNMFE Method | RDCNMFE Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU Runtime | CPU Runtime | |||||
| 1.3087 × 10−3 | 1.4793 × 10−1 | 128.368 s | 1.3087 × 10−3 | 1.4793 × 10−1 | 56.044 s | |
| 7.9192 × 10−4 | 1.4557 × 10−1 | 254.327 s | 7.9192 × 10−4 | 1.4557 × 10−1 | 60.044 s | |
| 4.8003 × 10−4 | 1.4453 × 10−1 | 390.405 s | 4.8003 × 10−4 | 1.4453 × 10−1 | 69.740 s | |
| 2.9118 × 10−4 | 1.4011 × 10−1 | 522.115 s | 2.9118 × 10−4 | 1.4011 × 10−1 | 76.308 s | |
| 1.7665 × 10−4 | 1.3271 × 10−1 | 650.523 s | 1.7665 × 10−4 | 1.3271 × 10−1 | 83.345 s | |
| 1.0718 × 10−4 | 1.2395 × 10−1 | 781.210 s | 1.0718 × 10−4 | 1.2395 × 10−1 | 92.238 s | |
| CNMFE Method | RDCNMFE Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Order | Order | ||||
| 1.2310 × 10−1 | – | 1.2310 × 10−1 | – | |||
| 3.3475 × 10−2 | 1.8787 | 3.3475 × 10−2 | 1.8787 | |||
| 8.5063 × 10−3 | 1.9765 | 8.5063 × 10−3 | 1.9765 | |||
| 2.0939 × 10−3 | 2.0223 | 2.0939 × 10−3 | 2.0223 | |||
| 1.2311 × 10−1 | – | 1.2311 × 10−1 | – | |||
| 3.3497 × 10−2 | 1.8779 | 3.3497 × 10−2 | 1.8779 | |||
| 8.5312 × 10−3 | 1.9732 | 8.5312 × 10−3 | 1.9732 | |||
| 2.1196 × 10−3 | 2.0090 | 2.1196 × 10−3 | 2.0090 | |||
| 1.2313 × 10−1 | – | 1.2313 × 10−1 | – | |||
| 3.3497 × 10−2 | 1.8767 | 3.3497 × 10−2 | 1.8767 | |||
| 8.5690 × 10−3 | 1.9683 | 8.5690 × 10−3 | 1.9683 | |||
| 2.1585 × 10−3 | 1.9891 | 2.1585 × 10−3 | 1.9891 | |||
| 1.2316 × 10−1 | – | 1.2316 × 10−1 | – | |||
| 3.3577 × 10−2 | 1.8750 | 3.3577 × 10−2 | 1.8750 | |||
| 8.6214 × 10−3 | 1.9615 | 8.6214 × 10−3 | 1.9615 | |||
| 2.2125 × 10−3 | 1.9622 | 2.2125 × 10−3 | 1.9622 | |||
| 1.2320 × 10−1 | – | 1.2320 × 10−1 | – | |||
| 3.3636 × 10−2 | 1.8729 | 3.3636 × 10−2 | 1.8729 | |||
| 8.6877 × 10−3 | 1.9530 | 8.6877 × 10−3 | 1.9530 | |||
| 2.2801 × 10−3 | 1.9293 | 2.2801 × 10−3 | 1.9293 | |||
| 1.2312 × 10−1 | – | 1.2312 × 10−1 | – | |||
| 3.3503 × 10−2 | 1.8777 | 3.3503 × 10−2 | 1.8777 | |||
| 8.5354 × 10−3 | 1.9728 | 8.5354 × 10−3 | 1.9728 | |||
| 2.1233 × 10−3 | 2.0072 | 2.1233 × 10−3 | 2.0072 | |||
| 1.2313 × 10−1 | – | 1.2313 × 10−1 | – | |||
| 3.3514 × 10−2 | 1.8773 | 3.3514 × 10−2 | 1.8773 | |||
| 8.5479 × 10−3 | 1.9711 | 8.5479 × 10−3 | 1.9711 | |||
| 2.1361 × 10−3 | 2.0006 | 2.1361 × 10−3 | 2.0006 | |||
| 1.2314 × 10−1 | – | 1.2314 × 10−1 | – | |||
| 3.3531 × 10−2 | 1.8767 | 3.3531 × 10−2 | 1.8767 | |||
| 8.5668 × 10−3 | 1.9687 | 8.5668 × 10−3 | 1.9687 | |||
| 2.1556 × 10−3 | 1.9907 | 2.1556 × 10−3 | 1.9907 | |||
| 1.2316 × 10−1 | – | 1.2316 × 10−1 | – | |||
| 3.3554 × 10−2 | 1.8759 | 3.3554 × 10−2 | 1.8759 | |||
| 8.5930 × 10−3 | 1.9653 | 8.5930 × 10−3 | 1.9653 | |||
| 2.1826 × 10−3 | 1.9771 | 2.1826 × 10−3 | 1.9771 | |||
| 1.2317 × 10−1 | – | 1.2317 × 10−1 | – | |||
| 3.3584 × 10−2 | 1.8749 | 3.3584 × 10−2 | 1.8749 | |||
| 8.6261 × 10−3 | 1.9510 | 8.6261 × 10−3 | 1.9510 | |||
| 2.2168 × 10−3 | 1.9603 | 2.2168 × 10−3 | 1.9603 | |||
| CNMFE Method | RDCNMFE Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Order | Order | ||||
| 6.1429 × 100 | 6.1429 × 100 | |||||
| 1.5320 × 100 | 2.0035 | 1.5320 × 100 | 2.0035 | |||
| 3.8003 × 10−1 | 2.0112 | 3.8003 × 10−1 | 2.0112 | |||
| 9.1957 × 10−2 | 2.0471 | 9.1957 × 10−2 | 2.0471 | |||
| 6.1438 × 100 | 6.1438 × 100 | |||||
| 1.5335 × 100 | 2.0022 | 1.5335 × 100 | 2.0022 | |||
| 3.8178 × 10−1 | 2.0061 | 3.8178 × 10−1 | 2.0061 | |||
| 9.3733 × 10−2 | 2.0261 | 9.3733 × 10−2 | 2.0261 | |||
| 6.1454 × 100 | 6.1454 × 100 | |||||
| 1.5359 × 100 | 2.0004 | 1.5359 × 100 | 2.0004 | |||
| 3.8443 × 10−1 | 1.9983 | 3.8443 × 10−1 | 1.9983 | |||
| 9.6452 × 10−2 | 1.9948 | 9.6452 × 10−2 | 1.9948 | |||
| 6.1476 × 100 | 6.1476 × 100 | |||||
| 1.5393 × 100 | 1.9978 | 1.5393 × 100 | 1.9978 | |||
| 3.8813 × 10−1 | 1.9876 | 3.8813 × 10−1 | 1.9876 | |||
| 1.0027 × 10−1 | 1.9527 | 1.0027 × 10−1 | 1.9527 | |||
| 6.1504 × 100 | 1.4643 × 101 | |||||
| 1.5435 × 100 | 1.9945 | 1.5435 × 100 | 1.9945 | |||
| 3.9289 × 10−1 | 1.9742 | 3.9289 × 10−1 | 1.9742 | |||
| 1.0516 × 10−1 | 1.9012 | 1.0516 × 10−1 | 1.9012 | |||
| 6.1447 × 100 | 6.1447 × 100 | |||||
| 1.5340 × 100 | 2.0021 | 1.5340 × 100 | 2.0021 | |||
| 3.8208 × 10−1 | 2.0054 | 3.8208 × 10−1 | 2.0054 | |||
| 9.3990 × 10−2 | 2.0233 | 9.3990 × 10−2 | 2.0233 | |||
| 6.1452 × 100 | 6.1452 × 100 | |||||
| 1.5348 × 100 | 2.0014 | 1.5348 × 100 | 2.0014 | |||
| 3.8295 × 10−1 | 2.0028 | 3.8295 × 10−1 | 2.0028 | |||
| 9.4885 × 10−2 | 2.0129 | 9.4885 × 10−2 | 2.0129 | |||
| 6.1460 × 100 | 6.1460 × 100 | |||||
| 1.5360 × 100 | 2.0005 | 1.5360 × 100 | 2.0005 | |||
| 3.8428 × 10−1 | 1.9989 | 3.8428 × 10−1 | 1.9989 | |||
| 9.6247 × 10−2 | 1.9973 | 9.6247 × 10−2 | 1.9973 | |||
| 6.1470 × 100 | 6.1470 × 100 | |||||
| 1.5376 × 100 | 1.9992 | 1.5376 × 100 | 1.9992 | |||
| 3.8613 × 10−1 | 1.9936 | 3.8613 × 10−1 | 1.9936 | |||
| 9.8147 × 10−2 | 1.9761 | 9.8147 × 10−2 | 1.9761 | |||
| 6.1484 × 100 | 6.1484 × 100 | |||||
| 1.5397 × 100 | 1.9975 | 1.5397 × 100 | 1.9975 | |||
| 3.8846 × 10−1 | 1.9868 | 3.8846 × 10−1 | 1.9868 | |||
| 1.0057 × 10−1 | 1.9496 | 1.0057 × 10−1 | 1.9496 | |||
| Real Time | CNMFE Method | RDCNMFE Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU Runtime | CPU Runtime | |||||
| 2.7163 × 10−4 | 1.2184 × 10−2 | 19.797s | 2.7163 × 10−4 | 1.2184 × 10−2 | 3.605 s | |
| 2.2003 × 10−3 | 9.9402 × 10−2 | 54.301s | 2.2003 × 10−3 | 9.9402 × 10−2 | 7.574 s | |
| 7.4754 × 10−3 | 3.3898 × 10−1 | 83.899s | 7.4754 × 10−3 | 3.3898 × 10−1 | 9.907s | |
| 1.7798 × 10−2 | 8.0907 × 10−1 | 141.050 s | 1.7798 × 10−2 | 8.0907 × 10−1 | 13.984 s | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, X.; Li, H. A POD-Based Reduced-Dimension Method for Solution Coefficient Vectors in the Crank–Nicolson Mixed Finite Element Method for the Fourth-Order Parabolic Equation. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030137
Chang X, Li H. A POD-Based Reduced-Dimension Method for Solution Coefficient Vectors in the Crank–Nicolson Mixed Finite Element Method for the Fourth-Order Parabolic Equation. Fractal and Fractional. 2025; 9(3):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030137
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Xiaohui, and Hong Li. 2025. "A POD-Based Reduced-Dimension Method for Solution Coefficient Vectors in the Crank–Nicolson Mixed Finite Element Method for the Fourth-Order Parabolic Equation" Fractal and Fractional 9, no. 3: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030137
APA StyleChang, X., & Li, H. (2025). A POD-Based Reduced-Dimension Method for Solution Coefficient Vectors in the Crank–Nicolson Mixed Finite Element Method for the Fourth-Order Parabolic Equation. Fractal and Fractional, 9(3), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030137






